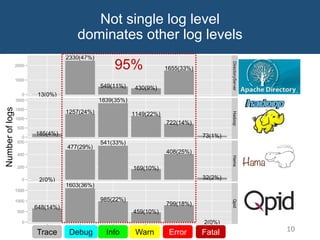
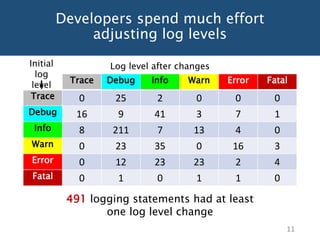
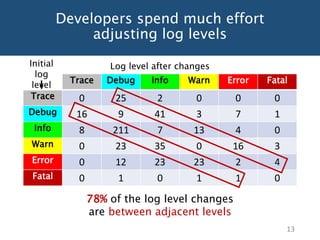
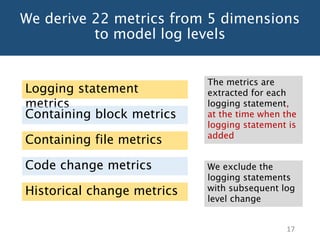
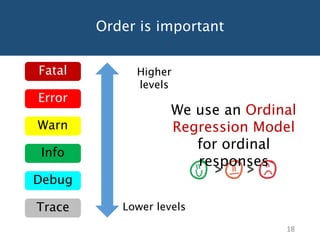
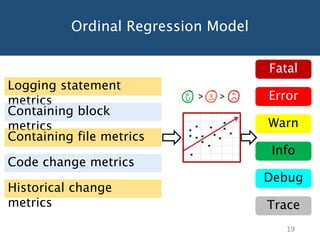
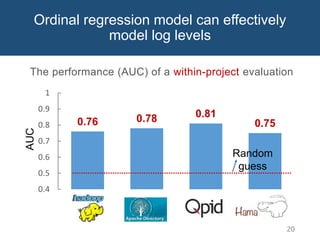
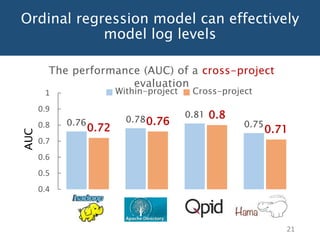
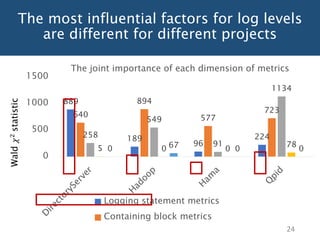
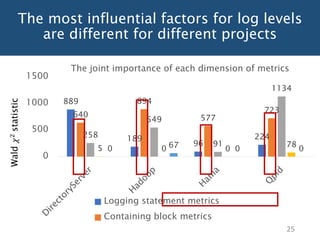
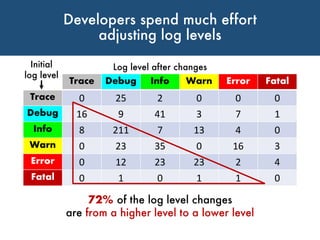
The document discusses choosing an appropriate log level when adding a new logging statement. It finds that an ordinal regression model can effectively model log levels, achieving an AUC of 0.76-0.81 in within-project evaluation and 0.71-0.8 in cross-project evaluation. The most influential factors for determining log levels vary between projects and include metrics related to the logging statement, containing code block, and file as well as code change and historical change metrics.




![Researchers and industrial experts
highlighted the challenge of choosing proper
log levels
7
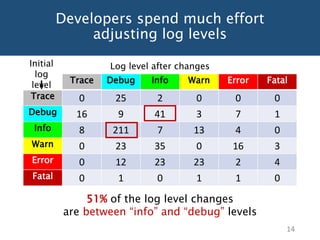
Developers spend much
efforts on adjusting log
levels
Severity levels are often
used inaccurately
[Oliner et al. CACM’12]
[Yuan et al. ICSE’12]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heng-saner-logging-levels-v6-180906165859/85/Which-Log-Level-Should-Developers-Choose-For-a-New-Logging-Statement-7-320.jpg)