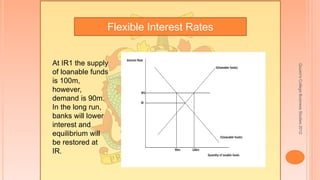
This document discusses some of the key tenants of classical economics from Adam Smith and J.B. Say from 1776 to 1930. It outlines Say's law that supply creates its own demand, and that wages, interest rates, and prices are flexible. This flexibility means that any disequilibriums in markets will be temporary and equilibrium will be restored. It provides examples of how flexible interest rates and flexible wages allow disequilibriums to be cleared through adjustments over time. The document also notes that classical economics considers some unemployment to be voluntary as individuals may choose not to work at the equilibrium wage rate.