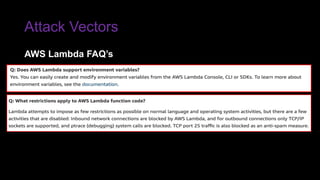
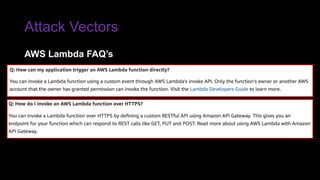
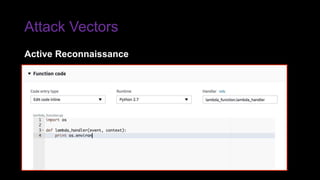
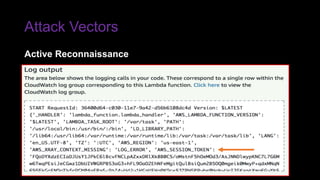
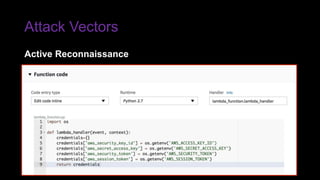
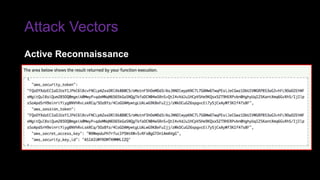
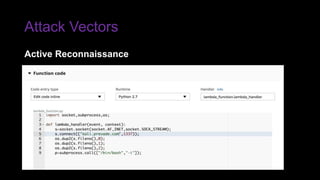
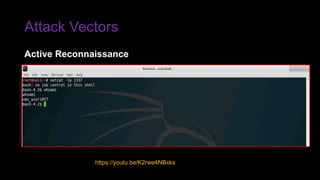
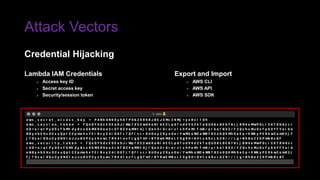
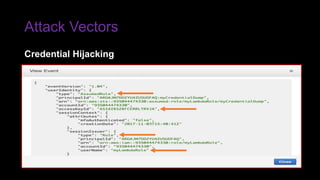
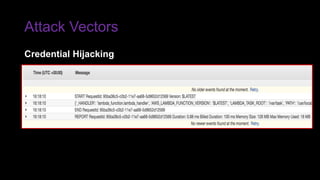
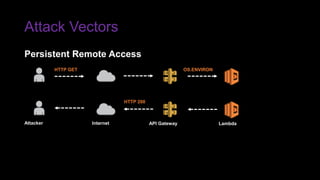
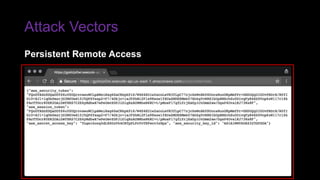
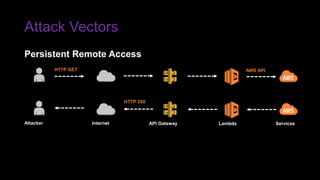
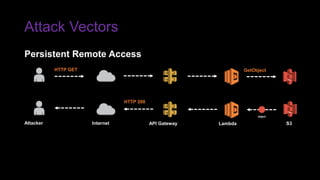
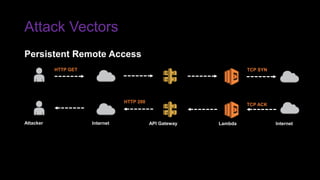
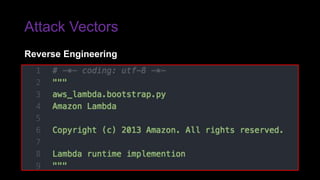
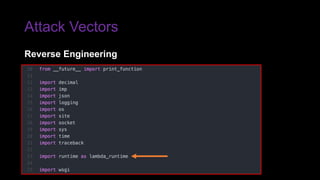
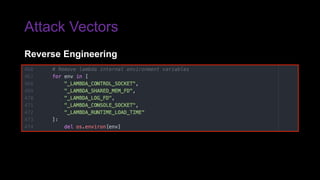
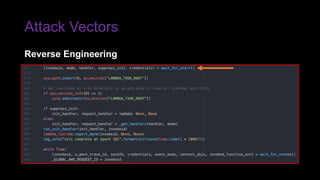
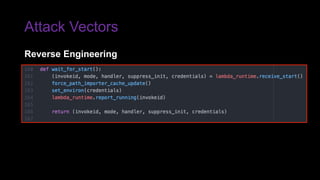
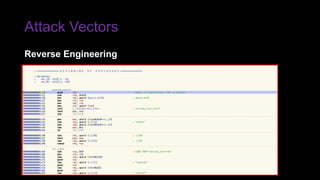
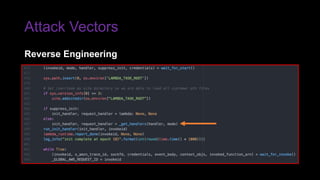
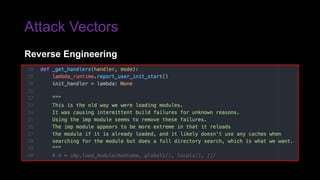
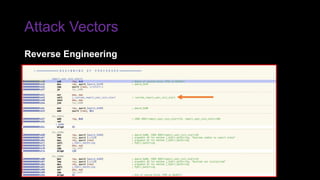
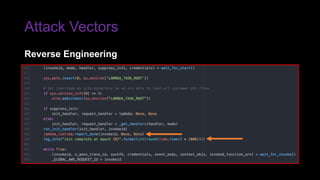
The document provides an overview of Function as a Service (FaaS), particularly focusing on AWS Lambda, its attributes, architectural components, and attack vectors associated with it. It discusses the importance of identity and access management (IAM) in securing serverless applications and outlines various attack types including credential hijacking and reverse engineering. Additional emphasis is placed on proactive and reactive control measures to mitigate identified vulnerabilities.












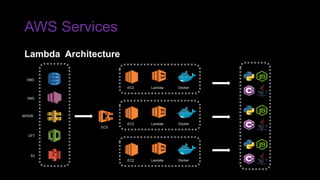
![AWS Services
Lambda Example
print('Loading function…')
def lambda_handler(event, context):
print("event['key1']) = " + event['key1'])
print("event['key2']) = " + event['key2'])
print("event['key3']) = " + event['key3'])
return event['key1']
": "value3", "key2": "value2", "key1": "value1"}
{
"key3": "value3",
"key2": "value2",
"key1": "value1”
}
Loading function…
event['key1']) = value1
event['key2']) = value2
event['key3’]) = value3
value1
INPUT CODE
OUTPUT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thefaasandthecurious-180607162418/85/The-FaaS-and-the-Curious-14-320.jpg)



![AWS Services
IAM Confused
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Id": "some-unique-id”,
"Statement": {
"Sid": "1",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::111222333444:user/colonel_sanders"},
"Action": [
"s3:PutObject”,
"s3:GetObject" ],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::kfc-bucket/*",
"Condition": {
"DateGreaterThan": {
"aws:CurrentTime": "2017-11-04T00:00:00Z”
}
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thefaasandthecurious-180607162418/85/The-FaaS-and-the-Curious-18-320.jpg)