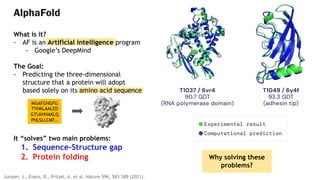
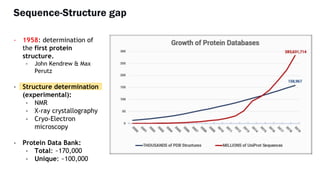
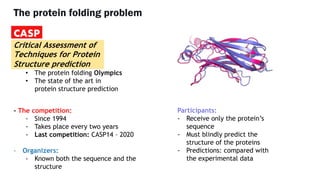
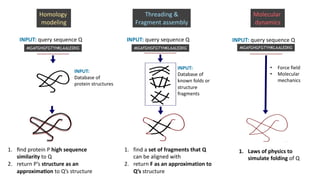
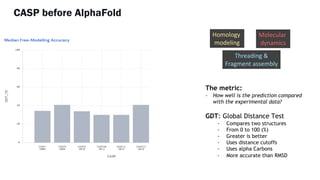
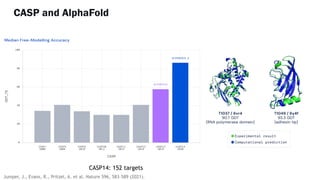
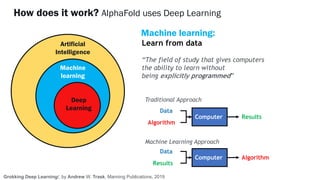
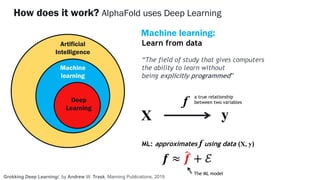
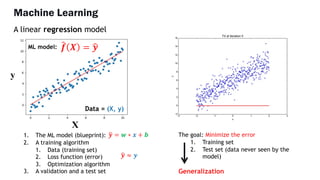
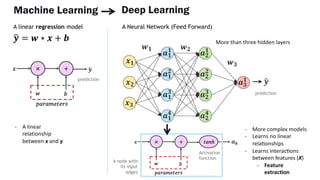
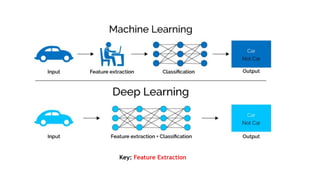
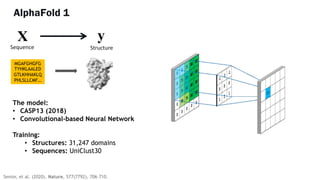
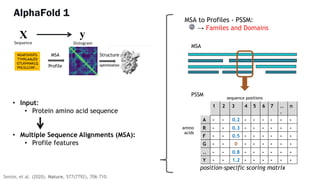
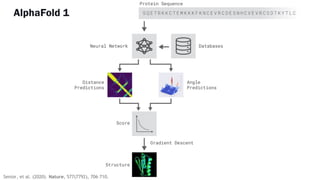
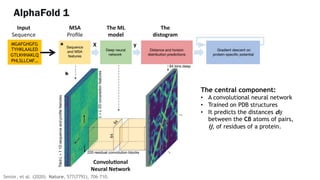
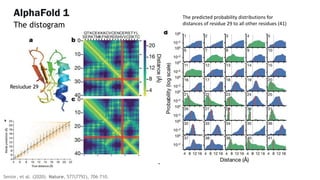
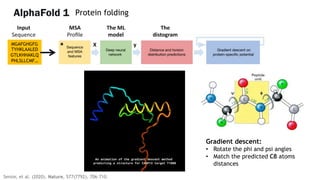
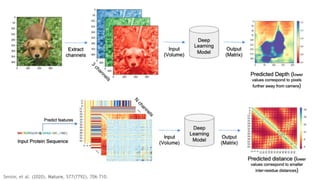
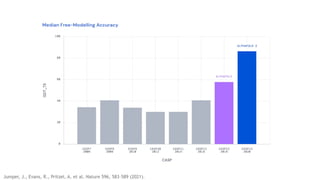
AlphaFold is an AI program developed by Google's DeepMind aimed at predicting a protein's three-dimensional structure from its amino acid sequence, addressing the longstanding protein folding problem. It utilizes deep learning techniques to analyze vast datasets of protein structures and sequences to improve accuracy in structure prediction, as demonstrated in competitions like CASP. The evolution from AlphaFold 1 to AlphaFold 2 includes advances in architectural methodologies and training, enhancing its predictive capabilities significantly.