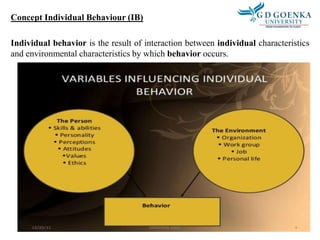
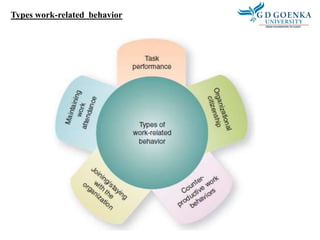
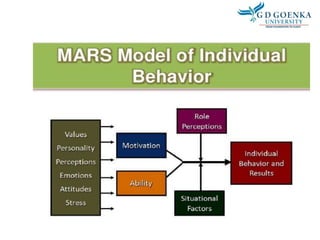
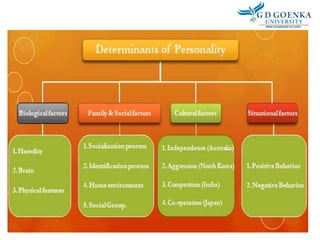
Individual behavior is shaped by both personal and environmental factors. Personal factors include age, gender, personality, values, and perceptions. Organizational factors that influence behavior are organizational culture, leadership style, and reward systems. Environmental factors such as the economy can also shape individual behavior in organizations. Personality is defined as an individual's unique pattern of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, and the five major personality attributes that influence organizational behavior are locus of control, Machiavellianism, self-esteem, self-monitoring, and risk taking.