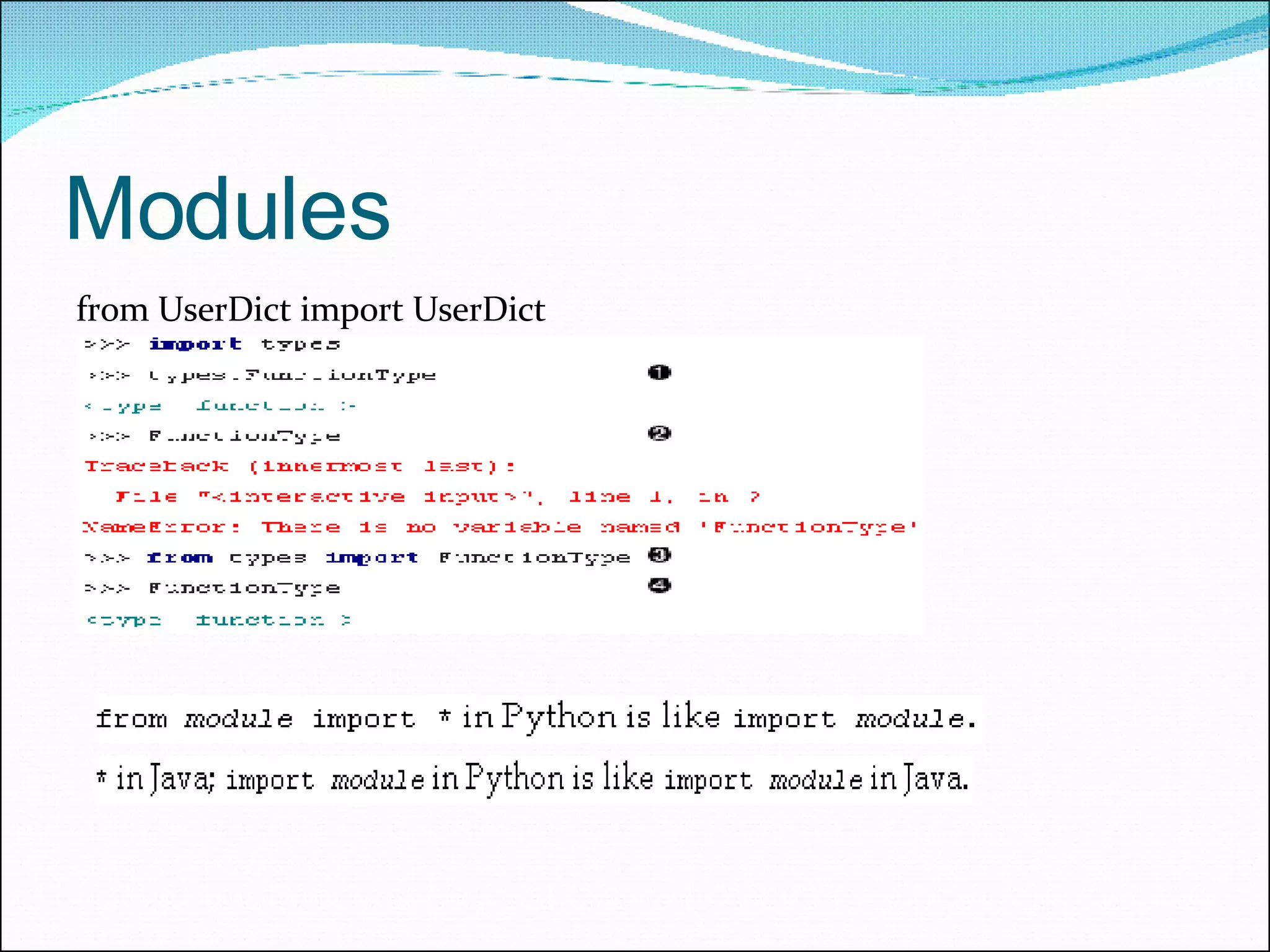
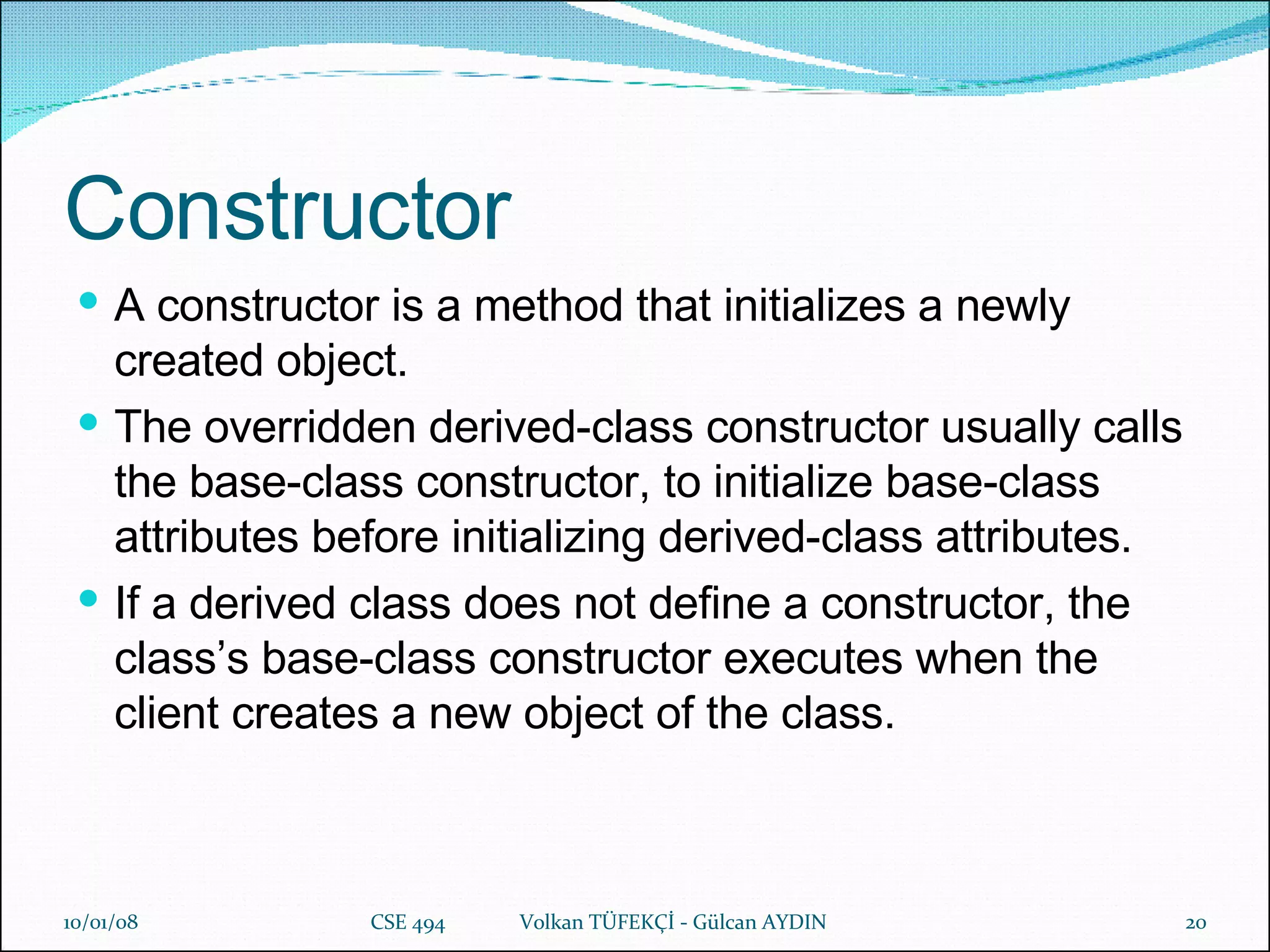
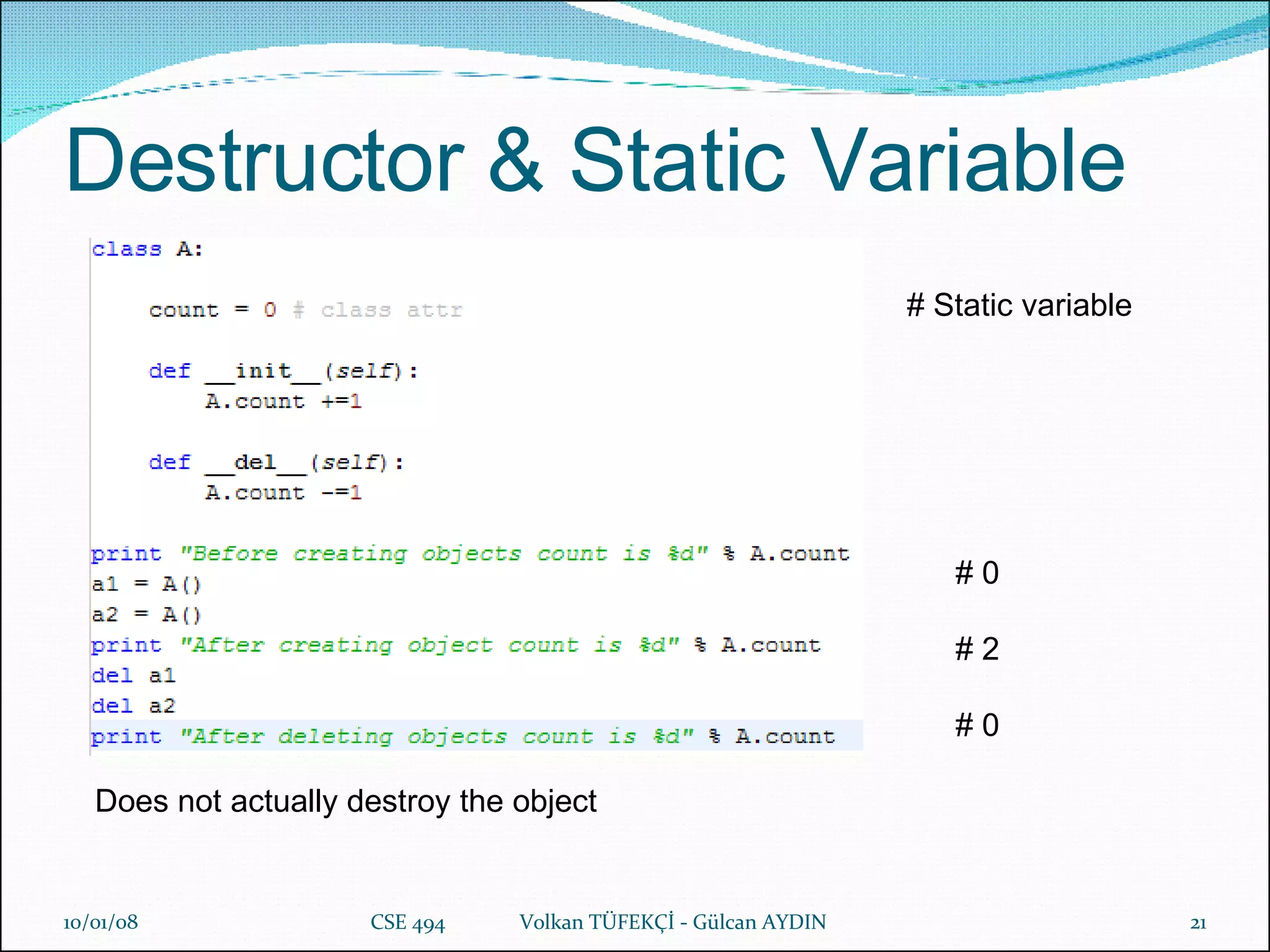
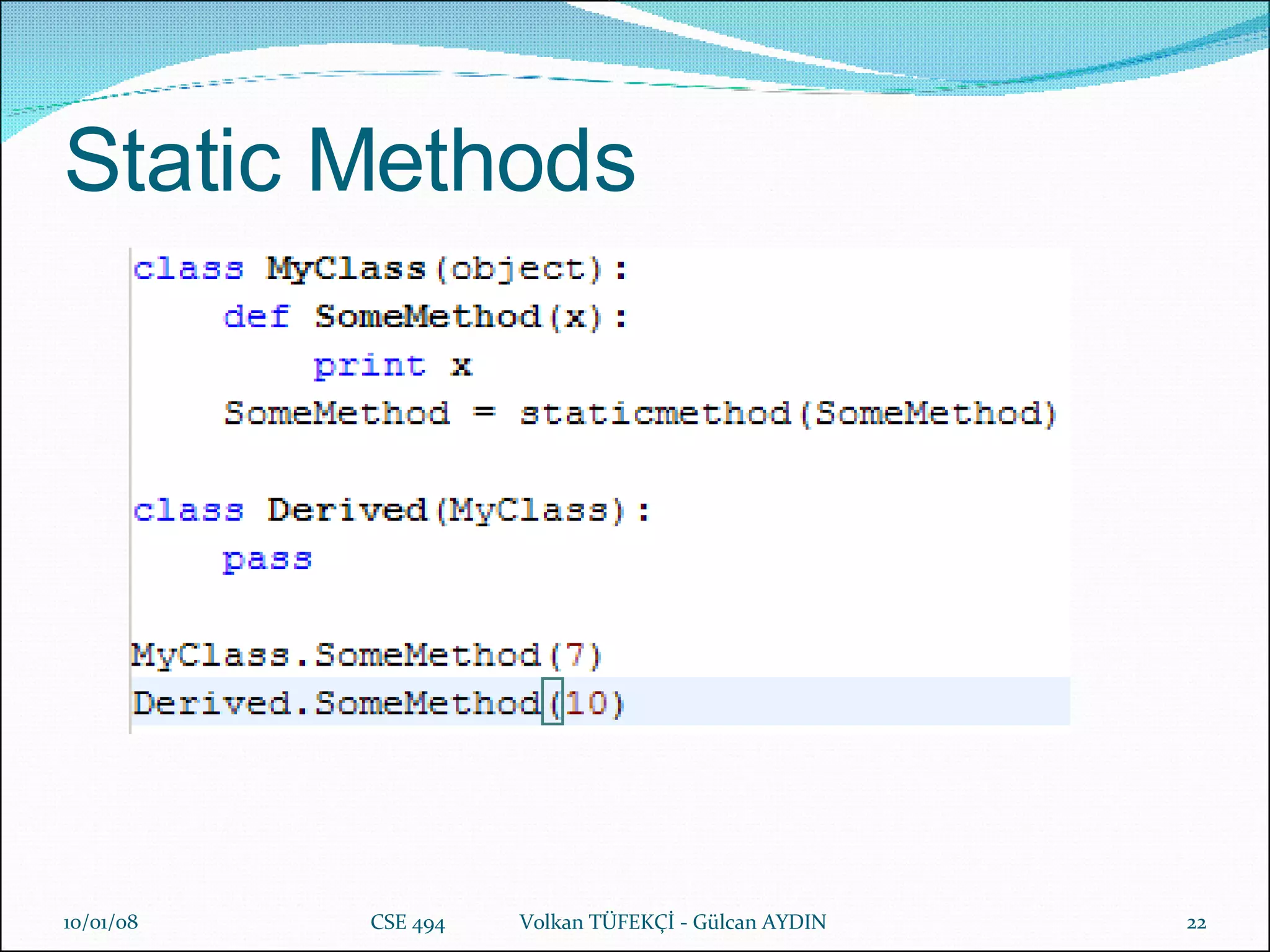
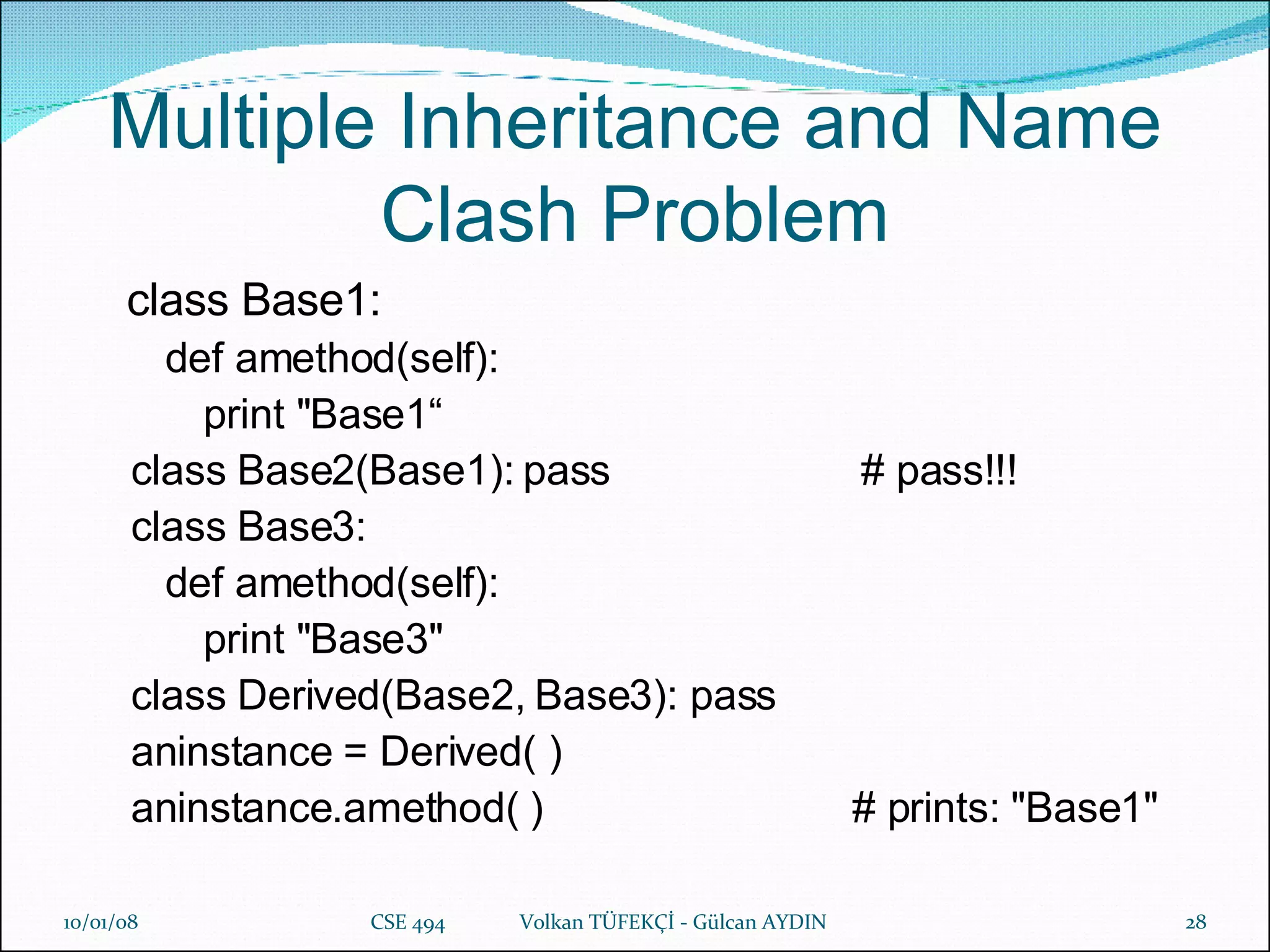
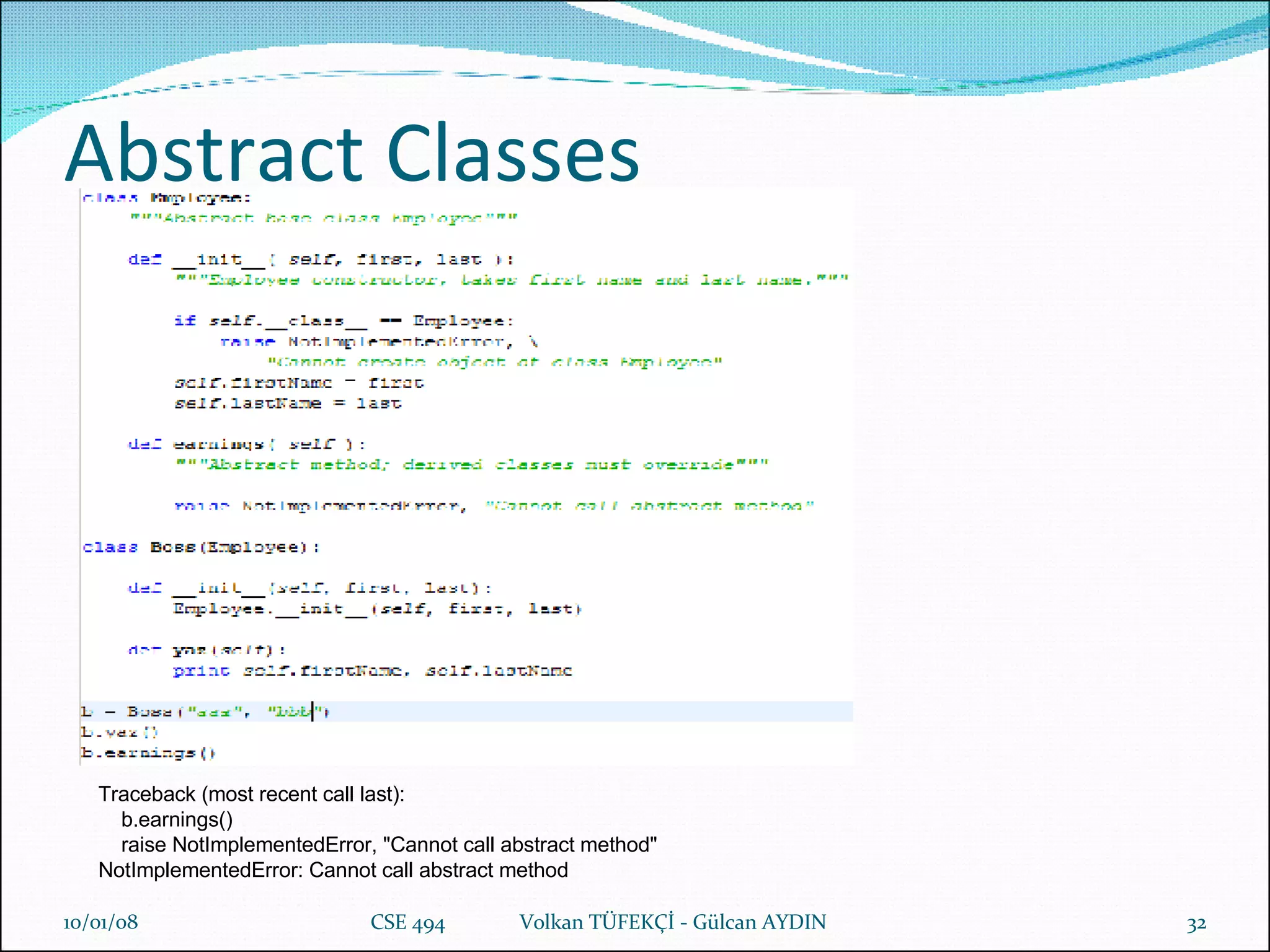
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Python's history, philosophy, and usage, illustrating its strengths as an object-oriented, multi-paradigm programming language. It discusses key features such as syntax, data structures like lists and dictionaries, object-oriented concepts including inheritance and encapsulation, and practical applications used by companies like NASA and Google. Additionally, it touches on advanced programming topics like polymorphism, composition versus inheritance, and the importance of data abstraction.





![Syntax All values in Python can be used as logic values. Some of the more “empty” ones, like [], 0, “” and None represent logical falsity, while most other values (like [0], 1 or “Hello, world”) represent logical truth. if 0 < month <= 12: doSomething() 29/05/09 CSE 494 Volkan TÜFEKÇİ - Gülcan AYDIN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-1199990631709236-5/75/Python-6-2048.jpg)
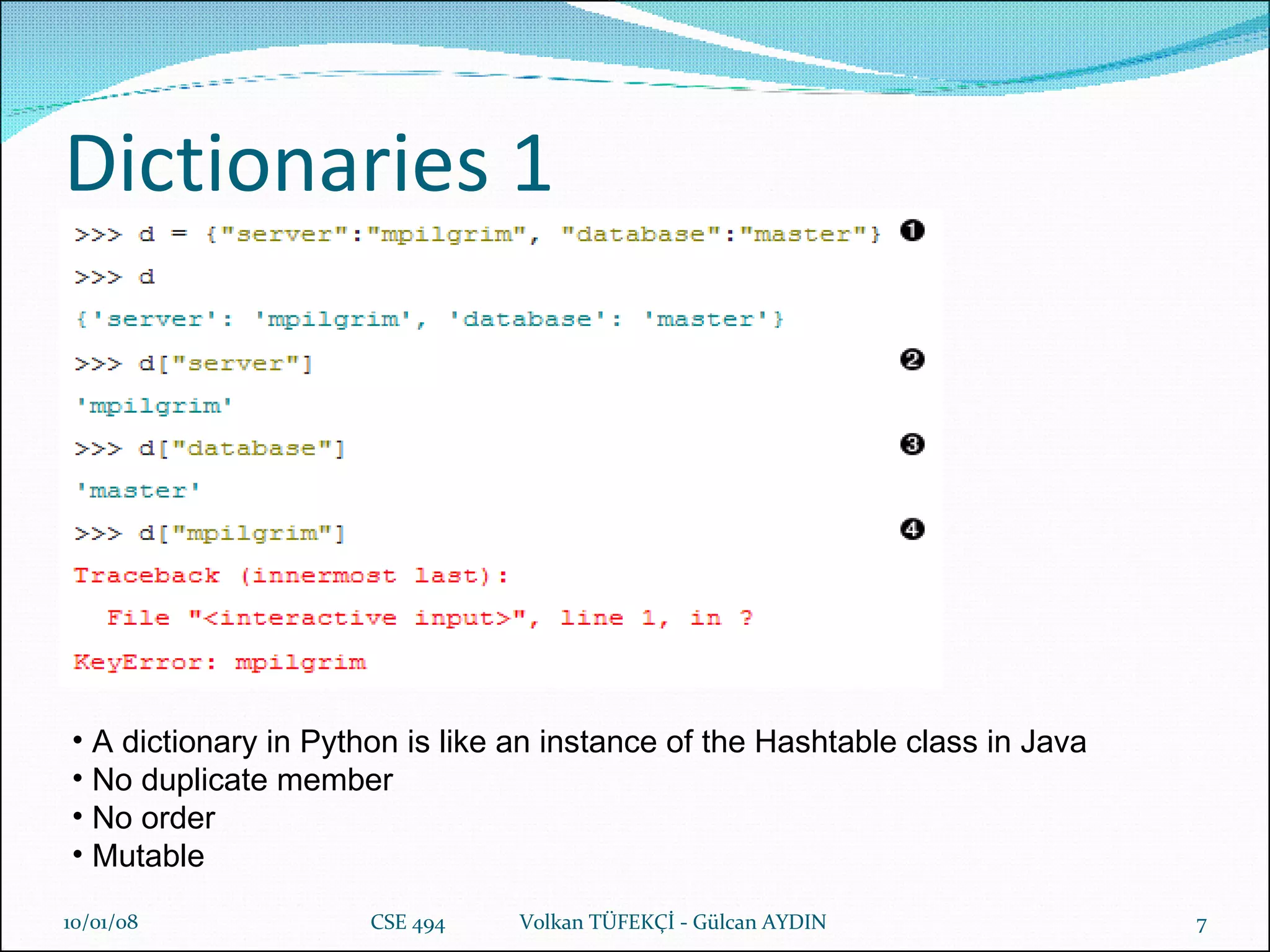




![List & Dictionary Examples L=[1,2,3,4,5] IMPORTANT : The value will be stored into a range of memory blocks, and what if we do this? L2=L It make L2 refers to the same memory blocks where L points to. Example; 29/05/09 CSE 494 Volkan TÜFEKÇİ - Gülcan AYDIN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-1199990631709236-5/75/Python-12-2048.jpg)