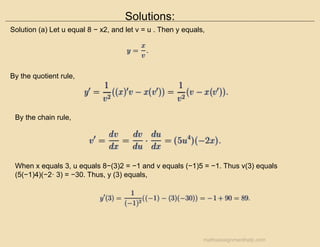
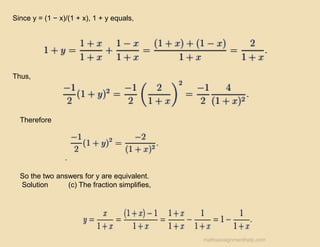
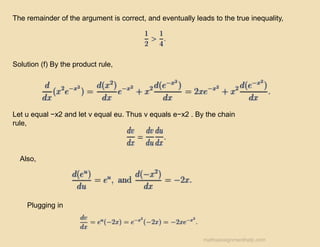
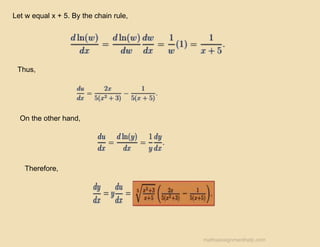
The document outlines guidelines for completing homework, emphasizing that while collaboration is encouraged, submitted work must be original and reflective of individual understanding. It includes example math problems related to calculus and finance, such as finding tangent lines and understanding the implications of loan and savings account interest rates. It also suggests using check-ins with classmates to verify reasoning in problem-solving.










![Solution (h) By the doubleangle formula,
cos(2φ) = (cos(φ))2 − (sin(φ))2 = 2(cos(φ))2 − [(cos(φ))2 + (sin(φ))2 ] = 2(cos(φ))2 − 1.
Substituting 2θ for φ gives,
Subsituting in cos(2θ) = 2(cos(θ))2 − 1 gives,
Solution (i) First of all, ln(x2) equals 2 ln(x).
Thus,
Let u equal 2 ln(x). Thus y equals sin(u). By the chain rule
mathsassignmenthelp.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mathhomeworkhelp-220208095843/85/Calculus-Homework-Help-15-320.jpg)











