Preventive maintenance elements and procedures
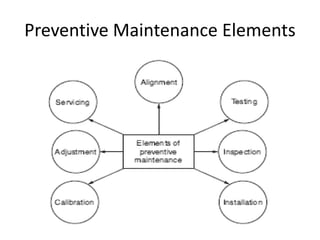
- 2. Preventive Maintenance Elements 1 Inspection: Periodically inspecting materials/items to determine their serviceability by comparing their physical, electrical, mechanical, etc., characteristics (as applicable) to expected standards 2. Servicing: Cleaning, lubricating, charging, preservation, etc., of items/ materials periodically to prevent the occurrence of incipient failures
- 3. Preventive Maintenance Elements 3. Calibration: Periodically determining the value of characteristics of an item by comparison to a standard; it consists of the comparison of two instruments, one of which is certified standard with known accuracy, to detect and adjust any discrepancy in the accuracy of the material/parameter being compared to the established standard value 4.Testing: Periodically testing or checking out to determine serviceability and detect electrical/mechanical-related degradation
- 4. Preventive Maintenance Elements 3. Calibration: Periodically determining the value of characteristics of an item by comparison to a standard; it consists of the comparison of two instruments, one of which is certified standard with known accuracy, to detect and adjust any discrepancy in the accuracy of the material/parameter being compared to the established standard value 4.Testing: Periodically testing or checking out to determine serviceability and detect electrical/mechanical-related degradation
- 5. Preventive Maintenance Elements 5.Alignment: Making changes to an item’s specified variable elements for the purpose of achieving optimum performance 6.Adjustment: Periodically adjusting specified variable elements of material for the purpose of achieving the optimum system performance 7.Installation: Periodic replacement of limited-life items or the items experiencing time cycle or wear degradation, to maintain the specified system tolerance
- 7. Corrective Maintenance Elements 1. Fail-repair: The failed item is restored to its operational state. 2. Salvage: This element of corrective maintenance is concerned with disposal of non-repairable material and use of salvaged material from non-repairable equipment/item in the repair, overhaul, or rebuild programs. 3. Rebuild: This is concerned with restoring an item to a standard as close as possible to original state in performance, life expectancy, and appearance. This is achieved through complete disassembly, examination of all components, repair and replacement of worn/unserviceable parts as per original specifications and manufacturing tolerances, and reassembly and testing to original production guidelines.
- 8. Corrective Maintenance Elements 4.Overhaul: Restoring an item to its total serviceable state as per maintenance serviceability standards, using the “inspect and repair only as appropriate approach”. 5. Servicing: Servicing may be needed because of the corrective maintenance action, for example, engine repair can lead to crankcase refill, welding on, etc. Another example could be that the replacement of an air bottle may require system recharging.
- 9. Maintenance Tasks Explanations of the terms used in the possible tasks are as follows: • Lubrication/servicing (all categories)—this involve any act of lubricating or servicing for maintaining inherent design capabilities. • Operational/visual/automated check (hidden functional failure categories only)— an operational check is a task to determine that an item is fulfilling its intended purpose. It does not require quantitative checks and is a failure-finding task. A visual check is an observation to determine that an item is fulfilling its intended purpose and does not require quantitative tolerances. This, again, is a failure-finding task. The visual check could also involve interrogating electronic units that store failure data. •
- 10. Maintenance Tasks • Inspection/functional check/condition monitoring (all categories)—an inspection is an examination of an item against a specific standard. A functional check is a quantitative check to determine if one or more functions of an item perform within specified limits. Condition monitoring is a task, which may be continuous or periodic to monitor the condition of an item in operation against preset parameters.
- 11. Maintenance Tasks • Restoration (all categories)—restoration is the work necessary to return the item to a specific standard. Since restoration may vary from cleaning or replacement of single parts up to a complete overhaul, the scope of each assigned restoration task has to be specified. • Discard (all categories)—discard is the removal from service of an item at a specified life limit. Discard tasks are normally applied to so-called single-cell parts such as cartridges, containers, cylinders, turbine disks, safe-life structural members, and the like.
- 12. Maintenance Procedure All frequent repairs and maintenance tasks should have a standard procedure that will specifically define the correct method required for competition. These procedures should include all of the information, such as: tools, safety concerns, and repair parts, required for the task and a step-by-step sequence of tasks required to complete the repair.
- 13. Maintenance Procedure Each procedure should be complete and contain all information required to complete the repair or recurring preventive maintenance task. The craftsperson should not be required to find or have supplemental information in order to complete the repair.
- 14. Maintenance Procedure A complete evaluation of the Standard Maintenance Procedures (SMPs) and actual practices should be conducted. The procedures should be compared with maintenance requirements defined by both the design review and the vendor’s O&M manuals. Actual maintenance practices can be by visual observation of similar repairs.
- 15. Maintenance Procedure This task should determine if all maintenance personnel assigned to or involved with the area that is being investigated consistently follow the SMPs. Special attention should be given to the routine tasks, such as lubrication, adjustments, and other preventive tasks. Determine if these procedures are being performed in a timely manner and if proper techniques are being used.
- 16. Maintenance Procedures Following are the Basic Maintenance procedures. Inspection Lubrication Measuring Operating Temperatures Maintenance tools
- 17. Inspection Inspection: The qualitative observation of an item’s performance or condition. Regular visual inspection of the machinery and systems in a plant is a necessary part of any predictive maintenance program. In many cases, visual inspection will detect potential problems that will be missed using the other predictive maintenance techniques. Routine visual inspection of all critical plant systems will add to the other techniques and ensure that potential problems are detected before serious damage can occur.
- 19. Inspection Most of the vibration-based predictive maintenance systems include the capability of recording visual observations as part of the routine data-acquisition process. Since the incremental costs of these visual observations are small, this technique should be incorporated in all predictive maintenance programs. All equipment and systems in the plant should be visually inspected on a regular basis. The additional information provided by visual inspection will augment the predictive
- 20. Inspection Continuous inspection by plant personnel is necessary to detect and correct mechanical defects or conditions which prevent efficient operation. The following must be checked on a continuing basis. (1) Each machine has a characteristic operating sound or appearance. A change from this normal sound or appearance requires the supervisor's immediate attention.
- 21. Inspection (2) Vibration is evidence of basic faults which should be corrected. Loose bearings may be either the cause or the result of vibration. Report all unusual vibration to the supervisor. (3) Cleanliness is essential for trouble-free performance of mechanical and electrical equipment. moisture, dirt, and oil cause deterioration of equipment systems.
- 22. Inspection (4) Conditions which cause excess heat must be eliminated. (5) Couplings should be checked for misalignment. In cases of mechanical troubles, always check alignment. Misalignment may result in overheated and worn bearings or cause stresses which result in failure of the motor shaft.
- 23. Inspection (6) Electrical overload shortens the life of a motor and contributes to unreliable performance. Motors are designed for greater mechanical overloads than electrical overloads. The motor shaft, frame, and bearings can stand several times the rated load for long periods of time, but wiring will overheat when overloads as low as 15 to 25 percent are imposed continuously. Electrical overloads increase the temperature of the windings. The allowable temperature rise is usually stamped on the nameplate.
- 24. Lubrication Lubrication is an important part of preventive maintenance. Proper lubrication prevents damage to wearing surfaces, reduces the maintenance required, and cuts power costs and equipment outages. Contaminants in lubricants produce wear and assist in the ultimate failure of the lubricated equipment. (1) Use of the proper type of lubricant for the application is critical to successful maintenance results. (2) Equipment manufacturer's detailed instructions should be consulted in all cases to ensure that the proper lubricant is being used.
- 25. Lubrication (2) In order to avoid plant failures due to improper lubrication, the following lubricating precautions should be observed. (a) Do not over lubricate. Over lubrication causes antifriction bearings to heat and may damage grease seals; it may also cause damage to the windings in electrical motors. (b) Do not lubricate totally enclosed or insufficiently guarded equipment.
- 26. Lubrication (c) Keep lubricant containers tightly closed, except when in use, to prevent contamination of he lubricant by the entrance of dust, grit, abrasives, and moisture. Lubricants should be stored in dust free areas. Before using lubricant containers, the spouts and lips should be wiped; before using grease guns, the gun and fitting should be wiped to ensure the absence of foreign matter. (3) The principal deteriorating elements in oil are dirt, water, oxidation, and excessive heat. If these are controlled, oil deterioration between lubrication periods is unlikely.
- 27. Measuring operating temperatures. Equipment cannot be maintained properly, unless limits of safe operating temperatures are known. Safe upper limits of operating temperatures are given by manufacturers and can be obtained on request. Use of touch to determine whether operating temperatures are under these maximum limits is unreliable, especially when operating temperatures are above 125°F.
- 28. Measuring operating temperatures. One of the following temperature measuring devices should be used instead. (1) A hand type portable pyrometer, if available in the range required, provides a satisfactory method for measuring external surface temperatures of mechanical equipment. (2) An ordinary mercury thermometer without a guard is satisfactory for measuring external surface or bearing temperatures. It should be calibrated for the range of use.
- 29. Measuring operating temperatures. Details of the use of a thermometer in each of these applications are as follows. (a) To measure surface temperature, fasten the thermometer to the surface with adhesive tape with the bulb touching the surface. Read only after indicated temperature has reached a constant value. (b) To measure bearing temperatures, insert the bare thermometer bulb inside the inspection hole at the top of the bearing. Fit cardboard around the thermometer to cover the inspection hole. Read after a constant value has been reached.