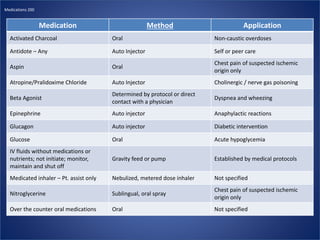
This document contains questions and answers related to various medical topics including chest pain, diabetes, cardiac arrest, respiratory distress, orthopedic injuries, and medications. It covers assessment, treatment, and medication administration guidelines for EMTs, AEMTs, and paramedics when encountering patients with these conditions. Key highlights include oxygen being the first treatment for chest pain patients, the importance of a 12-lead EKG, indications for aspirin and nitroglycerin administration, glucose levels requiring treatment, shockable cardiac arrest rhythms, epinephrine dosage for cardiac arrest, and splinting and pain management guidelines for orthopedic injuries.