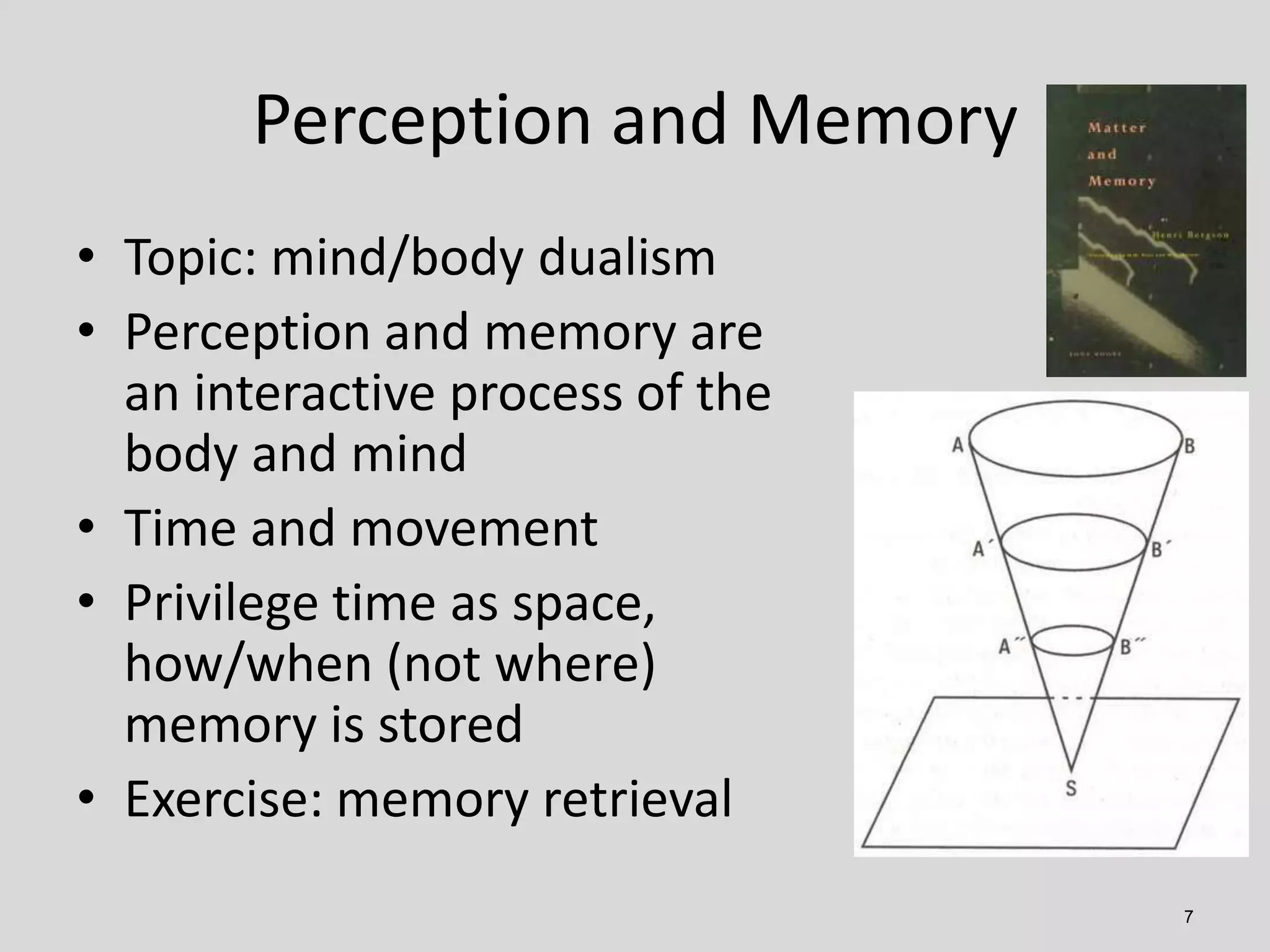
This document presents an exploration of the ethics surrounding cognitive nanorobots and their potential impact on human cognition, including issues of biocompatibility, security, and ethical implications. It discusses various models of ethics, integrating perspectives from historical philosophers and contemporary ethical considerations in the context of technology and cognition. The document also highlights potential applications and transformations in ethical paradigms that cognitive nanorobots may bring about.