Molecular Descriptors: Understanding Structural Complexity
•
0 likes•50 views
The time it takes to extract 1.7 million molecules from a database and process them for virtual screening is crucial for the drug discovery pipeline. The workflows used in this project take advantage of LLNL’s high performance computing for molecular descriptor calculations and molecular dynamics simulations. Molecular Descriptors are numerical values that characterize properties of molecules such as Molecular Weight and Hydrophobicity. These efforts will be able to help shrink the drug discovery pipeline from an average of 6 years to 1.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Recommended
NANO281 is the University of California San Diego NanoEngineering Department's first course on the application of data science in materials science. It is taught by Professor Shyue Ping Ong of the Materials Virtual Lab (http://www.materialsvirtuallab.org).NANO281 Lecture 01 - Introduction to Data Science in Materials Science

NANO281 Lecture 01 - Introduction to Data Science in Materials ScienceUniversity of California, San Diego
More Related Content
Similar to Molecular Descriptors: Understanding Structural Complexity
NANO281 is the University of California San Diego NanoEngineering Department's first course on the application of data science in materials science. It is taught by Professor Shyue Ping Ong of the Materials Virtual Lab (http://www.materialsvirtuallab.org).NANO281 Lecture 01 - Introduction to Data Science in Materials Science

NANO281 Lecture 01 - Introduction to Data Science in Materials ScienceUniversity of California, San Diego
Similar to Molecular Descriptors: Understanding Structural Complexity (20)
11.graph cut based local binary patterns for content based image retrieval

11.graph cut based local binary patterns for content based image retrieval
3.[18 30]graph cut based local binary patterns for content based image retrieval![3.[18 30]graph cut based local binary patterns for content based image retrieval](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![3.[18 30]graph cut based local binary patterns for content based image retrieval](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
3.[18 30]graph cut based local binary patterns for content based image retrieval
NANO281 Lecture 01 - Introduction to Data Science in Materials Science

NANO281 Lecture 01 - Introduction to Data Science in Materials Science
Analysis of the Boston Housing Data from the 1970 census

Analysis of the Boston Housing Data from the 1970 census
2017 - Plausible Bioindicators of Biological Nitrogen Removal Process in WWTPs

2017 - Plausible Bioindicators of Biological Nitrogen Removal Process in WWTPs
Chemistry - Chp 8 - Covalent Bonding - Study Guide

Chemistry - Chp 8 - Covalent Bonding - Study Guide
Recently uploaded
Recently uploaded (20)
PossibleEoarcheanRecordsoftheGeomagneticFieldPreservedintheIsuaSupracrustalBe...

PossibleEoarcheanRecordsoftheGeomagneticFieldPreservedintheIsuaSupracrustalBe...
Botany krishna series 2nd semester Only Mcq type questions

Botany krishna series 2nd semester Only Mcq type questions
Asymmetry in the atmosphere of the ultra-hot Jupiter WASP-76 b

Asymmetry in the atmosphere of the ultra-hot Jupiter WASP-76 b
Lucknow 💋 Russian Call Girls Lucknow Finest Escorts Service 8923113531 Availa...

Lucknow 💋 Russian Call Girls Lucknow Finest Escorts Service 8923113531 Availa...
Pests of mustard_Identification_Management_Dr.UPR.pdf

Pests of mustard_Identification_Management_Dr.UPR.pdf
Pulmonary drug delivery system M.pharm -2nd sem P'ceutics

Pulmonary drug delivery system M.pharm -2nd sem P'ceutics
Formation of low mass protostars and their circumstellar disks

Formation of low mass protostars and their circumstellar disks
9654467111 Call Girls In Raj Nagar Delhi Short 1500 Night 6000

9654467111 Call Girls In Raj Nagar Delhi Short 1500 Night 6000
Stunning ➥8448380779▻ Call Girls In Panchshil Enclave Delhi NCR

Stunning ➥8448380779▻ Call Girls In Panchshil Enclave Delhi NCR
Molecular Descriptors: Understanding Structural Complexity
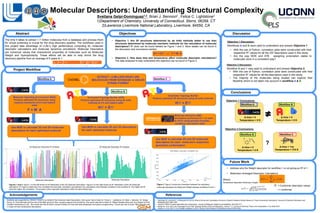
- 1. Δ time = 1ns Temperature = 310 K Svetlana was supported by CRADA TC02274 on behalf of the American Heart Association. She would like to thank Dr. Felice C. Lightstone, Dr. Brian J. Bennion, Dr. Sergio Wong, Dr. Drew Bennett and the rest of the BBS group for their constant support and mentoring. She would also like to thank Dr. Miguel Morales-Silva and Tony Baylis for their constant mentoring at LLNL. She would also like to thank Juanita Ordoñez for help with data preparation and python programming. I would also like to thank Talia Zeppelin and Li Linqiu for their constructive discussions. References • Hechinger M, Leonhard K, & Marquardt W (2012) What is Wrong with Quantitative Structure–Property Relations Models Based on Three-Dimensional Descriptors? Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling 52(8):1984-1993. • Labute P (2000) A widely applicable set of descriptors. Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modeling 18(4):464-477. • Malde AK, et al. (2011) An Automated Force Field Topology Builder (ATB) and Repository: Version 1.0. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation 7(12):4026-4037. • Gaulton A, et al. (2017) The ChEMBL database in 2018. Nucleic Acids Research 45(Database issue):D945-D954. Molecular Descriptors: Understanding Structural Complexity Svetlana Gelpí-Domínguez1,2, Brian J. Bennion2 , Felice C. Lightstone2 1)Department of Chemistry, University of Connecticut, Storrs, 06269, CT 2)Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, 94550, CA The time it takes to extract 1.7 million molecules from a database and process them for virtual screening is crucial for the drug discovery pipeline. The workflows used in this project take advantage of LLNL’s high performance computing for molecular descriptor calculations and molecular dynamics simulations. Molecular Descriptors are numerical values that characterize properties of molecules such as Molecular Weight and Hydrophobicity. These efforts will be able to help shrink the drug discovery pipeline from an average of 6 years to 1. • Objective 1. Are 3D structures determined by ab initio methods better to use than structures determined by molecular mechanic methods for the calculation of molecular descriptors? R2 plots can be found labeled as Figure 1 and 2. More details can be found in the discussion and conclusions section. • Objective 2. How does time and temperature affect molecular descriptor calculations? The data analyzed to help understand this objective can be found in Figure 3. Automated Topology Builder (ATB) Produce optimized 3D structures using ab initio methods at 0 K and implicit water HΨ = EΨ Molecular Operating Environment (MOE) Produce optimized 3D structures using classical mechanics at 0 K and implicit water F = M A 2. a EXTRACT ~2 MILLION DRUG LIKE MOLECULES FROM DATABASE in SMILES STRING FORMAT W Use MOE to calculate 2D and 3D molecular descriptors for each molecule’s respective geometric conformation Automated Topology Builder Produce optimized 3D structures using ab initio methods HΨ = EΨ Use MOE to calculate 2D and 3D molecular descriptors for each optimized molecule Use MOE to calculate 2D and 3D descriptors for each optimized molecule Abstract Objectives Project Workflow Discussion Conclusions Future Work Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations performed for 1 ns each at 310 K using periodic boundary conditions and explicit water Objective 1 Discussion: Workflows A and B were used to understand and answer Objective 1. • With the use of Python, correlation plots were constructed with their respective R2 values for all the 337 descriptors used in this study. • Are the way MOE and ATB assigning protonation states to molecules done in a consistent way? Objective 2 Discussion: Workflow B and C was used to understand and answer Objective 2. • With the use of Python, correlation plots were constructed with their respective R2 values for all the descriptors used in this study. • The majority of the molecules being studied can explore their flexibility which is not taken into account in workflow A & B. Objective 1 Conclusions: Objective 2 Conclusions: Figures 1 and 2. Figure 1 on the left shows an R2 distribution of the 2D molecular descriptors. Figure 2 on the right shows an R2 distribution of the 3D molecular descriptors. R2 helps us determine how correlated the descriptor calculation was between the calculations done between workflow A and workflow B. The higher the R2 value the higher the correlation. The grouped colors represent descriptors within the same family type. ReferencesAcknowledgements HΨ = EΨ vs. F = M A Workflow A Workflow B Workflow C • Boltzmann-Averaged Descriptor Calculations !! ! = !!!"#!!!!(!)/!" !! ! ! !"#!!!!(!)/!" Where: ! ! = !! ! ! (!)!! ∗ = Conformer descriptor values i = conformer Temperature-dependent Boltzmann weight: • Address why the Weight descriptor for workflow C is not giving an R2 of 1. Figure 3. Figure 3 shows the correlation between the calculated molecular descriptors for Molecular Weight between workflows B and C. 0 0.5 0.9 Molecular Descriptors Molecular Descriptors 2D Molecular Descriptor R2 Analysis 3D Molecular Descriptor R2 Analysis R2 0.1 0.6 0.8 Workflow A Workflow B Workflow C Δ time = 0 Temperature = 0 K Δ time = 0 Temperature = 0 K Workflow B Δ time = 0 Temperature = 0 K ?