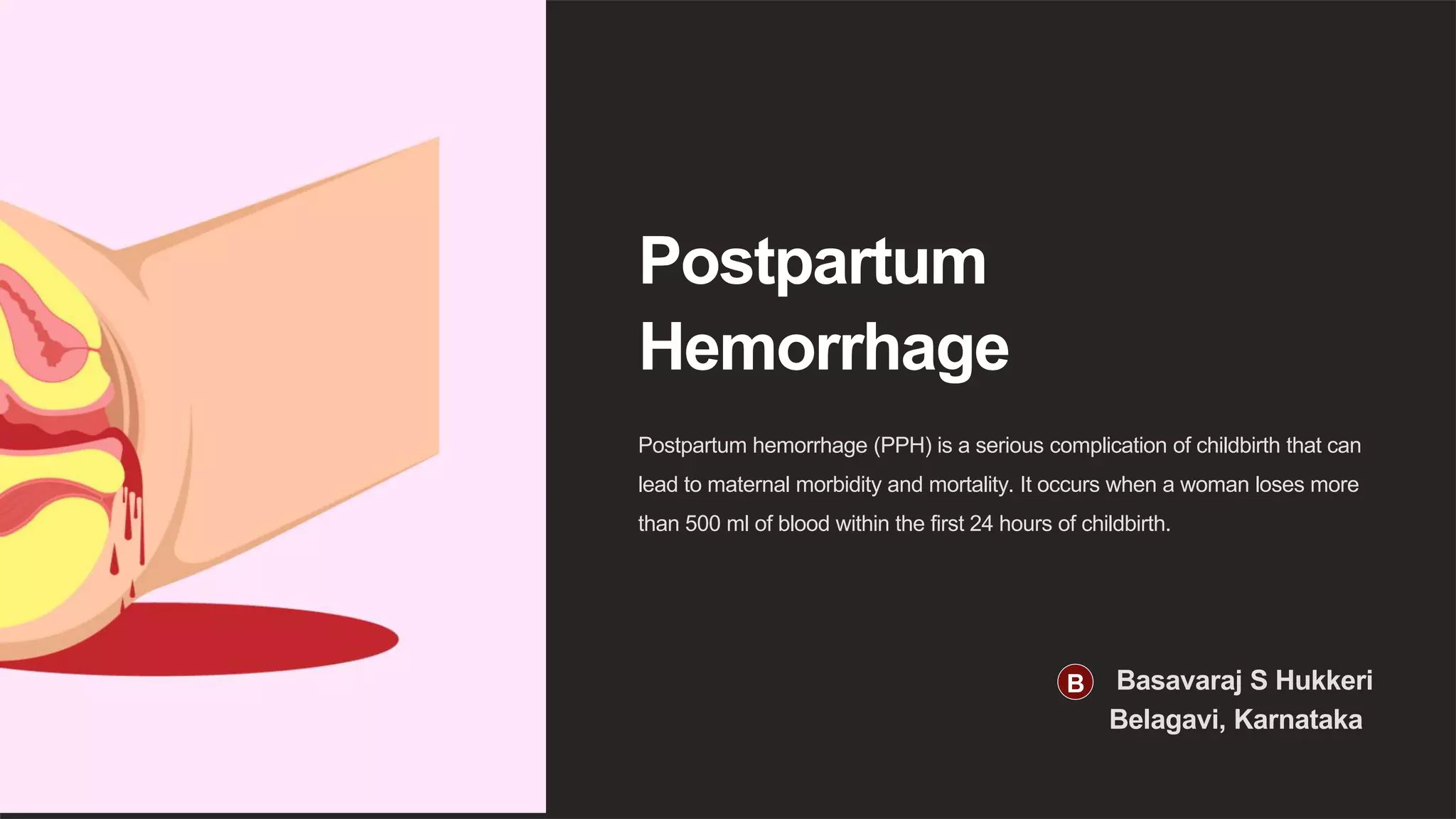
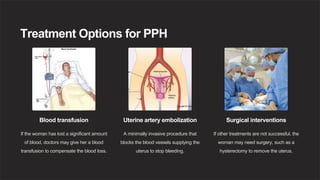
Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is excessive bleeding after childbirth, defined as blood loss over 500 ml within 24 hours of delivery. It can be caused by placenta previa, uterine atony, or perineal tears. Signs include tachycardia, hypotension, and cessation of urine output. Treatment involves blood transfusion, uterine artery embolization, or hysterectomy. Prevention strategies are active management of labor and use of uterotonic drugs to stimulate uterine contractions. Early recognition and treatment of PPH are essential due to the risk of maternal morbidity and mortality.