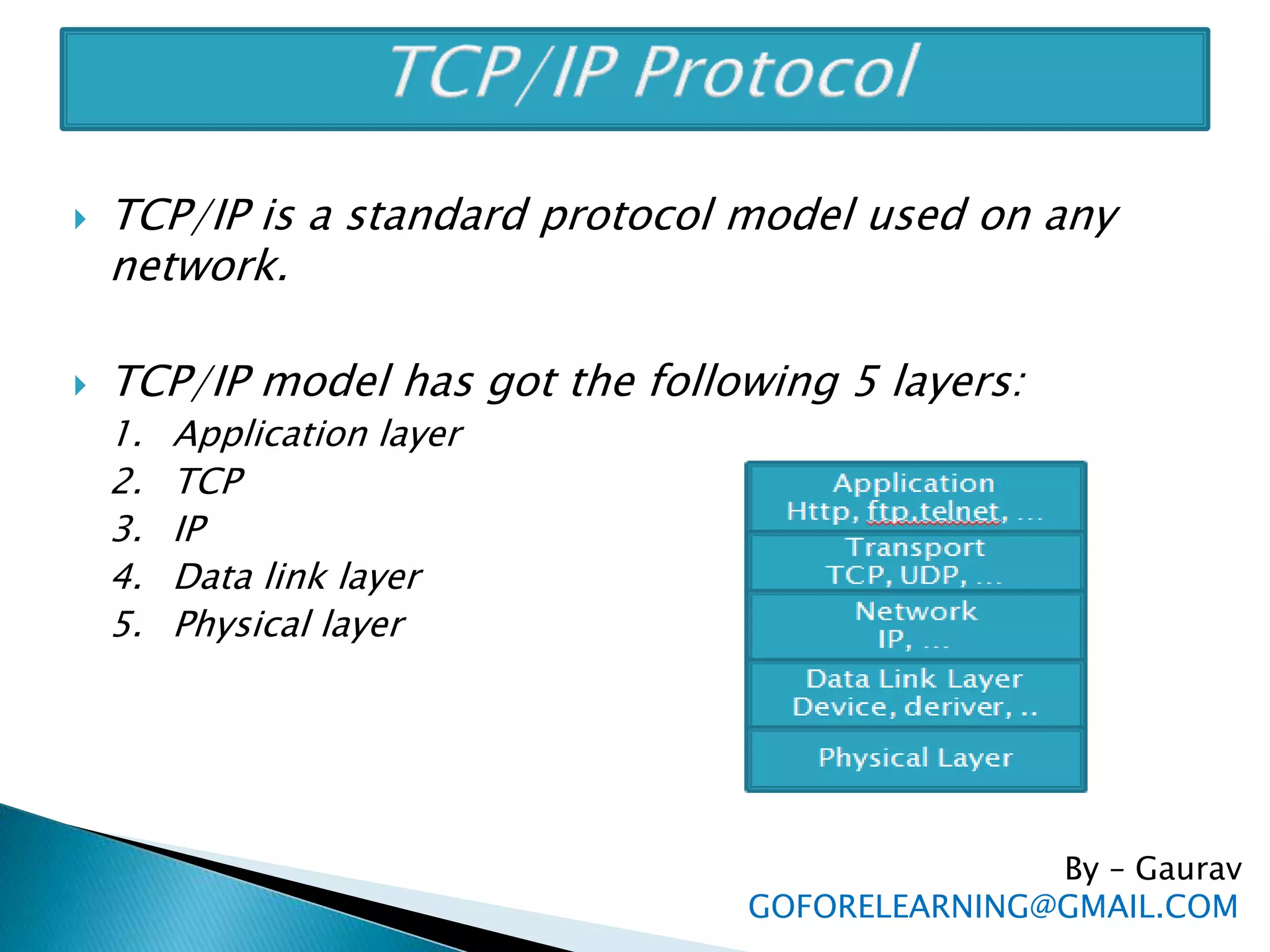
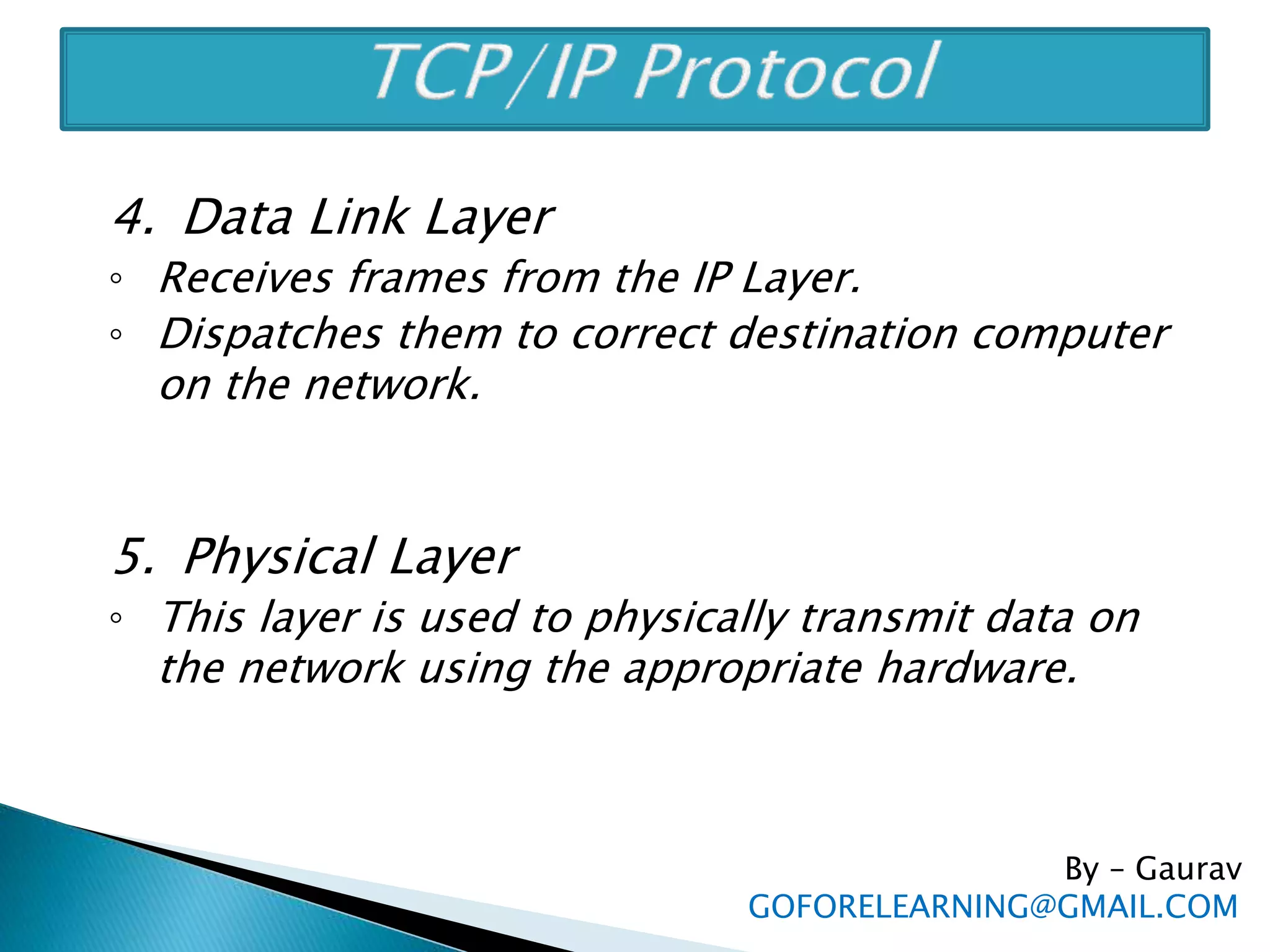
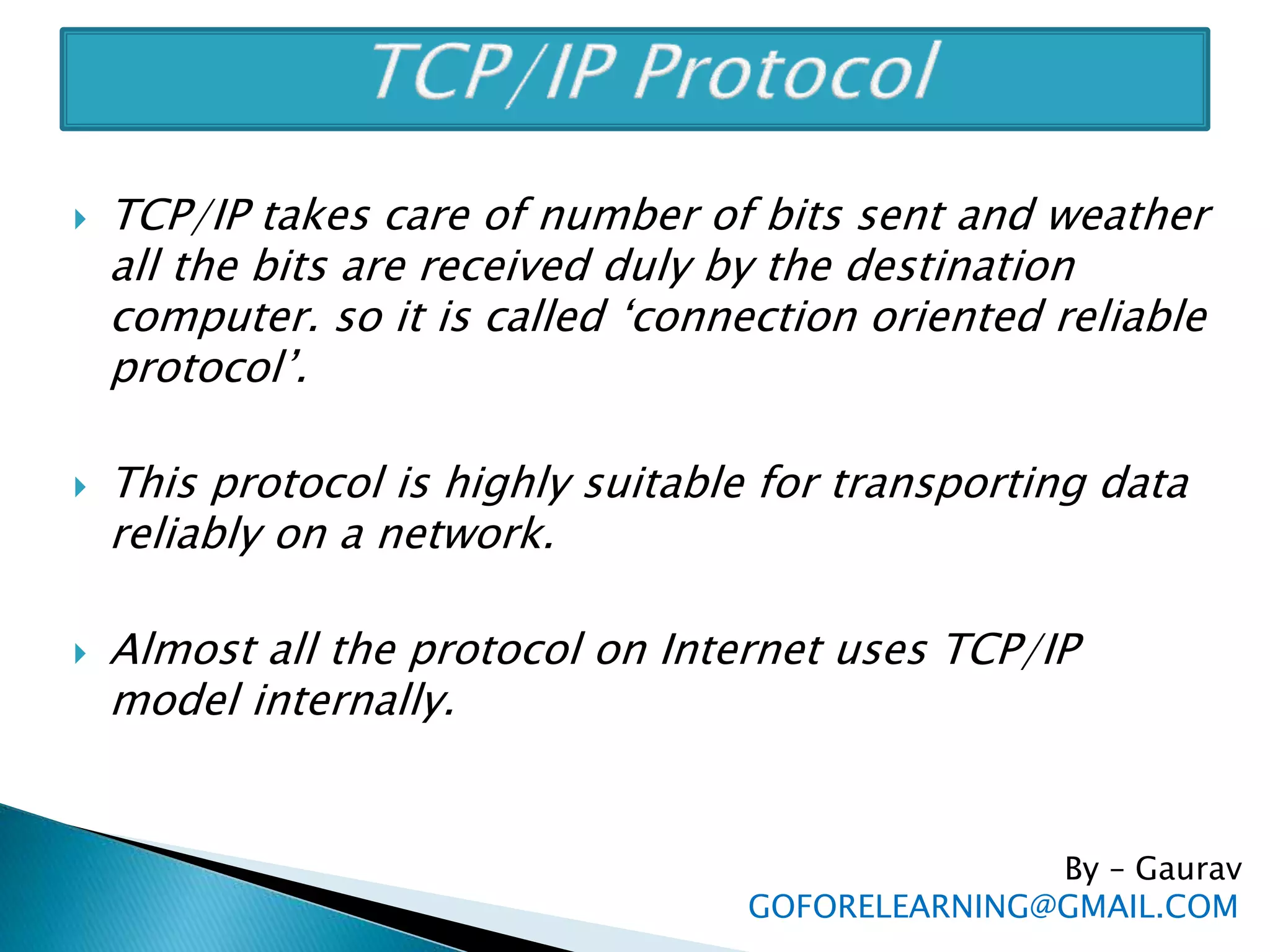
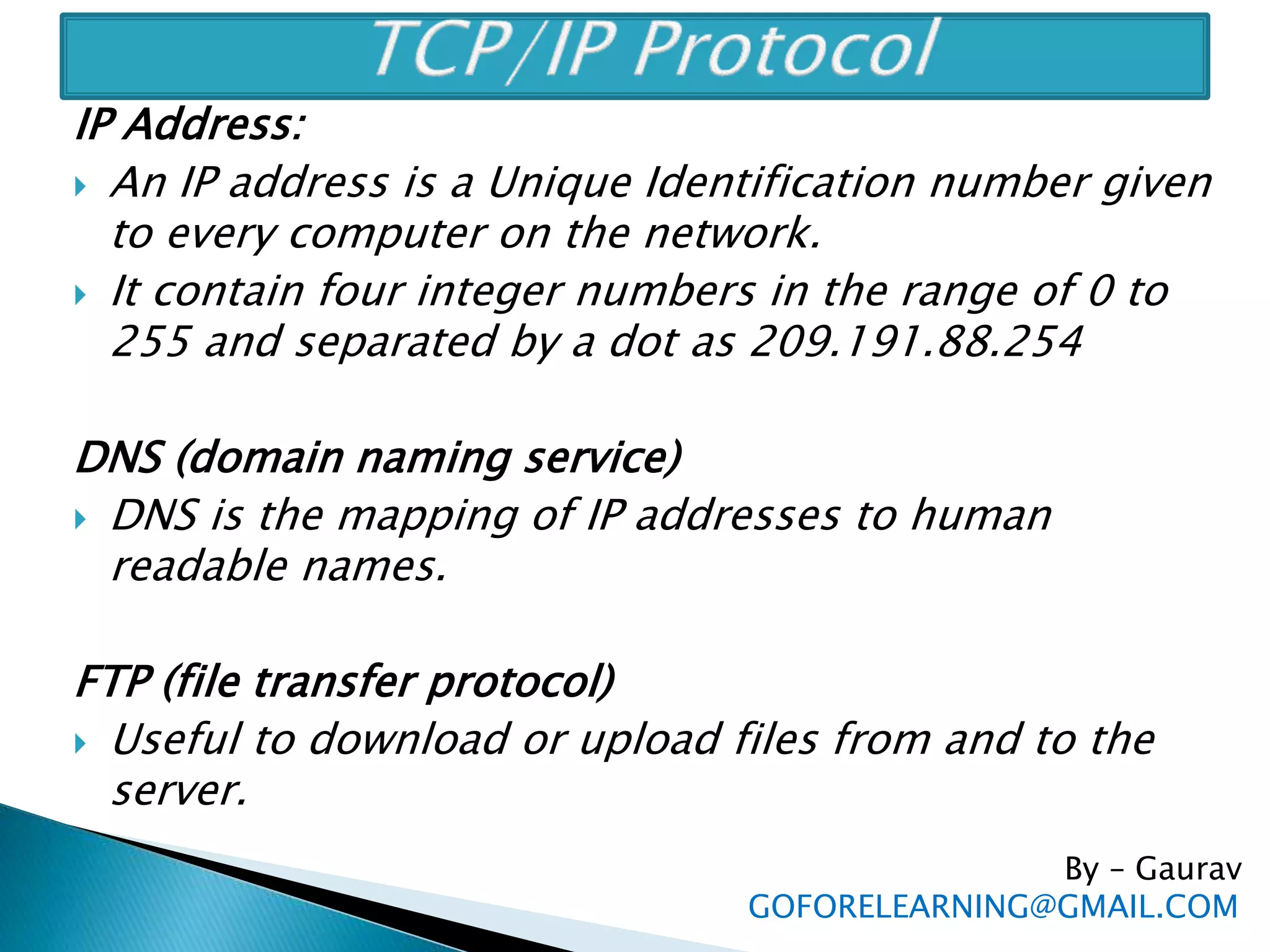
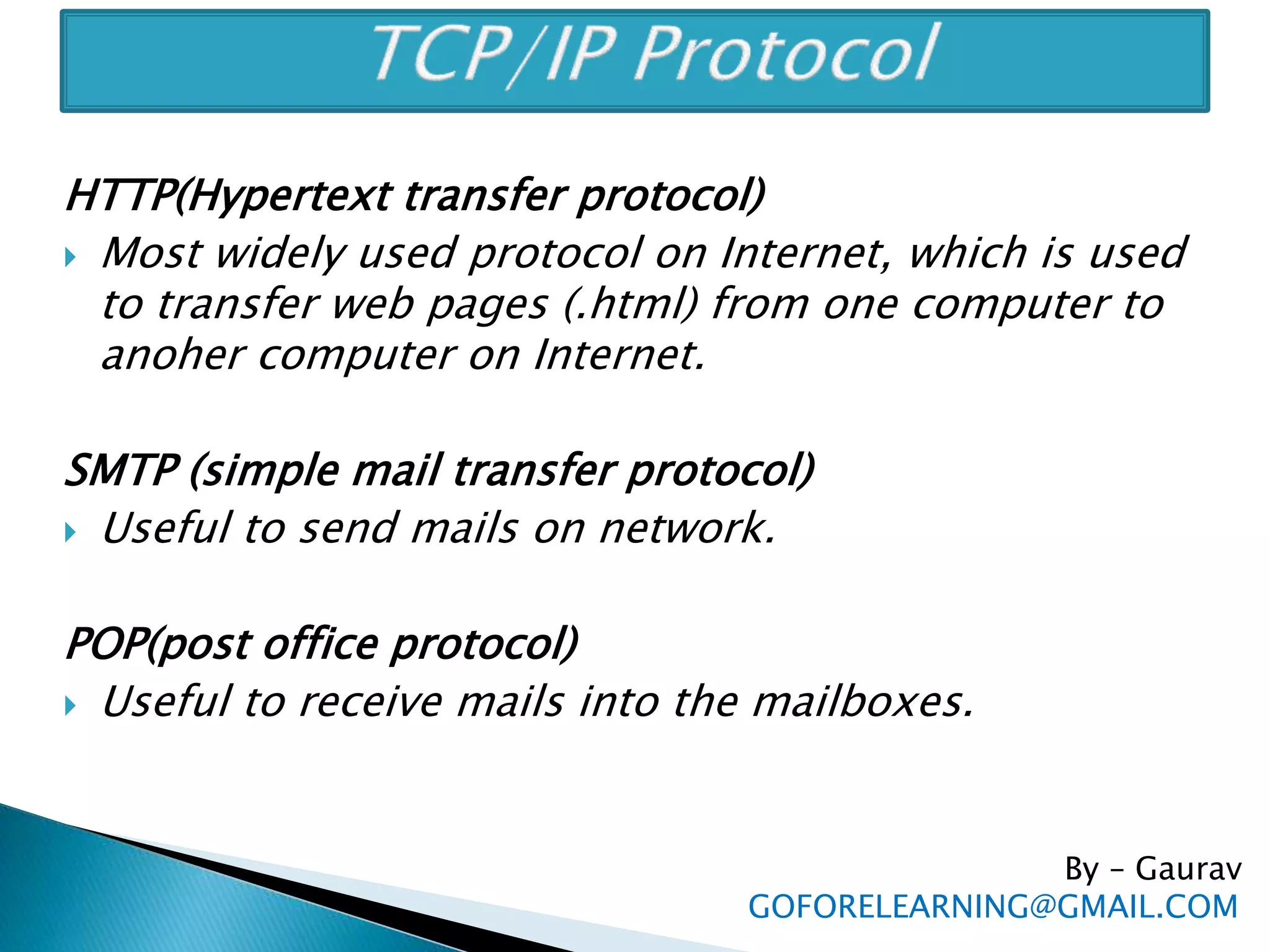
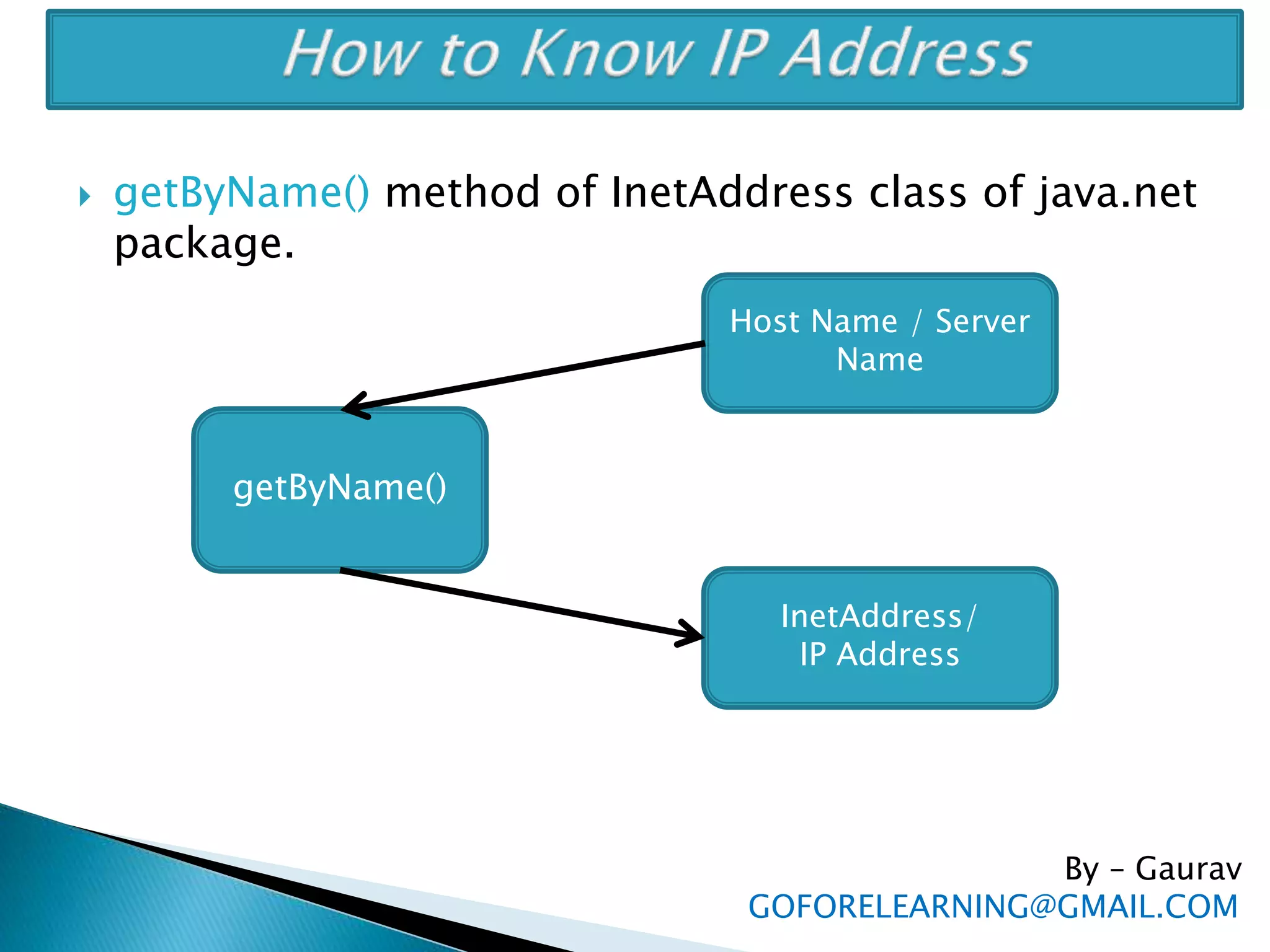
The document discusses the requirements and components of networking including hardware, software, protocols, and the TCP/IP model. It describes the five layers of the TCP/IP model in detail, including the application, TCP, IP, data link, and physical layers. It also discusses common network protocols like IP addresses, DNS, FTP, HTTP, SMTP, POP, UDP, and sockets. Finally, it provides examples of client-server programming using sockets in Java.