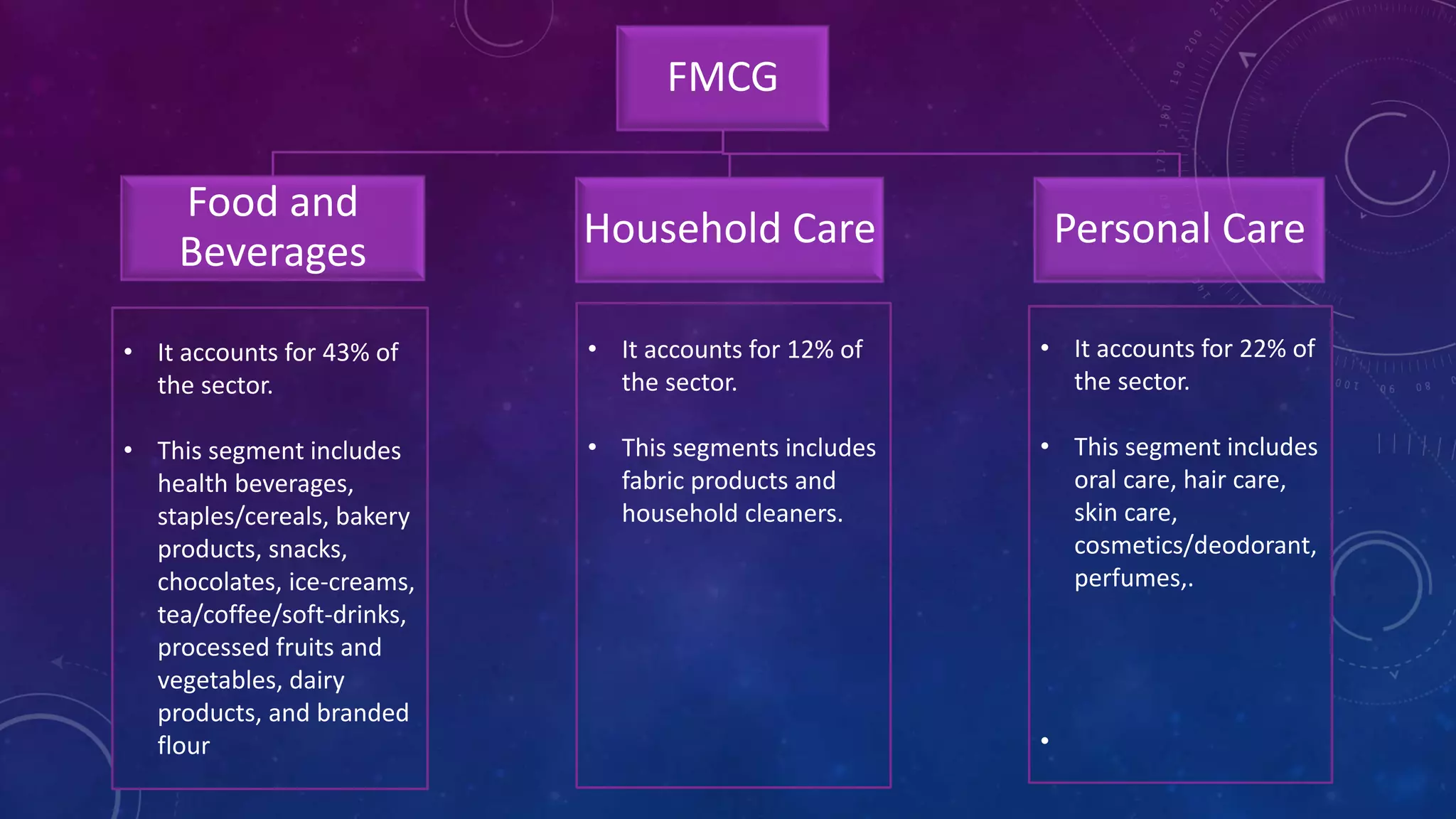
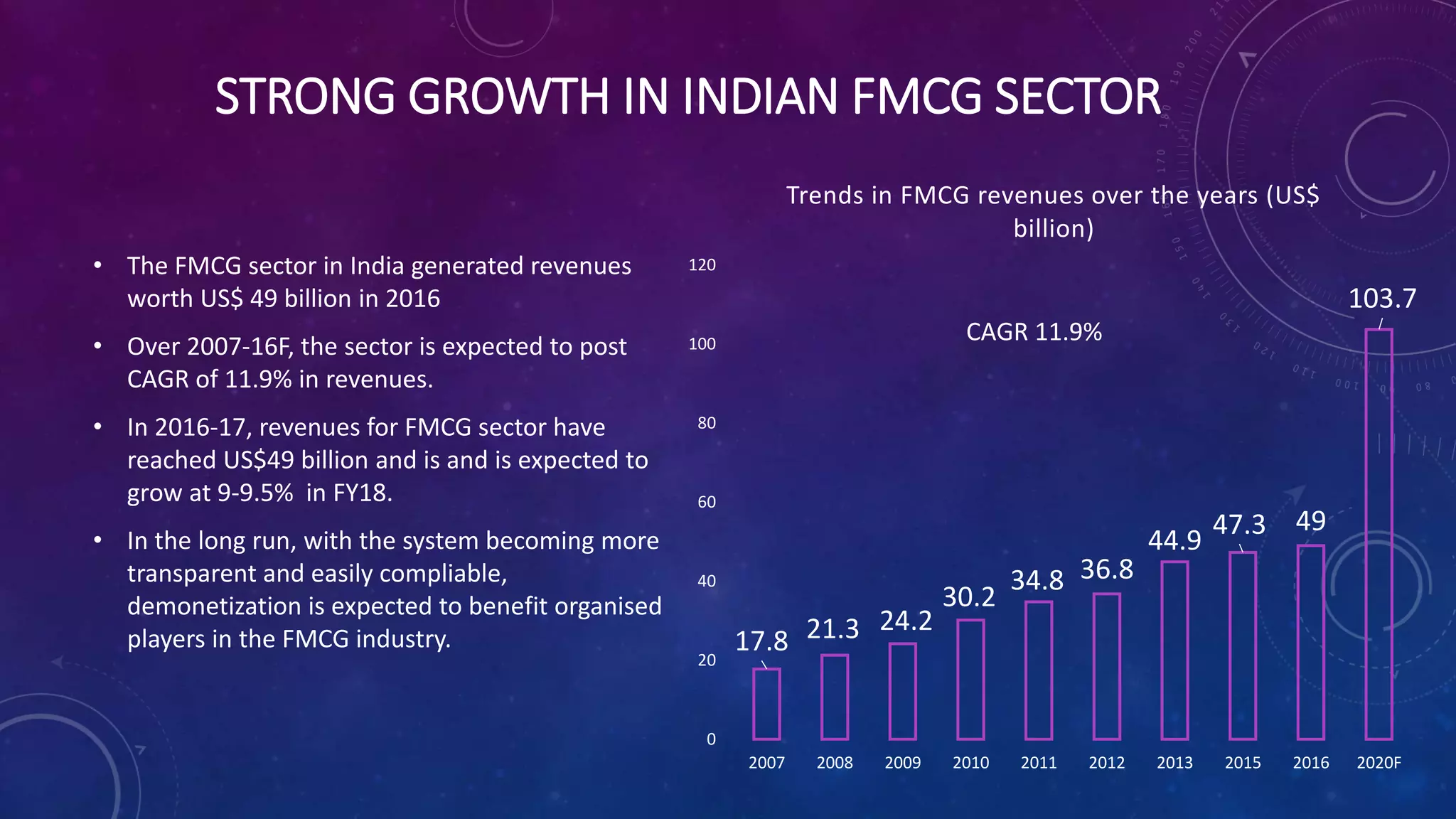
This document provides an overview of the FMCG sector in India. It notes that the FMCG sector accounts for around 3% of India's GDP and includes food and beverages, household care, and personal care products. The top FMCG companies in India are Hindustan Unilever, Patanjali, ITC, Nestle, and others. The FMCG sector is growing at a rate of 11.9% annually and urban areas account for 60% of revenues currently, though rural markets are growing rapidly as well. The industry faces high competition and potential substitutes but opportunities for growth include expanding in rural markets, developing innovative products, and increasing product penetration across India.