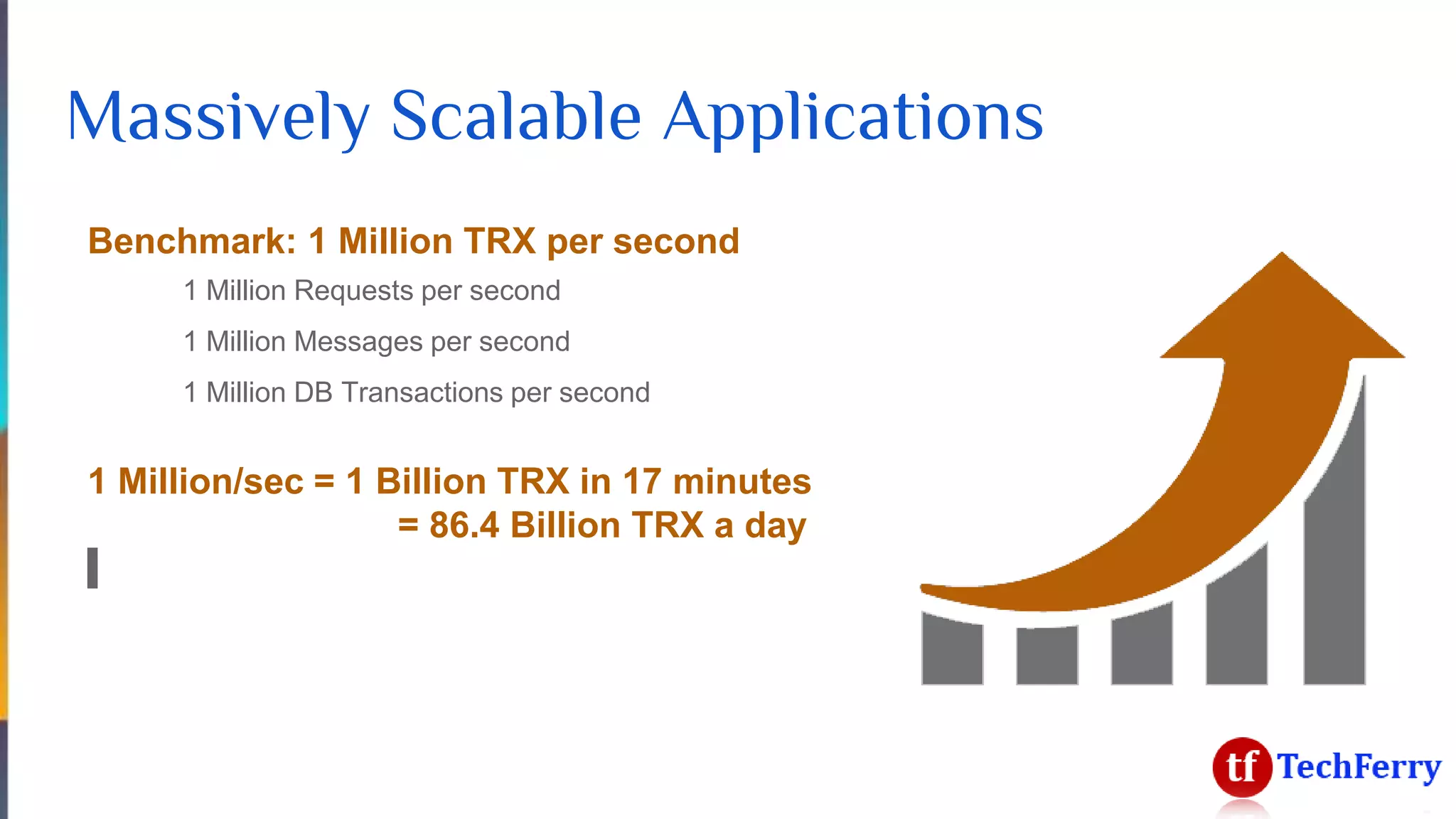
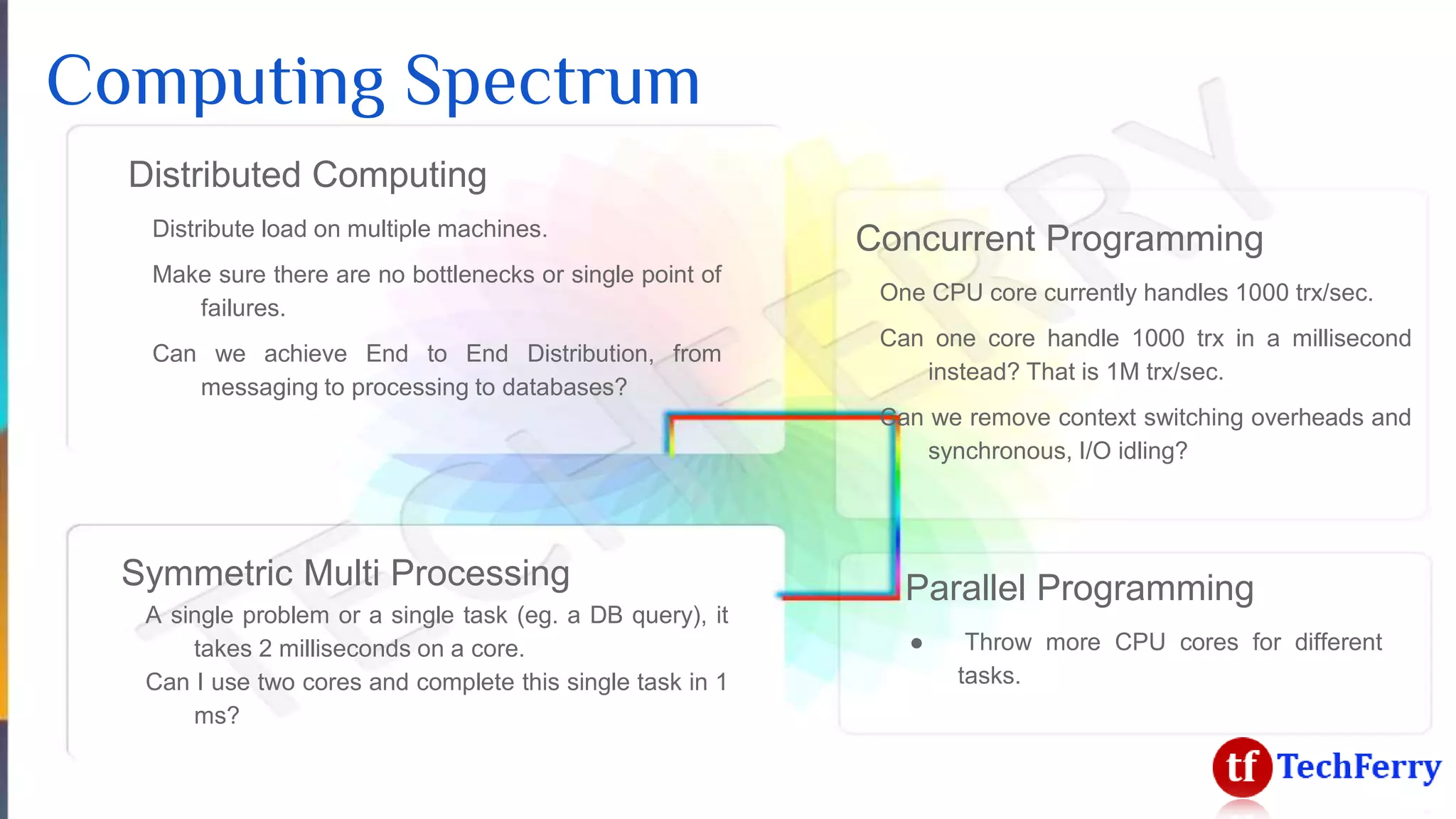
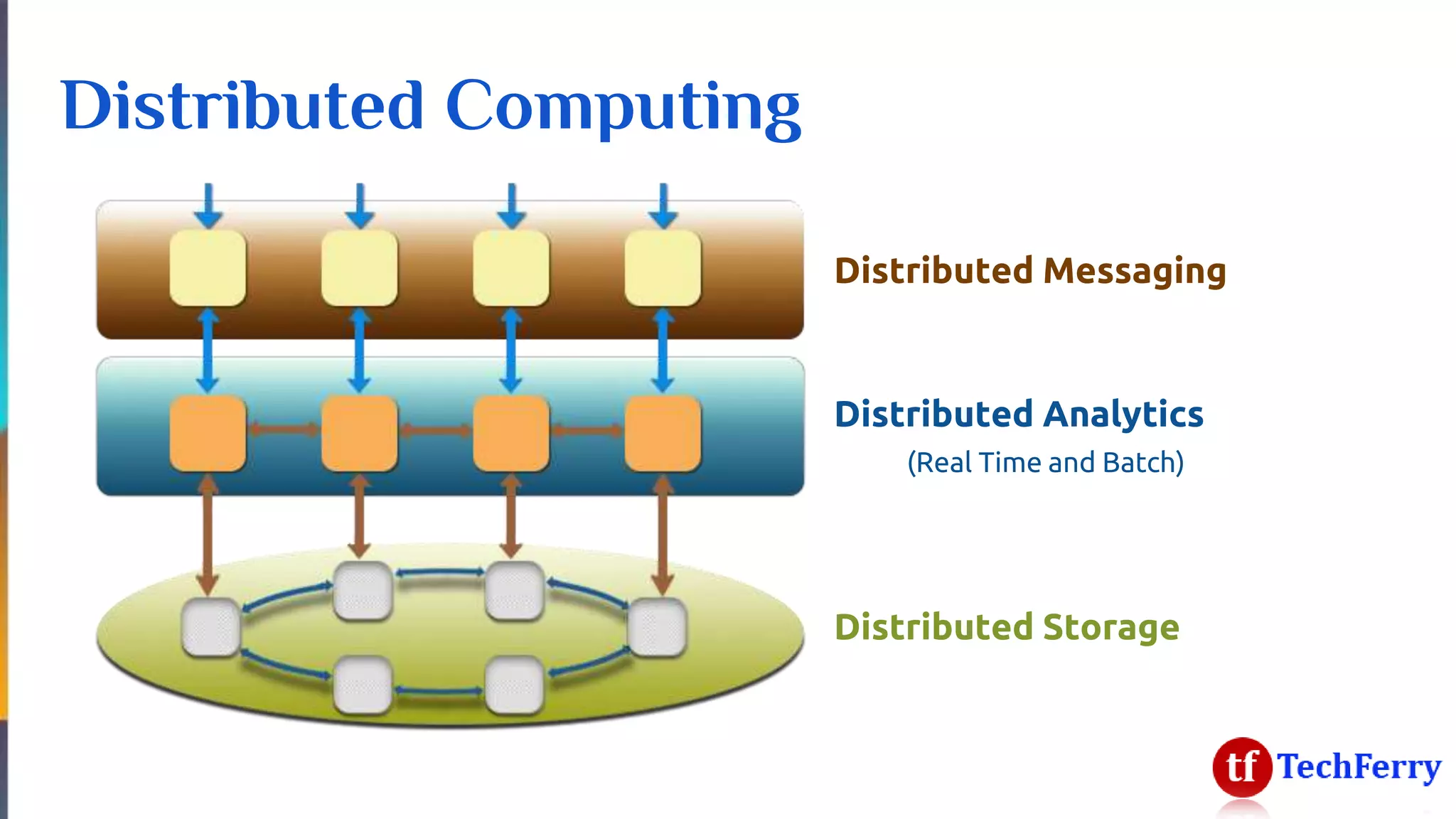
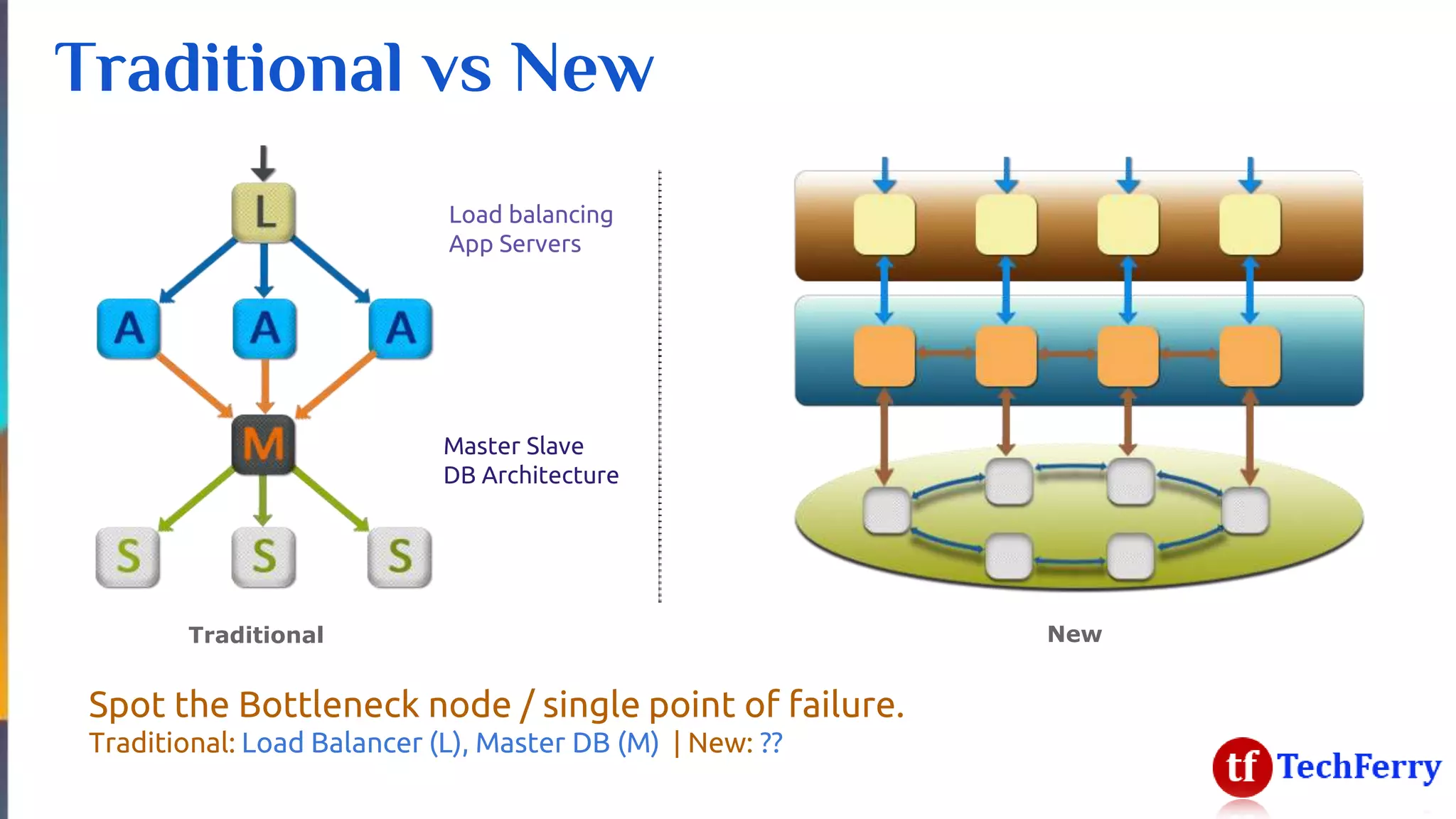
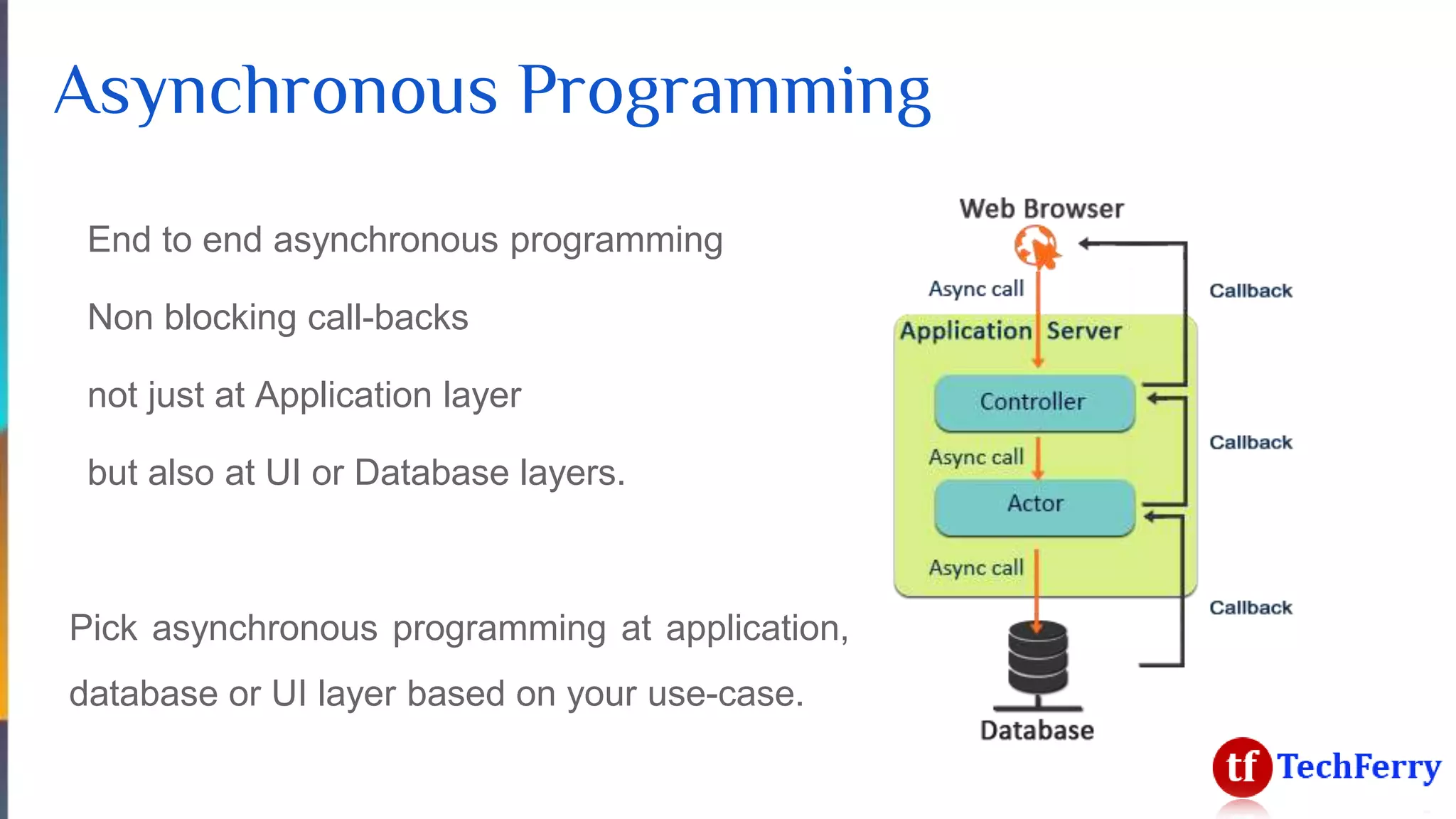
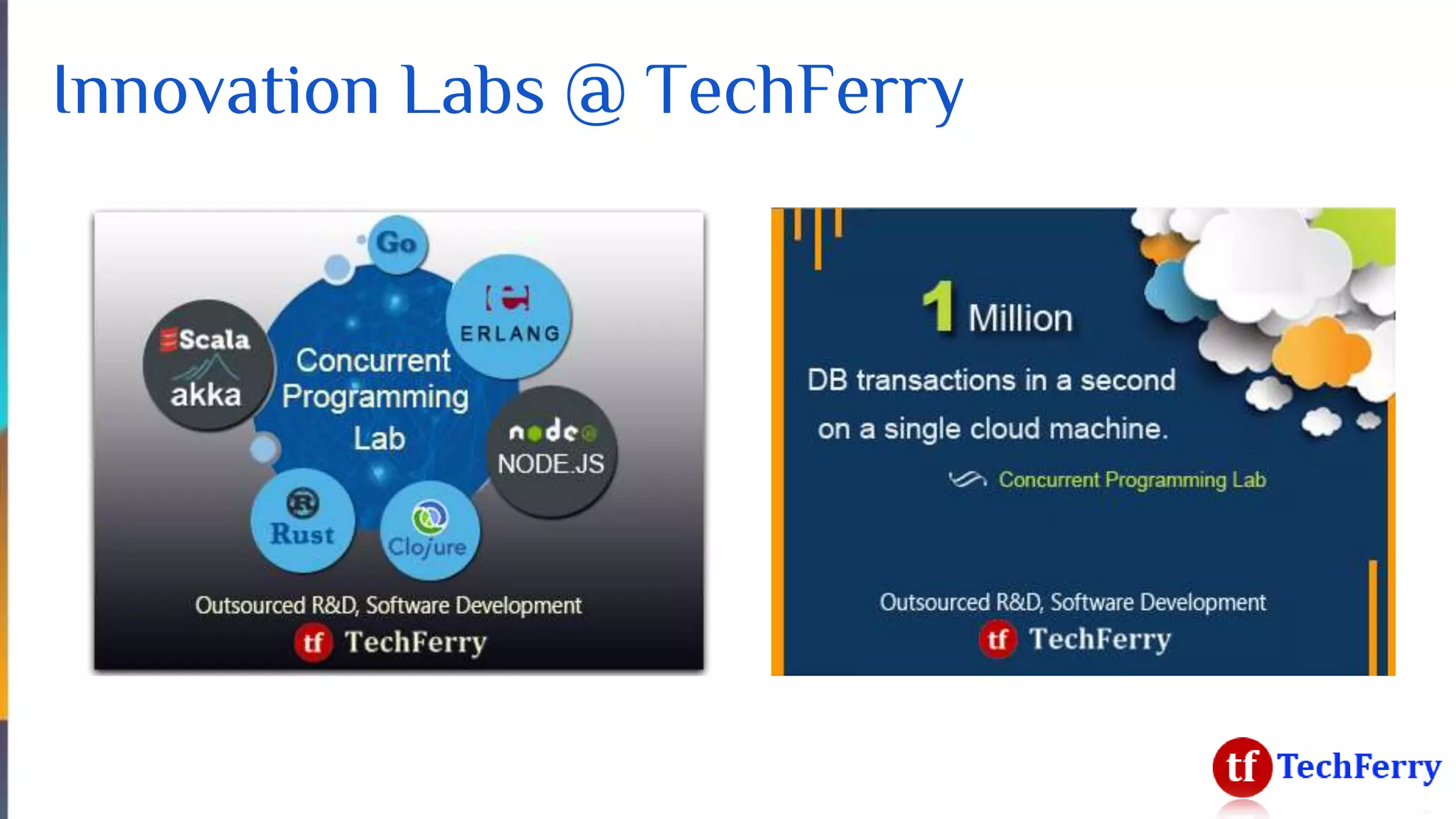
The document discusses massively scalable applications and the architecture needed to achieve high performance, such as processing millions of transactions per second. It outlines various strategies for scaling, including distributed computing, concurrent programming, and asynchronous programming, highlighting tools like Apache Kafka and Spark. Additionally, it touches on the advantages of using symmetric multi-processing and functional programming paradigms for efficiency in real-time analytics.