A3_POM.pdf
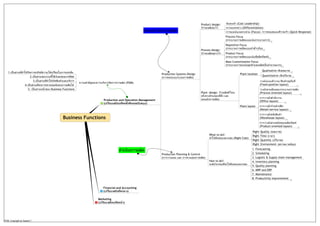
- 1. Business Functions
Production and Operation Management
( )
Production Systems Design
(การออกแบบระบบการผลิต)
Product design:
รูวาจะผลิตอะไร
ตนทุนตํ่า (Cost Leadership)
ความแตกตาง (Differentiation)
การมุงเนนเฉพาะสวน (Focus) /การตอบสนองที่รวดเร็ว (Quick Response)
Process design:
รูวาจะผลิตอยางไร
Process Focus
(กระบวนการผลิตแบบเนนกระบวนการ)
Repetitive Focus
(กระบวนการผลิตแบบทําซํ้าๆกัน)
Product Focus
(กระบวนการผลิตแบบเนนที่ผลิตภัณฑ)
Mass Customization Focus
(กระบวนการมุงเนนลูกคาและผลิตเป็ นจํานวนมาก)
Plant design: รูวาผลิตที่ไหน
(ทั้งทางดานของที่ตั้ง และ
แผนผังการผลิต)
Plant location
Qualitative เชิงคุณภาพ
Quantitative เชิงปริมาณ
Plant layout
วางผังแบบตัวงาน/สินคาอยูกับที่
(Fixed-position layout)
วางผังตามลักษณะกระบวนการผลิต
(Process-oriented layout)
การวางผังสํานักงาน
(Office layout)
การวางผังรานคาปลีก
(Retail/service layout)
การวางผังคลังสินคา
(Warehouse layout)
การวางผังตามชนิดของผลิตภัณฑ
(Product-oriented layout)
Production Planning & Control
(การวางแผน และ การควบคุมการผลิต)
What to do?:
ทําใหตนทุนเหมาะสม (Right Cost)
Right Quality (คุณภาพ)
Right Time (เวลา)
Right Quantity (ปริมาณ)
Right Environment (สภาพแวดลอม)
How to do?:
องคประกอบที่จะใหตนทุนเหมาะสม
1. Forecasting
2. Scheduling
3. Logistic & Supply chain management
4. Inventory planning
5. Quality planning
6. MRP and ERP
7. Maintenance
8. Productivity improvement
Financial and Accounting
( )
Marketing
( )
ความสําคัญของการบริหารจัดการการผลิต (POM)
1.เป็นสวนที่ทําใหกิจการธุรกิจมีความไดเปรียบในการแขงขัน
2.เป็นสวนของงานที่ใชเงินลงทุนมากที่สุด
3.เป็นสวนที่ทําใหเกิดสินคาและบริการ
4.เป็นสวนที่สามารถควบคุมตนทุนการผลิตได
5. เป็ นสวนหนึ่งของ Business Functions
กอนดําเนินการผลิต
ดําเนินการผลิต
POM, Copyright by Asanai T.
- 2. Business Functions
Production and Operation Management
( )
Production Systems Design
(การออกแบบระบบการผลิต)
Product design:
รูวาจะผลิตอะไร
ตนทุนตํ่า (Cost Leadership)
ความแตกตาง (Differentiation)
การมุงเนนเฉพาะสวน (Focus) /การตอบสนองที่รวดเร็ว (Quick Response)
Process design:
รูวาจะผลิตอยางไร
Process Focus
(กระบวนการผลิตแบบเนนกระบวนการ)
ขอดี
การผลิตมีความยืดหยุน
ผลิตไดหลากหลายผลิตภัณฑ
อุปกรณเครื่องจักรเป็ นแบบทั่วๆไป
เงินลงทุนไมสูงมาก
ขอเสีย
บุคลากรตองมีความชํานาญสูง
การวางแผนและควบคุมการผลิตทําไดคอนขางลําบาก
อัตราการใชงานอุปกรณเครื่องจักรตํ่า (5% to 25%)
Repetitive Focus
(กระบวนการผลิตแบบทําซํ้าๆกัน)
ขอดี
การผลิตมีมาตรฐานตามแบบที่ไดกําหนดไว
ใชเวลาในการผลิตนอยกวา process focus
ขอเสีย
ใชเงินลงทุนสูงกวา process focus
เครื่องมืออุปกรณมีความยืดหยุนนอยกวา process focus
Product Focus
(กระบวนการผลิตแบบเนนที่ผลิตภัณฑ)
ขอดี
ตนทุนผันแปรของผลิตภัณฑตํ่า
แรงงานไมตองมีทักษะมากนัก
การวางแผนและควบคุมการผลิตทําไดงาย
อัตราการใชอุปกรณเครื่องจักรสูง (70% to 90%)
ขอเสีย
ความยืดหยุนในผลิตภัณฑตํ่ามาก
ใชอุปกรณเครื่องจักรพิเศษดังนั้นเงินลงทุนจึงสูง
ใชพื้นที่มากในการผลิต
Mass Customization Focus
(กระบวนการมุงเนนลูกคาและผลิตเป็ นจํานวนมาก)
ขอดี
ผลิตไดในปริมาณมาก
และมีความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑสูง
เครื่องมืออุปกรณมีความยืดหยุน
และเปลี่ยนแปลงไดอยางรวดเร็ว
ขอเสีย
ตารางการผลิตซับซอน
ตนทุนคงที่สูง
Plant design: รูวาผลิตที่ไหน
(ทั้งทางดานของที่ตั้ง และ
แผนผังการผลิต)
Plant location
Qualitative เชิงคุณภาพ
การขนสง
ตลาดจําหนาย
แหลงวัตถุดิบ
แรงงาน
สภาพภูมิอากาศ
สิ่งแวดลอม
ราคา ขนาดของพื้นที่
ฮวงจุย ฯลฯ
Quantitative
เชิงปริมาณ
วิธีประเมินปัจจัย (Factor-rating method)
วิธีการวิเคราะหจุดคุมทุน (Break-even analysis)
วิธีการหาจุดศูนยกลาง (Center-of-gravity method)
วิธีตวแบบการขนสง (Transportation model)
Plant layout
วางผังแบบตัวงาน/สินคาอยูกับที่
(Fixed-position layout) เหมาะสําหรับโครงการใหญๆ
วางผังตามลักษณะกระบวนการผลิต
(Process-oriented layout) เหมาะสําหรับการผลิตที่มีความหลากหลายแตปริมาณการผลิตนอย
การวางผังสํานักงาน
(Office layout)
มุงเนนความสะดวกสบายการใชงานอุปกรณตางๆ
การสงผานเอกสาร/ขอมูล
การวางผังรานคาปลีก
(Retail/service layout) มุงเนนการใชเนื้อที่ชั้นจัดวางและความงายในการเลือกสินคา
การวางผังคลังสินคา
(Warehouse layout)
เนนที่การใชเนื้อที่
การเคลื่อนยายและคาใชจายในการจัดเก็บที่เกี่ยวของ
การวางผังตามชนิดของผลิตภัณฑ
(Product-oriented layout) เนนที่การใชเนื้อที่ ประสิทธิภาพการทํางานของบุคคลากรและเครื่องจักร
Production Planning & Control
(การวางแผน และ การควบคุมการผลิต)
What to do?:
ทําใหตนทุนเหมาะสม (Right Cost)
How to do?:
องคประกอบที่จะใหตนทุนเหมาะสม
Financial and Accounting
( )
Marketing
( )
ดําเนินการผลิต
ความสําคัญของการบริหารจัดการการผลิต (POM)
1.เป็นสวนที่ทําใหกิจการธุรกิจมีความไดเปรียบในการแขงขัน
2.เป็นสวนของงานที่ใชเงินลงทุนมากที่สุด
3.เป็นสวนที่ทําใหเกิดสินคาและบริการ
4.เป็นสวนที่สามารถควบคุมตนทุนการผลิตได
5. เป็ นสวนหนึ่งของ Business Functions
กอนดําเนินการผลิต
POM, Copyright by Asanai T.
- 3. ปรับปรุปวิธีการผลิต
ใช Technology ที่เหมาะสมและทันสมัย
พัฒนาองคกรทุกระดับอยางตอเนื่อง
มีวิธีการจัดการที่ดี
มีการจูงใจ
Business Functions
Production and Operation Management
( )
Production Systems Design
(การออกแบบระบบการผลิต)
Product design:
รูวาจะผลิตอะไร
Process design:
รูวาจะผลิตอยางไร
Plant design: รูวาผลิตที่ไหน
(ทั้งทางดานของที่ตั้ง และ แผนผังการผลิต)
Production Planning & Control
( )
What to do?:
(Right Cost)
Right Quality (คุณภาพ)
Right Time (เวลา)
Right Quantity (ปริมาณ)
Right Environment (สภาพแวดลอม)
How to do?:
1. Forecasting
Qualitative Forecasting
(Judgment Method)
วิธีสอบถามจากฝายขาย (Sales-Force Composites)
วิธีการสํารวจความคิดเห็นของลูกคา (Surveys of Customers and the General Population)
วิธีการรวบรวมความคิดเห็นของผูบริหาร (Jury of Executive Opinion)
วิธีการรวบรวมคิดเห็นของผูเชี่ยวชาญ หรือวิธีเดลไฟ (The Delphi Method)
Quantitative Forecasting
อนุกรมเวลา
(Time-series Models)
วิธี Naïve Method
วิธี คาเฉลี่ยเคลื่อนที่ (Moving Averages) ไมมีอิทธิพลของแนวโนมและอิทธิพลของฤดูกาล
วิธี Simple Exponential Smoothing
(ใหนํ้าหนักขอมูลลาสุดมากกวาขอมูลในอดีต) ไมมีอิทธิพลของแนวโนมและอิทธิพลของฤดูกาล
วิธี Holt’s Exponential Smoothing (หรือ Double Exponential Smoothing ) มีอิทธิพลของแนวโนม แตไมมีอิทธิพลของฤดูกาล
วิธี Winter’s Exponential Smoothing มีอิทธิพลของแนวโนม และมีอิทธิพลของฤดูกาล
ตัวแบบอาศัยเหตุ-ผล
(Associative models)
การพยากรณ โดยวิธี Least Square
การพยากรณ โดยวิธีเชิงสหสัมพันธ (Correlation Forecasting)
2. Scheduling/Aggregate Planning
(Passive strategies)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงระดับสินคาคงคลัง
การเปลี่ยนแปลงจํานวนพนักงาน
การเปลี่ยนแปลงเวลาการทํางาน
การจางผูผลิตรายอื่นแทน
การจางพนักงานชั่วคราว
(Active strategies)
การใชแรงกระตุนความตองการของลูกคา
การคางสงสินคาในชวงที่มีความตองการสูง
การผลิตสินคาตางชนิดในนอกชวงฤดูกาล
(Mixing options)
3. Logistic & Supply chain management
SCM
ผูป อนวัตถุดิบ (Supplier)
ผูผลิต (Manufacturer)
ตัวแทนจําหนายและกระจายสินคา (Distributor)
ผูคาสง (Wholesaler) และผูคาปลีก (Retailer)
ผูบริโภค (Customer)
Bullwhip Effect
(Risk Pooling)
ระบบกระจายศูนย (Decentralized System)
ระบบรวมศูนย (Centralized System)
Location pooling (การวมสถานที่ตั้ง)
Product pooling (การรวมผลิตภัณฑ)
Consolidated Distribution, Lead time pooling
(การรวมจุดกระจายสินคา)
Delayed differentiation, Lead Time risk pooling
(การหนวงเวลาการสรางความแตกตาง)
Capacity pooling
(การรวมกําลังการผลิต)
4. Inventory planning
How much to order? (Q)
จํานวนของการสั่งซื้อที่ประหยัดที่สุด
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
When to order? จุดสั่งซื้อ (Reorder Point)
Total inventory cost (TC)
(Purchase Cost)
Total Incremental Cost (TIC)
คาใชจายเตรียมการ
Preparation Cost (Cp หรือ Co)
คาใชจายในการสั่งซื้อ (Ordering cost)
คาใชจายในการติดตั้งเครื่องจักร (Setup cost)
คาใชจายในการถือครองสินคาคงคลัง
Holding Cost (Ch หรือ Cc)
คาดูแลรักษา (Storage cost)
คาดอกเบี้ย (Interest)
คาของชํารุด หรือ ของเสียหาย (Damage and Spoilage)
คาประกัน (Insurance)
ลาหสมัย (Obsolescence)
คาของหาย (Lost)
คาใชจายเมื่อสินคาขาดมือ
Shortage Cost (Cs)
คาเสียโอกาศ
การเสียคาใชจายโดยไมไดงาน
(Inventory Control Systems)
Red - line
Two - bin
(Computerized Systems)
ABC (ABC Inventory Classification)
Just - in - time (JIT)
5. Quality planning
TQM, ISO, 5ส.
7 QC Tools, House of Quality
Service blueprint
6. Material requirements planning (MRP)
and Enterprise resource planning (ERP)
ตารางการผลิตหลัก (Master production schedule, MPS)
รายการของวัสดุ (Bill of Materials, BOM)
รายการของสินคาคงคลัง (Inventory records)
7. Maintenance
8. Productivity improvement
Output / Input
เพิ่ม Output โดย Input เทาเดิม
เพิ่ม Output ใหมากกวาเพิ่ม Input
เพิ่ม Output และลด Input ในเวลาเดียวกัน
ลด Input โดยที่ Output เทาเดิม
ลด Input ในสัดสวนที่มากกวาลด Output
การเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการผลิต
Output
ทําใหเร็ว
ทําใหมากขึ้น
ทําใหดีขึ้น
Input ลดการสูญเสีย (7 wastes)
การเคลื่อนไหวที่ไมจําเป็น
การรอคอย
กระบวนการที่ขาดประสิทธิผล
ของเสีย / แกไขงานเสีย
การผลิต /ปฏิบัติงานปริมาณมาก
การเก็บวัสดุคงคลังที่ไมจําเป็น
การขนสง
Financial and Accounting
( )
Marketing
( )
ความสําคัญของการบริหารจัดการการผลิต (POM)
1.เป็นสวนที่ทําใหกิจการธุรกิจมีความไดเปรียบในการแขงขัน
2.เป็นสวนของงานที่ใชเงินลงทุนมากที่สุด
3.เป็นสวนที่ทําใหเกิดสินคาและบริการ
4.เป็นสวนที่สามารถควบคุมตนทุนการผลิตได
5. เป็ นสวนหนึ่งของ Business Functions
ดําเนินการผลิต
กอนดําเนินการผลิต
POM II, Copyright by Asanai T.