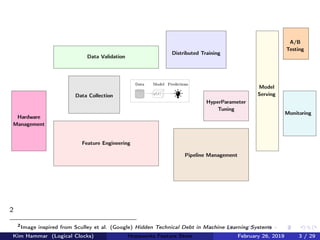
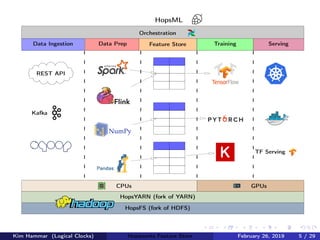
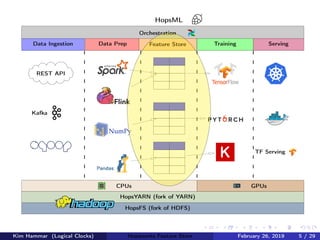
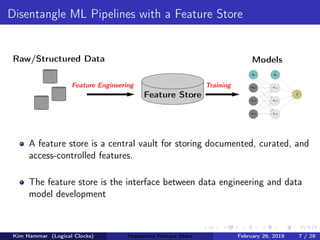
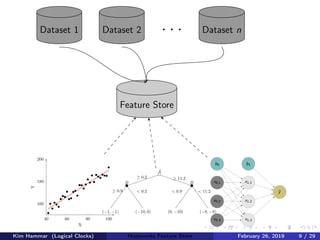
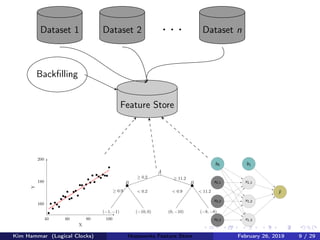
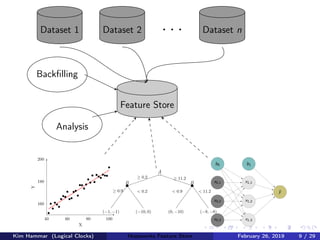
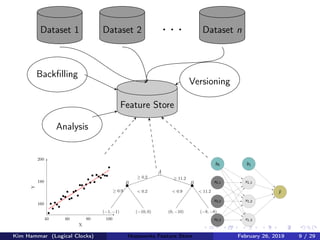
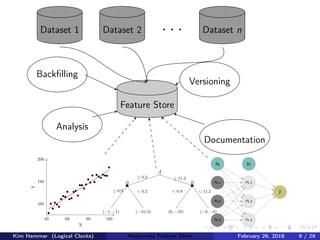
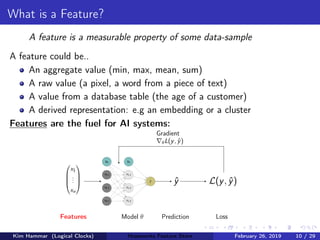
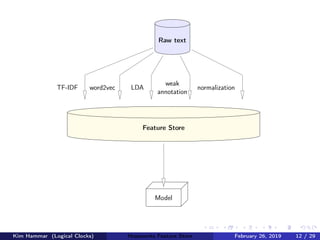
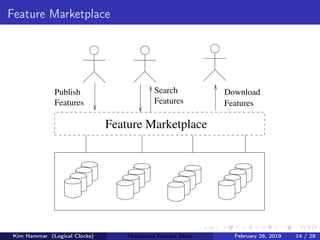
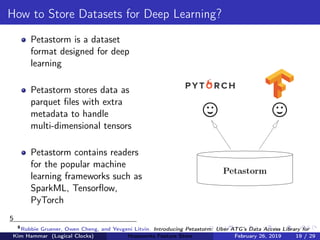
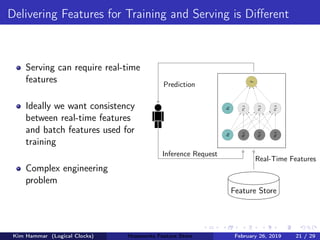
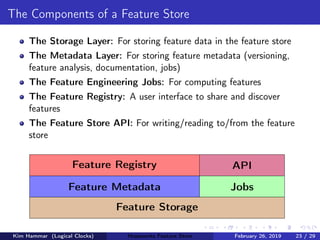
The document discusses the concept of a feature store, emphasizing its importance as a crucial data layer in machine learning pipelines that helps manage data effectively. It outlines the benefits of using a feature store for feature engineering, storage, and serving in ML applications, as well as providing a case study on the Hopsworks feature store. Additionally, it addresses challenges such as encouraging feature reuse, ensuring compatibility for deep learning datasets, and the integration of real-time and batch features.


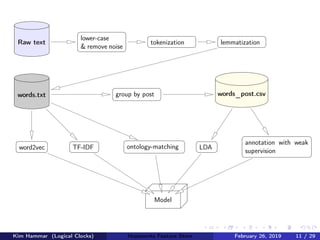

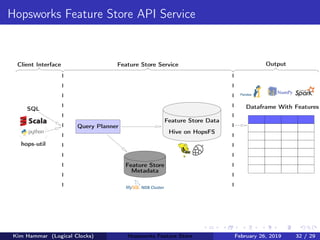
![Feature Store API Service
from hops import featurestore
features_df =
featurestore.get_features([
"average_attendance",
"average_player_age"
])
Feature Relationships
Feature Groups
Shared Storage
Feature Store API Service
Feature
Metadata
in ML pipelines
Include features
Figure: Feature Store API Service
Kim Hammar (Logical Clocks) Hopsworks Feature Store February 26, 2019 15 / 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spotifymlguildmeetup-190414181357/85/Kim-Hammar-Spotify-ML-Guild-Meetup-Feature-Stores-23-320.jpg)






![Hopsworks Feature Store API
Reading from the Feature Store:
from hops import featurestore
features_df = featurestore.get_features([
"average_attendance",
"average_player_age"
])
Writing to the Feature Store:
from hops import featurestore
raw_data = spark.read.parquet(filename)
pol_features = raw_data.map(lambda x: x^2)
featurestore.insert_into_featuregroup(pol_features , "pol_featuregroup")
Kim Hammar (Logical Clocks) Hopsworks Feature Store February 26, 2019 34 / 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spotifymlguildmeetup-190414181357/85/Kim-Hammar-Spotify-ML-Guild-Meetup-Feature-Stores-42-320.jpg)