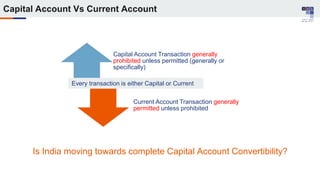
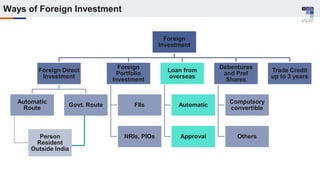
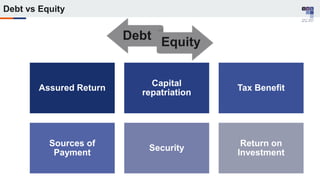
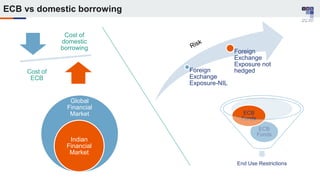
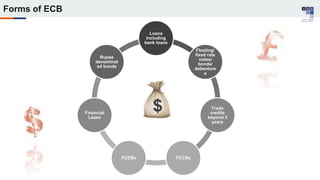
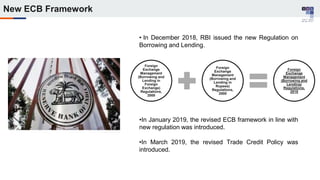
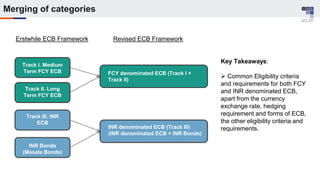
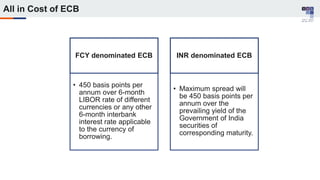
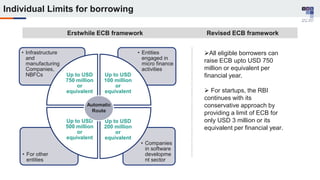
The document discusses the regulatory framework and recent changes regarding External Commercial Borrowing (ECB) in India, including eligibility criteria, borrowing limits, and end-use restrictions. It outlines different tracks for foreign investment, reforms introduced by the RBI, and the revised approach to funding for various entities like startups and real estate investment trusts. Key aspects include the permissible sources of funding, maturity periods, and compliance requirements for borrowers.