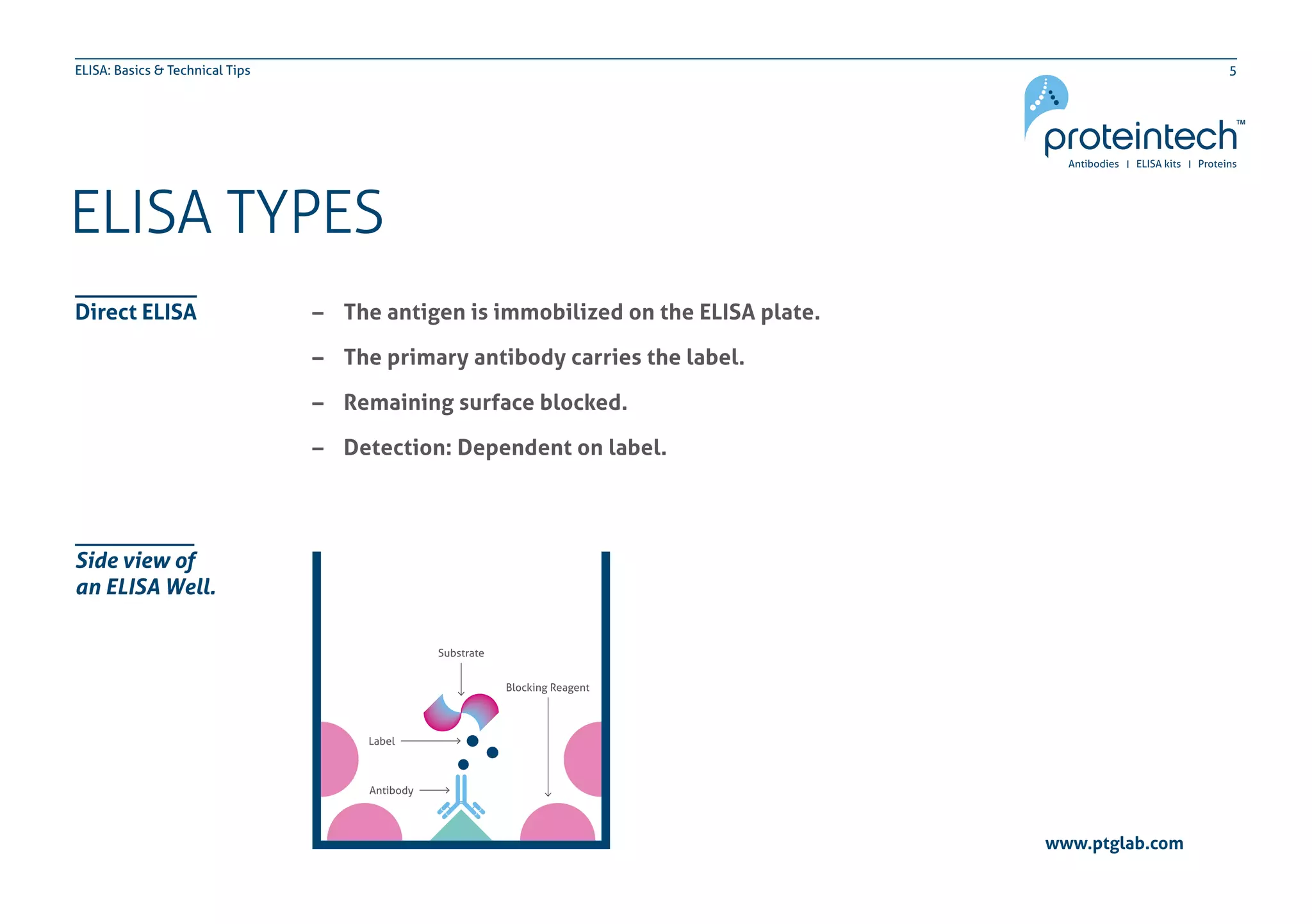
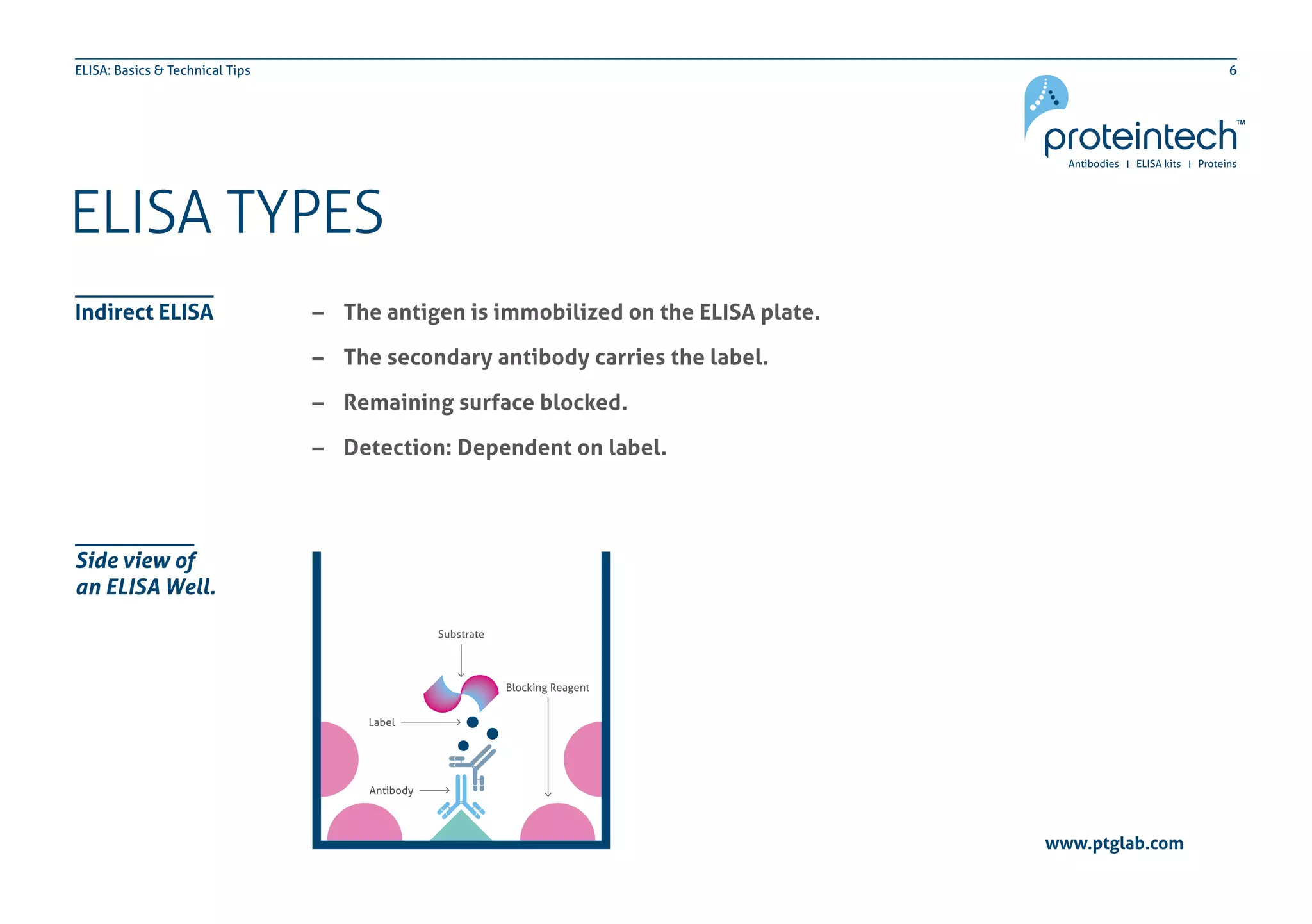
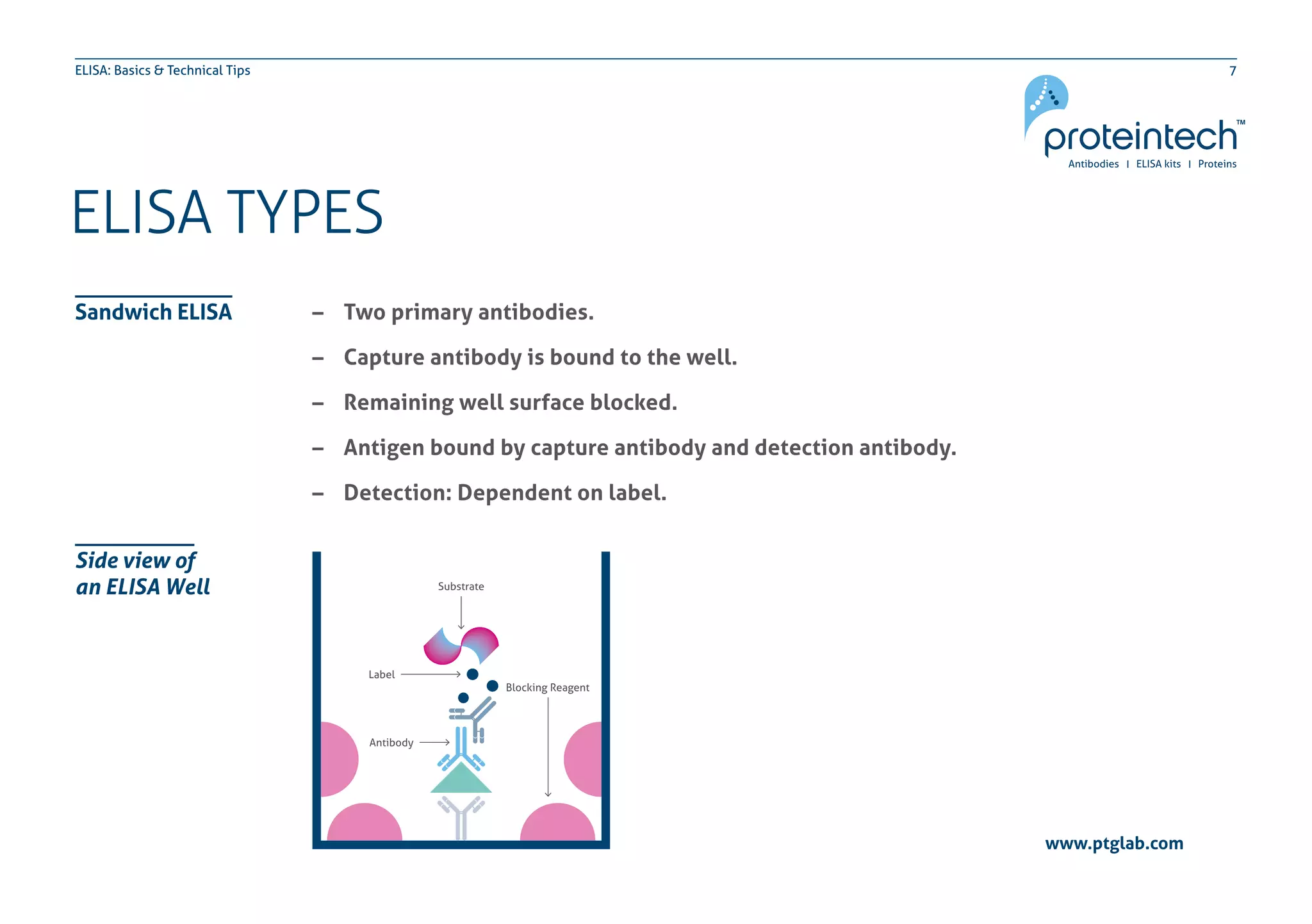
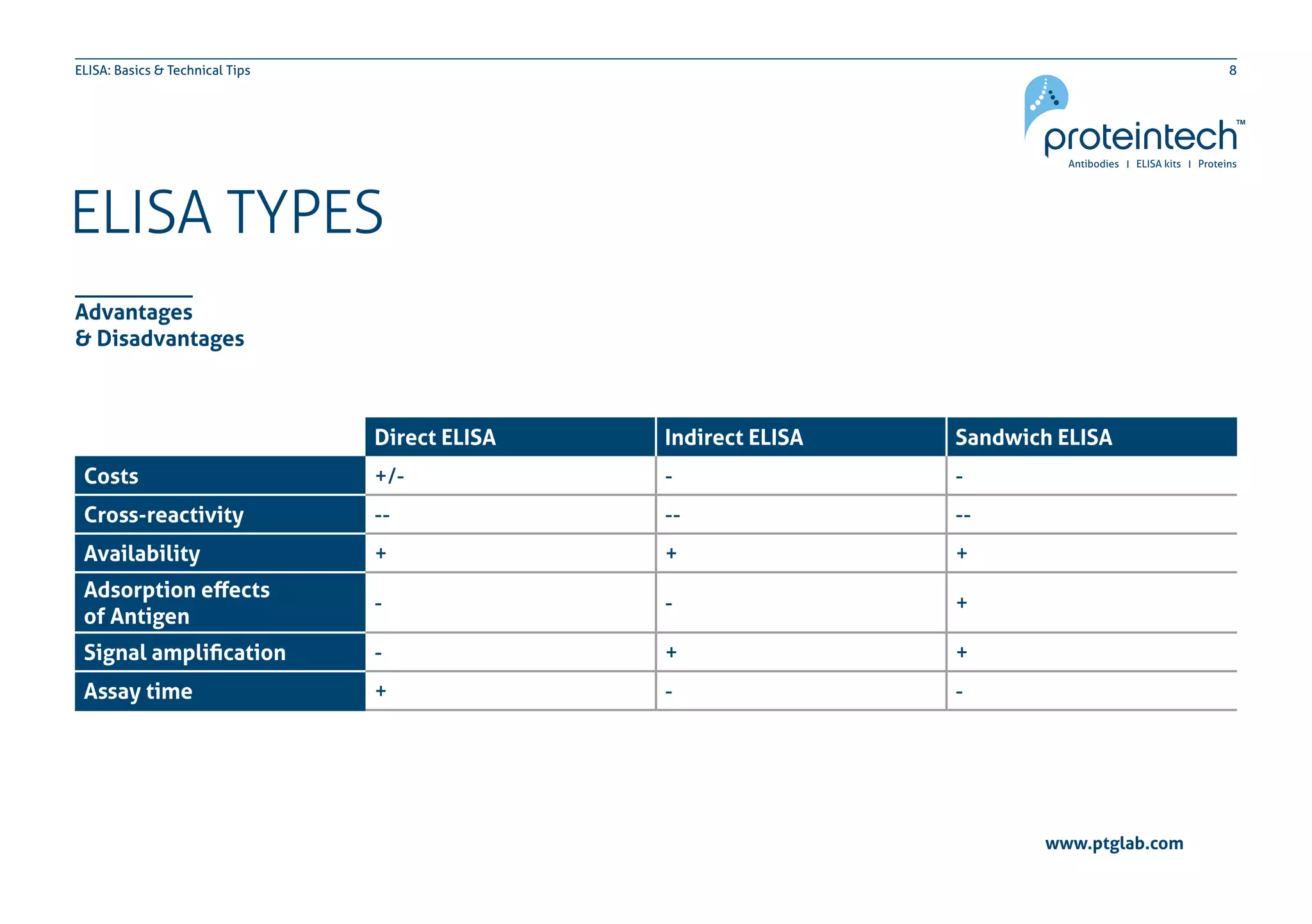
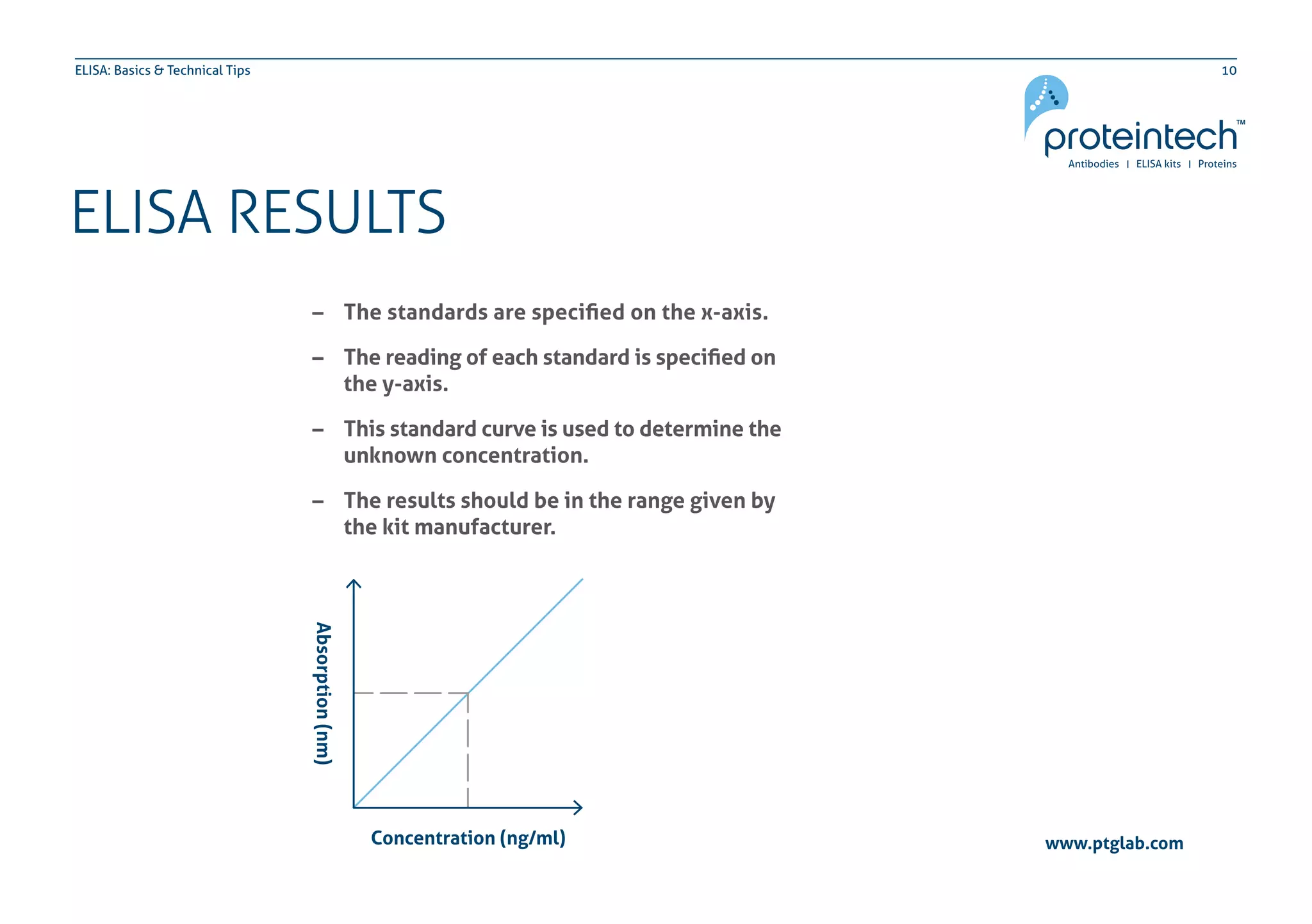
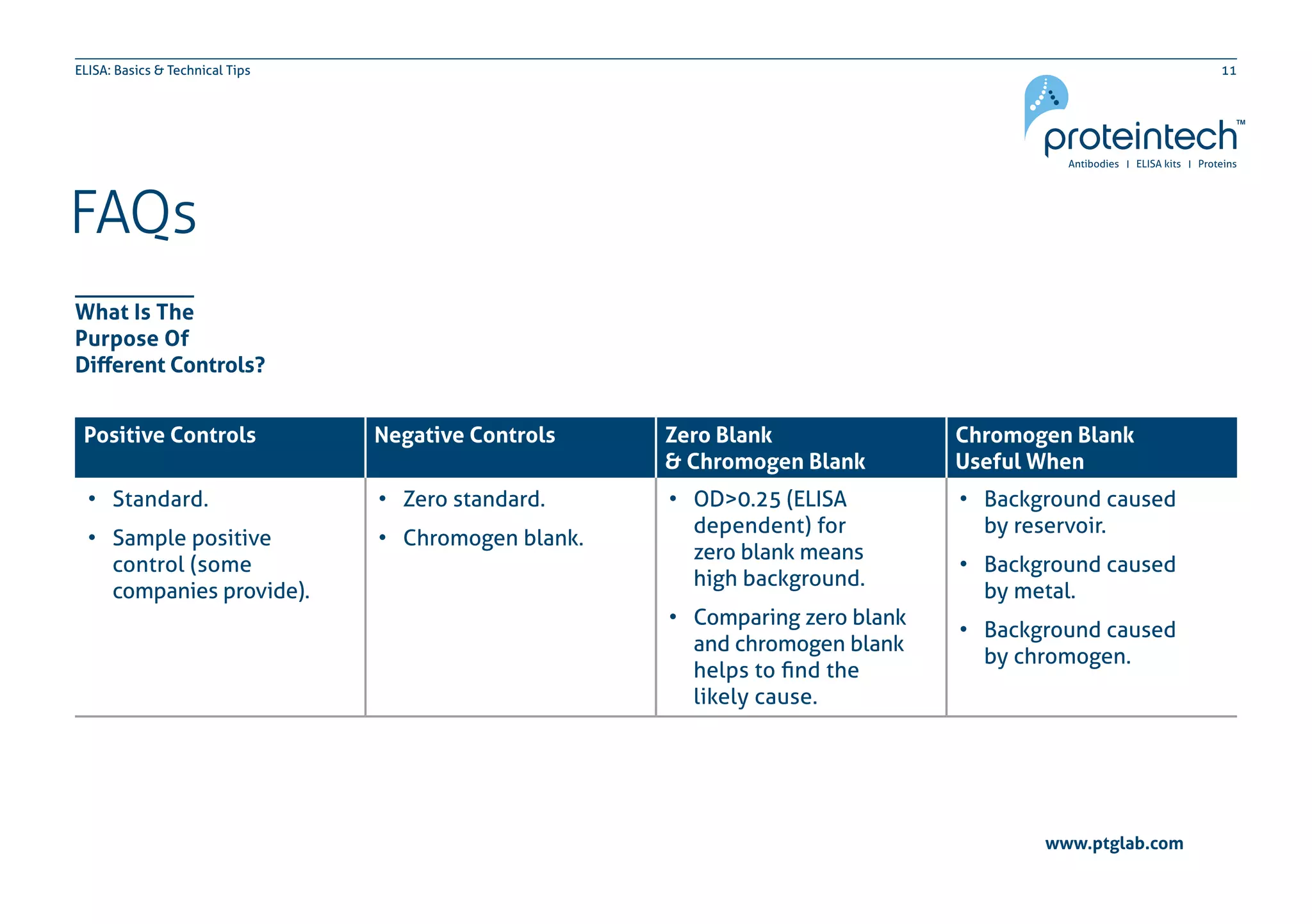
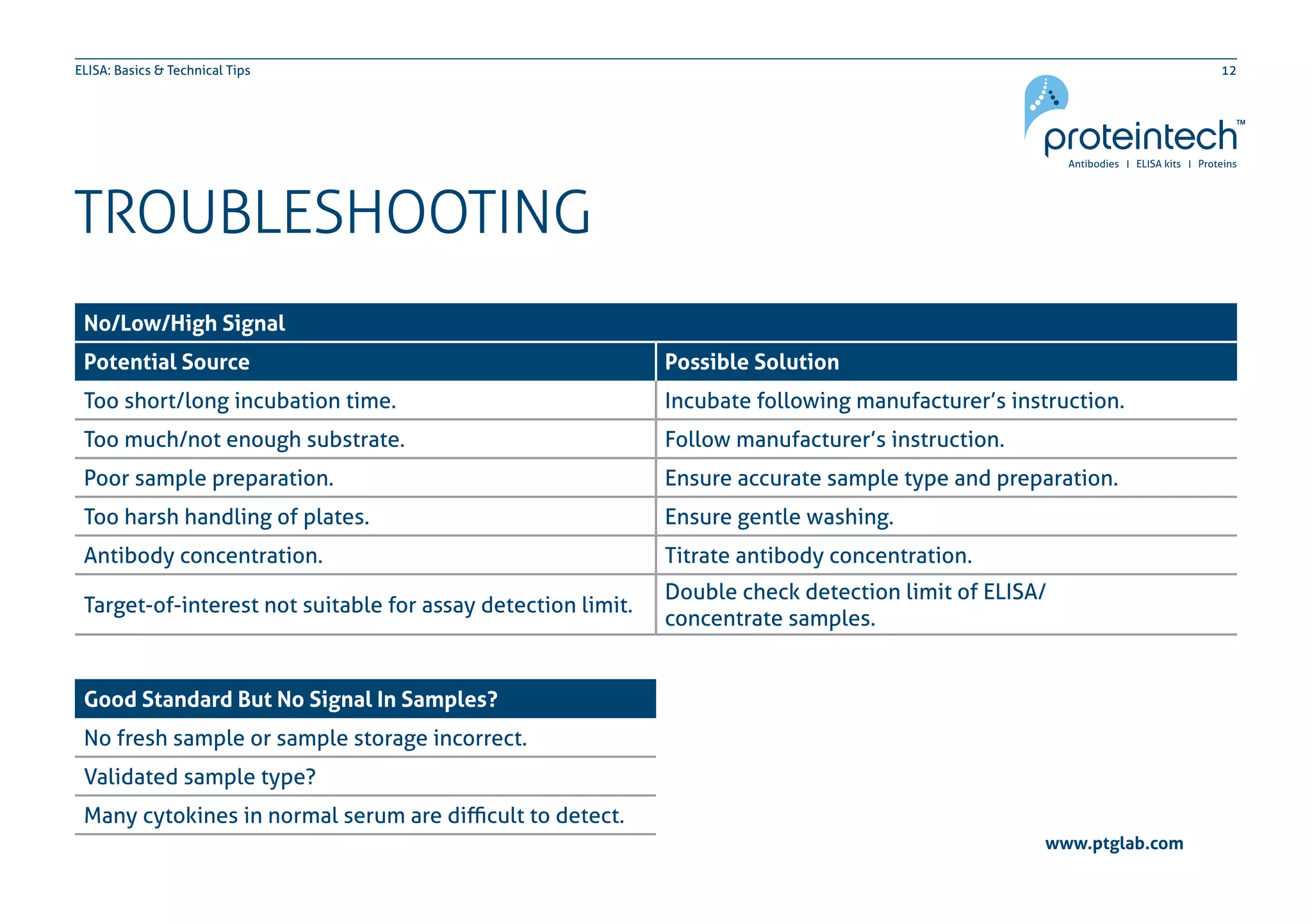
The document provides an overview of the enzyme-linked immuno-sorbent assay (ELISA), detailing its definition, types (direct, indirect, and sandwich), and the factors influencing its results. It includes troubleshooting tips and addresses common concerns regarding signal levels, control types, and interpretation of results. Additionally, the document contains contact information for technical support related to ELISA.