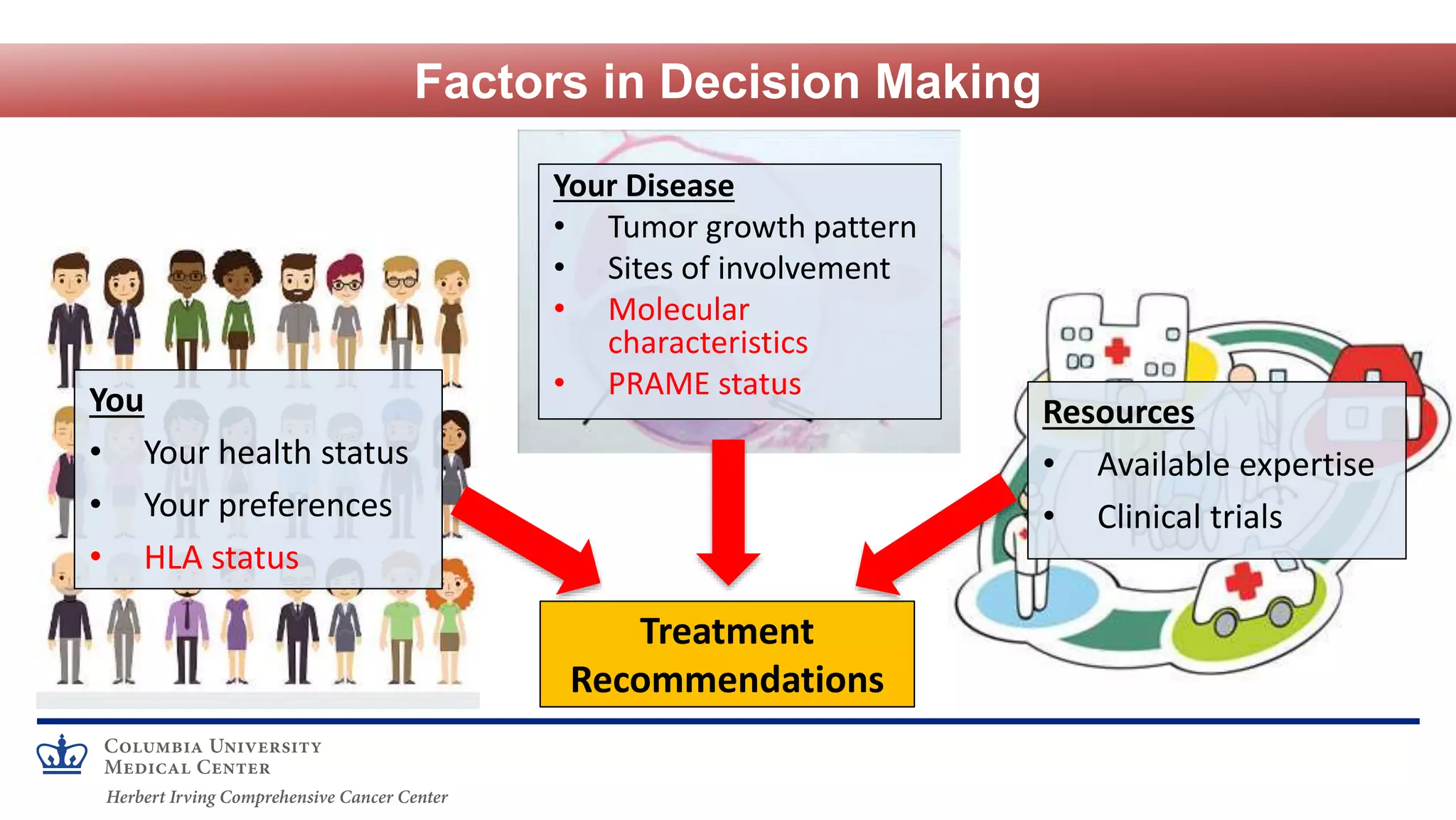
Richard Carvajal discusses navigating treatment options for uveal melanoma, focusing on immunotherapeutic strategies. He outlines several systemic treatment approaches including genetic, epigenetic, and immunological targeting. Checkpoint blockade with ipilimumab and nivolumab has shown some efficacy in uveal melanoma but responses are lower than in cutaneous melanoma potentially due to lower tumor mutation burden and PD-L1 expression. Adoptive T cell therapy clinical trials have also shown responses. Ipilimumab and nivolumab are being studied in the adjuvant and metastatic settings. Additional immunotherapies including T cell redirecting therapies targeting gp100 are in clinical trials. Combination strategies may be necessary to improve outcomes for