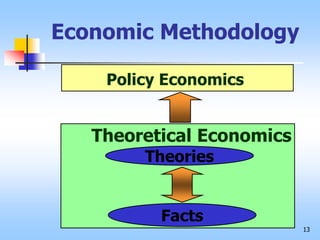
This document provides an overview of key concepts in economics. It discusses the economics perspective including scarcity, choice, and rational behavior. It also covers marginal analysis and marginal benefits and costs. The document then profiles several influential economists from the past like Adam Smith, John Maynard Keynes, David Ricardo, John Stuart Mill, and Karl Marx. It also examines economic methodology, including the scientific method, hypothesis testing, theory, and models. It analyzes analytical economics concepts such as terminology, generalization, and graphical expression. Finally, it outlines economic goals, divisions of economics between macro and micro, and differences between positive and normative economics.