SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS.pptx
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
1 like•15 views
Somatic embryogenesis is the process in which a single cell or a small group of cells follow a developmental pathway that leads to reproducible regeneration of non-zygotic embryos which are capable of producing a complete plant. These non-zygotic embryos may originate directly from other organs or parthenogenetic embryos (without fertilization) or androgenetic embryos (from the male gametophyte).
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
Similar to SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS.pptx
Similar to SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS.pptx (20)
Morphogenesis, organogenesis, embryogenesis & other techniques

Morphogenesis, organogenesis, embryogenesis & other techniques
micropropagation- a very useful technology in plant tissue culture.

micropropagation- a very useful technology in plant tissue culture.
PPT on Tissue Culture Class 10 CBSE Text Book NCERT.

PPT on Tissue Culture Class 10 CBSE Text Book NCERT.
More from Dr CHITHRA
More from Dr CHITHRA (7)
Recently uploaded
Mehran University Newsletter is a Quarterly Publication from Public Relations OfficeMehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024

Mehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024Mehran University of Engineering & Technology, Jamshoro
https://app.box.com/s/7hlvjxjalkrik7fb082xx3jk7xd7liz3TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Recently uploaded (20)
Python Notes for mca i year students osmania university.docx

Python Notes for mca i year students osmania university.docx
Seal of Good Local Governance (SGLG) 2024Final.pptx

Seal of Good Local Governance (SGLG) 2024Final.pptx
Ecological Succession. ( ECOSYSTEM, B. Pharmacy, 1st Year, Sem-II, Environmen...

Ecological Succession. ( ECOSYSTEM, B. Pharmacy, 1st Year, Sem-II, Environmen...
TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...
Russian Escort Service in Delhi 11k Hotel Foreigner Russian Call Girls in Delhi

Russian Escort Service in Delhi 11k Hotel Foreigner Russian Call Girls in Delhi
Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median and Mode

Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median and Mode
Role Of Transgenic Animal In Target Validation-1.pptx

Role Of Transgenic Animal In Target Validation-1.pptx
Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx

Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx
Z Score,T Score, Percential Rank and Box Plot Graph

Z Score,T Score, Percential Rank and Box Plot Graph
Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes

Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes
This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.

This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.
Presentation by Andreas Schleicher Tackling the School Absenteeism Crisis 30 ...

Presentation by Andreas Schleicher Tackling the School Absenteeism Crisis 30 ...
SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS.pptx
- 2. Somatic Embryogenesis: Somatic embryogenesis is a process by which somatic (non-reproductive) plant cells are induced to form embryos, which can develop into complete plants.
- 3. Challenges and limitations: Genetic stability of somatic embryos. Cost of production. Limited scalability for some plant species. Ethical and regulatory considerations in genetic modification
- 4. Somatic embryogenesis is the process in which a single cell or a small group of cells follow a developmental pathway that leads to reproducible regeneration of non-zygotic embryos which are capable of producing a complete plant. These non-zygotic embryos may originate directly from other organs or parthenogenetic embryos (without fertilization) or androgenetic embryos (from the male gametophyte).
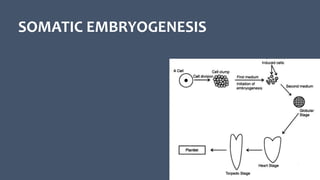
- 5. Key stages: Initiation: Dedifferentiated cells are induced to form embryogenic callus or somatic embryos. Proliferation: Rapid multiplication of embryogenic structures. Maturation: Development of somatic embryos into mature, plantable structures.
- 6. Factors influencing somatic embryogenesis: Growth regulators (auxins, cytokinins, etc.). Culture conditions (light, temperature, and nutrient medium). Genotype of the plant species. Applications: Clonal propagation of elite plant varieties. Genetic transformation and biotechnology applications. Germplasm conservation and preservation
- 7. 1. Direct Embryogenesis: The embryos initiate directly from the explant without callus formation and here some cells which are called as ‘Pre-embryonic determined cells’ (PEDC) initiates embryonic development, only those cells need to be released. Such cells are found mostly in embryonic tissues, certain tissues of young in vitro grown plants, hypocotyl, nucellus, embryo-sac, etc. 2. Indirect Embryogenesis: Here, the embryos are developed through cell proliferation i.e., callus formation. The cells from which embryos arise are called as ‘Induced embryogenic determined cells’ (IEDC). Here growth regulators with specific cultural conditions are required for initiation of callus and then redetermination of those cells into the embryo development.
- 11. SYNTHETIC SEEDS Synthetic seeds are artificial structures containing plant embryos or somatic embryos enclosed within protective coatings, similar to real seeds.
- 12. SYNTHETIC SEEDS
- 13. Components of synthetic seeds: Embryogenic tissue or somatic embryos. Encapsulation materials (e.g., alginate, gelatin). Protective coatings for storage and transport.
- 14. Types of synthetic seeds: i) Desiccated ii) Hydrated
- 15. i) Desiccated: Desiccated synthetic seeds are artificially created plant embryos that have been dehydrated to a low moisture content, allowing them to be stored for extended periods. These seeds are often used in agriculture and plant breeding for the preservation and easy distribution of valuable plant varieties. They can be rehydrated and planted to grow into mature plants, making them a convenient tool for plant propagation and preservation..
- 16. ii) Hydrated: Hydrated synthetic seeds are artificially created plant embryos that have been rehydrated after being in a desiccated or dehydrated state. This process involves adding water to the synthetic seeds to restore them to a suitable moisture content for germination. Once hydrated, these seeds can be planted to grow into mature plants. Hydrated synthetic seeds are used in plant propagation and agriculture, offering a convenient way to cultivate specific plant varieties with known traits. Hydrated synthetic seeds are artificially created plant embryos that have been rehydrated after being in a desiccated or dehydrated state. This process involves adding water to the synthetic seeds to restore them to a suitable moisture content for germination. Once hydrated, these seeds can be planted to grow into mature plants. Hydrated synthetic seeds are
- 17. Advantages: Ease of handling, storage, and transportation. Uniformity in plant quality. Reduced risk of disease transmission. Season-independent planting.
- 18. Potential applications in agriculture and horticulture: Rapid multiplication of valuable crops. Expansion of plant varieties to non-native regions. Improved crop yield and genetic consistency.
