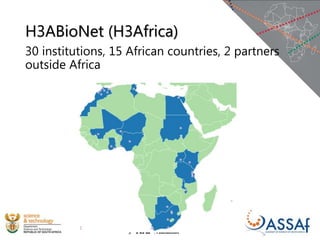
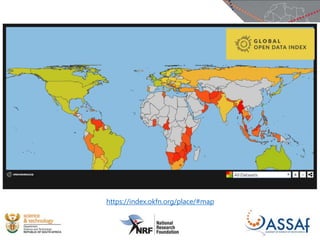
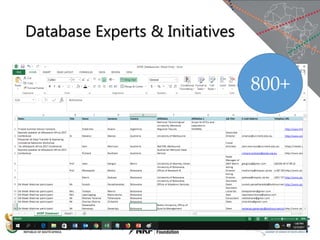
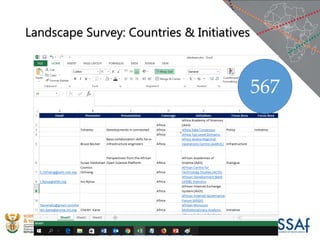
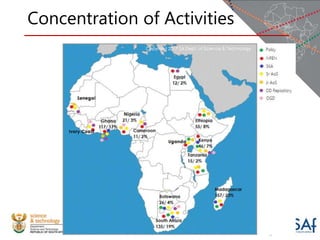
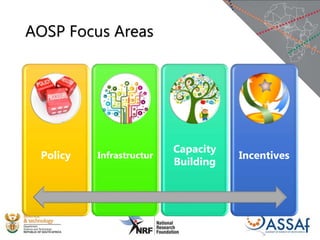
The document discusses the African Open Science Platform, which aims to promote open science across Africa. It provides context on initiatives like the Square Kilometre Array telescope project and H3ABioNet, which involve large-scale data collection and sharing across multiple African countries. The platform seeks to develop policies, build capacity, and provide incentives to support open data practices in line with FAIR principles. It also outlines the current research infrastructure landscape in Africa and initiatives to strengthen national research networks and cyberinfrastructure to enable open sharing and analysis of genomic and other data for the benefit of African societies.






















![Se
[Source: Colin Wright SADC/ET-ST1/1/2016/11 Document]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reserachinfrastructure-180514162404/85/The-African-Open-Science-Platform-Susan-Veldsman-30-320.jpg)



