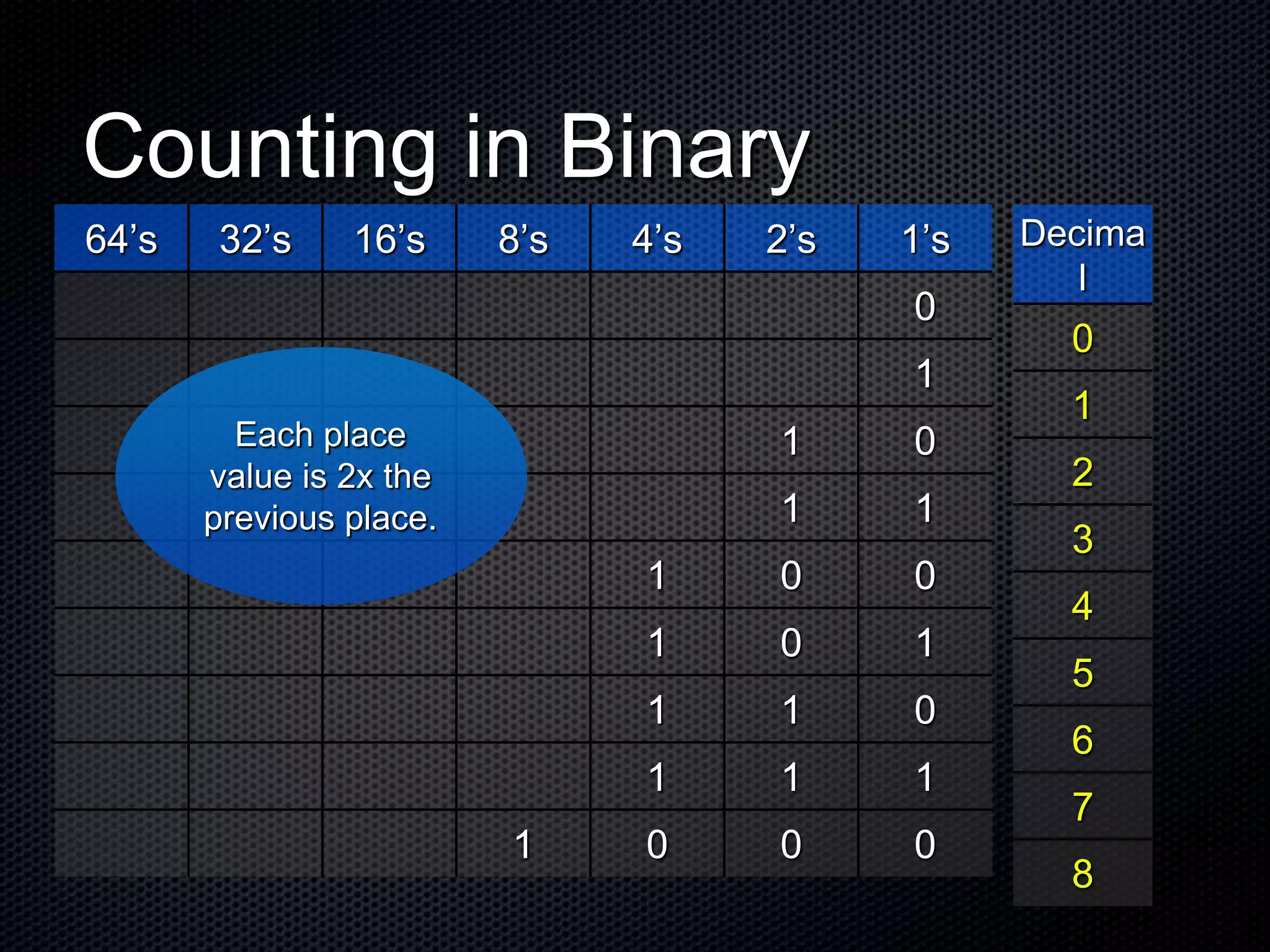
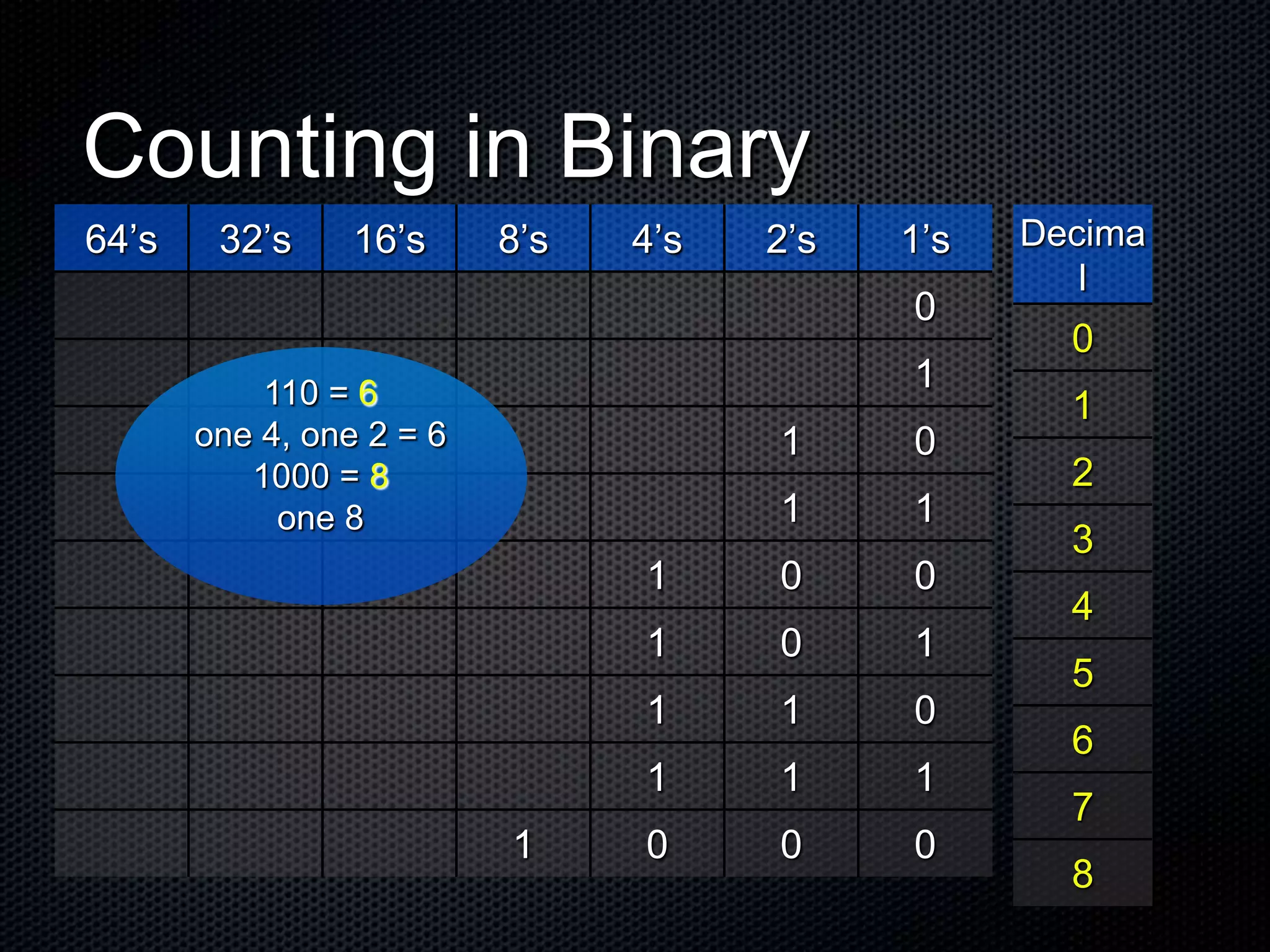
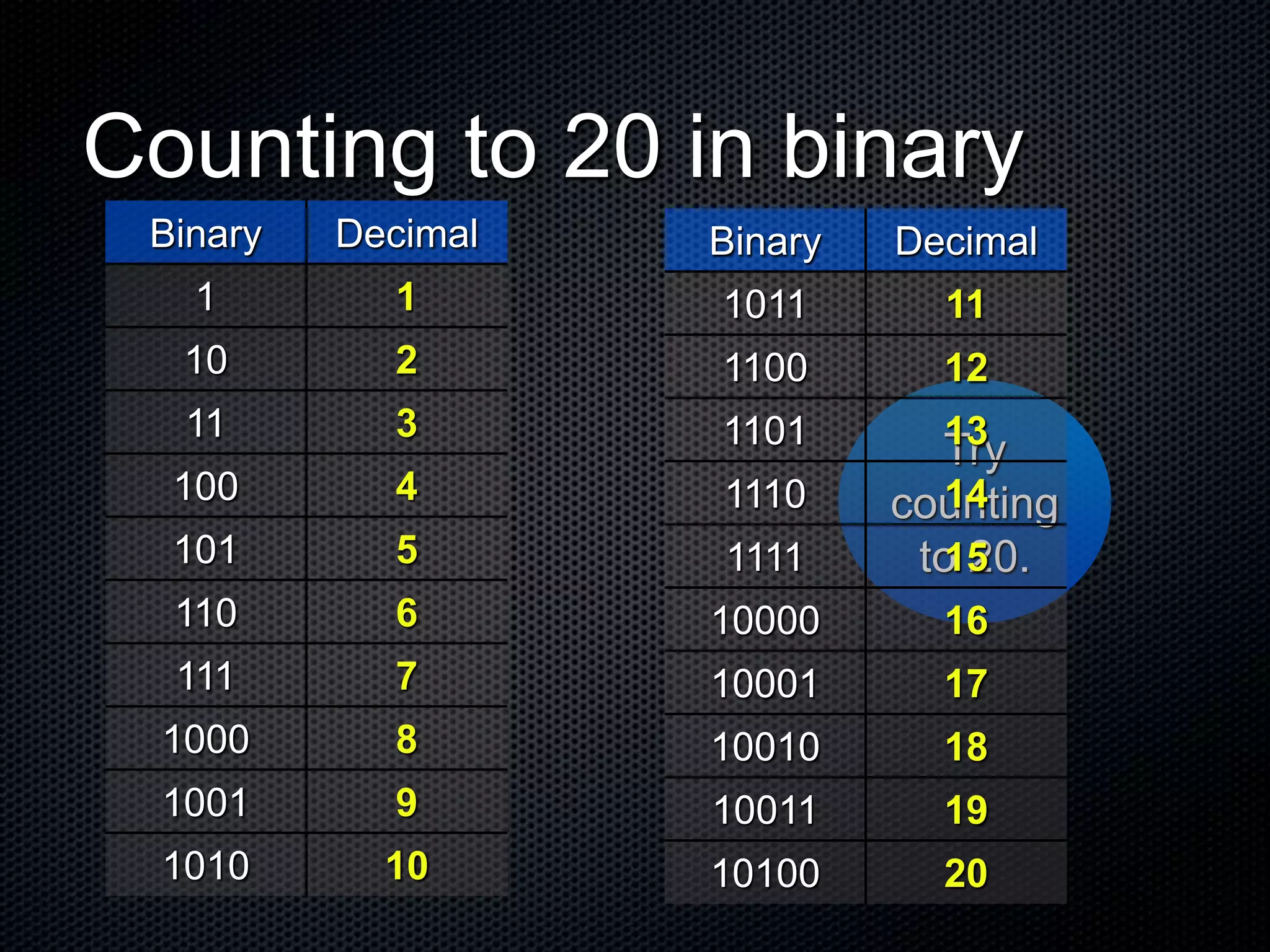
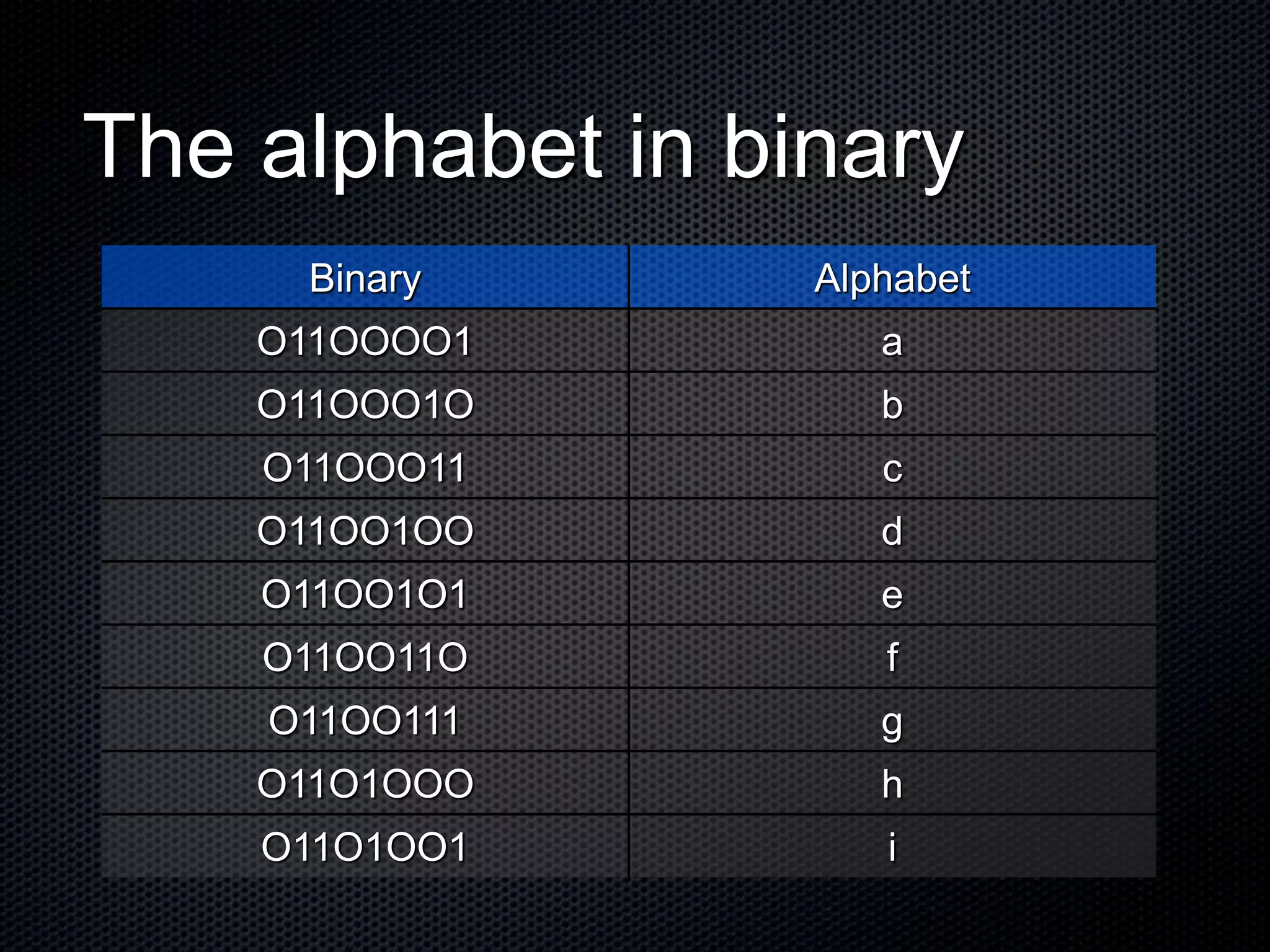
The document explains the concepts of binary code and its fundamental role in computer processing, highlighting the difference between the binary system (base 2) and the decimal system (base 10). It details how data is represented in binary using bits, which are the smallest units, and describes the structure of counting in both systems. Additionally, it includes examples and resources for further understanding of binary code and its applications in programming.