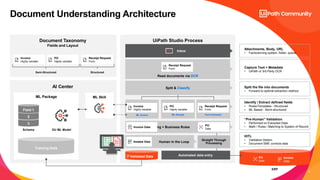
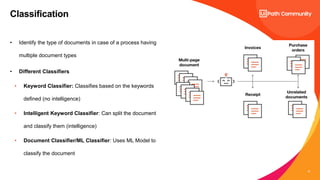
The document discusses UiPath's Document Understanding capabilities. It provides an overview of document understanding, the different types of documents that can be processed, and the approaches to document processing including rule-based and model-based. It describes the key components of UiPath's Document Understanding framework including loading taxonomy, document classification, data extraction, validation, and GenAI capabilities. It also includes a case study example of using document understanding to process 7000 invoices per month.






![7
Document Processing Approaches
Relies on ML models
Processes less structured
varying layouts like invoices or
receipts
Understands even unknown
complex documents
ǃ Requires pre-trained ML
models with further retraining
capabilities
Model-based
[template-less approach]
Relies on rules and templates
Processes fixed in format
structured data like forms or
licenses
High accuracy for already
known documents
ǃ Requires extra costs for
addition of templates/rules and
ongoing maintenance
ǃ Doesn’t work with unknown
documents
Rule-based
[template-based approach]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uipathdocumentunderstandingday2-231122040707-0946ef3b/85/UiPath-Document-Understanding_Day-2-pptx-7-320.jpg)








![18
Use Case Architecture
Shared Inbox
Download Invoice
Upload to
Sharepoint
Dispatcher Queue
ML Extractor
PDF Splitter Validate Results
Ifrules or
confidence not
meet?
HiTL
Reconciliation
Queue
Get Item &
Download
Digitize [OCR]
Load Taxonomy
Yes
No
Get Item From
Reconciliation
Queue
Add records to
Salesforce
FS_Dispatcher
FS_DU Performer
FS_ProcessReconciliation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uipathdocumentunderstandingday2-231122040707-0946ef3b/85/UiPath-Document-Understanding_Day-2-pptx-18-320.jpg)


