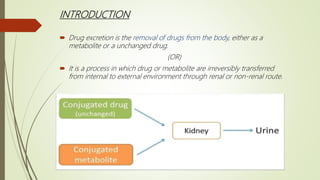
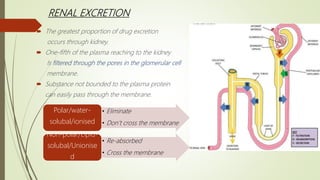
This document summarizes drug excretion, which is the removal of drugs from the body through various routes. The major routes of excretion are the kidneys (renal excretion), bile/liver (biliary secretion), lungs (pulmonary excretion), and feces. Renal excretion occurs through glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, and tubular secretion in the kidneys. Biliary secretion involves the active transport of drugs from liver cells into bile. Pulmonary excretion eliminates gaseous and volatile substances through exhaled breath. Factors like a drug's properties, age, disease states, and urine pH can impact the rate of excretion.