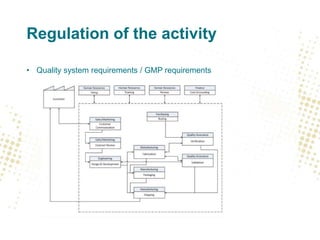
The document discusses the regulatory and legal aspects of 3D printing, focusing on its application in biofabrication, particularly for medical devices. It covers how the law views production facilities, materials, and processes involved, as well as implications for intellectual property and personal data management. Additionally, it emphasizes stricter regulations proposed for non-custom-made 3D printed medical devices, including quality system requirements and the handling of personal health data.