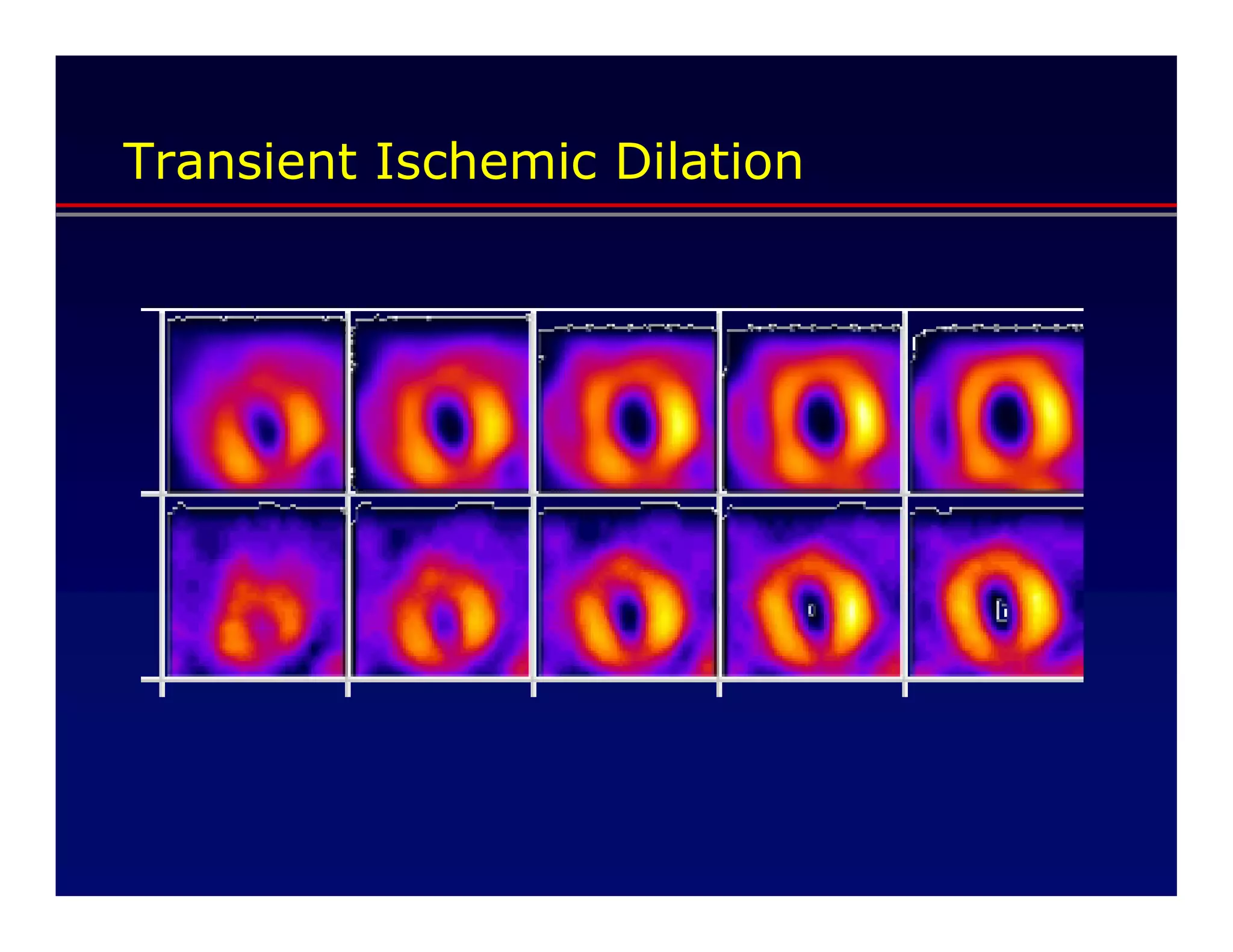
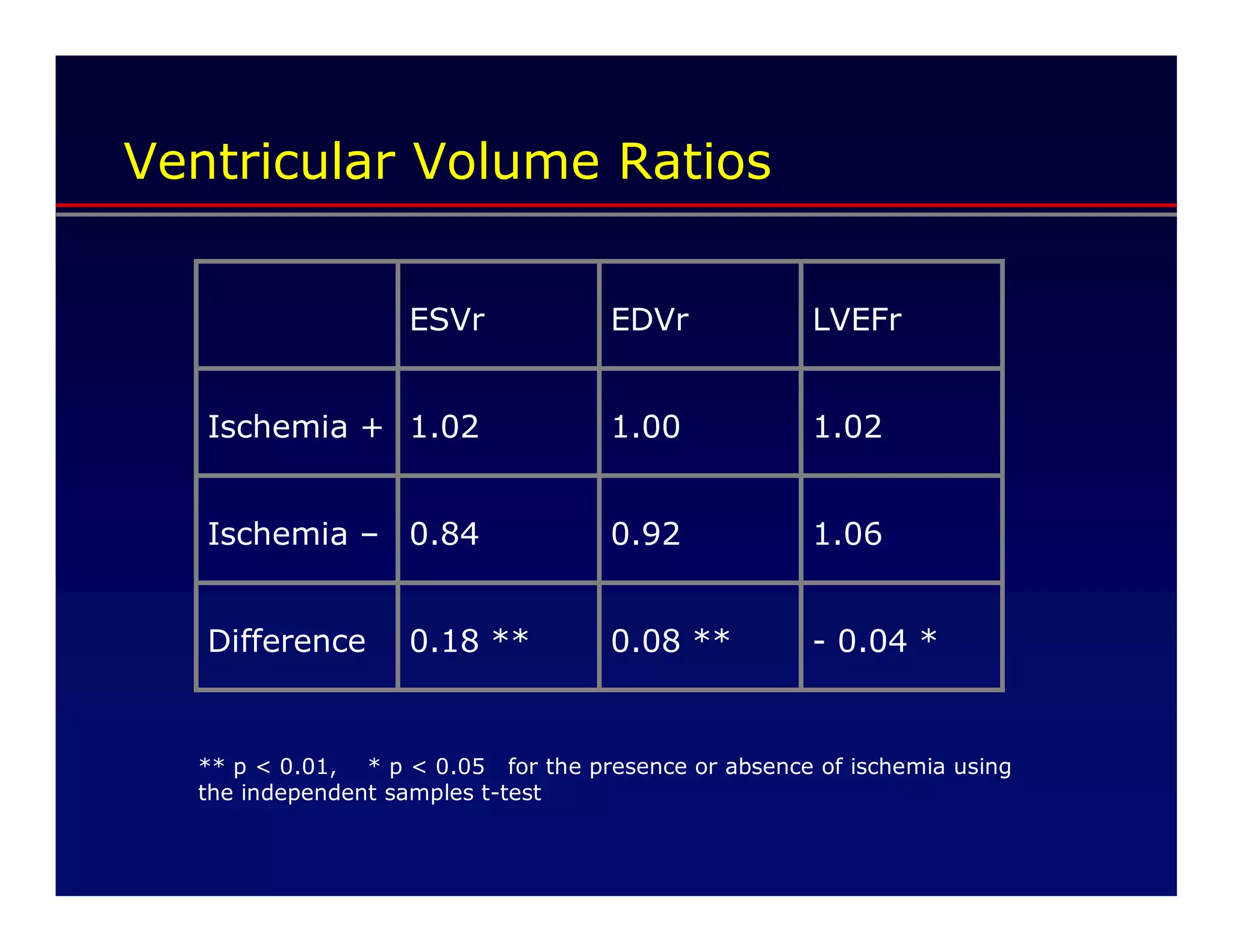
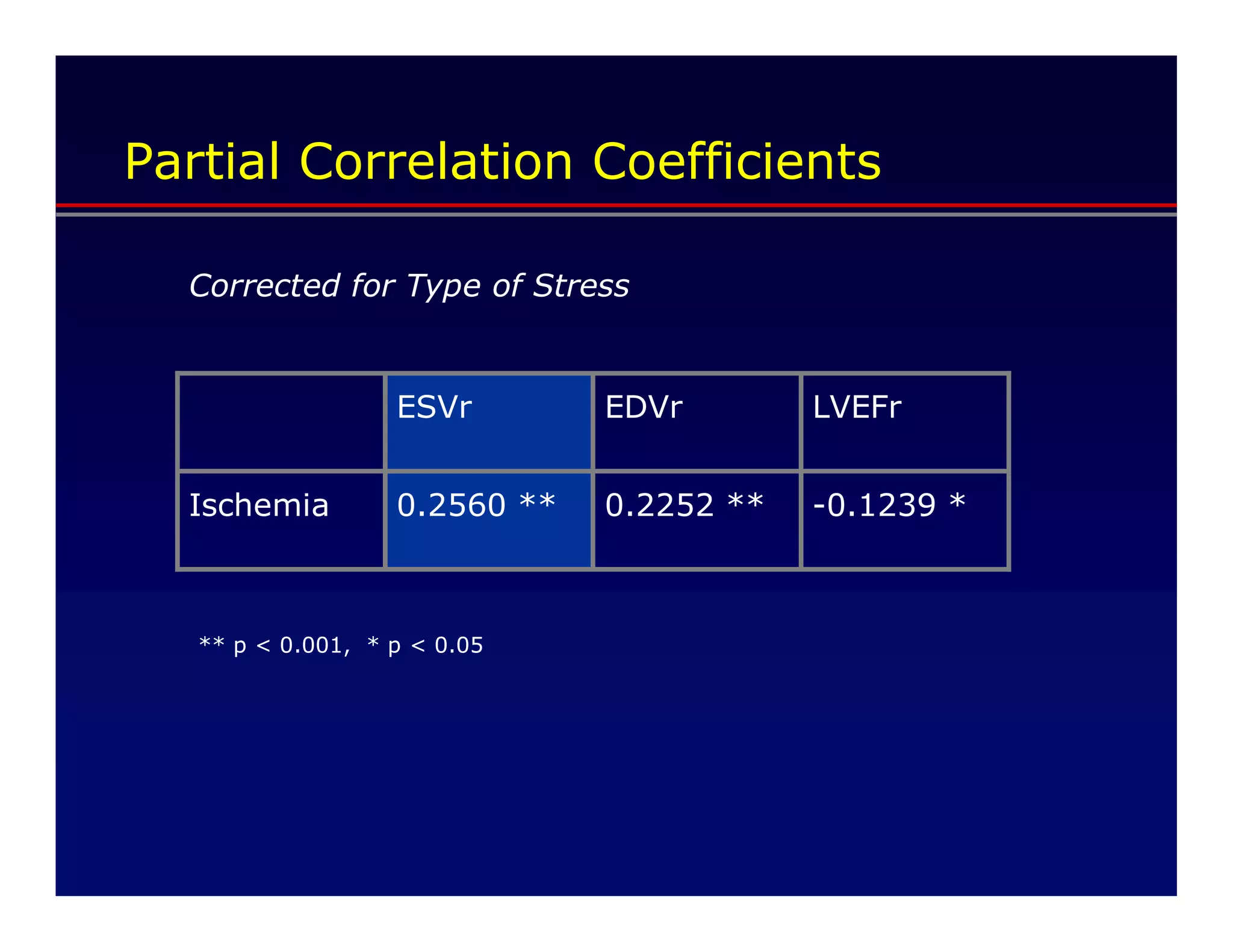
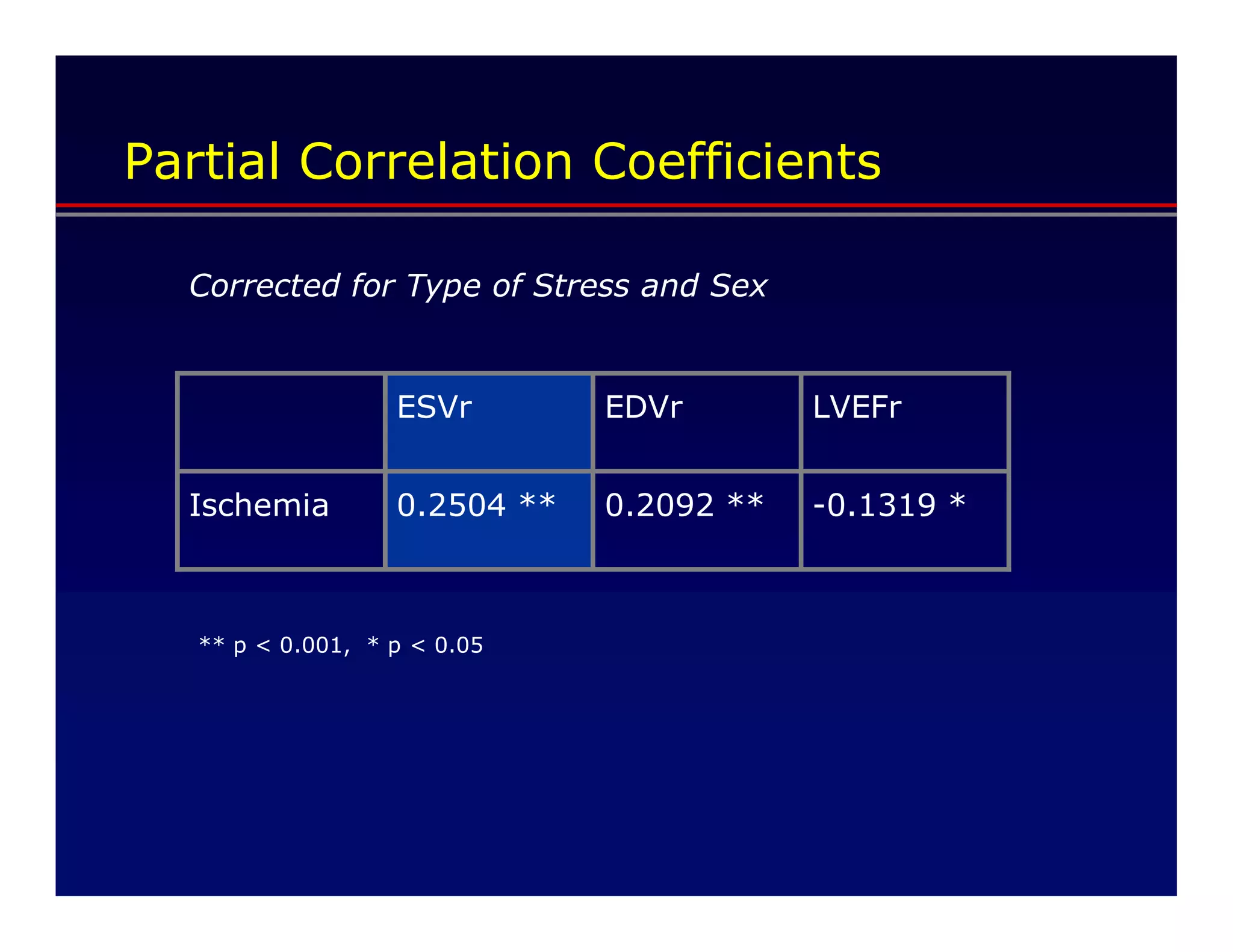
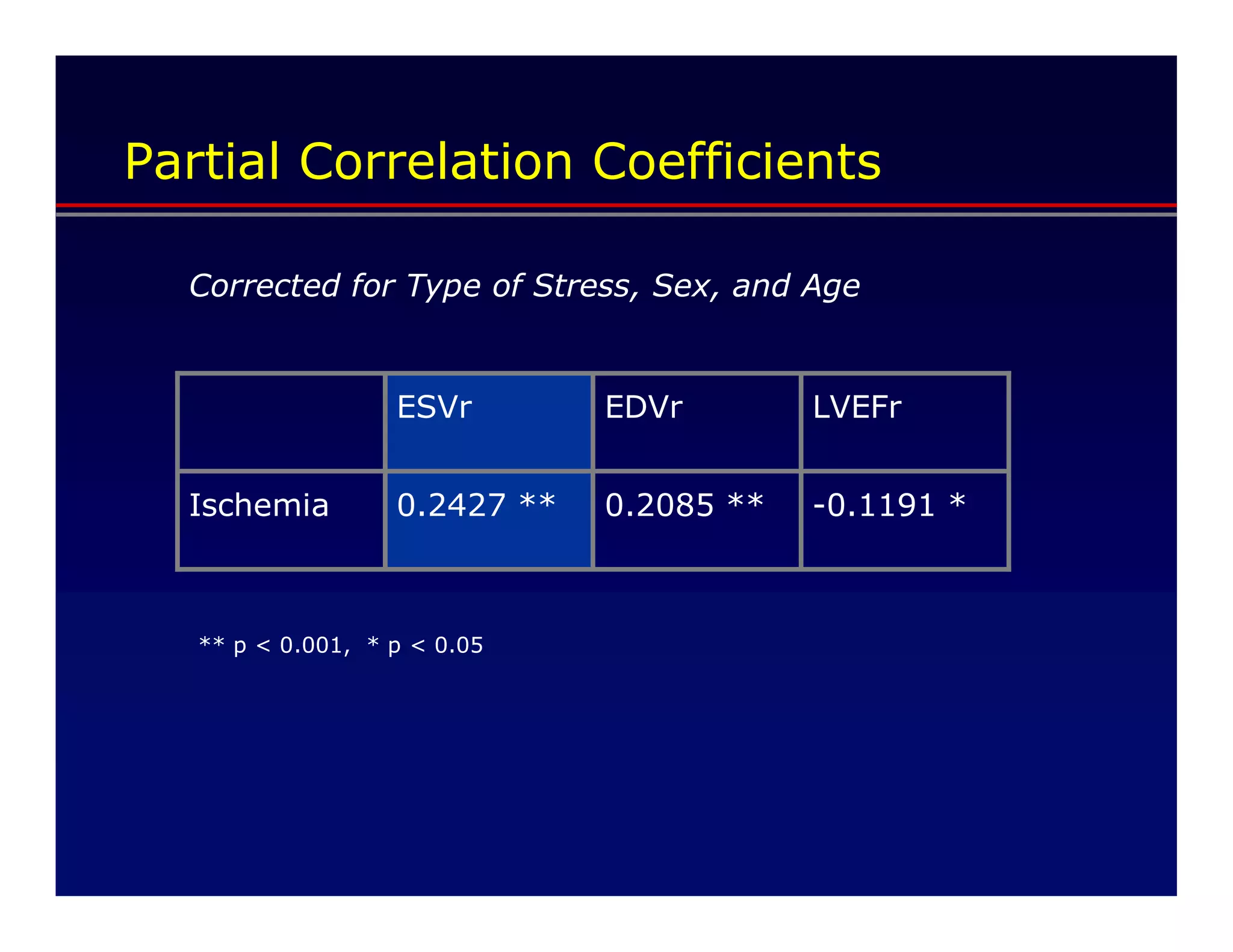
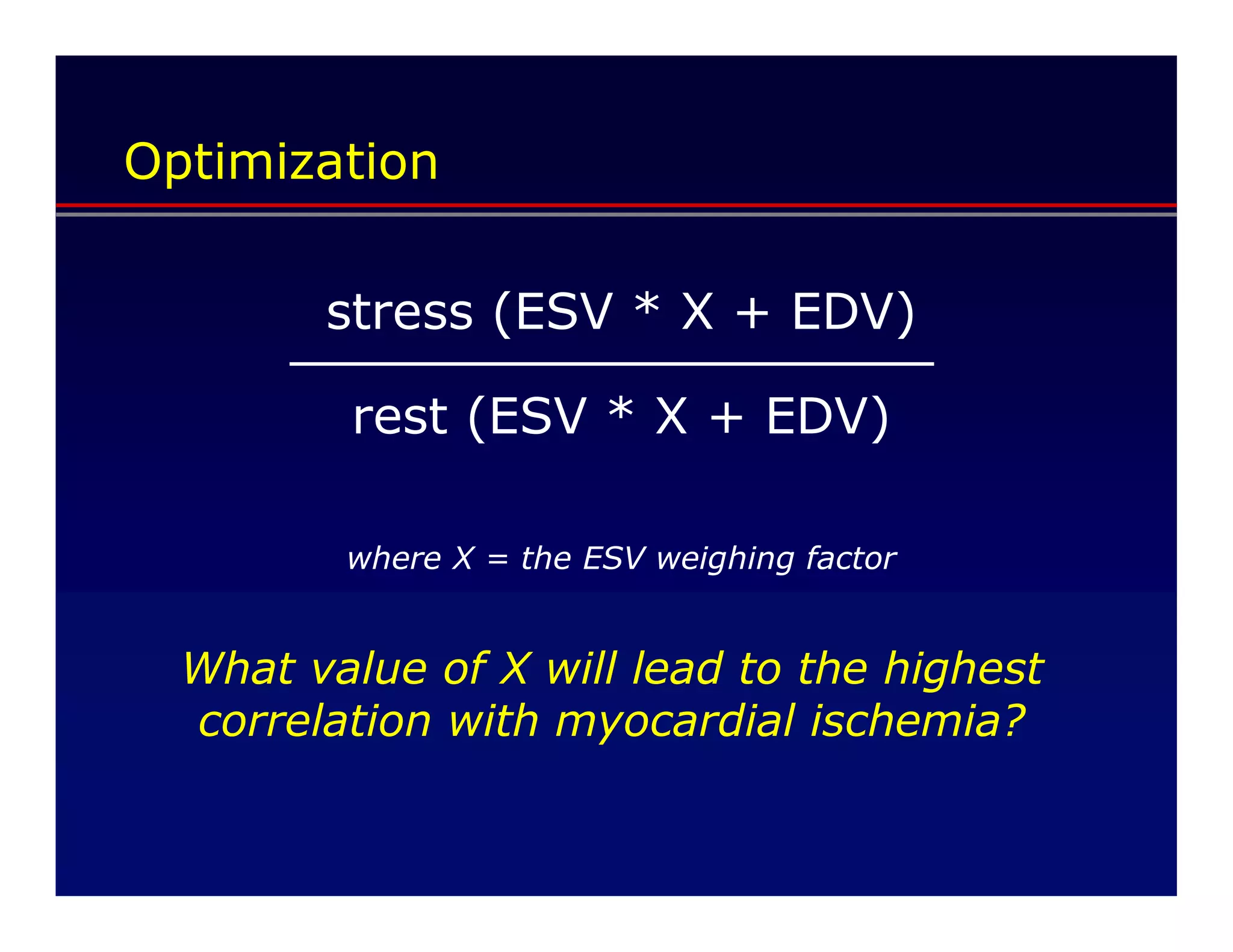
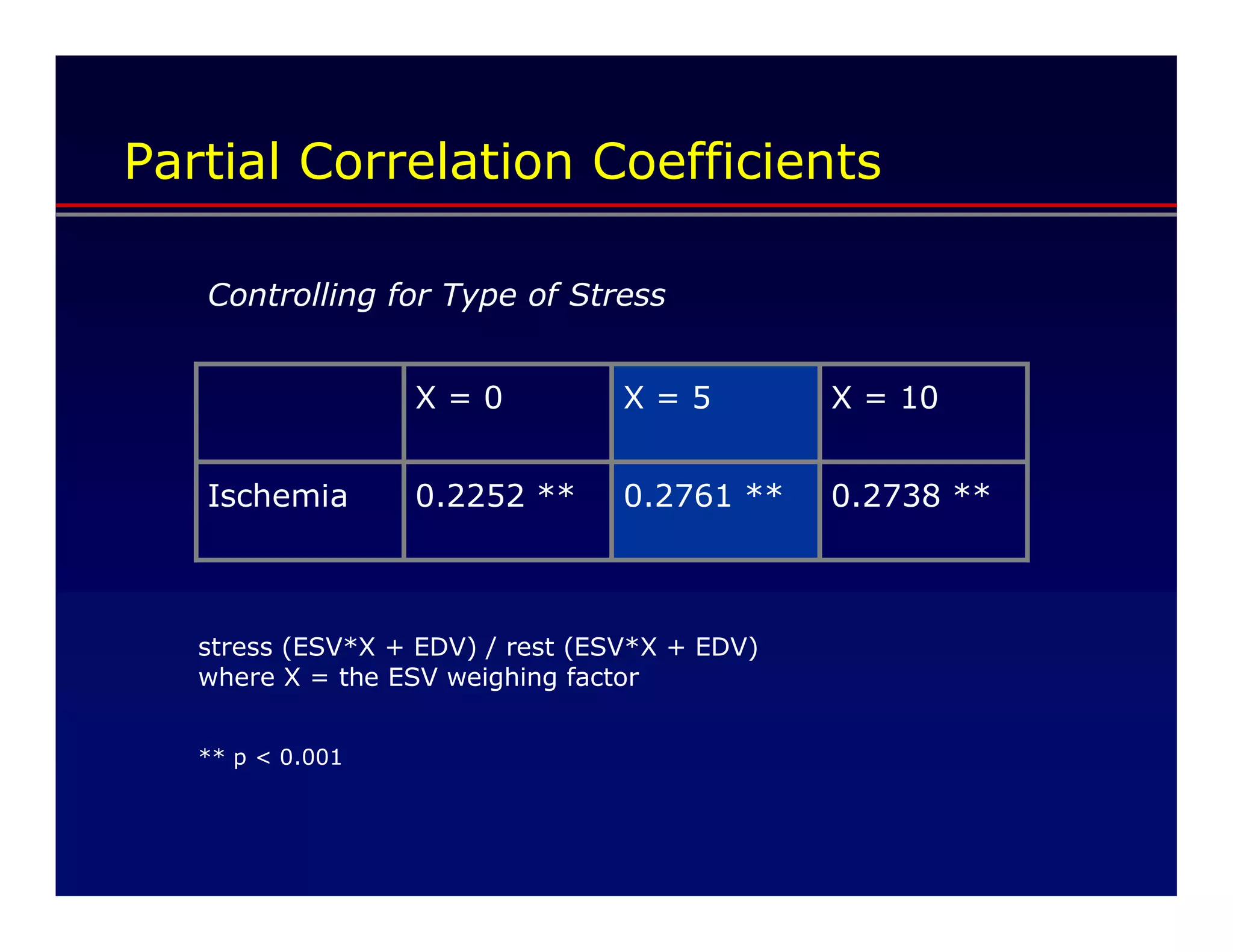
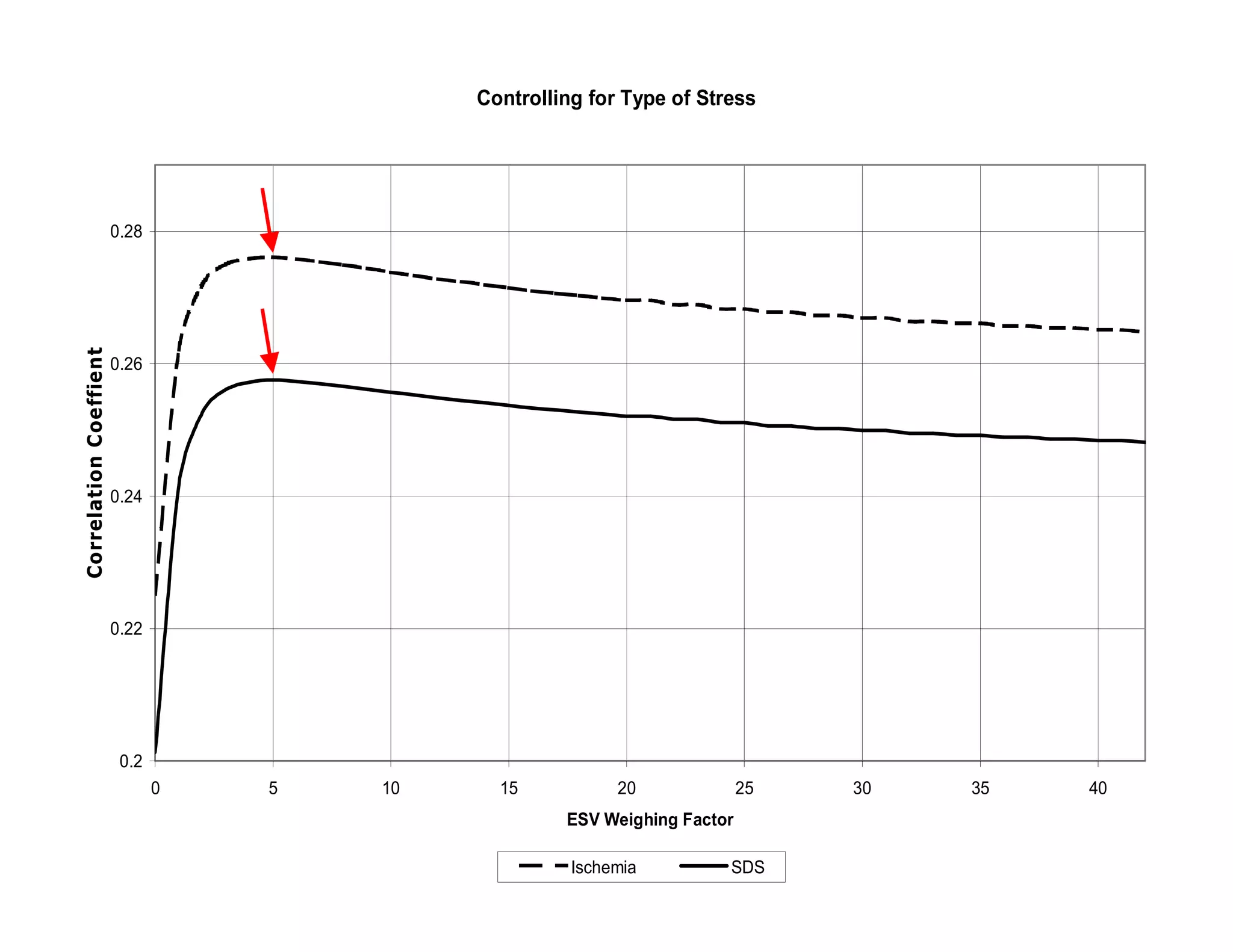
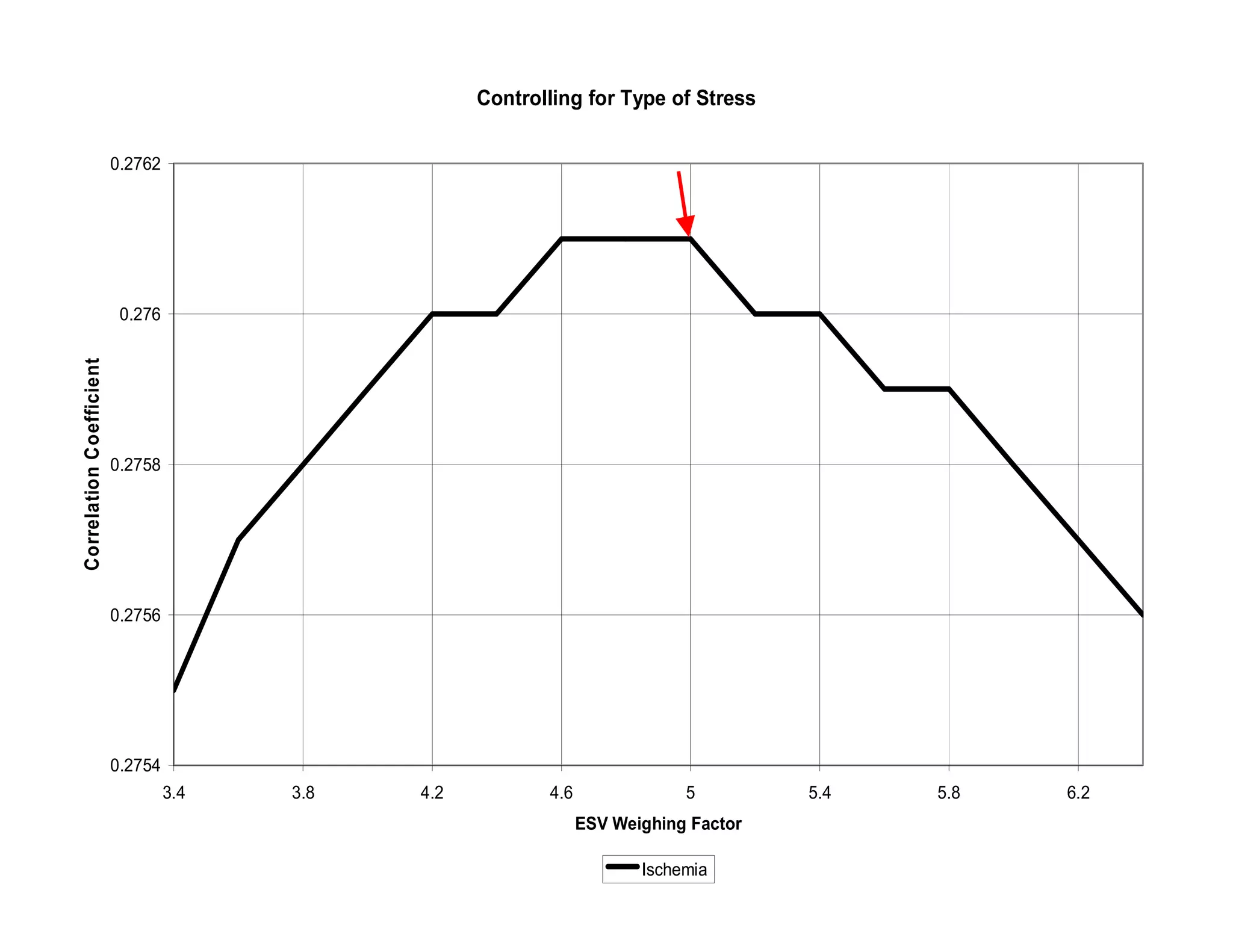
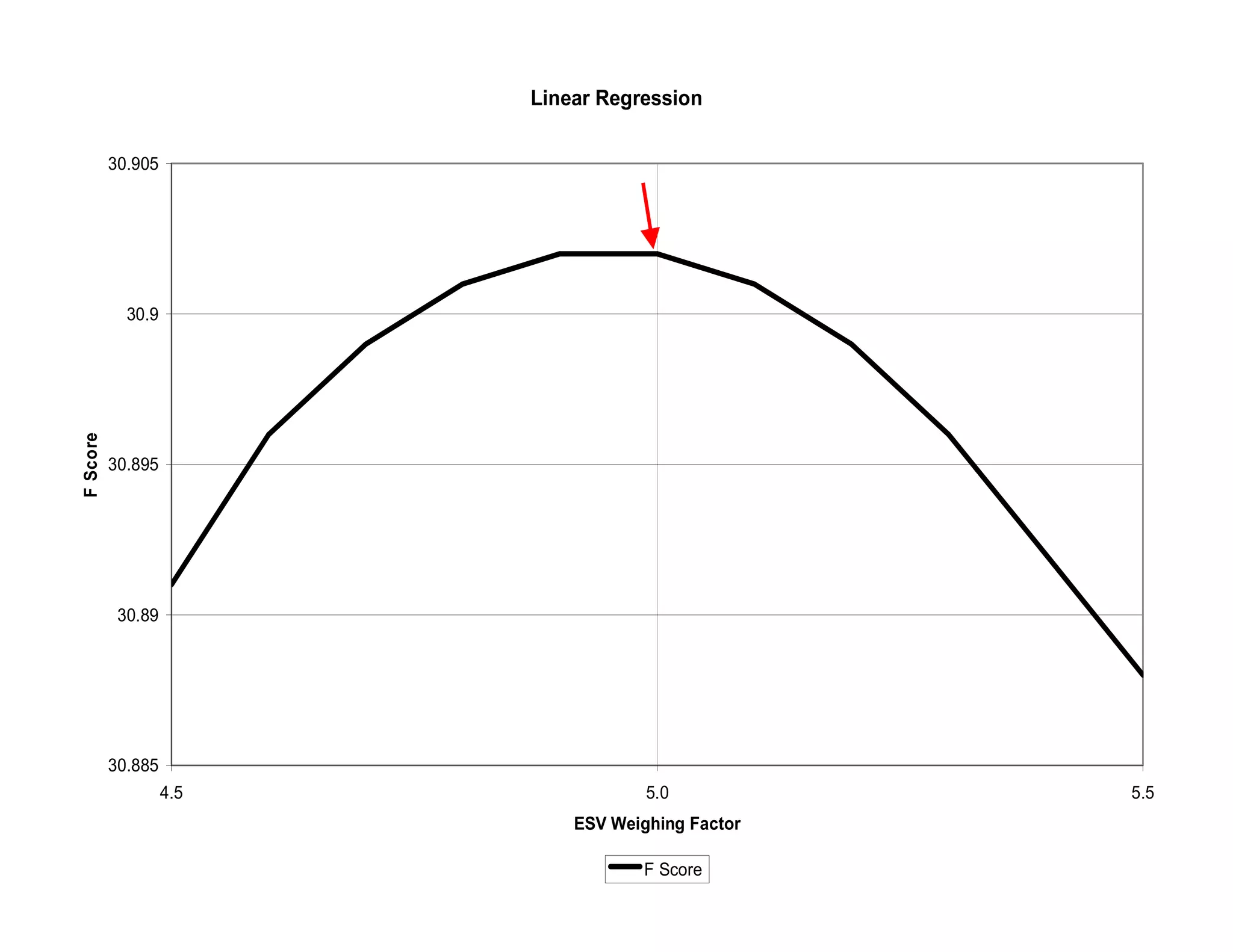
This document defines transient ischemic dilation (TID), which is the ratio of left ventricular size at stress compared to rest. The study found that the end-systolic volume ratio (ESVr) correlated most strongly with myocardial ischemia. Optimization analysis determined that a formula weighting the end-systolic volume by a factor of 5 provided the highest correlation between TID and ischemia. Therefore, the "complex average" that TID represents can be best described as stress (ESV x 5 + EDV) / rest (ESV x 5 + EDV).