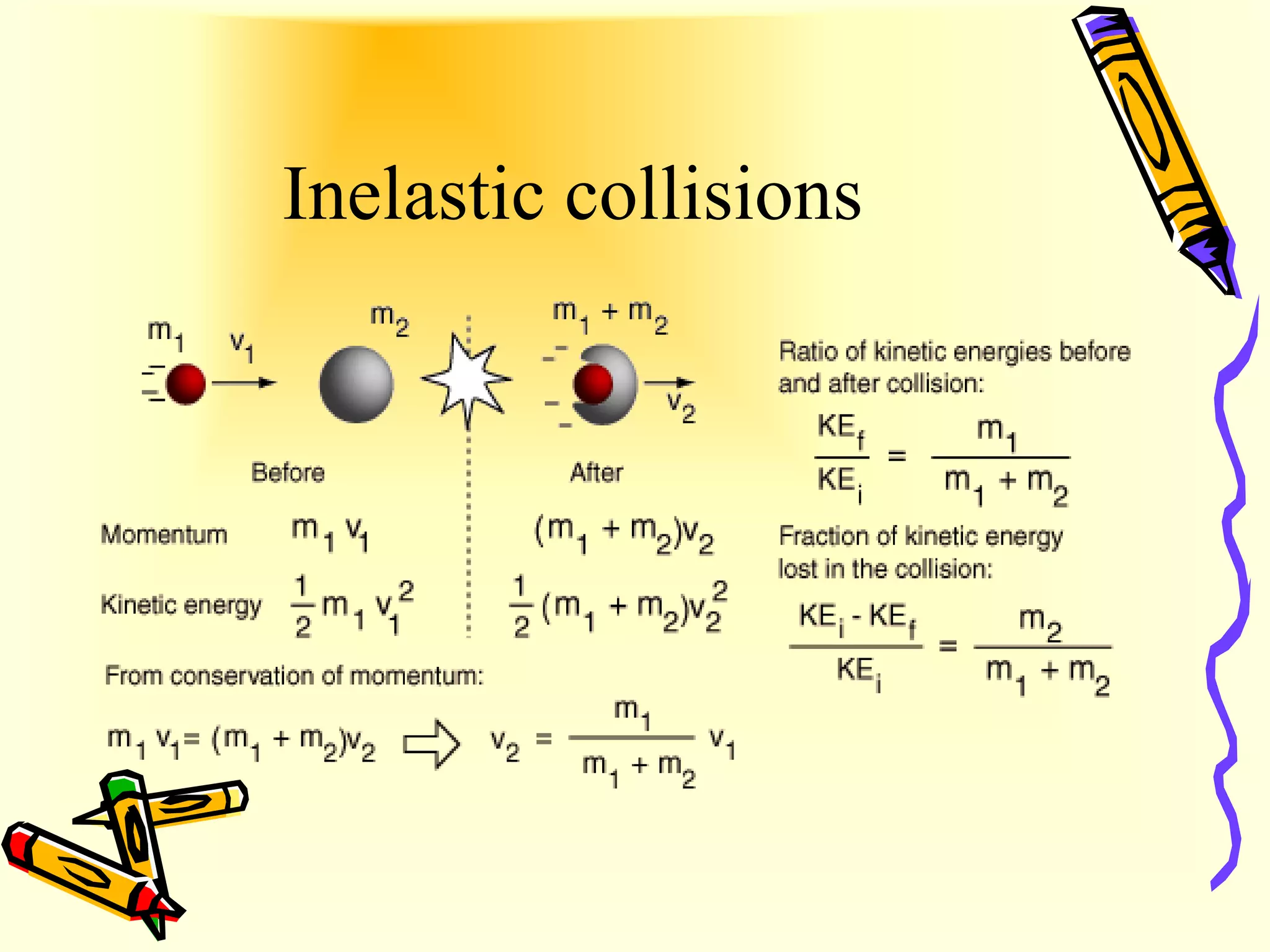
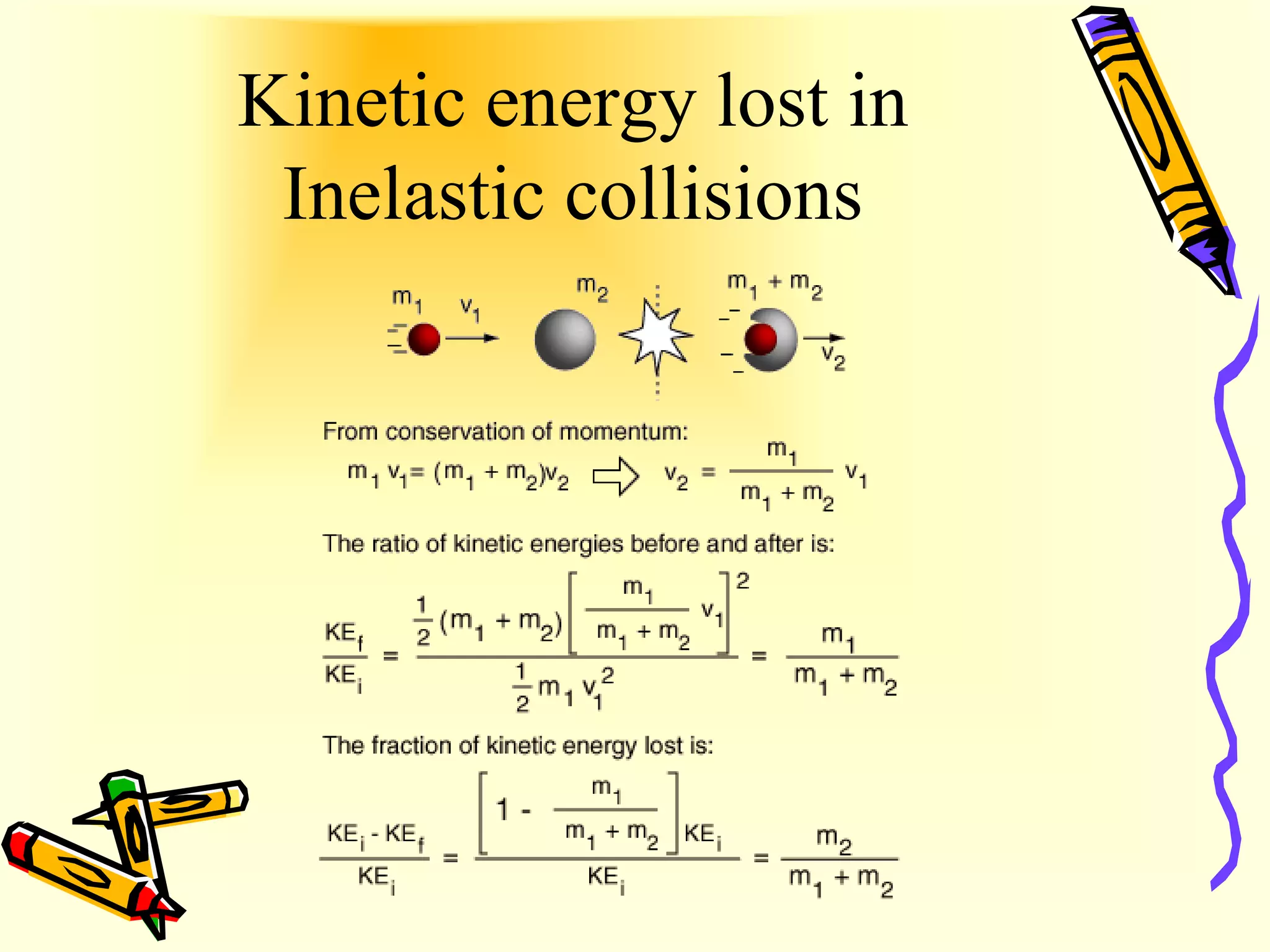
Ideal gas behavior can be explained by the kinetic energy and collisions of gas particles. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion, with some particles having more and some having less than the average kinetic energy at a given temperature. Elastic collisions between gas particles are perfectly frictionless, conserving kinetic energy, which explains why gas pressure does not decrease over time. Inelastic collisions involve kinetic energy being lost as heat through friction.