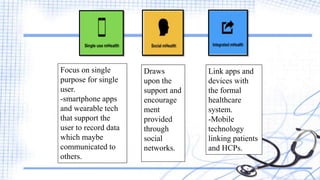
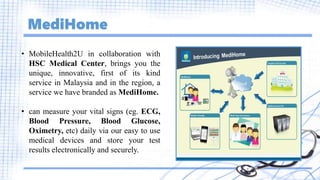
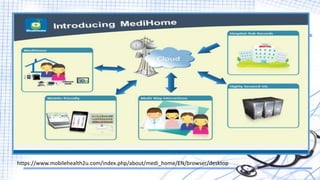
The document discusses the role of mobile technology in medical informatics, highlighting its ability to improve patient care, enhance communication, and streamline health management through applications and wearable devices. It emphasizes the advantages of mobile technology, such as promoting self-monitoring and facilitating sharing of health data, while also addressing security, complexity, and usability challenges faced by both providers and patients. Additionally, it outlines the general systems used in mobile healthcare, emphasizing the importance of cloud-based data sharing and effective framework designs for health management.