Kit
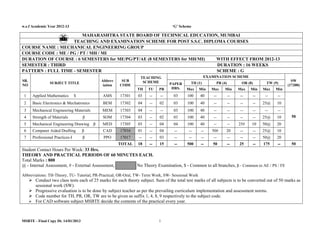
- 1. w.e.f Academic Year 2012-13 ‘G’ Scheme MSBTE - Final Copy Dt. 14/01/2013 1 MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION, MUMBAI TEACHING AND EXAMINATION SCHEME FOR POST S.S.C. DIPLOMA COURSES COURSE NAME : MECHANICAL ENGINEERING GROUP COURSE CODE : ME / PG / PT / MH / MI DURATION OF COURSE : 6 SEMESTERS for ME/PG/PT/AE (8 SEMESTERS for MH/MI) WITH EFFECT FROM 2012-13 SEMESTER : THIRD DURATION : 16 WEEKS PATTERN : FULL TIME - SEMESTER SCHEME : G SR. NO SUBJECT TITLE Abbrev iation SUB CODE TEACHING SCHEME EXAMINATION SCHEME SW (17300)PAPER HRS. TH (1) PR (4) OR (8) TW (9) TH TU PR Max Min Max Min Max Min Max Min 1 Applied Mathematics $ AMS 17301 03 -- -- 03 100 40 -- -- -- -- -- -- 50 2 Basic Electronics & Mechatronics BEM 17302 04 -- 02 03 100 40 -- -- -- -- 25@ 10 3 Mechanical Engineering Materials MEM 17303 04 -- -- 03 100 40 -- -- -- -- -- -- 4 Strength of Materials β SOM 17304 03 -- 02 03 100 40 -- -- -- -- 25@ 10 5 Mechanical Engineering Drawing β MED 17305 03 -- 04 04 100 40 -- -- 25# 10 50@ 20 6 Computer Aided Drafting β CAD 17016 01 -- 04 -- -- -- 50# 20 -- -- 25@ 10 7 Professional Practices-I β PPO 17017 -- -- 03 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 50@ 20 TOTAL 18 -- 15 -- 500 -- 50 -- 25 -- 175 -- 50 Student Contact Hours Per Week: 33 Hrs. THEORY AND PRACTICAL PERIODS OF 60 MINUTES EACH. Total Marks : 800 @ - Internal Assessment, # - External Assessment, No Theory Examination, $ - Common to all branches, β - Common to AE / PS / FE Abbreviations: TH-Theory, TU- Tutorial, PR-Practical, OR-Oral, TW- Term Work, SW- Sessional Work Conduct two class tests each of 25 marks for each theory subject. Sum of the total test marks of all subjects is to be converted out of 50 marks as sessional work (SW). Progressive evaluation is to be done by subject teacher as per the prevailing curriculum implementation and assessment norms. Code number for TH, PR, OR, TW are to be given as suffix 1, 4, 8, 9 respectively to the subject code. For CAD software subject MSBTE decide the contents of the practical every year.
- 2. w.e.f Academic Year 2012-13 ‘G’ Scheme MSBTE - Final Copy Dt. 14/01/2013 173026 Course Name : Mechanical Engineering Group Course Code : ME/PG/PT/MH/MI Semester : Third Subject Title : Basic Electronics & Mechatronics Subject Code : 17302 Teaching and Examination Scheme: Teaching Scheme Examination Scheme TH TU PR PAPER HRS TH PR OR TW TOTAL 04 -- 02 03 100 -- -- 25@ 125 NOTE: Two tests each of 25 marks to be conducted as per the schedule given by MSBTE. Total of tests marks for all theory subjects are to be converted out of 50 and to be entered in mark sheet under the head Sessional Work. (SW) Rationale: This subject is classified under core technology group and forms an important course of mechanical branch of engineering. The course envisages identification and testing of components, their principles of working and applications of various electronic devices, signal conditioning and processing. This subject introduces the concepts of mechatronics and PLC. This subject is prerequisite for the subject mechanical measurement and control as well as for mechatronics. General Objectives: The students will be able to: - 1. Identify and test different electronic components. 2. Use principles of circuit operations and its applications. 3. Distinguish various elements in analogue and digital electronics. 4. Understand applications of electronics in mechanical field for measurement and control. 5. Understand working of different types of transducers and their applications. 6. Understand concept of mechatronics and PLC.
- 3. w.e.f Academic Year 2012-13 ‘G’ Scheme MSBTE - Final Copy Dt. 14/01/2013 173027 Learning Structure: Application Procedure Principle Concept Facts Identify and test electronic devices, understand the electronic circuits and their applications in analog and digital electronics and for mechanical as well as in automobile field ,Mechatronics Assembly of components, Measurement of voltage, current, power, frequency using multimeter, data conversion PLC programming Ohm’ law, Kirchoff’s laws, principles for transducer(s) working, Principle of PLC Semiconductor theory, voltage, current, power, Thermal runaway rectification, filter, amplification, oscillation, multivibrator regulation, signal conditioning, data conversion , DAS, Mechatronics Resistor, Capacitor, Inductor, Diode, Transistor, Integrated Circuits, Heat Sink Multimeter, Transducers, Logic gates, Flip-flop and counters, Signal conditioning and PLC
- 4. w.e.f Academic Year 2012-13 ‘G’ Scheme MSBTE - Final Copy Dt. 14/01/2013 173028 Theory Topic and Contents Hours Marks 1: Solid-State Devices and Diode Circuits Specific objectives Students will be able to Draw energy band diagram and compare various types of materials Draw symbols ,state working principle and list out ,applications of electronics devices in electronics and mechanical field Sketch circuit diagram , state working with waveform for rectifier circuits Sketch block diagram and state functions of various blocks of regulated power supply Content 1.1 Fundamentals of solid state Devices– 10 Marks Material classification conductors, semiconductors and insulators, Energy band diagram intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors Solid state Devices -- schematic symbols, working principle and applications of Diode, Zener diode, BJT, FET,UJT, Photo-devices- LDR, Photo diode, Photo-transistor, LED, 7 segment display opto-coupler, LCD type and operation [No constructional details are expected] 1.2 Diode Circuits : 04 Marks Rectifier circuits Circuit diagram, working principle and waveforms for Half wave, Full wave-and Bridge rectifier, comparison w. r. t efficiency, PIV , ripple factor and applications Filters circuits C, inverted L and CLC filter circuit diagram and operation of these filters. 1.3 Regulated power supply 04Marks Concept of load regulation , line regulation , block diagram and functions of each block [Note Mathematical calculations is not expected for any subtopic ] 10 18 2: Transistor Circuits Specific objectives Students will be able to Explain working of BJT, Biasing of BJT and concept of thermal runaway Compare CB , CC and CE configuration Write operation of single stage amplifier. Draw circuits of RC, direct and transformer coupled amplifier and compare their performance Content : 2.1 Tansistor 06 Marks Working of NPN and PNP transistor, Configurations CB., CC and CE , Biasing circuits, concept of thermal runway , construction and use of heat sink [No need of design and mathematical analysis ] 2.2 BJT Circuits 08 Marks BJT as an amplifier single stage amplifier, Multistage amplifier, RC coupled, direct coupled and transformer coupled amplifier, their frequency response and applications BJT as a switch 08 14 3: Analog Circuits Specific objectives Student will be able to Explain and draw block diagram of IC 741, circuits of op amp as
- 5. w.e.f Academic Year 2012-13 ‘G’ Scheme MSBTE - Final Copy Dt. 14/01/2013 173029 inverting, non-inverting, differential amplifier, adder, substractor, integrator , differentiator, and Instrumentation amplifier Explain and draw block diagram of IC 555, circuits of timer as BMV , AMV and MMV State Barkhausen criteria and compare oscillator circuits Content: 3.1 Operational amplifier 08 Marks IC741 Block diagram, pin diagram, specifications, and applications Op amp configurations- Inverting , Non-inverting and differential circuit diagram and operation of these circuits Op amp as adder, subtractor , integrator and differentiator Instrumentation amplifier [simple numerical are expected ] 3.2 Timers 06 Marks IC 555–Block diagram pin diagram specifications, Concept of multivibrator IC 555 as AMV, BMV, MMV. 3.3 Oscillator Marks 04 Concept of oscillator, Barkhausen criteria Comparison of RC , LC and Crystal oscillator [ no any special circuit is expected] 08 18 4: Digital Circuits Specific objectives Student will be able to Draw symbol and write truth table of all logic gates , various combinational circuits, sequential circuits Compare microprocessor and microcontroller Content: 4.1 Logic gates 04 Marks Study of logic gates, symbol, truth table NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOR, XOR, XNOR 4.2 Combinational Circuits 04 Marks Half and Full adder, substractor, Multiplexer, de multiplexer, decoder and encoder, applications [only block diagram , truth table and simple circuits] 4.3 Sequential Circuits 10 Marks Flip Flops Block diagram of RS,JK, Master Slave JK, D and T, Triggering mechanism Application of flip flop Basics of counter, asynchronous counter, Decade counter, Ring counter, Shift register. [only circuit diagram and operation is expected not details of timing diagram] Concept of Microprocessor and microcontroller Features of 8085 and 8051. Comparison of microprocessor and microcontroller Applications 14 18 5: Transducers and Signal Conditioning Specific objectives Student will be able to Define, state characteristics and Classify transducers Draw block diagrams and explain operation of ADC, DAC, AC and DC signal conditioning. Explain and draw block diagram of single and multi-channel DAS and data logger. Content : 5.1 Transducers 06 Marks Definition, Classification characteristics of transducer, Active and passive, primary and secondary, Electrical, mechanical optical transducer their examples, selection criteria. 5.2 Signal conditioning Marks 08 08 14
- 6. w.e.f Academic Year 2012-13 ‘G’ Scheme MSBTE - Final Copy Dt. 14/01/2013 1730210 Introduction to Data converter ADC and DAC [only principle of operation and applications] Signal conditioning need and Block diagram of AC and DC signal conditioning, DAS - single channel multi-channel , applications Data loggers 6: Mechatronics and PLC Specific objectives Student will be able to State meaning, need and basic concept of mechatronics. State features of real time mechatronics State applications, advantage disadvantages of mechatronics State operation with block diagram of CNC, FMS, AVCS CIM Robotics, State working of basic PLC architecture and write simple programs. Content: 6.1 Fundamentals of mechatronics 10 Marks Concept of mechatronics, basic elements of mechatronics, Overview of mechatronics design process modeling and simulation, prototyping and deployment .Introduction to real time mechatronics system, advantages and disadvantages, applications. Functional diagram, approach to CNC, flexible manufacturing system (FMS), Computer integrated machine (CIM), Robotics, Advance vehicle condition system ( AVCS) [only brief information ] 6.2 Programmable Logic Controller(PLC) 08 Marks Basic PLC structure, principle of PLC, architecture and components, PLC programming, selection of PLC, Concept of Nano PLC, PLC applications, Ladder diagrams, Ladder diagram circuits Simple Ladder programming examples 16 18 Total 64 100 Practical: Skills to be developed: Intellectual Skills: 1. Identification and selection of components. 2. Interpretation of circuits and signals. 3. Understand working of mechatronics systems and PLC Motor Skills: 1. Drawing of circuits. 2. Measurement of various parameters using multimeter. 3. Testing of components using IC tester. 4. Follow standard test procedure. List of Practical- 1. Identify various passive components such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, switches, transformers, breadboard and cables and write their specifications. 2. Identify various active electronic components such as diode, BJT, FET, UJT, LED, Photodiode. 3. Use of multimeter (analogue and digital) for current, voltage and resistance measurement Testing of various electronics components. 4. Measure frequency and voltage using CRO. 5. Construct rectifier circuits on breadboard and observe waveforms on CRO 6. Measure load regulation of un-regulated power supply and regulated power supply.
- 7. w.e.f Academic Year 2012-13 ‘G’ Scheme MSBTE - Final Copy Dt. 14/01/2013 1730211 7. Trace the given RC coupled amplifier and plot frequency response f and determine its bandwidth. 8. Construct Op Amp as inverting amplifier and Non Inverting amplifier on breadboard and observe the waveforms on CRO. 9. Verify truth tables for logic gates- . NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOR, XOR, XNOR Testing of an IC using IC tester. 10. Assemble a square wave oscillator for 100 Hz using IC 555. (Use as table multivibrator). 11. Write simple PLC program and execute on PLC (2 exercises). [Note: Expected group size for practical no. 1 and 2 is one, for practical no.3 to 10 is 2 and for practical no 11 it may be 4 ] Assignments Assignments are part of term work. Assignment shall include observation of systems from mechatronics point of view. Individual shall prepare report consisting of functional block diagram of the system , specifications of major components and system operation I. Observe and prepare report on mechatronics used in camera system II. Observe and prepare report on mechatronics used in robotic system (Where ever possible arrange visit to manufacturing unit where mechatronics is used for production purpose and prepare report.) Note Teachers are expected to make students familiar with the Data Books and Operation Manuals and also encourage them to visit related websites. Learning Resources: Books: Sr. No. Author Title Publisher , Edition 01 Boylestad Electronics devices and circuit Theory Pearson (Tenth edition) 02 Shalivahnan Electronics Devices and circuits TMH 03 Baru Vijay Basic Electronics Engg. Wiley India Pvt.Ltd (first edition) 04 De Debasnis Ghatak Kamakhya Basic Electronics Pearson (First edition ) 05 Bolton Mechatronics Pearson (Fourth edition ) 06 K.P.Ramchandran, G.K.Vijayaraghavan M.S.Balsundarm Mechatronics (intergrated mechanical electronics systems) Wiley india pvt.ltd ,(first edition) Journals – Manufactures catalogues IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics. Mechatronics Journal – Elsevier 1. IS, BIS and International Codes: NF E 01-010 2008 – AFNOR (French standard NF E 01-010) XP E 01-013 2009 – AFNOR (French standard NF E 01-013) 2. Websites: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mechatronic
- 8. 1 CURRICULUM REVISION PROJECT 2012 TEACHER GUIDE FOR SUBJECT: BASIC ELECTRONICS & MECHATRONICS (17302) THIRD SEMESTER MECHANICAL ENGINEERING GROUP JUNE 2013 MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION, Mumbai
- 9. 2 FIRST PRINT, JUNE 2013 CURRICULUM DEVELOPMENT CELL, MSBTE, MUMBAI. TEACHER’S GUIDE AND SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER Designation Team of Design Education Technology Consultant Prof.C.R.Joshi Project Period MAY 2013 TO June 2013 Coordinator Mr.Akole K.P. Government Polytechnic Nandurbar kp.akole@rediffmail.com 9158323194 Subject Experts 1. Mrs.V.K.Khobare B.V.J.N.I.O.T (0125) khobarevidya@gmail.com 9922402042 2. Mrs.M.T.Dangat A.I.S.S.M.S.’S Poly. geetanjalee_dm@yahoo.com 9423041214 © 2012, Maharashtra State Board of Technical Education, 49, Kherwadi, Aliyawar Jung Road, Bandra (East), Mumbai-400051. Maharashtra State, India. No part of this Laboratory Manual be reproduced in any form or by any means, without permission in writing from MSBTE Mumbai.
- 10. 3 1. APPROACH TO CURRICULUM DESIGN 1.1 Background: MSBTE is introducing the revised curriculum from the academic year 2012-13. There are many institutions in the state running different diploma courses. In order to ensure uniform and effective implementation of the curriculum it is necessary that every teacher is aware of approach for curriculum design, educational principles to be adopted, learning resources to be used and evaluation methods. The teacher guide prepared for each subject will provide the inputs related to above mentioned aspects to achieve uniform and effective implementation of curriculum of various subjects. 1.2 CURRICULUM PHILOSOPHY MSBTE has adopted systems approach while designing the scientific based curriculum since 1995. The same approach has been adopted while revising the curriculum in semester pattern. Fig. No. 1 shows the systems diagram. This diagram provides the holistic view for curriculum designing, development, implementation and evaluation The input to polytechnic education system is the students having 10+ qualifications. The teaching learning process occurs in the institution for six/eight semesters. The output of the system i. e. Diploma pass out is normally the input to industries. (Some students do go for higher education). While designing the curriculum the expectations of the industries play a major role. Due to globalization and competition the industries expect that pass outs have generic and technological skills along with right attitude. To fulfill the needs derived from systems approach following conceptual framework is considered: 1.3 Curriculum: “Curriculum is an educational program designed and implemented to achieve specified educational objectives” This definition takes into account the fact that Education is purposeful There is an organized plan of action contemplated Such a plan is translated into action through appropriate strategies of implementation.
- 11. 4 REGULATING AGENCIES M.H.R.D., A.I.C.T.E. 5) MGT MOE DTE, DIIC, MSBTE POLYTECHNICS 3 INPUT 1. Students 2. State level 4) PROCESS EDUCATIONAL PROCESSES 2) OUTPUT 1) CUSTOMER RO level Administrator Principals State Institutional Curriculum LRDC Instructional Student’s HODs Planning Planning Design & Design Learning Teachers & Develop LRUC Tech. Support Staff Ministerial Staff 3. Identified Resource, ENABLING Persons PROCESSES 4. Identified Faculty (Trainers) I.I.I. ` 6) RESOURCES PHYSICAL HUMAN INFORMATION FINANCE TIME ENERGY Feed Back Fig 1 Systems Approach External 1. Industries 2. Service Sector Manpower having knowledge, skills and attitudes required to use, operate, evaluate, update and maintain MIS Diploma Engineer with desired skills I.I.I. H.R.D. Organisational Development M.I.SState Project Planning Internal Staff of: 1. MOE 2. DTE/ DIIC/ MSBTE & Regional Offices AND Faculty
- 12. 5 1.4 Curriculum goals 1. To develop confidence in students by providing more exposure to industry experience and world of work at global level. 2. To provide conceptual knowledge and develop analytical ability 3. To develop communication skill with good English by providing sufficient practice 4. To enhance latest technical knowledge industry interaction and media 5. To develop learning to learn skills and life skills to cope up with industrial culture 6. To impart managerial skills by providing appropriate theoretical inputs 7. To develop problem solving ability through technical projects. 1.5 DESIRED SKILLS Industries expect from the diploma engineer the abilities and skills of general nature and specific to the job performance. The curriculum aims at developing life skills and technological skills so that the diploma pass outs would be suitable for industry. The skills are listed below: Life Skills: Search information from various sources Develop communication ability Develop Presentation skill Work as a member of a team/group and as leader Collect field data Develop Learning to learn Write report for given task/work/project Develop computer proficiency Develop observation skills Technological Skills: Diploma engineers should possess following intellectual and motor skills in order to satisfactorily perform duties assigned to them:
- 13. 6 Intellectual skills. After studying the students will be able to: 1. Identification and selection of components. 2. Interpret circuit diagrams and specifications of electronic systems in technical/ service manuals for installation, testing and commissioning. 3. Calibrate and test measuring instruments. 4. Locate faults in various instruments 5. Interpret test results 6. Select proper transducer for applications 7. Understand need of signal conditioning circuits 8. Understand working of mechatronics systems and PLC 9. Use of appropriate software for PLC Motor skills: After studying the students will be able to: 1. Draw circuits diagrams 2. Measure various parameters using multimeter 3. Test various components using IC tester 4. Troubleshoot various electronic systems 5. Develop soldering skills 6. Install hardware devices 7. Operate electronic equipments 8. Test proto type circuits using appropriate equipments 1.6 Salient Changes in the curriculum: For First Semester Basic Science is divided into two parts- Basic Physics and Basic Chemistry. Theory examination of both parts as well as practical examination of both parts will be conducted on separate days. Sum of theory marks of both parts shall be considered for passing theory examination of Basic Science. Similarly it is applicable to practical examination. It is mandatory to appear for theory and practical examination of both parts. Candidate remaining absent in any examination of any section will not be declared successful for that exam head. For second semester Applied Science is divided into two sections- Applied Physics and Applied Chemistry where the theory examination of 50 marks each and practical examination of 25 Marks each will be conducted separately and the minimum passing marks for Engineering Science will be the combination of both the sections. . It is mandatory to
- 14. 7 appear for theory and practical examination of both parts. Candidate remaining absent in any examination of any section will not be declared successful for that exam head. The components of Development of Life Skills were taught in two semesters. In Development of Life Skills –I the topics related to personal development, such as Learning to Learn Skills, personality development, presentation skills etc. were included. In Development of Life Skills – II the topics related to Team Building, Leadership, group behavior etc. were covered. In the revised curriculum the scope of development of life skills has been broaden to include behavioral science component. Therefore the subject Development of Life Skills – II has been renamed and it is now included at Vth Semester in the revised curriculum under the title Behavioral Science. The subject of Professional Practices was introduced to integrate the skills acquired in Development of Life Skills, through technical subjects from second to sixth semester. The experience in implementing the contents of the subject shows that there are limited activities possible in second semester as the technical knowledge given to the students is very limited. Also at sixth semester the student are doing projects in which they are performing many activities included in the Professional Practices and therefore it is proposed that the subject of Professional Practices be prescribed only for three semesters vis. Third, fourth and fifth semesters. Introduction of Environment Studies at fourth Semester for all courses From the experience of implementation of Elective Subjects at V and VI semesters in last five years, it is proposed to have only one elective either at the sixth semesters for all courses. However the specialized courses like Medical Electronics, Electronics and Video Engineering will not have provision for electives. For elective, student will have to choose one from the given two/three subjects. While revising the curriculum redundant /obsolete topics/sub topics are being replaced by new/advance technology topics/sub topics. Embedded Technology and P.L.C. subjects are made compulsory. More emphasis has given on integrated circuits.
- 15. 8 2. OBJECTIVES 2.1 Introduction Objectives are the statements which describe the expected learning outcome. Such statements enable teachers to plan instructional process with appropriate resources. These objectives also provide a direction to frame proper questions to assess the learning outcome. During last decade there has been research on cognitive approach in psychology. This approach is based on biological structure of brain and meta-cognitive knowledge dimension. Important elements of this approach which form basics of learning are explained below. 2.2 Basic Model of Learning The basic model of learning is as shown below: GENERIC DIAG. – Stimulus and Response Fig. 2: Generic Diagram of Learners. Stimulus: The information is received by senses from many things in surroundings. It activates senses for experience. It is called as stimulus. It. includes people, objects, events, symbols etc. For example: teachers, friends, instruments, drawings, text etc are stimulus for students. GENERIC DIAG.- STIMULUS & RESPONSE Objects People Events Symbols SELF ACT. SELF ESTEEM SOC. BELONG. SECURITY BASIC NEEDS COG. PHY. VERB. STIMULUS EMOTIONAL CENTRERESPONSE FEEDBACK COGNITIO SR STM/ WM LTM Learner Memory
- 16. 9 Cognition: Cognition is the act of knowing. It deals with mental activities of the learner. It is triggered due to stimulus. It involves memory, its components structure of knowledge in memory and various processes in memory. The study of the same is done to know how learning takes place. Emotional Centre: Stimulus may be pleasant or unpleasant feelings. It decides whether learner will approach to stimulus situation or avoid it. This is the effect of emotions of learners in emotion centre. Response: When stimulus stimulate the learner reacts. This response may be mental response like reflection of face (cognition), physical movement (motor skills) or verbal response like communication. The response always aims at changing the stimulus situation. Feedback: When teacher asks the question, you answer it. Then based on the content of the answer, teacher says whether it is ‘correct’ or ‘wrong’. This is feedback. Thus it may be the information about the changed stimulus situation provided after response by the learner. Feedback helps learner to compare changed stimulus to expected change in stimulus. Basic Concepts: Different forms used in the study of memory and its working are as below: Memory: It is the ability to recall the information, which has been previously learnt through experience. In context of memory structure, it is the location learned information is stored. Storage: It is process of putting information in the memory. Encoding: In memory, the information is not stored in original form but in numerical form, verbal form, visual images etc. Encoding is the process of modifying information from one form to another form. It helps to store information easily. It also stores new information to existing knowledge. Retrieval: It is the process to find the information that is previously stored in the memory so that it can be put to use. Components of Memory: The most prevalent view of human memory states that memory has three distinct components viz. Sensory Register (SR) Working Memory (WM) or Short Term Memory (STM) Long Term Memory (LTM)
- 17. 10 Control Process: This is the process of movement of information from one memory component to another memory component. Perception: It is the final image formed in WM after processing the information from SR and LTM. The final image consists of visual image supported by elaboration and emotional content. 2.3 Domains of Learning: Learning is a process by which students develop relatively permanent change in mental associations through experience. This is how learning is defined by cognitive psychologists. Behavioral; psychologists define learning as a relatively permanent change in behavior. There are following domains of learning: A: Cognitive Domain relates to intellectual skills or abilities B: Affective Domain relates to emotions, feelings, likes, dislikes etc. C: Psychomotor Domain relates to manipulative skills of hands, legs. Eye-hand coordination in Engineering & Technology courses, endeavor is made to design curriculum with a focus on development of cognitive skills through classroom teaching. Where as manipulative (psychomotor) skills are developed in workshops, laboratories & seminars where students work individually or in a group. Development of affective skills attitudes and value is supposed to be acquired through projects and co curricular activities. These are also developed from the work culture or institutions. How far a student has developed these abilities/skills especially from cognitive and psychomotor domains is assessed on the basis of suitable examinations. When classroom and laboratory teaching is viewed in this light, evaluation becomes an integral part of teaching – learning process. 2.3 LEVELS OF LEARNING: Question paper is a tool/ instrument designed to test the extent of learning of the student. Various questions set in a question paper should assess the abilities of students to respond to level of learning. Dr. Bloom a German educationist classified levels of learning in cognitive domain for SR WM LTM
- 18. 11 the purpose of writing objectives and assessment. Dr. Bloom’s revised taxonomy is based on cognitive psychology and is two dimensional. First dimension is cognitive process dimension ad other is knowledge dimension. Details of these two dimensions are given below. 2.4.1 Cognitive Domain: Dr. Benjamin Bloom (1956) analysed questions asked in various examinations in American situation and proposed a hierarchical arrangement of instructional objectives (Intellectual abilities) tested by these questions. The lowest level of cognitive learning achieved by a student is demonstrated by the recall of information that the student retrieves from his long term memory. So, the storage and retrieval of specific facts, concepts, principles, laws, definitions, properties, procedures etc. directly from memory was classified as a knowledge level objective. Thus questions testing memory of students were treated as at the lowest level of the hierarchy of intellectual abilities. The other levels of hierarchy proposed by Dr. Bloom in 1956 relate to the degree of information processing required in the brain needed to provide answer to a question. The various levels in the cognitive hierarchy proposed by Dr. Bloom in 1956 and further revised in 2001 are given below in the diagrammatic form.
- 19. 12 Following are the details of each level which indicate the general and specific objectives. Further appropriate verbs are given which are useful in setting good questions. In this table only four levels are considered for diploma students. Description of the Major Levels in the cognitive Domain (Bloom’s Taxonomy) Illustrative General Instructional Objectives Illustrative verbs for stating specific learning outcomes Remember – Knowledge is defined as the remembering of previously learned material. This may involve the recall of a wide range of material, from specific facts to complete theories, but all that is required to mind of the appropriate information. This represents the lowest level of learning outcomes in the cognitive domain Knows common terms, specific facts, basic concepts, principles, methods & procedures Define, describe, identify label, list, match, name, outline, reproduce, select, state Understand – This is defined as the ability to grasp the meaning of material. This may be shown by translating material from one form to another (words or numbers) by interpreting material (explaining or summarizing), and by estimating future Understands fact, principles Interprets verbal material, Interprets charts, tables, graphs. Translates verbal Convert, distinguish estimate, explain, extend, generalize, give examples; infer, paraphrase, predict, rewrite, summarize, Remember Understand Apply Analyse Evaluate Create 1 2 3 4 5 6
- 20. 13 trends (predicting consequences or effects). Draw sketches these learning outcomes go one step beyond the simple remembering of material and represent the lowest level of understanding. material to mathematical formula. Estimates consequences implied in data. Justifies methods & procedures. draw labeled sketches. Apply – Application refers to the ability to use learned material in new and concrete situations. This may include the application of such things as concepts, principles, rules, methods, laws and theories. Learning outcomes in this area require a higher level of understanding than those under the level described earlier. Applies principles to new situations. Applies theories to practical situations. Solves mathematical problem. Construct charts, graphs Demonstrates correct usage of a procedure Change, compile, demonstrate, discover manipulate, modify operate, predict, prepare, produce, show, solve, use. Analyze – Analysis refers to the ability to break down material into its component parts so that its organizational structure may be understood. This may include the identification of the parts, analysis of the relationship between parts, and recognition of the organizational principles involved. Learning outcomes here represent a higher intellectual level than “understand” and apply because they require an understanding of both the content and the structural form of the material. Recognizes unstated assumptions and logical fallacies in reasoning. Distinguishes between facts and inferences. Evaluates relevance/ adequacy of data. Breakdown, diagram, differentiate, discriminate, distinguish, identify illustrate, infer, outline, point out, relate, select, separate, subdivide. 2.4.2 Categories of Knowledge Dimension After considering the various designations of knowledge types, especially developments in cognitive psychology that have taken place since the original framework of Bloom’s taxonomy, knowledge is categorised in 4 types – Factual , Conceptual, Procedural and Meta- cognitive. Factual Knowledge (A) is knowledge of discrete, isolated content elements. It includes knowledge of terminology and knowledge of specific details and elements. In contrast, Conceptual Knowledge (B) is knowledge of “more complex, organised knowledge form”. It includes knowledge of classifications and categories, principles and generalizations and theories, models and structures. Procedural Knowledge (C) is “knowledge of how to do something”. It includes knowledge of skills and algorithms, techniques and methods, as well as knowledge of criteria used to determine and/or justify “when to do what” within specific fields and disciplines.
- 21. 14 Meta-cognitive knowledge (D) is “knowledge about cognition in general as well as awareness of and knowledge about one’s own cognition. It encompasses strategic knowledge, knowledge about cognitive tasks, including contextual and conditional knowledge; and self-knowledge”. Assessment is required to be done on the basis of categories of knowledge and levels of learning. Table below indicates the two dimensional grid based on Blooms Taxonomy for setting questions. Knowledge Dimension COGNITIVE PROCESS DIMENSION 1 Remember 2 Understand 3 Apply 4 Analyze A. Factual Knowledge B. Conceptual Knowledge C. Procedural Knowledge D. Meta-cognitive Knowledge 2.5 Components of Curriculum: 2.5.1 Rationale: It indicates the logical basis for the inclusion of the subject in the curriculum It also indicates the importance of the subject related to entire curriculum. Rationale tells the students the connection of subjects related to study of higher level subjects and also the use in their job/profession. 2.5.2 Objectives: Objectives indicate what the student will be to do/perform after he completes the study of the subject. It also in other words indicate the scope of the subject. Objectives indicate what is achievable and hence gives direction ot the student about how to study the subject, what important things are to be observed and performed during practicals. Just as rationale indicates the use of the knowledge gained while studing the subject, objectives indicate how efficiently and effectively one can work if the objectives are fulfilled while studying the subject.
- 22. 15 2.5.3 Learning Structure: It graphically/pictorially indicates the content of the curriculum of the subject and what is to be learnt in the subject. As you know that Cognitive Domain knowledge is divided in four components as mentioned in the Two dimensional grid. Of this Factual, Conceptual and Procedural knowledge components are identified in the curriculum of the subject along with the applications. Facts, Concepts, Principles are used in developing procedures and applications. So these are given sequentially below procedure as Principles, Concepts and Facts in their order. Learning structure also provide an idea about how to develop the subject logically to achieve the objectives. 2.5.4 Contents: List of topics and subtopics to be included in the curriculum of the subject is given in the contents. This helps in achieving the rationale and objectives identified. Contents indicate the importance of the topics, sub topics in development of the subject and accordingly weightages in terms of Hours required to teach the subject components, so that the desired learning takes place. Marks to be allotted while testing the knowledge gained by the student are also indicated. 2.5.5 Practicals: While designing the curriculum the objectives are identified. To achieve these objectives students have to develop certain intellectual and motor skills. These skills are developed through well designed Practicals. So in the curriculum the list of the skills to be developed through Practicals is given. The list of Practicals is so developed that after performing the Practicals identified skills will be developed. Here it is necessary that the teacher gives enough opportunity to all the students to perform the practical properly to develop the skills in each one of them. The skills will be developed if the students actually perform certain activities or tasks. Therefore it is necessary that any practical included in the curriculum necessarily involve some activities to be done by the students. So one has to think and innovate to modify the study experiments so that students will be asked to perform some activity. It could be in terms of identifying components, listing of materials used for manufacturing the components, stating importance of use of certain materials etc. So any curriculum of a subject is so designed that it achieves the objectives of that subject as well fulfill the objectives of the entire curriculum 3. CONTENT ANALYSIS 3.1 Components of Content Analysis: As we have discussed earlier, any curriculum or syllabus of a SUBJECT given to the teacher is organised in terms of UNITS which include TOPICS or SUB-TOPICS as the case may be
- 23. 16 indicating the TIME in which it is expected to be taught to the students. Components of a topic or part thereof are analysed here at a micro level. Before we begin actual teaching of any topic (lesson), we must carefully and critically analyse it so that we can plan for teaching - select appropriate media, methods and techniques of teaching and arrange the suitable resources to be required. This analysis of the content of a Topic results in identification of the following components of the content: 1. Facts 2. Concepts 3. Principles (rules, laws, theories) 4. Applications 5. Procedures 6. Skills (Psychomotor Skills), and 7. Attitudes (underlying affective behaviors as quite often these are not specifically mentioned in the curriculum, still they are to be developed lesson after lesson gradually). When we undertake the exercise of content analysis, we ourselves understand the subject fully well and at the same time we become clear as to what we are going to teach. It also gives us an idea as to which methods of teaching and media of instruction we should prepare and use and also what resources including time we will require. This analysis will also enable us to design assignments as well as how we are going to assess students learning. Since the nature of the components of content (I to 7) differs from one another. These are learned by the students differently as different mental processes are involved in learning these components. The immediate implication of this varying nature of components is that these need to be taught differently and assessed differently. For example, if you look at components I to 5 all of which belong to Cognitive Domain of Learning; Component 6 belongs to Psychomotor Domain and Component 7 belongs to Affective Domain (cannot be taught as these attitudes are caught), you will find that these differ from one another. The classification of human behaviors (activities) into the above three domains of learning entails the use of entirely different methods and media of instruction. Different locations of learning (classroom, laboratories, workshops, field visits) need to be selected.
- 24. 17 Now we will discuss these components in some detail and see how each one of these should be taught and assessed differently. 3.1.1 FACTS: These are universally accepted and commonly understood items about which there cannot be much argument and discussion. These are required only to be informed. For example: The sun rises in east and sets in the west; names of scientists and the year in which their theories were propounded; the rules and regulations of admission and examination prescribed by the University are some of the examples of facts. Sometimes, they need not be emphasised in the class as the students already know them. But information can be passed on by word of mouth, if deemed necessary. 3.1.2 CONCEPTS: A concept is an abstraction or an idea that permits the learner to classify a variety of related phenomena into a convenient and meaningful category. Concept of something is like a picture formation of that thing which helps in conceptualizing it. Gagne says that concept learning produces a certain fundamental change in human performance that is independent of subject or content. Concepts can be divided into the following two categories: 1. Concrete Concepts: those which can be seen, touched and manipulated e.g. house, book, table, chair, cat, dog, any machine or apparatus, overhead projector, chalkboard and duster. 2. Abstract Concepts: those which cannot be seen and touched and handled but can only be imagined e.g. force, work, fractions, decimal, bending moment, moment of inertia, friction, heat, and induction. Teaching of concrete concepts is not that difficult because the teacher can show the object physically or its picture. On the contrary, teaching of an abstract concept offers difficulty to the teacher as well as for students to understand. These concepts can be learned by heart without understanding as children mug up Nursery Rhymes without understanding even a single word. But at the stage of higher tearing, this type of rote learning is not desirable. Adolescents (teenagers) and adults do not accept things without understanding.
- 25. 18 3.1.3 Concept Attributes: We identify a concept and understand it, once we are told about its qualities characteristics, and features. They are technically called concept attributes. While teaching a concept to our students we must spell out as many attributes as possible for better understanding of the concept. Example: The Concept of Automation Attributes: 1. Automation is an automatic system without manual operation. 2. Automation increases speed of system. 3. Automation requires less time. 4. Automation requires less manpower. 5. Automation used for Remote control. 6. Automation used for material transfer (conveyer belt) in process industry. Towards the end of this Theme Paper a number of examples of concept attributes are given for your guidance. The following questions pertaining to a concept (object or process) will be helpful in writing concept attributes: 1. What it is. 2. What are its constituent parts. 3. How it works. 4. How it is similar to and different from other known concepts. 5. What are its uses? 3.1.4 PRINCIPLES: A principle is a statement of relationship between two or more concepts. Principles are sometimes called rules, laws or generalizations. In others words, relationship between two or more concepts which is scientific and universally true is called a Principle. For Example: (related concepts are underlined) 1. Actions and reactions are equal and opposite. 2. Ohm's law I = V/R is a principle, where I (Current), V (Voltage), and R
- 26. 19 (Resistance) are the concepts. While teaching a principle we must recall the concepts which it involves. These concepts might have been taught in the previous lesson. As you already know, concept learning is a prerequisite to Principle learning. Thus we recall the concepts of current, voltage and resistance by asking questions to the students. Only after that we must tell the relationship among these i.e. Ohm's Law. 3.1.5 APPLICATIONS: Whatever principles, laws and theories have been learned are only academic exercises unless these are applied to solve a practical problem. In other words, we call this application transfer of learning to a new situation. If you recall, the process of learning dealt with in Theme Paper 2, you will appreciate that the litmus test of learning having occurred is its application in a new situation or solving a new problem. For example: 1. Ohm's law can be applied to find out the unknown quantity (voltage, current, and resistance). 2. Design of a structure can be made based on related principles and theories. 3. Principles of learning and events of instruction can be applied in ‘Designing a lesson Plan' and 'Presenting the lesson in the classroom". 4, The above principles can also be applied while preparing textbooks, workbooks, learning packages and laboratory manuals to be used by the students. 3.1.6 PROCEDURES: While analysing the content of a topic you might come across certain standard procedures which are prescribed to perform an operation or a given task. These procedures should be clearly identified and taught accordingly not to be left to chance. We should not pre-suppose that the students understand them. We cannot afford to take these things for granted. For Example: 1. Procedure of obtaining digital signal from analog signal 2. Procedure of obtaining analog signal from digital signal
- 27. 20 3.1.7 SKILLS (PSYCHOMOTOR): A skill is an ability to perform a task expertly and well. The skilled performance; must meet a pre-specified standard of acceptable performance. A skill has the following three characteristics: 1. It represents a chain of motor responses; 2. It involves the co-ordination of hand and eye movements, and 3. It requires the organization of chains into complex response patterns. Skills could be intellectual (thinking, understanding); interactive (communication skills) and social (socialising, mixing up with others) also. But normally when we use the word skills, it refers to psychomotor skills. For Example: 1. Soldering the components on the P.C.B. 2. Operating the controls on the front panel of instruments 3. Making proper circuit connections, and 4. Switching on the circuit.. Laboratories and workshops of Polytechnics are the locations where these skills are developed among the students under the guidance of expert instructors of operators. Drill and practice are the main methods of teaching and learning these skills through model demonstrations and careful observations thereof. Alongside developing these skills, desirable attitudes like cooperation, team work, leadership, safety, cost consciousness are also developed. 3.2 TEACHING OF CONCEPTS; In order to teach concepts effectively the following steps have been suggested by De Cecco & Crawford (1974). Steps Suggested: 1. Describe the performance expected of the student after he has learned the concept. 2. Reduce the number of attributes to be learned in complex concepts and make important attributes dominant. 3, Provide the student with verbal indicators (explanation). 4. Provide positive and negative examples (non-examples) of the concept. 5. Present the examples in close succession or simultaneously. 6. Provide occasions for student responses and the reinforcement of these responses, and 7. Assess the learning of the concept.
- 28. 21 3.3 TEACHING OF PRINCIPLES: De Cecco & Crawford (1974) has suggested the following steps for teaching principles effectively. Steps: 1. Describe the performance expected of the student after he has learned the principle. 2. Decide and indicate which concepts or principles the students must recall in learning the new principle. 3. Assist the student in the recall of component concepts. 4. Help the student in the recall of component concepts. 5. Help the student to combine the concepts and put them in a proper order. 6. Provide for practice of the principle and for reinforcement of student responses. 7. Assess the learning of the principle. 3.4 CONCLUSION: To sum up, it can be said that. it is essential for the teachers to develop the skills of 'Content Analysis' of their subjects. It brings content clarity among teachers themselves. More importantly, Content Analysis will be a pre-requisite for writing Instructional Objectives of the topic to be taught. You will study Instructional Objectives in a separate Teaching and learning process is bound to be effective once these crucial academic activities are undertaken. 4.0 CURRICULUM COURSE NAME : MECHANICAL AND PRODUCTION ENGINEERING /PRODUCTION TECHNOLOGY COURSE CODE : ME/PT/PG/MH/MI/FE SEMESTER/YEAR : THIRD SEM SUBJECT TITLE : BASIC ELECTRONICS & MECHATRONICS SUBJECT CODE : 17302 Teaching and Examination Scheme: Teaching Scheme Examination Scheme
- 29. 22 TH TU PR PAPER HRS. TH PR OR TW TOTAL 04 -- 02 03 100 -- 25@ 125 TH – Theory PR – Practical @ - Internal Assessment TW - Termwork NOTE: Two tests each of 25 marks to be conducted as per the schedule given by MSBTE. Total of tests marks for all theory subjects are to be converted out of 100 and to be entered in mark sheet under the head Sessional Work. (SW) Rationale: This subject is classified under core technology group and forms an important course of mechanical branch of engineering. The course envisages identification and testing of components, their principles of working and applications of various electronic devices, signal conditioning and processing. This subject introduces the concepts of mechatronics and PLC. This subject is prerequisite for the subject mechanical measurement and control as well as for mechatronics. General Objectives: The students will be able to: - 1. Identify and test different electronic components. 2. Use principles of circuit operations and its applications. 3. Distinguish various elements in analogue and digital electronics. 4. Understand applications of electronics in mechanical field for measurement and control. 5. Understand working of different types of transducers and their applications. 6. Understand concept of mechatronics and PLC. Learning Structure: ApplicationIdentify and test electronic devices, understand the electronic circuits and their applications in analog and digital electronics and for mechanical as well as in automobile field ,Mechatronics
- 30. 23 Procedure Principle Concept Facts Assembly of components, Measurement of voltage, current, power, frequency using multimeter, data conversion PLC programming Ohm’ law, Kirchoff’s laws, principles for transducer(s) working, Principle of PLC Semiconductor theory, voltage, current, power, Thermal runaway rectification, filter, amplification, oscillation, multivibrator regulation, signal conditioning, data conversion , DAS, Mechatronics Resistor, Capacitor, Inductor, Diode, Transistor, Integrated Circuits, Heat Sink Multimeter, Transducers, Logic gates, Flip-flop and counters, Signal conditioning and PLC
- 31. 24 Theory: Topic and Content Hours Marks 1: Solid-State Devices and Diode Circuits Marks 18 Specific objectives Students will be able to Draw energy band diagram and compare various types of materials Draw symbols ,state working principle and list out ,applications of electronics devices in electronics and mechanical field Sketch circuit diagram , state working with waveform for rectifier circuits Compare performance of rectifier circuits Sketch block diagram and state functions of various blocks of regulated power supply Define rectifier efficiency, PIV rating ,Load regulation , Line regulation Content 1.1 Fundamentals of solid state Devices– Marks 10 Material classification conductors, semiconductors and insulators, Energy band diagram intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors Solid state Devices -- schematic symbols, working principle and applications of Diode, Zener diode, Varactor diode, BJT, FET,UJT Power electronics devices DIAC, TRIAC, SCR, Photo-devices- LDR, Photo diode, Photo-transistor, LED , 7 segment display opto- coupler, LCD type and operation [No constructional details are expected] 1.2 Diode Circuits : Marks 04 Rectifier circuits Circuit diagram, working principle and waveforms for Half wave, Full wave-and Bridge rectifier, comparison w. r. t efficiency, PIV , ripple factor and applications Filters circuits C, inverted L and CLC filter circuit diagram and operation of these filters. 1.3 Regulated power supply Marks 04 Concept of load regulation , line regulation , block diagram and functions of each block [Note Mathematical calculations is not expected for any subtopic ] 10 18 2:Tansistor Circuits Marks 14 Specific objectives Students will be able to Explain working of BJT, Biasing of BJT and concept of thermal runaway Compare CB , CC and CE configuration Write operation of single stage amplifier. Draw circuits of RC, direct and transformer coupled amplifier
- 32. 25 and compare their performance State applications of BJT as an amplifier in electronics and mechanical field Content : 2.1 Transistor Marks 06 Working of NPN and PNP transistor, Configurations CB., CC and CE ,Biasing circuits, concept of thermal runway , construction and use of heat sink [No need of design and mathematical analysis ] 2.2 BJT Circuits Marks 08 BJT as an amplifier single stage amplifier, Multistage amplifier, RC coupled, direct coupled and transformer coupled amplifier, their frequency response and applications BJT as a switch 08 14 3 : Analog Circuits Marks 18 Specific objectives Student will be able to Explain and draw block diagram of IC 741, circuits of op amp as inverting, non-inverting, differential amplifier, adder, subtractor, integrator and differentiator Draw and state working principle , need of instrumentation amplifier Solve simple numerical based on these circuits Explain and draw block diagram of IC 555, circuits of timer as BMV , AMV and MMV State Barkhausen criteria and compare oscillator circuits Content: 3.1 Operational amplifier Marks 08 IC741 Block diagram, pin diagram , specifications, and applications Op amp configurations- Inverting, Non-inverting and differential circuit diagram and operation of these circuits. Op amp as adder, subtractor , integrator and differentiator, Instrumentation amplifier [simple numerical are expected ] 3.2 Timers Marks 06 IC 555–Block diagram pin diagram specifications, Concept of multi- vibrator IC 555 as AMV, BMV, MMV. 3.3 Oscillator Marks 04 Concept of oscillator, Barkhausen criteria Comparison of RC , LC and Crystal oscillator [ no any special circuit is expected] 08 18 4 : Digital Circuits Marks 18 Specific objectives Student will be able to Draw symbol and write truth table of all logic gates , various combinational circuits, sequential circuits List out applications of digital circuits in mechanical and electronics field Compare microprocessor and microcontroller Content: 4.1 Logic gates Marks 04 Study of logic gates, symbol, truth table NOT, AND, OR, NAND, 14 18
- 33. 26 NOR, XOR, XNOR 4.2 Combinational circuits Marks 04 Half and Full adder, subtractor, Multiplexer, de multiplexer, decoder and encoder, applications [only block diagram , truth table and simple circuits] 4.3 Sequential circuits Marks 10 Flip Flops Block diagram of RS,JK, Master Slave JK , D and T, Triggering mechanism Application of flip flop Basics of counter, asynchronous counter, Decade counter, Ring counter, Shift register. [only circuit diagram and operation is expected not details of timing diagram ] Concept of Microprocessor and microcomputer Features of 8085 and 8051. Comparison of microprocessor and microcomputer Applications 5 : Transducers and Signal Conditioning Marks 14 Specific objectives Student will be able to Define, state characteristics and Classify transducers Draw block diagrams and explain operation of ADC, DAC, AC and DC signal conditioning. Explain and draw block diagram of single and multi-channel DAS and data logger. State these circuits applications in electronics and mechanical field Content : 5.1 Transducers Marks 06 Definition, Classification characteristics of transducer, Active and passive, primary and secondary, Electrical, mechanical optical transducer their examples, selection criteria. 5.2 Signal conditioning Marks 08 Introduction to Data converter ADC and DAC [only principle of operation and applications ] Signal conditioning need and Block diagram of AC and DC signal conditioning, DAS - single channel multi-channel , applications Data loggers 08 14 6 : Mechatronics and PLC Marks 18 Specific objectives Student will be able to State meaning, need and basic concept of mechatronics. State features of real time mechatronics State applications, advantage disadvantages of mechatronics State operation with block diagram of CNC, FMS, AVCS CIM Robotics, State working of basic PLC architecture Write simple program of PLC. Content: 6.1 Fundamentals of mechatronics Marks 10 Concept of mechatronics, basic elements of mechatronics, Overview 16 18
- 34. 27 of mechatronics design process modeling and simulation , prototyping and deployment .Introduction to real time mechatronics system, advantages and disadvantages, applications. Functional diagram, approach to CNC, flexible manufacturing system (FMS), Computer integrated machine (CIM), Robotics, Advance vehicle condition system ( AVCS) [only brief information ] 6.2 Programmable Logic Controller(PLC) Marks 08 Basic PLC structure, principle of PLC, architecture and components, PLC programming, selection of PLC , Concept of Nano PLC , PLC applications , Ladder diagrams ,Ladder diagram circuits Simple Ladder programming examples Total 64 100 Practical: Skills to be developed: Intellectual Skills: i1. Identification and selection of components. i2. Interpretation of circuits and signals. i3. Understand working of mechatronics systems and PLC Motor skills: m1. Drawing of circuits. m2. Measurement of various parameters using multimeter. m3. Testing of components using IC tester. m4. Follow standard test procedure. List of Practical- 1. Identify various passive components such as resistors , capacitors , inductors, switches, transformers , breadboard and cables and write their specifications. 2. Identify various active electronic components such as diode, BJT , FET , UJT, SCR, DIAC , TRIAC , LED , Photodiode. 3. Use of multimeter (analogue and digital) for current, voltage and resistance measurement Testing of various electronics components. 4. Measure frequency and voltage using CRO. 5. Construct rectifier circuits on breadboard and observe waveforms on CRO 6. Measure load regulation of un-regulated power supply and regulated power supply. 7. Trace the given RC coupled amplifier and plot frequency response f and determine its bandwidth. 8. Construct Op Amp as inverting amplifier and Non Inverting amplifier on breadboard and observe the waveforms on CRO. 9. Verify truth tables for logic gates- . NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOR, XOR, XNOR Testing of an IC using IC tester. 10 Assemble a square wave oscillator for 100 Hz using IC 555.(Use astable multivibrator). 11 Write simple program for PLC Program 1 and execute on PLC .
- 35. 28 12 Write simple program for PLC Program 1 and execute on PLC . Assignments Assignments are part of term work. Assignment will include observation of systems from mechatronics point of view. Individual will prepare report consisting of functional block diagram of the system , specifications of major components and system operation I. Observe and prepare report on mechatronics used in camera system II. Observe and prepare report on mechatronics used in robotic system Where ever possible arrange visit to manufacturing unit where mechatronics is used for production purpose and prepare report. Note Teachers are expected to make students familiar with the Data Books and Operation Manuals and also encourage them to visit related websites. Learning Resources: 1. Books: Sr. No. Author Title Publisher , Edition 01 Boylestad Electronics devices and circuit Theory Pearson (Tenth edition) 02 Shalivahnan Electronics Devices and circuits TMH 03 Baru Vijay Basic Electronics Engg. Wiley India Pvt.Ltd (first edition) 04 De Debasnis Ghatak Kamakhya Basic Electronics Pearson (First edition ) 05 Bolton Mechatronics Pearson (Fourth edition ) 06 K.P.Ramchandran, G.K.Vijayaraghavan M.S.Balsundarm Mechatronics (intergrated mechanical electronics systems) Wiley India Pvt.Ltd ,(first edition) Journals – Manufactures catalogues IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics. Mechatronics Journal – Elsevier 2. IS, BIS and International Codes: NF E 01-010 2008 – AFNOR (French standard NF E 01-010) XP E 01-013 2009 – AFNOR (French standard NF E 01-013) 3. Websites: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mechatronic 5. IMPLEMENTATION STRATEGY: for Basic Electronics and Mechatronics subject of ME course III semester
- 36. 29 5.1 Planning of Lectures for a Semester with Content Detailing: ( Note Teaching and learning process must be carried out by considering mechanical l engineering candidates .Always remember candidate level is diploma second year and mechanical branch. They have not learned any topic related to electronics. Only few concepts are learned in Physics. Books are given for example .Any standard book can be used which is given in curriculum) Topic I Name: 1: Solid-State Devices and Diode Circuits Marks 18 Facts: Energy band diagram ,Semiconductor, P-N Junction Diode Concepts: Zener diode, BJT, FET,UJT Photo-devices- LDR, Photo diode, Photo-transistor, LED , 7 segment display ,opto-coupler, LCD, Load and Line regulation Principles: V- I characteristics of Diode & Zener Diode , V- I characteristics of BJT , FET, UJT Application-Rectifiers , Filter Reference Material: Books: Title: 1) Electronics Devices and Circuits Author: -S Salivahanan , N Sureshkumar and A Vallavaraj Tata McGraw-Hill ( Second Edition ) For 1.1 Material classification Page No 11 to 14 , Semiconductor material page no.67to 70,82 Diode Page No ,92,93 96 to 98 , Zener diode Page No 123 TO125 BJT Page No 149 to 153 FET Page No 192 TO 200 UJT Page No 584 TO 586 , LCD Page No 789 TO 792 Opto coupler Page No 800 to 802 LED Page No 787 TO 789 Photo diode Page No 144 to 147 Title 2) Electronic Devices & Circuits Theory author Rrobert l. Boylestad & Louis Nashelsky Material classification, semiconductor material Page No 1 to 9 Diode Page No 10 to 12 ,36 Zener diode Page No 38 LED Page No 41 BJT Page No 131 TO 132 FET Page No 368 TO 370 Photo diode Page No 813 Opto coupler Page No 858 For 1.2 Diode Circuits Title 1)Electronic Devices & Circuit Theory Author-Robert l. Boylestad & Louis Nashelsky Rectifiers- Page No 76 to 82 Filters- Page No 773 to 780 For 1.3 Regulated power supply Title: 1) Electronics Devices and Circuits Author: -S Salivahanan , N Sureshkumar and A Vallavaraj Tata McGraw-Hill ( Second Edition ) Regulated power supply- Page No 617 to 636 (rectifiers ,filters, regulated power supply) Teaching Aids: Samples of Electronics components, transparencies,
- 37. 30 notes, white board and marker pens PPT with Sample: PPT of various components with their symbols & list of applications & V-I characteristics. PPT of rectifier circuits , filters & regulated power supply with waveforms Websites: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/semiconductor devices http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/dc power supply [ Note Mathematical calculations not expected for any subtopic ] Lecture No. Topic/ Subtopic to be covered (No need to explain fabrication, detail characteristics, mathematical analysis for all devices) 1 Subject rationale Importance of electronics in mechanical engineering Review of Material classification conductors, semiconductors and insulators, Energy band diagram intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors. 2 working principle, schematic symbols and applications of Diode and Zener diode. 3 Working principle, Schematic symbols, and applications of BJT. 4 Working principle, Schematic symbols, and applications of FET and UJT . Schematic symbols, working principle and applications SCR And Varactor diode 5 Schematic symbols, working principle and applications of Diac ,Triac, Photo- devices- LDR, Photo diode, Photo-transistor, LED . 6 Working principle and applications of 7 segment display, opto-coupler, LCD type and operation. [No constructional details are expected] 7 Circuit diagram, working principle and waveforms for Half wave, Full wave-and Bridge rectifier, comparison w. r. t efficiency, PIV , ripple factor and applications.(no derivation) 8 Circuit diagram, working principle and waveforms for Filters circuits C, inverted L and CLC filter circuit diagram and operation of these filters. comparison of filters.(no derivation) 9 Meaning of load regulation, line regulation , block diagram and functions of each block of regulated power supply. (only defination) 10 Summery of semiconductor devices and there applications for mechanical engineering. Topic2 Name : Transistor Circuits Facts-BJT Concept-Configuration, biasing circuits, amplifiers, thermal runaway, heat sink, multistage amplifiers Principle-Biasing rule of BJT, stability factor, relation between α and β Applications- RC coupled amplifiers, direct coupled amplifier, transformer couple amplifier, BJT as a switch Reference Material: Books: Title: 1) Electronics Devices and Circuits Author: -S Salivahanan ,
- 38. 31 N Sureshkumar and A Vallavaraj Tata McGraw-Hill ( Second Edition) Page No. 149 to 162 Transistor biasing Page No 174 to 185 Title 2) Electronic Devies & Circuitr Theory Author-Robert l. Boylestad & Louis Nashelsky Page No. 131 to 145 Book: 1) Electronics Devices and Circuits Author: -S Salivahanan , N Sureshkumar and A Vallavaraj Tata McGraw-Hill ( Second Edition) BJT amplifier- Page No 272 to 284 Multistage Amplifiers- Page No 349 to 384 Teaching Aids: Samples of components, transparencies, notes, white board and marker pens charts PPT with Sample: PPT of NPN and PNP transistor symbols & list of application. PPT of Single stage and multistage amplifier with different coupling PPT of CB, CC and CE configuration with comparison Websites: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/transistor Lecture no. Topic/ Subtopic to be covered 1 Review of Transistor , Working of NPN and PNP transistor, Transistor current equation.(only schematic diagram) 2 Configurations CB, CC and CE and its comparison.(based on voltage gain ,current gain, input resistance, output resistance and application)(no derivarion) 3 Meaning of Biasing circuits-classification-Self bias, Fixed bias and voltage divider biasing.(only circuit diagram) 4 Concept of thermal runway, construction and use of heat sink ,Material selection. [No need of design and mathematical analysis ] 5 BJT as an amplifier- single stage amplifier. (only circuit diagram and operation, voltage gain ,current gain, input resistance, output resistance, Bandwidth and application ) 6 Multistage amplifier-RC coupled. (only circuit diagram ,operation, Parameters :voltage gain ,current gain, input resistance, output resistance, Bandwidth and application, Numerical for calculation of voltage gain in dB and without dB ) 7 Direct coupled and transformer coupled amplifier, their frequency response and applications. (only circuit diagram , operation) 8 BJT as a switch.(compare with mechanical switch ) Topic 3 Name-Analog circuits Facts-Analog signal Concepts- Integrated circuits ,Op-amp, Timers, Oscillators Principle-Barkhausen criteria Applications- Op-amp as adder, subtractor, integrator, differentiator, multi- vibrator, instrumentation amplifier
- 39. 32 Books- Electronics Devices and Circuits Author: -S Salivahanan , N Sureshkumar and A Vallavaraj Tata McGraw-Hill ( Second Edition) For 3.1 IC741-page no.707-708,710 Inverting , Non-inverting and differential circuit- page no 716-717 Adder, subtractor- page no 727-729 Integrator and differentiator and Instrumentation amplifier- page no 731-732,735-737 For 3.2 Electronics Devices and Circuit theory Author - Robert L.Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky Pearson IC555–Block diagram ,pin diagram and specifications Multivibrator using IC 555 as AMV, BMV, MMV page no -752 -755 For 3.3 Oscillator Concept of oscillator, Barkhausen criteria Comparison of RC , LC (tuned circuit)and Crystal oscillator- page no 789- 801 Teaching Aids: Transparencies, notes, white board and marker pens. Charts PPT PPT of IC 741 and IC 555 and its application. PPT of oscillators Website http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/oscillator Lecture no. Topic/ Subtopic to be covered 1 Concept of integrated circuit and ideal op-amp specifications (List only) IC741 Block diagram, pin diagram , specifications, and applications 2 Op amp Configurations diagram and operation of these circuits - Inverting , Non-inverting and differential circuit. (diagram , operation and formulae no derivation) 3 Op amp as adder, subtractor (diagram , operation and formulae no derivation) 4 Integrator and differentiator and Instrumentation amplifier using 3 op-amp (diagram , operation and formulae no derivation)[simple numerical are expected ] 5 Timers IC 555–Block diagram ,pin diagram and specifications 6 Concept of multivibrator using IC 555 as AMV, BMV, MMV. diagram , operation and formulae no derivation) 7 Oscillator Meaning of Electronic oscillator with the analogy of mechanical oscillator(pendulum or spring), tuned circuit, feedback in amplifier, Barkhausen criteria 8 Comparison of RC , LC and Crystal oscillator using block diagram [ no any special circuit is expected] Name-Digital Circuits
- 40. 33 Topic 4 Facts-Analog signal Concepts- Digital signal, logic gates ,Flip-flops ,counter, Microprocessor and microcontroller, Adder ,Subtractor Applications-Microprocessor and Microcontroller applications Books- Electronics Devices and Circuits Author: -S Salivahanan , N Sureshkumar and A Vallavaraj Tata McGraw-Hill ( Second Edition) For 4.1 Study of logic gates, symbol, truth table NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOR, XOR, XNOR page no -864-869, For 4.2 Half and Full adder, subtractor, Multiplexer (2:1,4:1), de multiplexer(1:2,1:4) Decoder and Encoder, applications - page no 873-880 For 4.3 Block diagram of RS,JK Flip-Flop ,Race around condition, Master Slave JK , D and T, Triggering mechanism(Edge and Level), Application of flip-flops, Decade counter, Ring counter, Shift register page no -883-893 Microprocessor and Microcontroller- page no 919-923,929-932 Teaching Aids: transparencies, notes, white board and marker pens , Charts PPT PPT of logic gates symbols ,truth table and logic equation PPT of Adder, subtractor, Mux, Demux, encoder and decoder. PPT of Flip flops, counter ,register PPT of comparison of Microprocessor and Microcontroller Websites: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/digital Lecture no. Topic/ Subtopic to be covered 1 Meaning of logic gates(with examples), symbol, truth table NOT, AND, OR (not required internal circuit diagram) (for 2 input) 2 Symbol, truth table for NAND, NOR, XOR, XNOR (for 2 input) 3 Half and Full adder, subtractor, [only block diagram , truth table and application] 4 Multiplexer (2:1,4:1), de multiplexer(1:2,1:4) [only block diagram , truth table] 5 Decoder and encoder, applications [only block diagram , truth table and comparison] 6 Block diagram of RS,JK Flip-Flop, Race around condition[only circuit diagram ,operation and application is expected, not details of timing diagram ] 7 Master Slave JK , D and T [only circuit diagram ,operation and applications is expected, not details of timing diagram ] 8 Triggering mechanism with reference to noise (Edge and Level only waveform), Application of flip-flops 9 Meaning of digital counter, asynchronous counter (4 Bit)[only circuit diagram and operation is expected ,not details of timing diagram ] 10 Decade counter, Ring counter, [only circuit diagram and operation is
- 41. 34 expected not details of timing diagram ] 11 Shift register, comparison of counter and shift register [only circuit diagram and operation is expected not details of timing diagram ] 12 Definition of Microprocessor and Features of 8085 13 Definition of Microcontroller and Features of 8051. 14 Comparison of microprocessor and Microcontroller and their Applications(Mechanical engineering ) Topic5 Name-Transducers & signal conditioning Facts- LED, LDR, Photodiode Concepts- Transducer: Active and passive, primary and secondary,Electrical , mechanical. Data converter ADC and DAC, AC and DC signal conditioning, DAS, Data loggers Books- Electronics Devices and Circuits Author: -S Salivahanan , N Sureshkumar and A Vallavaraj Tata McGraw-Hill ( Second Edition) Definition, Classification and characteristics of Active and passive, primary and secondary, Electrical , mechanical and optical transducer, their examples, selection criteria- page no 757-771 Title-Mechatronics ( Integrated Mechanical Electronic System) Author-K.P.. Ramchandran, G K Vijayaraghavan & M S Balsundaram. Publication- Wiley India Pvt.Ltd ,(First Edition) For Transducers Page No 29 to 40 Signal Conditioning Page No 181 to 199 Data Converter Page No 465 to 473 DAS, Data Logger Page No 452 to 45 Introduction to Data converter ADC and DAC Page No -893-898 For Signal Conditioning Data Converter Book Instrumentation Devices and Circuits Author C S Rangan , G R Sharma , and V S Mani pub . Tata Mc Graw- Hill Pub. Co. Page No 363 to 3380 For DAS Book Instrumentation Devices and Circuits Author C S Rangan , G R Sharmaq , and V S Mani pub . Tata Mc Graw- Hill Pub. Co. Page No 351 355 to 358 For Data logger Book Instrumentation Devices and Circuits Author C S Rangan , G R Sharmaq , and V S Mani pub . Tata Mc Graw- Hill Pub. Co. Page No 439 , 440 Teaching Aids: transparencies, notes, white board and marker pens , Charts PPT : PPT of classification of transducer PPT of ADC and DAC. PPT of DAS, Data logger Websites: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/transducer Lecture Topic/ Subtopic to be covered
- 42. 35 no. (focus on practical utility of electronics in mechanical field) 1 Definition and, characteristics of Active and passive transducer, their examples ,selection criteria 2 Classification and characteristics of primary and secondary, Classification of transducers on the basis of signal :Electrical , mechanical and optical transducer their examples ,selection criteria 3 Introduction to Data converter ADC[only principle of operation and applications] 4 Introduction to Data converter DAC [only principle of operation and applications] comparison of ADC and DAC 5 Signal conditioning need and only Block diagram of AC signal conditioning, 6 Only Block diagram of DC signal conditioning, 7 DAS - single channel multi-channel and applications 8 Data loggers (Explanation and applications) Topic 6 Name-Mechatronics & PLC Facts- Mechanical system, CNC. Concepts-mechatronics, elements of mechatronics, Robotics, AVCS Books- For 6.1 Title-Mechatronics (Iintegrated Mechanical Electronic System) Author-K.P.. Ramchandran, G K Vijayaraghavan & M S Balsundaram. Publication- Wiley India Pvt.Ltd ,(First Edition) Page No. 1 to5 ,20 to 27 Robotics system Page No. 792 to 800 CNC system Page No. 771 to 776 PLC Introduction , operating principle, Internal architecture , programming , application programs Page No. 697 to 756 Title- Introduction to mechatronics author- Appuu kuttan K. K. Publication- oxford page no 1 To 20 For 6.2 Title- Process Control Instrumentation Technology Author- C.D. Johnson Publication PHI ( 7TH edition) page no 393 to 414 Teaching Aids: Lecture on PLC and Mechatronics in VLC(virtual learning center) as per timetable of MSBTE, transparencies, notes, white board and marker pens Charts PPT : PPT of PLC and Ladder diagram Websites: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mechatronic Lecture no. Topic/ Subtopic to be covered (Try to give examples related to machine tools, automobile A/C refrigerator engineering. plant, traction system etc.) 1 Definition and requirement of mechatronics, basic elements of mechatronics. 2 Mechatronics design process 1) modeling 2)simulation 3)prototyping and 4)deployment. 3 Define real time system and features, advantages and disadvantages of Mechatronics. 4 List of various mechatronics system and Functional block diagram , basic
- 43. 36 components and explanation of CNC. 5 Comparison with conventional system , types of CNC such as CNC machining centre , CNC turning section , CNC lathes , CNC milling and drilling , CNC special purpose machines (only list ) Advantages over conventional systems. 6 Flexible manufacturing system (FMS), Computer integrated machine (CIM),( diagram and explanation). 7 Definition of Robotics, Components of Robot such as drive system, control system, measuring system, sensors system. Block schematic. 8 Classification of Robots such as based on Geometric configuration , No. of axis of rotation , end effectors or grippers, type of control and level of sophistication of controller Cylindrical, Cartesian , spherical , articulated , mechanical gripper , magnetic gripper , suction cup , adhesive type . open loop control , close loop control , limited sequence control , point to point control continuous path robot , Intelligent robot, Robot applications(Only List) 9 Advance vehicle condition system (AVCS), Block Schematic and function of each. 10 Definition of PLC, Features of PLC, Basic structure of PLC, internal architecture of PLC I/O devices 11 How PLC differs from computer , Classification of PLC based on number of Input and Outputs- Micro, Small , medium and Large , List of PLC application , Selection of PLC ,(Names only) 12 PLC programming Memory , program scan , PLC programming methods ,Ladder diagram with Difference between Electrical and PLC ladder , Ladder diagram symbols 13 PLC programming instructions, Examine if open, Examine if Closed, Output Energies(OLE), Output latch and Unlatch Instructions, Timer and Counter ( only introduction ) 14 Ladder diagram for OR , AND ,EXOR , NOT , NAND , NOR and their simple combinations 15 Timing and Counting Operations(Min 3 programs)- Timer with single input and single output operation, Sequential operations for outputs such as Motor control simple programs (These programs shall be implemented during practical Writing PLC program for given Process description Washing System, Conveyor System, and Elevator systems No theory questions shall be ask on complex process during theory exam . ) 16 Revision 5.2 Planning and Conduct of Test: There will be two test each of 25 marks conducted as per schedule given in MSBTE academic calendar Sr.No Class Test Marks Topics 1 Class Test 1 25 1. Solid state devices and diode circuits. 2. Transistor Circuits 3. Analog circuits
- 44. 37 2 Class Test 2 25 4. Digital circuits 5. Transducer and Signal Conditioning 6. Mechatronics and PLC 5.3 Details about conduct of assignments: Assignments are part of term work. Assignment will include observation of systems from mechatronics point of view. Individual will prepare report consisting of functional block diagram of the system , specifications of major components and system operation I. Observe and prepare report on mechatronics used in camera system II. Observe and prepare report on mechatronics used in robotic system Where ever possible arrange visit to manufacturing unit where mechatronics is used for production purpose and prepare report. 5.4 Strategies for Conduct of Practical: Teacher should be available for complete 2 hours for practical a. Approach for design of manual : Basic approach of Lab manual is to develop better understanding of subject and develop intellectual skills and motor skills as per subject objectives. While designing the experiment, various activities should be added in the experiments so that the contents can be related to applications in the industry. Suggestions for effective conduct of practical and assessment: Subject teacher shall prepare Laboratory planning (D2) format in duplicate. One copy of D2 shall be displayed on lab/department notice board for student information. Subject teacher shall conduct practical as per planning and assess regularly At the beginning of the semester, Lab assistant and subject teacher should check the equipments to conduct practical are in proper working condition Teacher should use laboratory manual developed for the subject Basic Electronics and Mechatronics. Conduct the practical as per instruction in lab manual Teacher shall perform the experiment before demonstration/conduct of practical. Confirm resources, equipments, data book and components. Use charts whenever necessary. Display the given data of each experiment in the lab More opportunities are provided to students for hands on skills development. There should be one revision practical after every three regular practical’s so that students grasp the content deeply. Teacher should make the assessment report of student during repletion round. Teacher should assess the student on the basis of his/her participation in a group and performance in a group during practical as per MSBTE rule. Continues assessment shall be done by asking questions at the end of practical. Teacher should give marks out of 10 for each practical. Industrial visit shall be arranged to provide more learning of some specific practicals.
- 45. 38 b. Preparation for conduct of practical Experimental set up with sample reading (expected result) should be prepared by concerned teacher before the commencement of each experiment Teacher should give the instruction regarding proper handling of instruments, precautions and safety while performing the experiment 5.5 Additional guidelines to conduct course smoothly. Use of ICT based teaching learning, PPTs, internet, readymade charts/graphs, CD/VCDs methods, video may help students to learn subject easily. Prefer use of recommended reference books for teaching/learning purpose. Preparation of subject notes will definitely be fruitful for students. Overview of topics covered in last lecture at start of current lecture is expected. Assignment or homework based on last lecture or related to next lecture may be helpful for all students. Preparation and circulation of chapter wise question bank based on sample question paper, MSBTE old question papers will definitely give good idea to students about subject. Showing of components, portable electronic equipments, working models simulations, project boards will definitely give brief idea about subject to understand electronic equipment’s to the students 6. Mode of assessment: 6.1 Class Test: It is proposed that there will be two tests each of 25 Marks. The tests will be conducted as per the MSBTE Schedule Teacher should prepare model answer of class test question papers. After completion of test, subject teacher should display model answer on departmental notice board. Teacher should show answer paper of class test to the students and discuss about the mistakes. Teacher should maintain the record of class test as per MSBTE norms. 6.1.1 Guidelines for Setting Class Test Question Paper: Question no.1 attempt any three out of four(3*3=9) Question no.2 attempt any two out of four(2*4=8) Question no.3 attempt any two out of four(2*4=8)
- 46. 39 6.1.2 Sample Test Papers: Sample Test Paper 1 Roll No. Institute Name: Course Name: ME/PT/PG/MH/MI/FE Course Code: 17302 Semester: Third Subject: Basic Electronics & Mechatronics. Marks: 25 Time: 1 hour Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory 2. Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary 3. Figures to the right indicate full marks 4. Assume suitable data if necessary 5. Preferably, write the answers in sequential order Q1. Attempt any three 3*3=9 a) Draw the symbols of UJT, LDR, Zener Diode. b) Draw V-I characteristics of PN junction diode and define cut in voltage. c) Describe BJT acts as switch with analogy of mechanical switch. d) Draw neat circuit diagram of instrumentation amplifier. e) State four characteristics of op-amp. Q2. Attempt any two 4*2=8 a) Compare BJT & FET. (any four points) b) Draw center tapped FWR with capacitor filter & describe its working with wave forms. c) Draw two stage RC coupled amplifier. State its any two advantages and disadvantages. Q3. Attempt any two 4*2=8 a) What is thermal runaway? What is the use of heat sink in transistor? b) Draw Non-inverting amplifier & describe its working. state gain equation. c) Compare CB and CE configuration for BJT. 17302
- 47. 40 Sample Test Paper 2 Roll No. Institute Name: Course Name: ME/PT/PG/MH/MI/FE Course Code: 17302 Semester: Third Subject: Basic Electronics & Mechatronics. Marks: 25 Time: 1 hour Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory 2. Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary 3. Figures to the right indicate full marks 4. Assume suitable data if necessary 5. Preferably, write the answers in sequential order Q1. Attempt any three 3*3=9 a) Draw functional block diagram of IC555 timer & describe function of each. b) State Barkhausen criteria in oscillator. c) Draw Symbol and write logic equation & truth table for NOR, AND, X-OR. d) State six features of 8085 microprocessor. e) Define transducer and give its classification. Q2. Attempt any two 4*2=8 a) What is Data Logger? State applications of data logger b) Define Mechatronics. Describe basic elements of mechatronics. c) Draw Ladder diagram for XOR gate Q3. Attempt any two 4*2=8 a) Draw block Schematic of AVCS and give function of each block. b) Draw decade counter and write truth table. c) Compare ADC and DAC. 17302
- 48. 41 6.2.3 Sample Question Paper: Exam Seat No. Maharashtra State Board of Technical Education Course Name: ME/PT/PG/MH/MI/FE Course Code: 17302 Semester: Third Subject: Basic Electronics & Mechatronics. Marks:100 Time: 3 hours Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory 2. Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary 3. Figures to the right indicate full marks 4. Assume suitable data if necessary 5. Preferably, write the answers in sequential order Q1. A) Attempt any six 2*6=12 a) Sketch symbol and label the terminals of i) Diode ii) Phototransistor b) What is Filter? c) State input and output terminals in CB & CC configuration. d) Sketch pin diagram of IC 741 and label all pins. e) Draw logical symbol of 4:1 multiplexer? f) Identify active transducers from following transducers i) thermocouple ii) strain gauge iii) RTD iv) piezoelectric transducer v) LVDT g) What is mechatronics? h) State types of real time mechatronics system. Q1. B) Attempt any two 4*2=08 a) Sketch circuit diagram, input, and output waveform of half wave rectifier. b) How Op Amp offers high input impedance ? List out any four specifications of ideal op- amp. c) Sketch block diagram of CNC system from mechatronics view and state function of each block. Q2. Attempt any Four 4*4=16 a) Which biasing method is most commonly used for BJT? Sketch circuit diagram for the same. b) Why multistage amplifier circuit is used? List out any two coupling methods used for multistage amplifier. c) Draw circuit diagram of inverting amplifier. Calculate the gain if Rf=12KΩ, Ri=3KΩ d) Sketch pin-out diagram of IC 555. Label all pins and state functions of each pin. 17302
- 49. 42 e) What is oscillator? Which type of feedback is used in oscillator? State types of oscillator. f) What is full adder? Sketch logical circuit of full adder along with truth table. Q3. Attempt any four 4*4=16 a) How BJT acts as an amplifier? (with help of circuit diagram). b) Write truth table & sketch symbol of NOR and NAND gate. c) Sketch 4 bit asynchronous counter circuit. d) What is Decoder? Draw logic diagram of 3:8 decoders write its truth-table. e) State classification of transducer on the basis of signals with one example each.. f) State two reasons that mechatronics system is getting popular ? State it’s any four applications. Q4. Attempt any four 4*4=16 a) What is PLC? Sketch architecture of PLC and Label all blocks. b) Calculate gain of multistage amplifier if gain of 1st stage is 15dB and gain of 2nd stage is 3 dB. c) List four criteria to select PLC for any particular applications? d) What is Data Logger? State applications of Data Logger. e) State the Role of DAS. f) How opto coupler act as an isolator? Q5. Attempt any four 4*4=16 a) State meaning of ADC & DAC. List out types of ADC. b) Compare active and passive transducer on the basis of any four parameters. c) State applications of 7 segment display and opto-coupler. (any four applications of each) d) What is FET? Why it is called as voltage controlled device? e) Draw construction of decade counter using T flip flop. f) Sketch schematic symbol of opto coupler. State its application. Q6. Attempt any four 4*4=16 a) Draw block diagram of regulated DC power supply and sketch waveforms after each stage b) Define Load regulation and Line regulation. c) State Barkhausen criteria for oscillation. State advantages of crystal oscillator. d) Compare microprocessor and microcontroller. (any four points) e) Draw Ladder diagram for Start –Stop logic with one input push button for start and one push button for stop and one output for motor to activate solenoid valve f) Draw logical circuit diagram of S-R flip flop and write its truth table
- 50. 17302 13141 3 Hours / 100 Marks Seat No. P.T.O. Instructions – (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4) Figures to the right indicate full marks. (5) Assume suitable data, if necessary. (6) Mobile Phone, Pager and any other Electronic Communication devices are not permissible in Examination Hall. Marks 1. a) Attempt any SIX of the following: 12 i) Draw the symbols and label the terminals of 1) Photo diode 2) UJT ii) Define rectifier. iii) Draw the symbols and label the terminals of 1) NPN Transistor 2) PNP Transistor iv) Sketch pin diagram of IC 741 and label all its pins. v) Write any two applications of Multiplexer and Demultiplexer. vi) What is transducer? How are they classified. vii) What is mechatronics? Write its applications. viii) What are the advantages of FMS. (Any four)
- 51. 17302 [ 2 ] Marks b) Attempt any TWO of the following: 08 i) Draw the circuit diagram along with the necessary waveforms for fullwave bridge rectifier. ii) Calculate the gain of inverting and noninverting amplifier if Rf = 21kW and Ri = 3kW. iii) List any four advantages and applications of CNC system. 2. Attempt any FOUR of the following: 16 a) What is thermal runaway? How it is avoided? b) How transistor works as a switch also draw a necessary circuit and waveform for it. c) Sketch circuit diagram for integrator using opamp also draw output waveforms for square wave and sine wave input. d) Sketch circuit diagram for AMV using IC555 also draw necessary waveforms and write the equation for output frequency. e) Compare RC and LC oscillator w.r.t. following points : i) Voltage gain ii) Oscillating frequency iii) Components used for oscillation iv) Application. f) What is full adder? Sketch logical circuit for it along with its truth table. 3. Attempt any FOUR of the following: 16 a) Compare RC coupling and transformer coupling w.r.t. following points i) Coupling element ii) Distortion iii) Voltage gain iv) Applications
- 52. 17302 [ 3 ] Marks b) Draw the logical symbol and truth table for 2 input NAND and EXOR gate. c) Draw JK flip flop using NAND gate and what is the race around condition? d) Draw the logical circuit for 4:1 multiplexer along with its truth table. e) Compare electrical and mechanical transducers w.r.t. i) power supply requirement ii) reliability iii) life time iv) example f) State functions and applications of robotic system. 4. Attempt any FOUR of the following: 16 a) What is advance vehicle condition system. Explain briefly. b) Draw the circuit for single stage transistor amplifier also write the requirements of multistage amplifier. c) Sketch block diagram for PLC and state function’s of each block. d) What is data logger? Write its applications. (Any four) e) Draw the block diagram of multichannel DAS. f) Compare PN junction diode and Zener diode w.r.t. i) direction of conduction ii) application iii) reverse breakdown iv) symbol P.T.O.
- 53. 17302 [ 4 ] Marks 5. Attempt any FOUR of the following: 16 a) What is AC signal conditioning? State types of circuit used for ac signal conditioning. b) State selection criteria for transducers. c) Compare BJT and FET w.r.t. i) terminals ii) type’s iii) input impedance iv) controlling factor d) What is optocoupler? Write its type also write its advantages. e) Compare microprocessor and microcontroller w.r.t. i) components ii) access time iii) number of opcodes iv) hardware required f) Define doping? Which type of impurity is added to form Ptype and Ntype semiconductor. 6. Attempt any FOUR of the following: 16 a) Draw block diagram of regulated power supply also draw necessary waveforms at various points. b) Define load regulation and line regulation. c) What is Barkhausen criteria? Which type of feedback is used in an oscillator? Sate types of oscillator. d) State different triggering methods also draw neat waveform for each triggering method. e) Write the selection factors for PLC. f) Draw decade counter also write its truth table.
- 54. 17302 13141 3 Hours / 100 Marks
- 55. P.T.O. *17302* 17302 21314 3 Hours/100 Marks Instructions: (1) Allquestions arecompulsory. (2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (3) Figures to the right indicate full marks. (4) Assume suitabledata, ifnecessary. (5) Mobile Phone, Pager and any other Electronic Communication devices are not permissible in Examination Hall. MARKS 1. Attempt any five : 20 a) Draw the energy band diagram for various type of material and compare them (two points). b) Draw the circuit diagram and explain the working of half wave rectifier. c) Draw the symbol of PNP transistor and explain its working. d) Compare RC and LC oscillator. e) Develop the truth table for XOR and XNOR gate. Also draw their symbols. f) With a suitable example explain the concept of primary and secondary transducer. g) List the advantages and disadvantages of mechatronic system. 2. Attempt any four : 16 a) What is semiconductor ? Explain intrinsic and extrinsic type of semiconductors. b) Develop a circuit for Op-Amp as a) Adder b) Subtractor. c) What is multiplexer ? Draw logical symbol of 4 : 1 multiplexer. d) Explain the selection criteria for the transducer for any application. e) What is PLC ? Draw the block diagram and state the applications of PLC. f) Draw the block diagram of CNC machine and explain its operation. 3. Attempt any four : 16 a) Explain the following terms : a) Load regulation b) Line regulation. b) Explain RC coupled amplifier with the help of neat diagram. Seat No.
- 56. MARKS c) What is instrumentation amplifier ? What are its advantages ? d) Explain the operation of astable multivibrator using IC 555. e) Compare microprocessor and microcontroller (4 points). f) Develop a ladder diagram to verify followingBollean equation. i) A + B + C = Y ii) A.B.C = X iii) A.B + C = Z. 4. Attempt any four : 16 a) Draw the symbol of LDR. Write its working principle and state any two applications. b) Explain the need of biasing circuit. List the types of biasing circuits for BJT. c) List and explain any four specification of IC 741. d) What is flip-flop ? List the types of flip-flop and state its applications (two). e) Explain the operation of analog to digital convertor. f) State the features of real time mechatronics. 5. Attempt any four : 16 a) List any four criteria for the selection of PLC for an application. b) Draw and explain single channel data acquisition system. c) What is Half adder ? Draw the logical circuit of half adder along with its truth table. d) Draw the circuit diagram of inverting amplifier. Calculate the gain if Ω= k12Rf and Ω= k1RI e) Calculate the gain of multistage amplifier if the gain of first stage is 12 dB and gain of second stage is 4 dB. f) Compare full wave and half wave rectifier (for any four points). 6. Attempt any four : 16 a) Draw the symbol and list four applications of a) FET b) UJT b) Compare CB and CE configuration for BJT (4 points). c) Draw a labelled pin diagram of IC 555. List its two specifications. d) Sketch 4-bit asynchronous counter. e) Identify active and passive transducers from the list below. a) Thermocouple b) RTD c) Strain gauge d) Piezoelectric crystal f) With the help of neat labelled diagram explain FMS. ––––––––––––––––––––––– 17302 -2- *17302*
- 57. 17302 14115 3 Hours / 100 Marks Seat No. P.T.O. Instructions – (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (3) Figures to the right indicate full marks. (4) Assume suitable data, if necessary. (5) Mobile Phone, Pager and any other Electronic Communication devices are not permissible in Examination Hall. Marks 1. a) Attempt any SIX of the following: 12 (i) Sketch symbol and label the terminals of: 1) Zener diode 2) UJT. (ii) What is rectifier? List types of rectifier. (iii) State input and output terminals in CB and CE configurations of BJT. (iv) Draw the circuit diagram of an inverting amplifier using IC 741 op-amp. (v) Draw logical symbol of 1:4 demultiplexer.
- 58. 17302 [ 2 ] Marks (vi) Identify passive transducers from following: 1) stain gauge 2) thermocouple 3) thermistor 4) photo voltaic cell. (vii) List advantages of Mechatronics. (viii) State the types of real time Mechatronic systems. b) Attempt any TWO of the following: 08 (i) Sketch circuit diagram and input and output waveforms of CLC filter. (ii) Draw the block diagram of CNC system and state function of each block. (iii) Draw neat circuit diagram of op-amp as summing amplifier and derive expression for 3 inputs applied. 2. Attempt any FOUR of the following: 16 a) List the different coupling methods of multistage amplifier. Draw the circuit diagram of RC coupled amplifier. b) What is oscillator? Which type of feedback is used in oscillator? State types of oscillator. c) What is half adder? Sketch logical circuit of half adder along with truth table. d) List different biasing methods of BJT. Sketch circuit diagram of voltage divider biasing method. e) Draw the block diagram of IC 555 and label it. f) Draw the circuit diagram of non-inverting amplifier using op-amp. Derive the expression for gain.
- 59. 17302 [ 3 ] Marks 3. Attempt any FOUR of the following: 16 a) What is encoder? Draw logic diagram of priority encoder. Write its truth table. b) Why mechatronic systems are getting popular? Explain. State its any four applications. c) Explain with the help of circuit diagram, how BJT acts as a switch? d) Draw symbol and write truth table of NAND and XOR gate. e) Sketch 4-bit ring counter circuit. f) State different selection criteria for tranducers. 4. Attempt any FOUR of the following: 16 a) State working principle of LED. Give two applications of LED. b) Calculate the gain of multistage amplifier if gain of 1st stage is 30 dB and gain of 2nd stage is 6 dB. c) Draw architecture of PLC and label all blocks. List two advantages of PLC. d) Explain with the help of an example, ladder diagram. e) State the types of DAS. State its applications. f) What is data logger? State applications of data logger. P.T.O.
