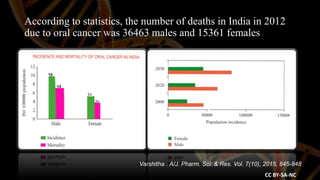
This document discusses cyclinD1 and its role as a marker for oral cancer progression. It finds that cyclinD1 expression increases from normal epithelium to leukoplakia to oral squamous cell carcinoma. Higher cyclinD1 expression correlates with poorer tumor differentiation and worse patient outcomes like early death or recurrence. The study concludes that cyclinD1 overexpression may help identify high-risk oral cancer patients and serve as a prognostic marker.