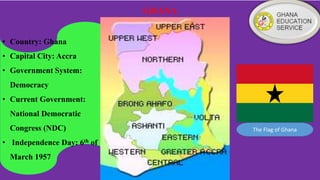
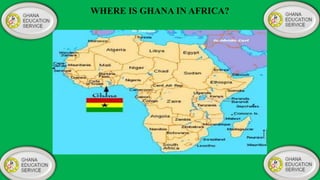
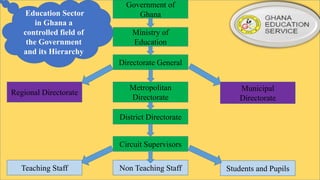
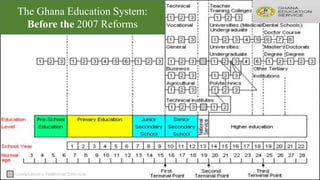
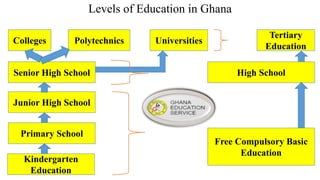
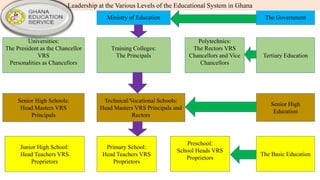
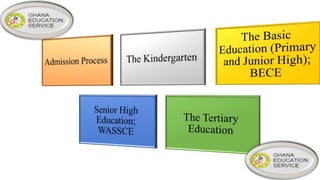
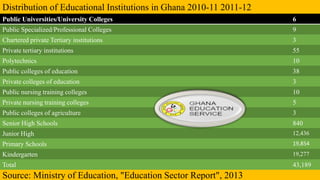
Ghana operates under a democratic government, with its capital in Accra and the National Democratic Congress currently in power. The education system is primarily government-controlled, with a significant budget allocation focused on providing equal quality education through various reforms since independence in 1957. Key educational documents and statistics highlight the structure and distribution of institutions across different educational levels, emphasizing the government's commitment to improving the education sector.