02 Fertilization & Implantation.ppt
- 2. OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define the terms ‘fertilization & implantation’. Describe the phases of fertilization and its outcome. Describe the cleavage and the stage at which implantation occurs. Describe the process of implantation. Define the normal site of implantation. Describe the abnormal sites of implantation (ectopic pregnancy)
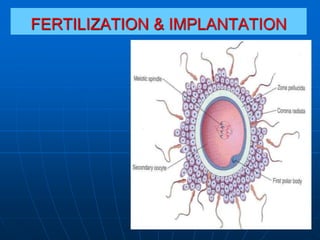
- 3. Fertilization It is the fusion of male & female gametes. It is a complex process, that begins with contact between a sperm & an oocyte. It ends by the intermingling of maternal & paternal chromosomes.
- 4. Viability of Gametes Human oocytes are usually fertilized within 12 hours after ovulation. Oocyte cannot be fertilized after 24 hours as it shortly degenerates thereafter. Human sperms do not survive for more than 48 hours.
- 5. Sperm Capacitation Freshly ejaculated sperms are unable to fertilize the 2ry oocyte. They must undergo a series of changes known as capacitation. Capacitation occurs in the female reproductive tract. It takes about 7-8 hours. Sperms that have undergone capacitation become hyperactive & highly motile.
- 6. Site of Fertilization Usually occurs in ampulla of the uterine tube. It may occur in other parts of the tube but never in the uterus. Chemical signals from oocyte attract the sperms, also uterine tube contraction helps the sperm to ascend.
- 7. Stage 1: Passage of sperm through Corona Radiata It results from: 1- Action of an enzyme called hyaluronidase released from the acrosome of the sperm which helps in dispersal of corona radiata cells. 2- Constant propulsive force of the sperm's tail.
- 8. Stage 2: Penetration of Zona Pellucida Constant propulsive force from the sperm’s flagellating tail. acrosomal enzymes (esterases, acrosin & neuraminidase) allow the sperm to create a tract through the zona pellucida
- 9. Stage 3: Fusion of plasma membranes of the oocyte & the sperm. Entry of sperm contents into the oocyte. Stage 4: Completion of second meiotic division of the 2ry oocyte and formation of female pronucleus.
- 10. Stage 5. Formation of male pronucleus Stage 6. Fusion of pronuclei & formation of the zygote and preparation of first mitotic division
- 11. Results of Fertilization • Stimulates the penetrated 2ry oocyte to complete its 2nd meiotic division. • Restores the diploid number of chromosomes in the zygote (46). • Determines the chromosomal sex of the embryo. • Initiates cleavage (cell division) of the zygote.
- 12. Sex of the Embryo • Embryo's chromosomal sex is determined at the time of fertilization. • Sex is determined by the type of sperm (X or Y) that fertilizes the oocyte. • So, it is the father whose gamete decides the sex of the embryo.
- 13. Chromosomes in zygote • Zygote is genetically unique. • Half of its chromosomes come from the father and the other half comes from the mother. • zygote contains 46 chromosomes (diploid). • New combination is formed which is different from either of the parents. • This mechanism forms biparental inheritance and leads to variation of the human species.
- 14. Cleavage Repeated mitotic division of the zygote. Begins about 30 hours after fertilization. There is rapid increase in the number of cells. The cells which is called (blastomeres) become smaller with each division. Normally occurs as the zygote passes along the uterine tube to the uterus During cleavage, zygote is within the zona pellucida.
- 15. After 8-cell stage, the cells become compactly arranged compaction 16 cell stage is called morula. It is formed about 3 days after fertilization and enters the uterus.
- 16. Fluid filled space called the blastocyst cavity (blastocele) appears inside the morula. Now Blastomeres are separated into: Outer cell layer, the trophoblast, which gives rise to embryonic part of placenta. Inner cell mass (embryoblasts) which gives rise to the embryo.
- 17. At this stage, the conceptus is called Blastocyst. It has two poles: embryonic & abembryonic. Zona pellucida gradually degenerates and disappears. Blastocyst takes its nourishment from uterine secretions. It enlarges in size. It is ready to get attached and implanted to the uterine wall. Embryonic pole Abembryonic pole
- 18. Implantation 6 days after fertilization: Blastocyst attaches to the endometrial epithelium, at its embryonic pole.
- 19. Trophoblast proliferates rapidly and differentiates into two layers: Inner cellular cytotrophoblast, and Outer mass of syncytiotrophoblast (multinucleated protoplasm with no cell boundaries). Finger like processes of syncytiotrophoblast extend through the endometrium and invade the endometrial connective tissue.
- 20. By the end of 7th day, the blastocyst gets implanted in the superficial compact layer of the endometrium and derives its nourishment from the eroded endometrium.
- 21. The blastocyst gradually embed deeper in the endometrium and the defect in the endometrial epithelium is filled by closing plug (day 10).
- 22. The defect gradually disappear as the endometrial epithelium is repaired (day 12 & 13) Blood filled lacunae appear in the syncytiotrophoblast which filled with maternal blood, establishing primitive uteroplacental circulation.
- 23. Implantation Sites Uterine: Usually occurs in the posterior wall of the body of uterus near the fundus. Implantation in the lower segment leads to placenta Praevia Extrauterine: leading to ectopic pregnancies: Fallopian tube Ovary Abdomen Cervical