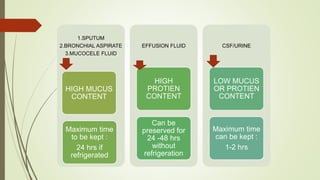
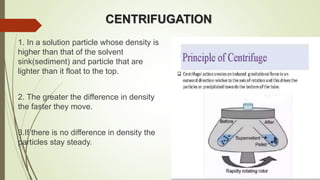
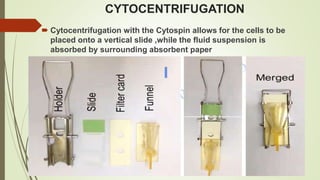
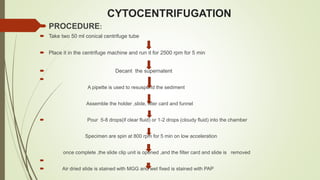
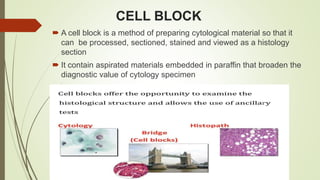
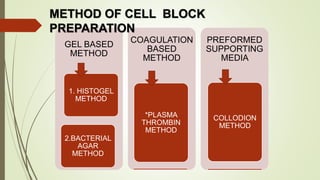
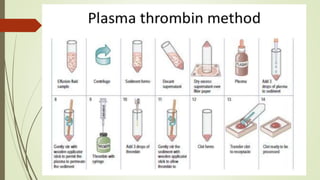
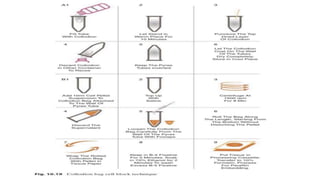
This document discusses cytology techniques used to examine cells from body fluids and tissues. It describes how body fluids are collected and transported to the laboratory for processing. Common processing techniques include direct smears, centrifugation, cytocentrifugation, cell blocks and liquid-based preparations. Cell blocks allow cell pellets to be embedded in paraffin for sectioning, staining, and diagnostic evaluation like histology samples. This increases the sensitivity and specificity of cytology exams by enabling additional ancillary testing. The document provides details on various cell block preparation methods and their advantages.