Consistence deformation of trusses
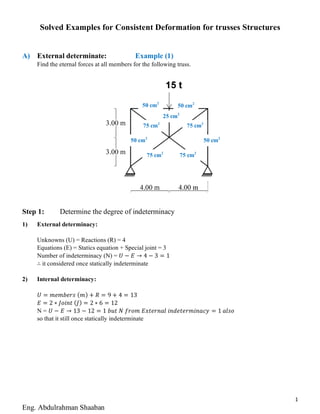
- 1. 1 Eng. Abdulrahman Shaaban Solved Examples for Consistent Deformation for trusses Structures A) External determinate: Example (1) Find the eternal forces at all members for the following truss. Step 1: Determine the degree of indeterminacy 1) External determinacy: Unknowns (U) = Reactions (R) = 4 Equations (E) = Statics equation + Special joint = 3 Number of indeterminacy (N) = 𝑈 − 𝐸 → 4 − 3 = 1 ∴ it considered once statically indeterminate 2) Internal determinacy: 𝑈 = 𝑚𝑒𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟𝑠 ( 𝑚) + 𝑅 = 9 + 4 = 13 𝐸 = 2 ∗ 𝐽𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡 ( 𝐽) = 2 ∗ 6 = 12 N = 𝑈 − 𝐸 → 13 − 12 = 1 𝑏𝑢𝑡 𝑁 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑚 𝐸𝑥𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑛𝑎𝑙 𝑖𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑐𝑦 = 1 𝑎𝑙𝑠𝑜 so that it still once statically indeterminate 50 cm2 50 cm2 50 cm2 50 cm2 75 cm2 75 cm2 75 cm2 75 cm2 25 cm2
- 2. 2 Eng. Abdulrahman Shaaban Step 2: Select proper statically determinate main system Step 3: Coding members, calculate angles for inclined members and find reactions: 𝜃1 = tan−1(3 4⁄ ) = 36.870 Step 4: Find all internal forces at all members due to original loads Hint: using joint method without details for each individual joint just find the force and but its value and its type (use [+ve] for tension force and [-ve] for compression value) directly on the figure. 1 2 3 45 6 7 8 9 0 7.5 7.5 θ1 θ1 θ1 θ1 0 0 -7.5 -10-10 -7.5 12.5 12.5 -15 0 7.5 7.5 θ1 θ1 θ1 θ1
- 3. 3 Eng. Abdulrahman Shaaban Step 5: Find all internal forces at all members due to applying unit redundant. Step 6: Construct a table to summarize results and facilitation of calculation procedures. Member L (cm) A (cm2 ) N0 (t) N1 (t) N0N1*L/A N1 2 *L/A Nf 1 500 75 0 -1.25 0.00 10.42 -8.84 2 500 75 0 -1.25 0.00 10.42 -8.84 3 600 50 -7.5 +0.75 -67.50 6.75 -2.20 4 400 50 -10 +1 -80.00 8.00 -2.93 5 400 50 -10 +1 -80.00 8.00 -2.93 6 600 50 -7.5 +0.75 -67.50 6.75 -2.20 7 500 75 +12.5 -1.25 -104.17 10.42 3.66 8 500 75 +12.5 -1.25 -104.17 10.42 3.66 9 300 25 -15 0 0.00 0.00 -15.00 Σ -503.33 71.17 Step 7: Calculate the true value of redundant by the following eqn: 𝑥1 = −𝑁0N1 ∗ L/A 𝑁1 2 ∗ 𝐿/𝐴 = 7.07 Step 8: Calculate the final internal force at each member by the following eqn: 𝑁𝑓 = 𝑁0 + 𝑥1 ∗ 𝑁1 Step 9: Draw the final normal force diagram -1.25 +0.75 +1+1 +0.75 -1.25 -1.25 0 1 0 0 θ1 θ1 1 -1.25 -8.84 -2.2 -2.93-2.93 -2.2 3.66 3.66 -15 7.07 7.5 7.5 7.07 -8.84
- 4. 4 Eng. Abdulrahman Shaaban Example (2) Step 1: Determine the degree of indeterminacy 1) External determinacy: U = 4 E = 3 N = 𝑈 − 𝐸 → 4 − 3 = 1 ∴ it considered once statically indeterminate 2) Internal determinacy: 𝑈 = 𝑚 + 𝑅 = 19 + 4 = 23 𝐸 = 2 ∗ 𝐽 = 2 ∗ 11 = 22 N = 𝑈 − 𝐸 → 23 − 22 = 1 𝑏𝑢𝑡 𝑁 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑚 𝐸𝑥𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑛𝑎𝑙 𝑖𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑐𝑦 = 1 𝑎𝑙𝑠𝑜 so that it still once statically indeterminate Step 2: Select proper statically determinate main system 2A 2A 2A 2A 2A2A 3A
- 5. 5 Eng. Abdulrahman Shaaban Step 3: Coding members, calculate angles for inclined members and find reactions: 𝜃1 = tan−1(6 2⁄ ) = 71.560 𝜃2 = tan−1(3 2⁄ ) = 56.310 Step 4: Find all internal forces at all members due to original loads θ2 θ1 1 2 3 4 5 678 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 1212 0 1212 0 -6.33 -6.33 -6.33 -6.33 -7.21 -8-13.34-8 -7.21 +6 +10.67 +10.67 +6 +7.21 +4.81 -4.81 +4.81 -4.81 +7.21
- 6. 6 Eng. Abdulrahman Shaaban Step 5: Find all internal forces at all members due to applying unit redundant. Step 6: Construct a table to summarize results and facilitation of calculation procedures. Member L (m) A N0 (t) N1 (t) N0N1*L/A N1 2 *L/A Nf 1 2√10 2 -6.33 +1.58 -31.63 7.89 -1.20 2 2√10 2 -6.33 -1.58 31.63 7.89 -11.46 3 2√10 2 -6.33 -1.58 31.63 7.89 -11.46 4 2√10 2 -6.33 +1.58 -31.63 7.89 -1.20 5 √13 1 -7.21 +1.80 -46.79 11.68 -1.37 6 4 1 -8 +2 -64.00 16.00 -1.51 7 4 3 -13.34 +2 -35.57 5.33 -6.85 8 4 1 -8 +2 -64.00 16.00 -1.51 9 √13 1 -7.21 +1.80 -46.79 11.68 -1.37 10 4 1 +6 -1.5 -36.00 9.00 1.13 11 4 2 +10.67 -3 -64.02 18.00 0.93 12 4 2 +10.67 -3 -64.02 18.00 0.93 13 4 1 +6 -1.5 -36.00 9.00 1.13 14 √13 1 +7.21 -1.80 -46.79 11.68 1.37 15 √13 1 -4.81 0 0.00 0.00 -4.81 16 √13 1 +4.81 0 0.00 0.00 4.81 17 √13 1 +4.81 0 0.00 0.00 4.81 18 √13 1 -4.81 0 0.00 0.00 -4.81 19 √13 1 +7.21 -1.80 -46.79 11.68 1.37 Σ -550.78 169.64 00 1 1 -1.58+1.58 -1.58 +1.58 +1.8 +2 +2+2 +1.8 -1.5 -1.8 0 0 0 0 -1.8 -3 -3 -1.5
- 7. 7 Eng. Abdulrahman Shaaban Step 7: Calculate the true value of redundant by the following eqn: 𝑥1 = −𝑁0N1 ∗ L/A 𝑁1 2 ∗ 𝐿/𝐴 = 3.25 Step 8: Calculate the final internal force at each member by the following eqn: 𝑁𝑓 = 𝑁0 + 𝑥1 ∗ 𝑁1 Step 9: Draw the final normal force diagram 1212 3.25 -11.46 -1.2 -11.46 -1.2 -1.37 -1.51-6.85 -1.37 +1.13 +0.93 +0.93 +1.13 +4.81 -4.81+1.37 +4.81 -4.81 +1.37 3.25 -1.51
- 8. 8 Eng. Abdulrahman Shaaban B) Internal determinate: Example (3) Find the eternal forces at all members for the following truss. Step 1: Determine the degree of indeterminacy 1) External determinacy: U = 4 E = 3 + 1 = 4 N = 𝑈 − 𝐸 → 4 − 4 = 0 ∴ it considered statically determinate 2) Internal determinacy: 𝑈 = 𝑚 + 𝑅 = 13 + 4 = 17 𝐸 = 2 ∗ 𝐽 = 2 ∗ 8 = 16 N = 𝑈 − 𝐸 → 17 − 16 = 1 so that it considered once statically indeterminate Step 2: Select proper statically determinate main system
- 9. 9 Eng. Abdulrahman Shaaban Step 3: Coding members, calculate angles for inclined members and find reactions: 𝜃1 = tan−1(3 4⁄ ) = 36.870 Step 4: Find all internal forces at all members due to original loads Step 5: Find all internal forces at all members due to applying unit redundant. 26 64 64 0 1 2 3 456 7 8 11 θ1 26 64 64 0 -10 +8+29.34 -8 -26.67 +64 -43.33 -29.34 +16 +6 0 0 0 0 1 1 -0.6 0 00 0 0 -0.8 -0.8 -0.6 +1 9 10
- 10. 10 Eng. Abdulrahman Shaaban Step 6: Construct a table to summarize results and facilitation of calculation procedures. Member L (m) A N0 (t) N1 (t) N0N1*L/A N1 2 *L/A Nf 1 4 1 -29.34 0 0.00 0.00 -29.34 2 4 1 -8 -0.8 25.60 2.56 -19.17 3 5 1 -10 0 0.00 0.00 -10.00 4 4 1 +8 0 0.00 0.00 8.00 5 4 1 +29.34 -0.8 -93.89 2.56 18.17 6 4 1 +64 0 0.00 0.00 64.00 7 5 1 -43.33 0 0.00 0.00 -43.33 8 3 1 +16 -0.6 -28.80 1.08 7.62 9 5 1 -26.67 +1 -133.35 5.00 -12.71 10 5 1 0 +1 0.00 5.00 13.96 11 3 1 +6 -0.6 -10.80 1.08 -2.38 Σ -241.24 17.28 Step 7: Calculate the true value of redundant by the following eqn: 𝑥1 = −𝑁0N1 ∗ L/A 𝑁1 2 ∗ 𝐿/𝐴 = 13.96 Step 8: Calculate the final internal force at each member by the following eqn: 𝑁𝑓 = 𝑁0 + 𝑥1 ∗ 𝑁1 Step 9: Draw the final normal force diagram 64 64 26 -2.38 -10 +8+64 -43.33 -29.34 +18.17 -19.17 +7.62 -12.71 +13.96 0
- 11. 11 Eng. Abdulrahman Shaaban Example (4) Step 1: Determine the degree of indeterminacy 1) External determinacy: U = 3 E = 3 N = 𝑈 − 𝐸 → 3 − 3 = 0 ∴ it considered statically determinate 2) Internal determinacy: 𝑈 = 𝑚 + 𝑅 = 15 + 3 = 18 𝐸 = 2 ∗ 𝐽 = 2 ∗ 8 = 16 N = 𝑈 − 𝐸 → 18 − 16 = 2 so that it considered twice statically indeterminate Step 2: Select proper statically determinate main system
- 12. 12 Eng. Abdulrahman Shaaban Step 3: Coding members, calculate angles for inclined members and find reactions: 𝜃1 = tan−1(3 4⁄ ) = 36.870 Step 4: Find all internal forces at all members due to original loads. Step 5: Find all internal forces at all members due to applying unit redundant. 9 1 9 6 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 12 13 14 15 7 10 11 θ1 9 +4.5 9 6 +4.5 0 0 -9 0 -7.5 0 +7.5 1 -0.8 -0.8 -0.6-0.6 +1 0 0 00 +1 1 -0.6 -0.6 -0.8 -0.8 0 0 0 0 N2 N1 N0
- 13. 13 Eng. Abdulrahman Shaaban Step 6: Construct a table to summarize results and facilitation of calculation procedures. Member L (m) A N0 (t) N1 (t) N2 (t) N0N1*L/A N0N2*L/A N1 2 *L/A N2 2 *L/A N1N2*L/A Nf 1 3 1 +4.5 -0.6 0 -8.1 0 1.08 0 0 6.36 2 3 1 +4.5 0 -0.6 0 -8.1 0 1.08 0 2.64 3 4 1 0 0 -0.8 0 0 0 2.56 0 -2.48 4 3 1 0 0 -0.6 0 0 0 1.08 0 -1.86 5 3 1 -9 -0.6 0 16.2 0 1.08 0 0 -7.14 6 4 1 0 -0.8 0 0 0 2.56 0 0 2.48 7 4 1 0 -0.8 -0.8 0 0 2.56 2.56 2.56 0.00 8 2.5 1 +7.5 +1 0 18.75 0 2.5 0 0 4.40 9 2.5 1 0 +1 0 0 0 2.5 0 0 -3.10 10 2.5 1 +7.5 +1 0 18.75 0 2.5 0 0 4.40 11 2.5 1 0 +1 0 0 0 2.5 0 0 -3.10 12 2.5 1 0 0 +1 0 0 0 2.5 0 3.10 13 2.5 1 -7.5 0 +1 0 -18.75 0 2.5 0 -4.40 14 2.5 1 0 0 +1 0 0 0 2.5 0 3.10 15 2.5 1 -7.5 0 +1 0 -18.75 0 2.5 0 -4.40 Σ 45.6 -45.6 17.28 17.28 2.56 Step 7: Calculate the true value of redundant by the following eqns: 𝛿10 + 𝑥1 𝛿11 + 𝑥2 𝛿12 = 0 𝛿20 + 𝑥1 𝛿21 + 𝑥2 𝛿22 = 0 𝛿10 = ∫ 𝑁0 𝑁1 𝑙 𝐸𝐴 𝑑𝑙 𝛿20 = ∫ 𝑁0 𝑁2 𝑙 𝐸𝐴 𝑑𝑙 𝛿11 = ∫ 𝑁1 𝑁1 𝑙 𝐸𝐴 𝑑𝑙 𝛿22 = ∫ 𝑁2 𝑁2 𝑙 𝐸𝐴 𝑑𝑙 𝛿12 = 𝛿21 = ∫ 𝑁1 𝑁2 𝑙 𝐸𝐴 𝑑𝑙 45.6 + 𝑥1 ∗ 17.28 + 𝑥2 ∗ 2.56 = 0 −45.6 + 𝑥1 ∗ 2.56 + 𝑥2 ∗ 17.28 = 0 𝑥1 = −3.097 𝑥2 = 3.097 Step 8: Calculate the final internal force at each member by the following eqn: 𝑁𝑓 = 𝑁0 + 𝑥1 ∗ 𝑁1 + 𝑥2 ∗ 𝑁2
- 14. 14 Eng. Abdulrahman Shaaban Step 9: Draw the final normal force diagram 9 +6.36 9 6 +2.64 -2.48 -1.86 -7.14 +2.48 +4.4 -3.1 -4.4 0 +3.1
