http://en.oreilly.com/mysql2011/public/schedule/detail/17301
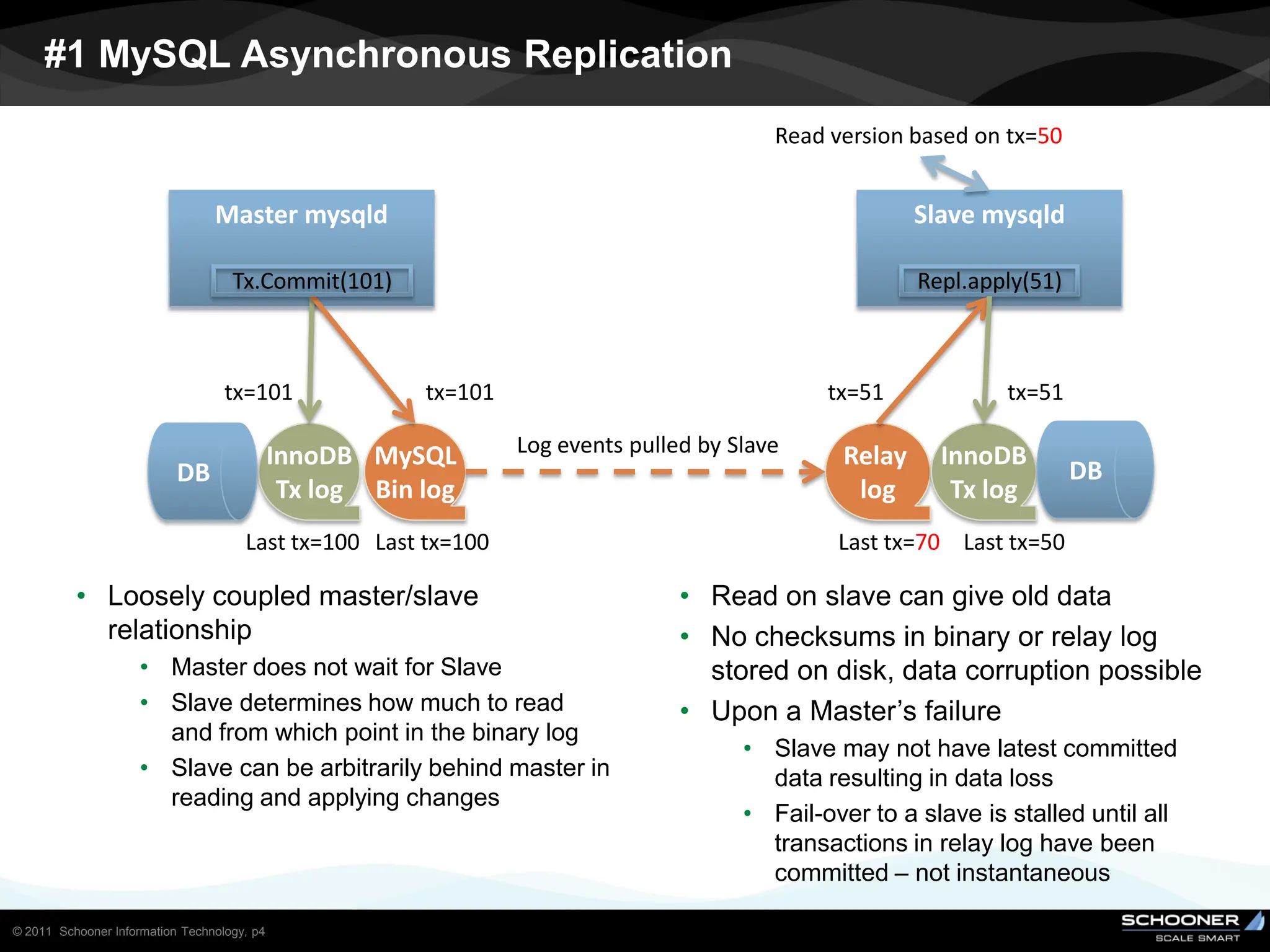
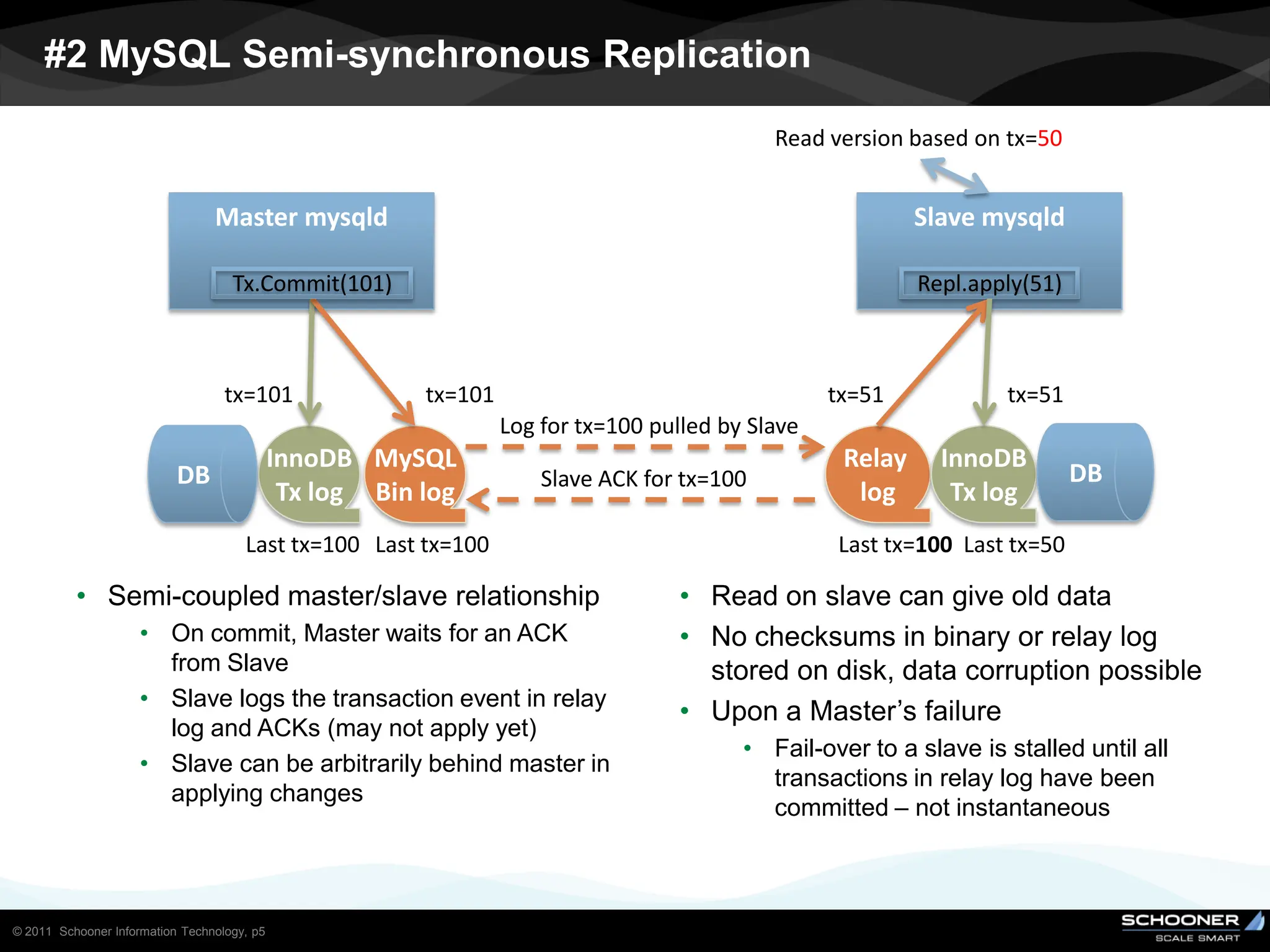
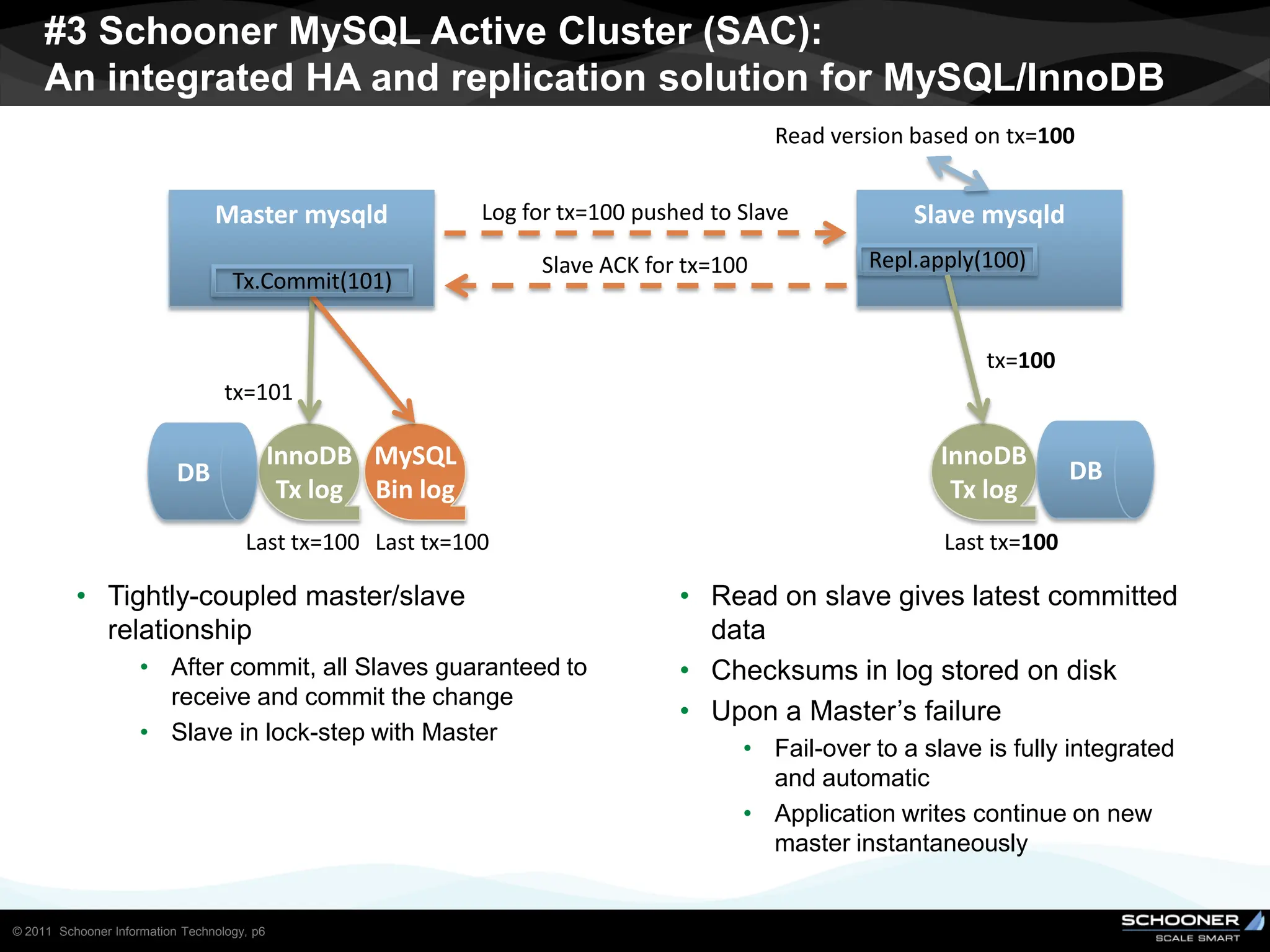
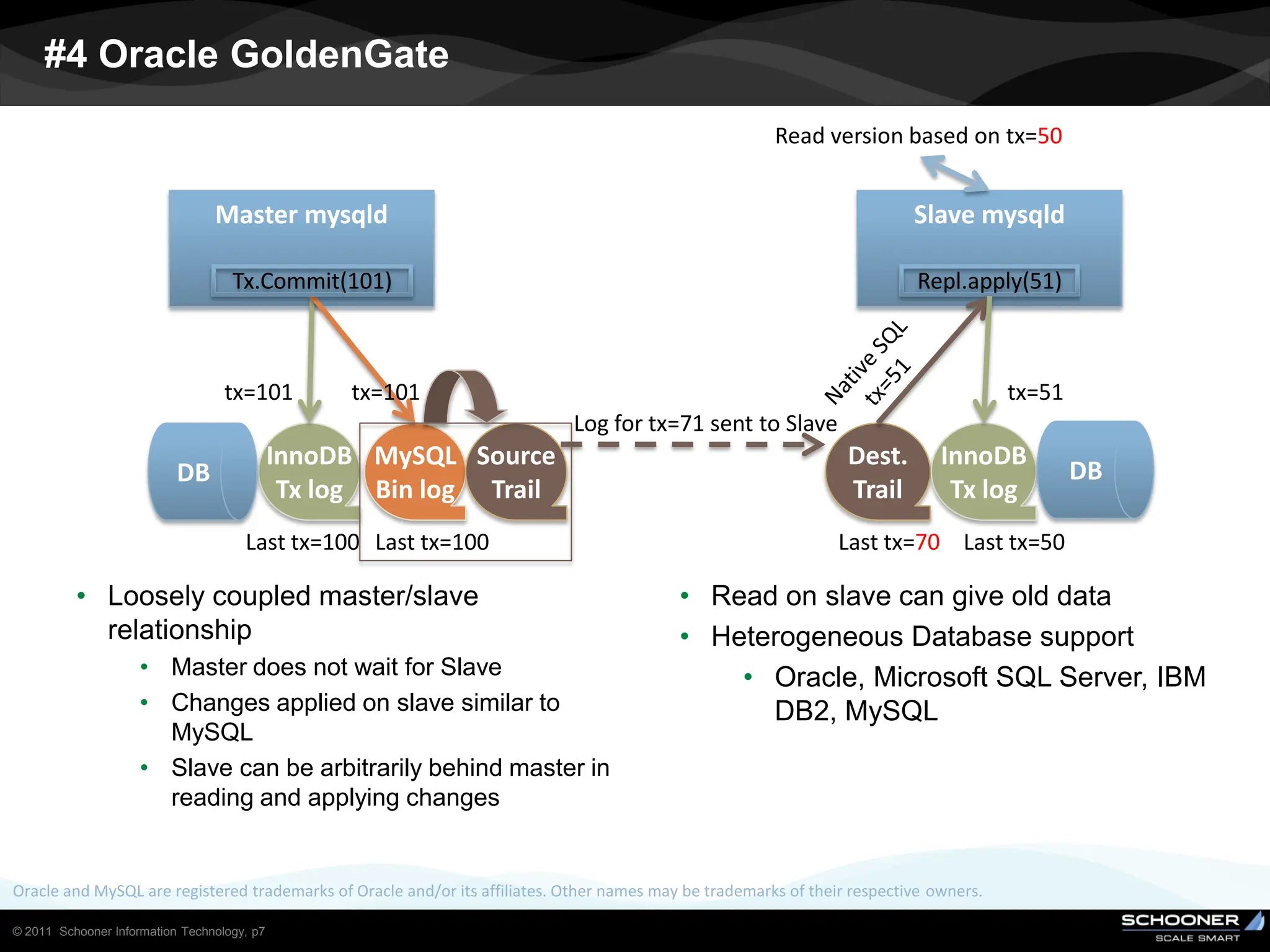
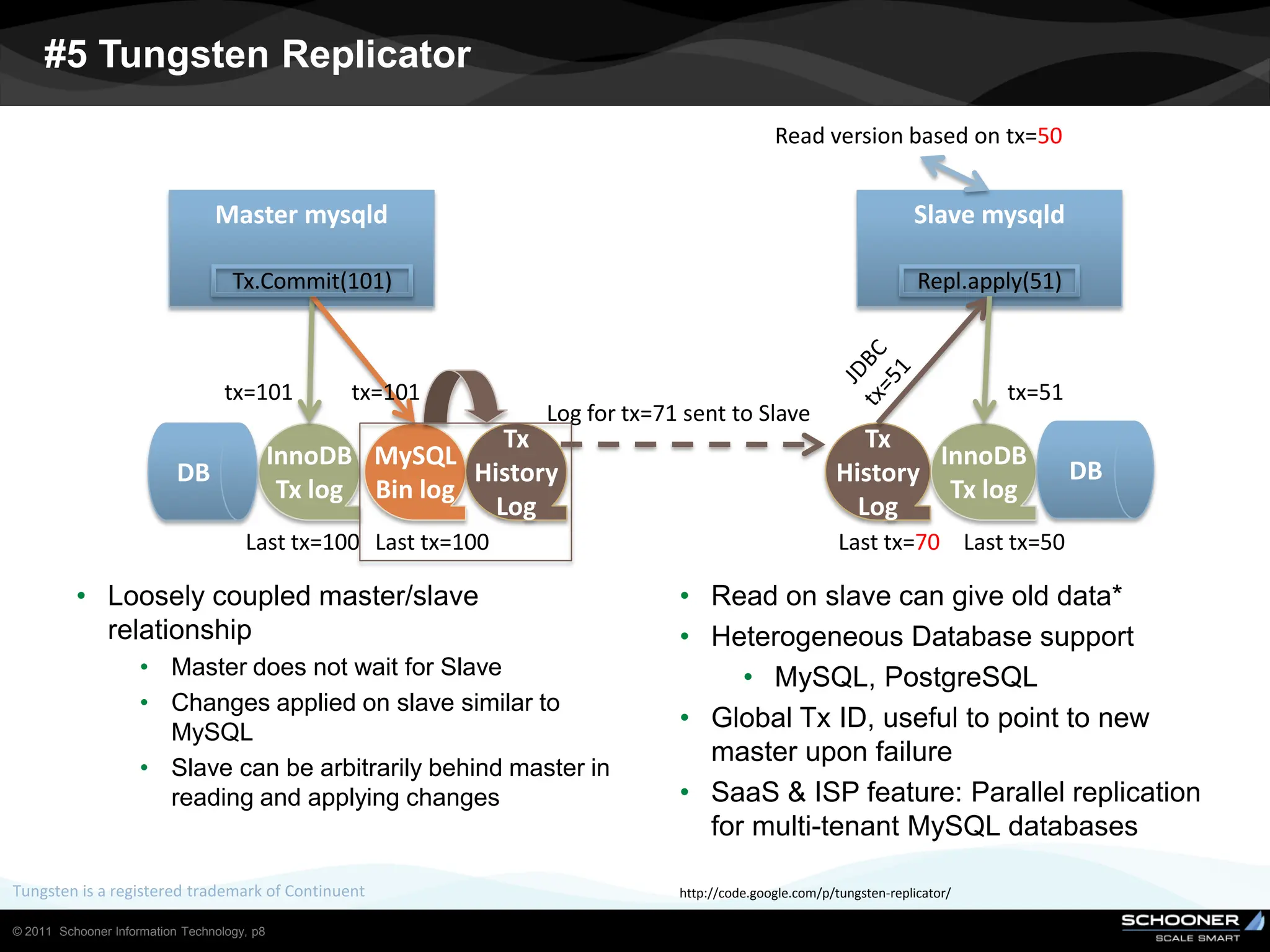
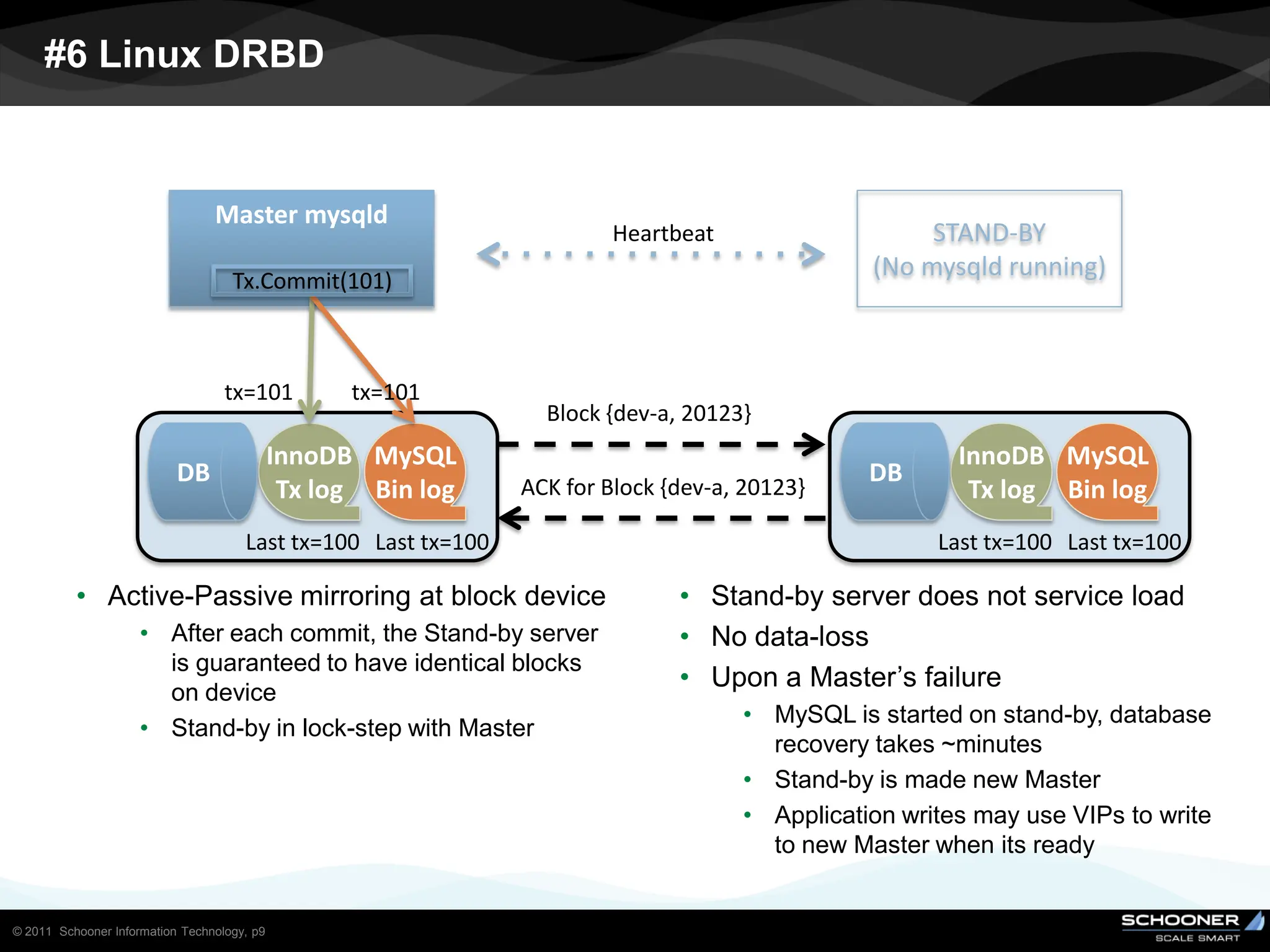
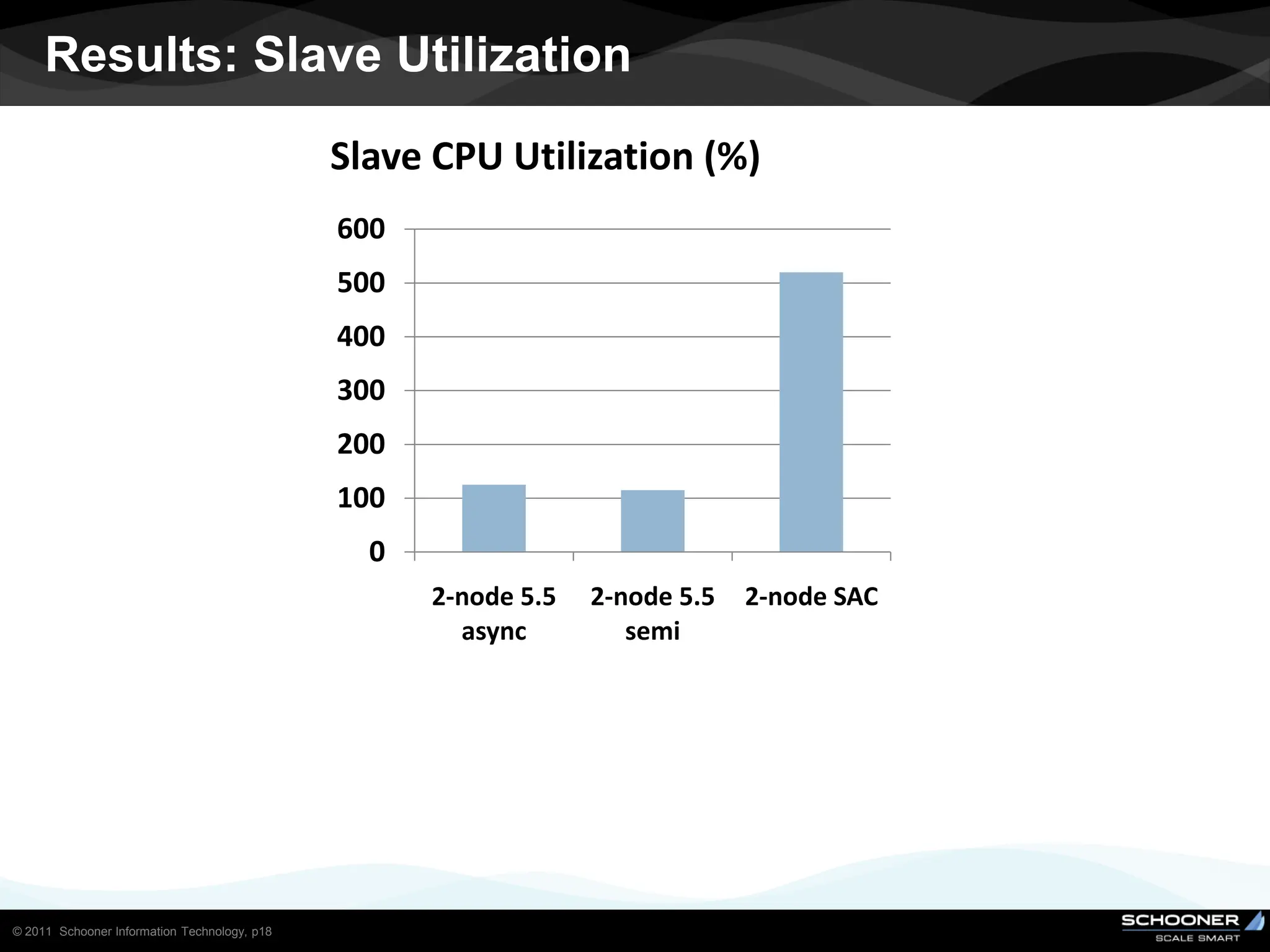
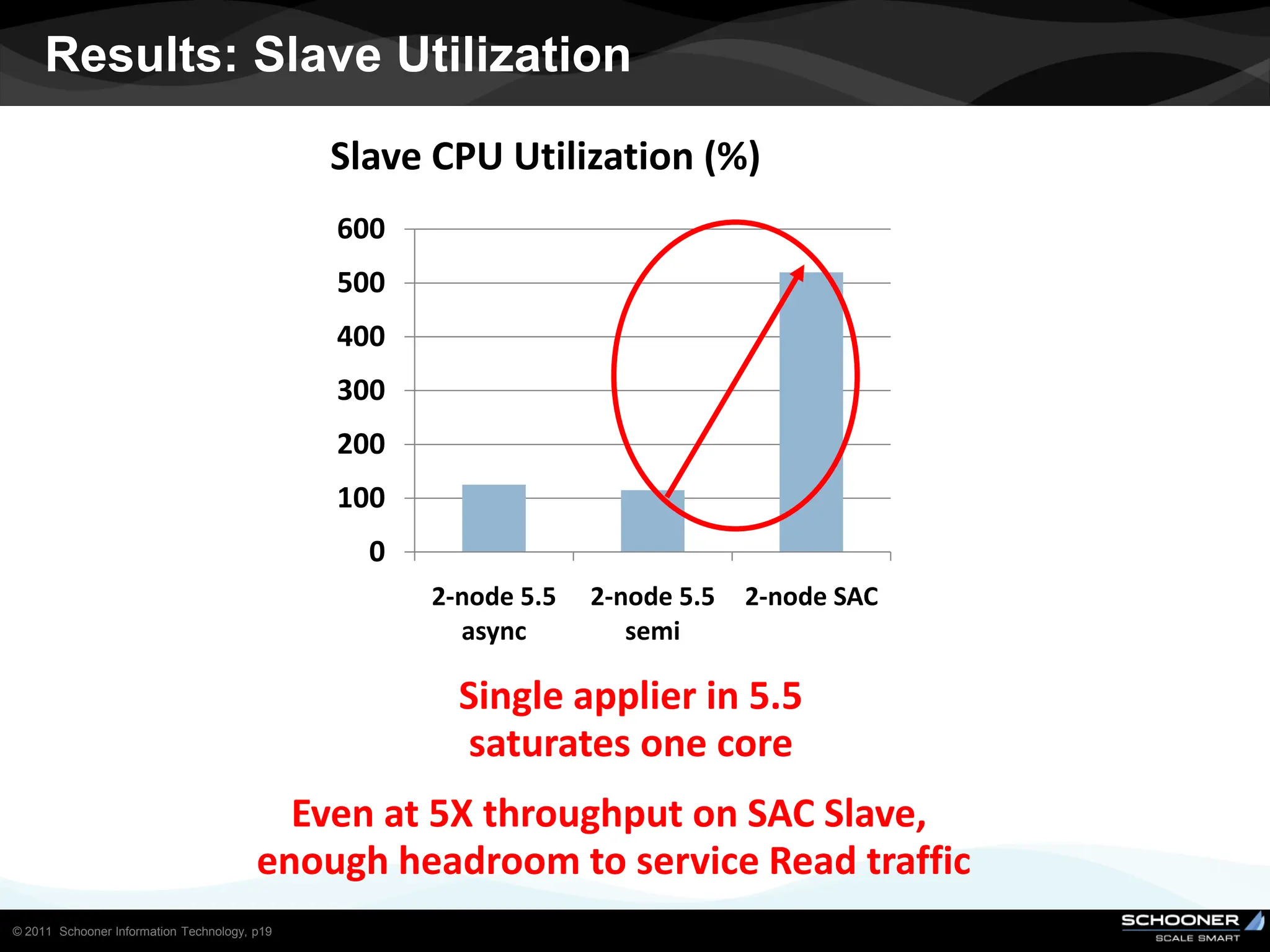
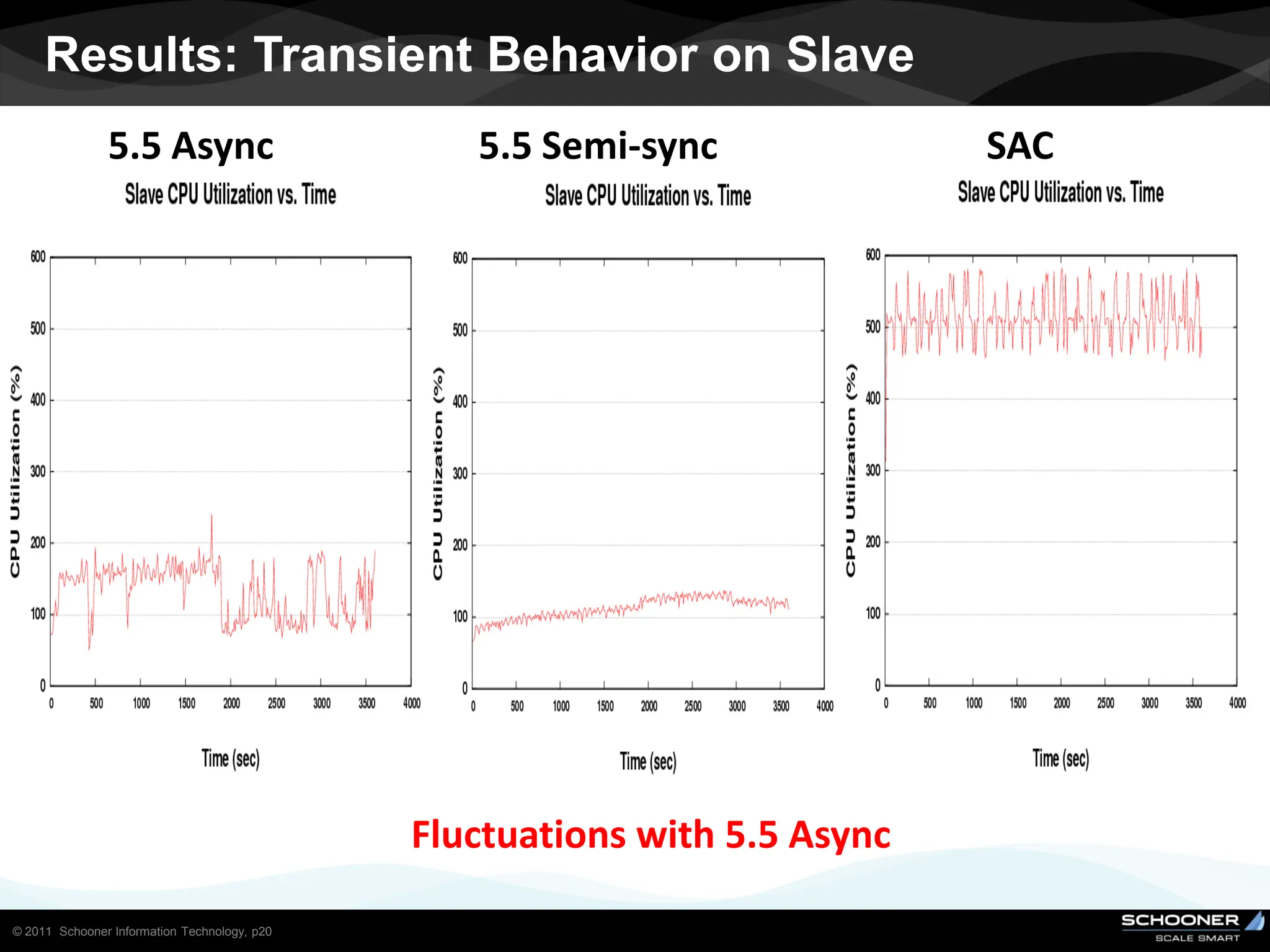
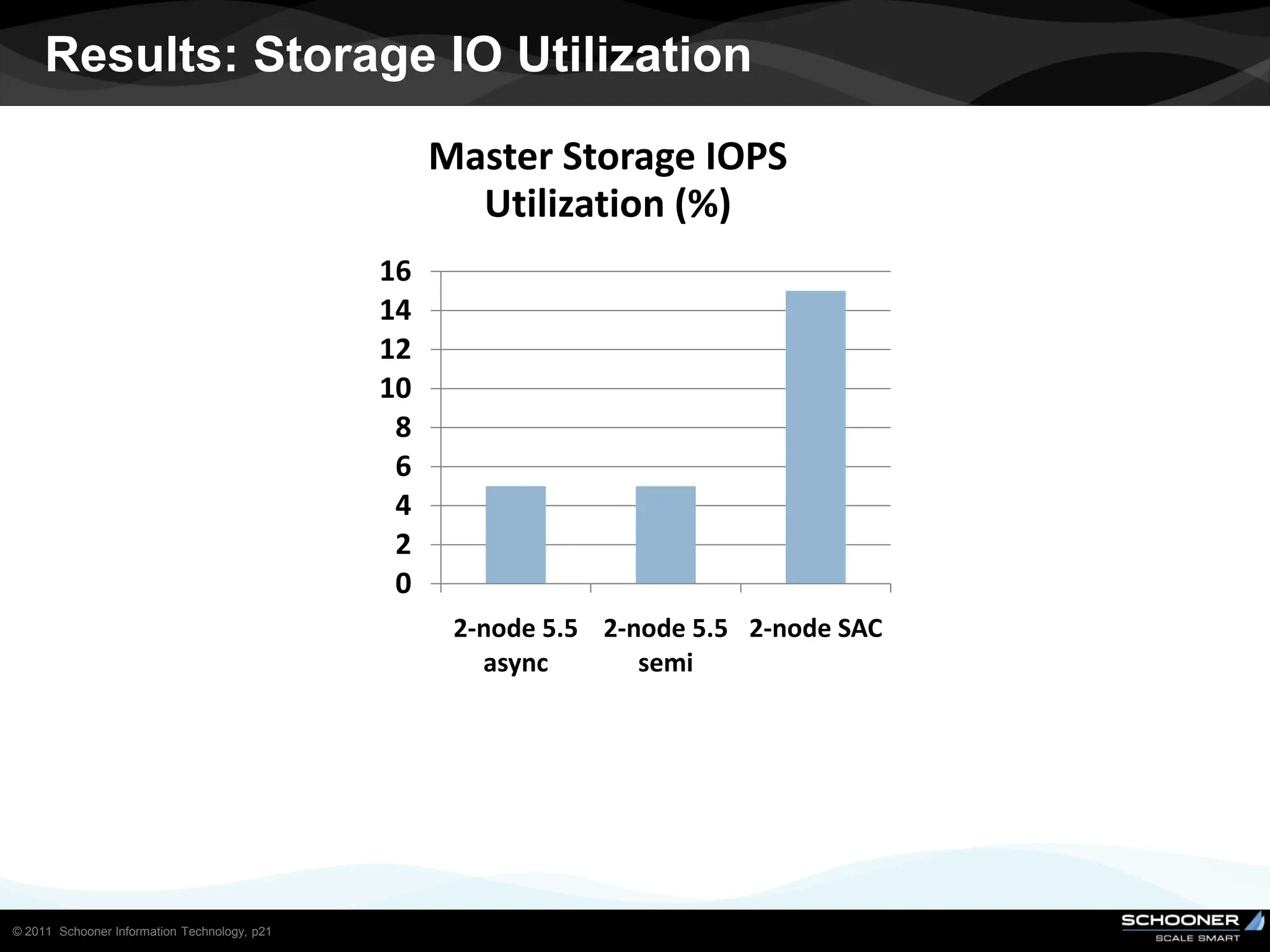
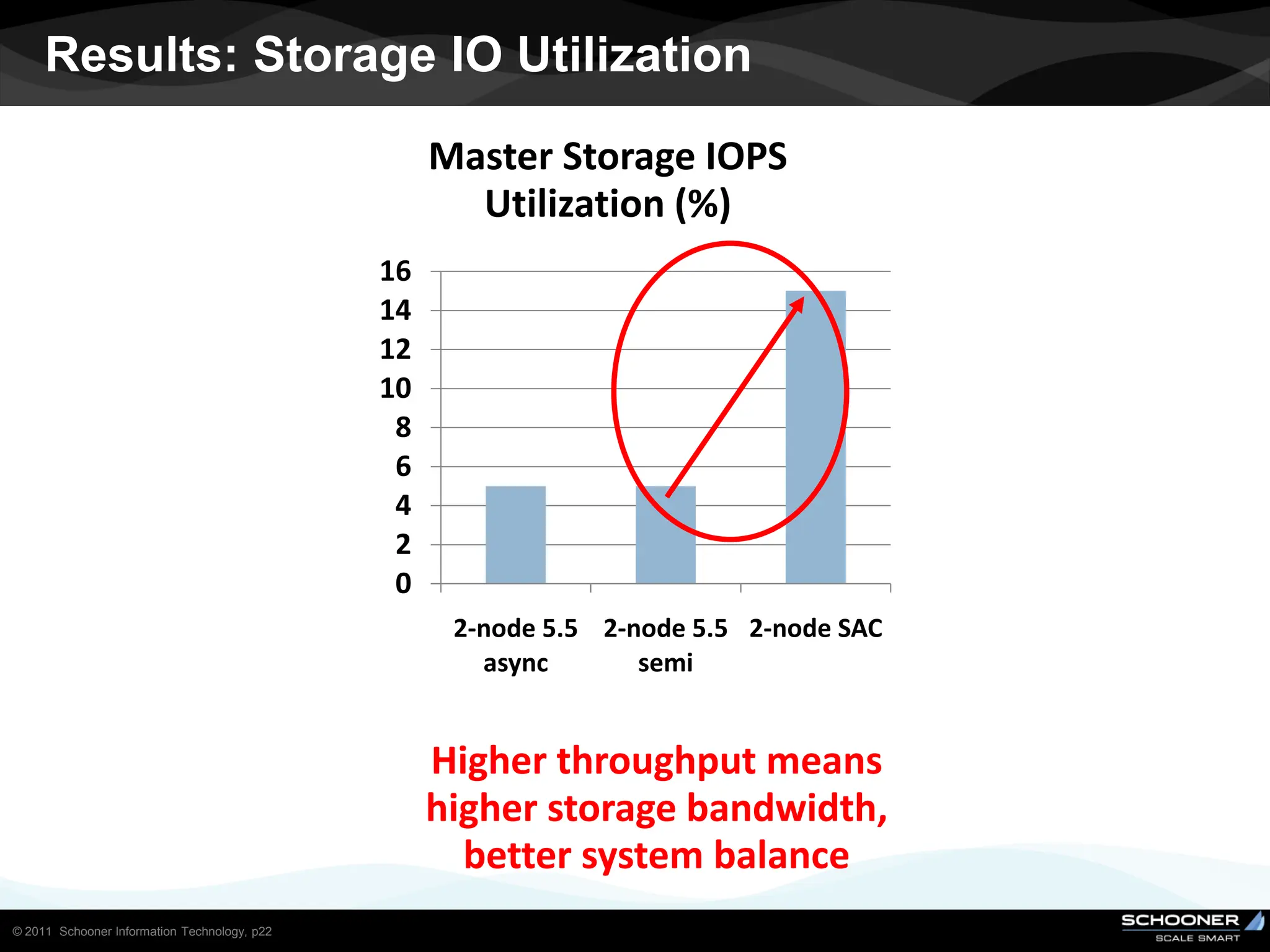
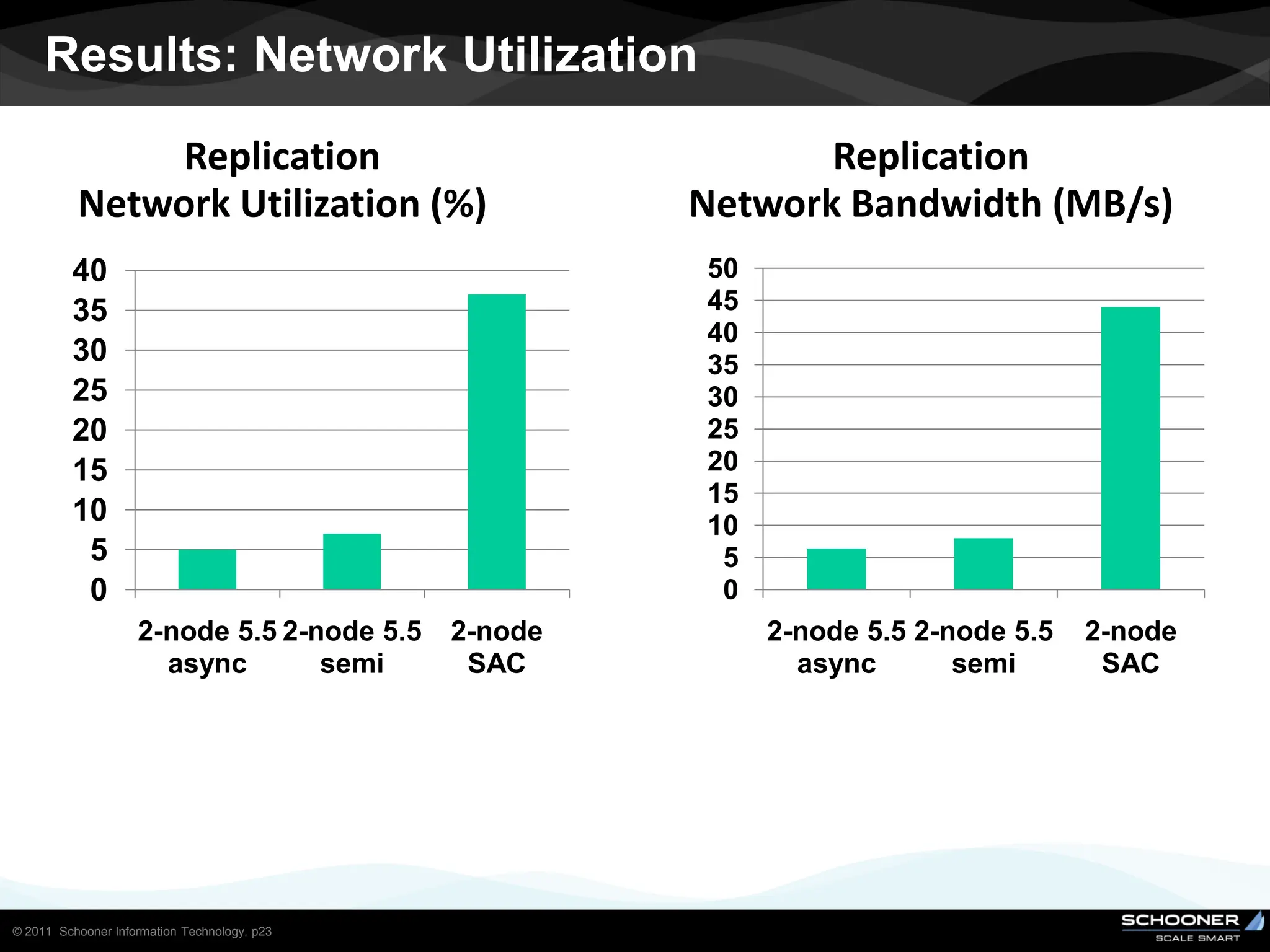
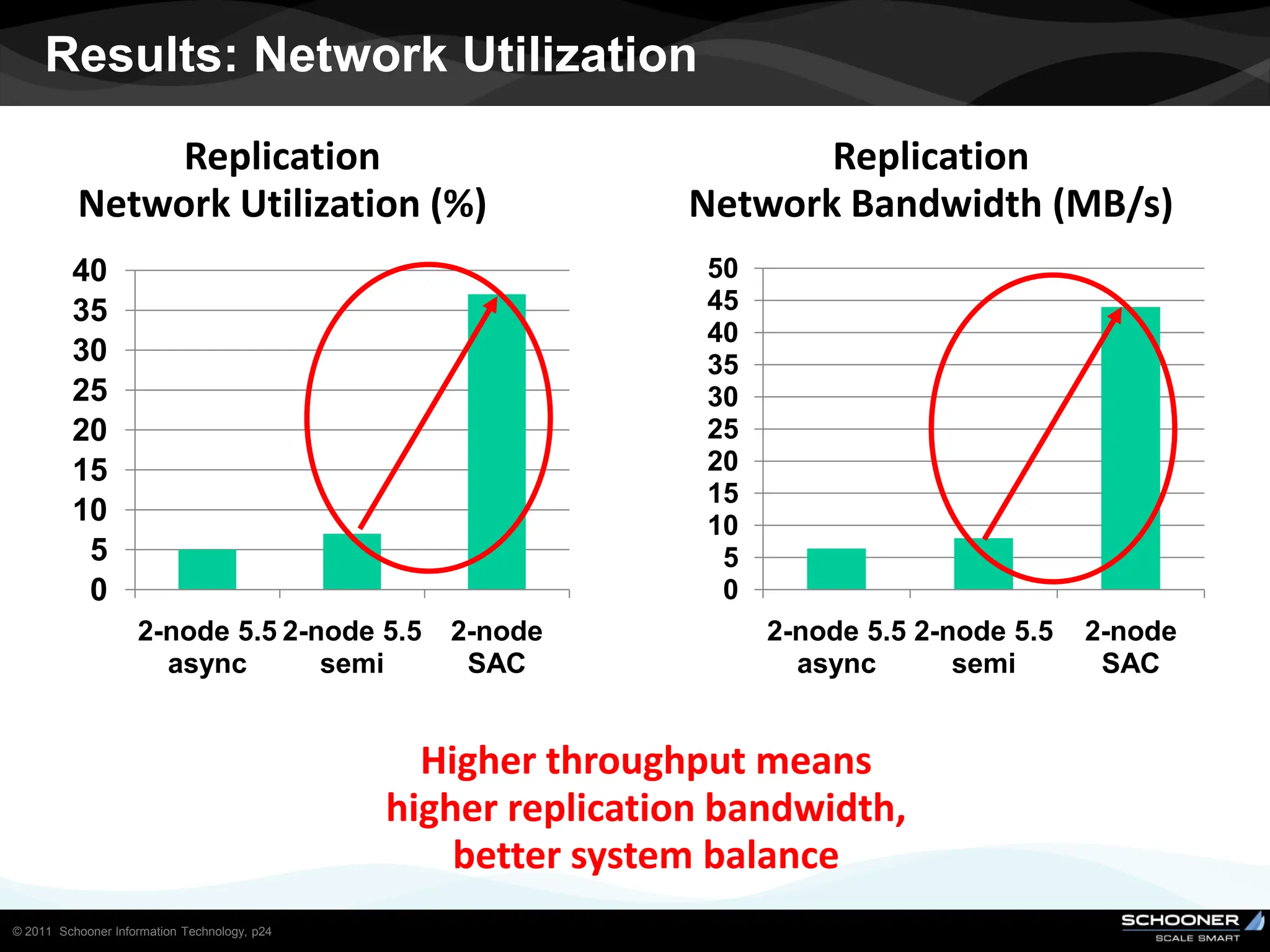
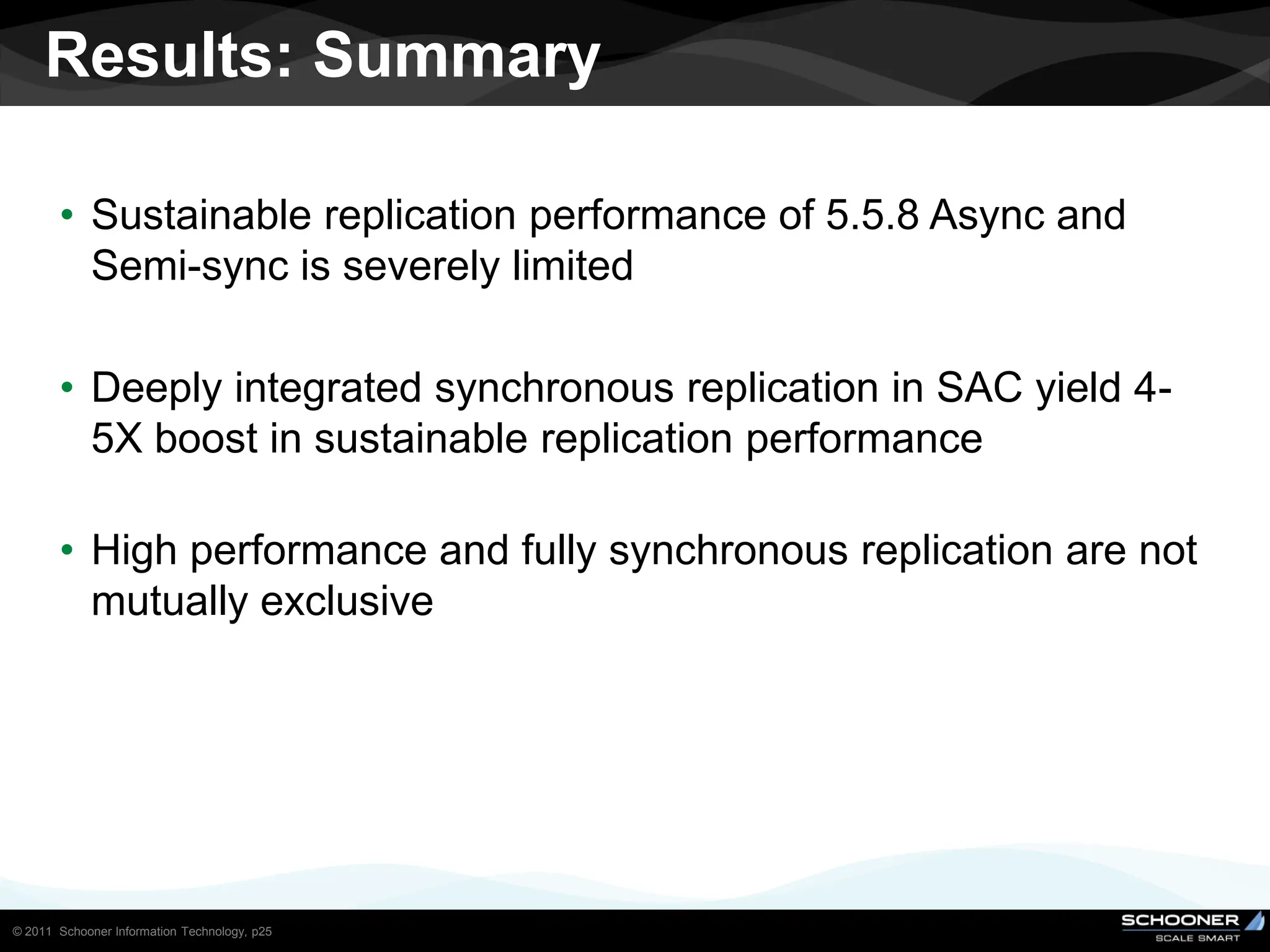
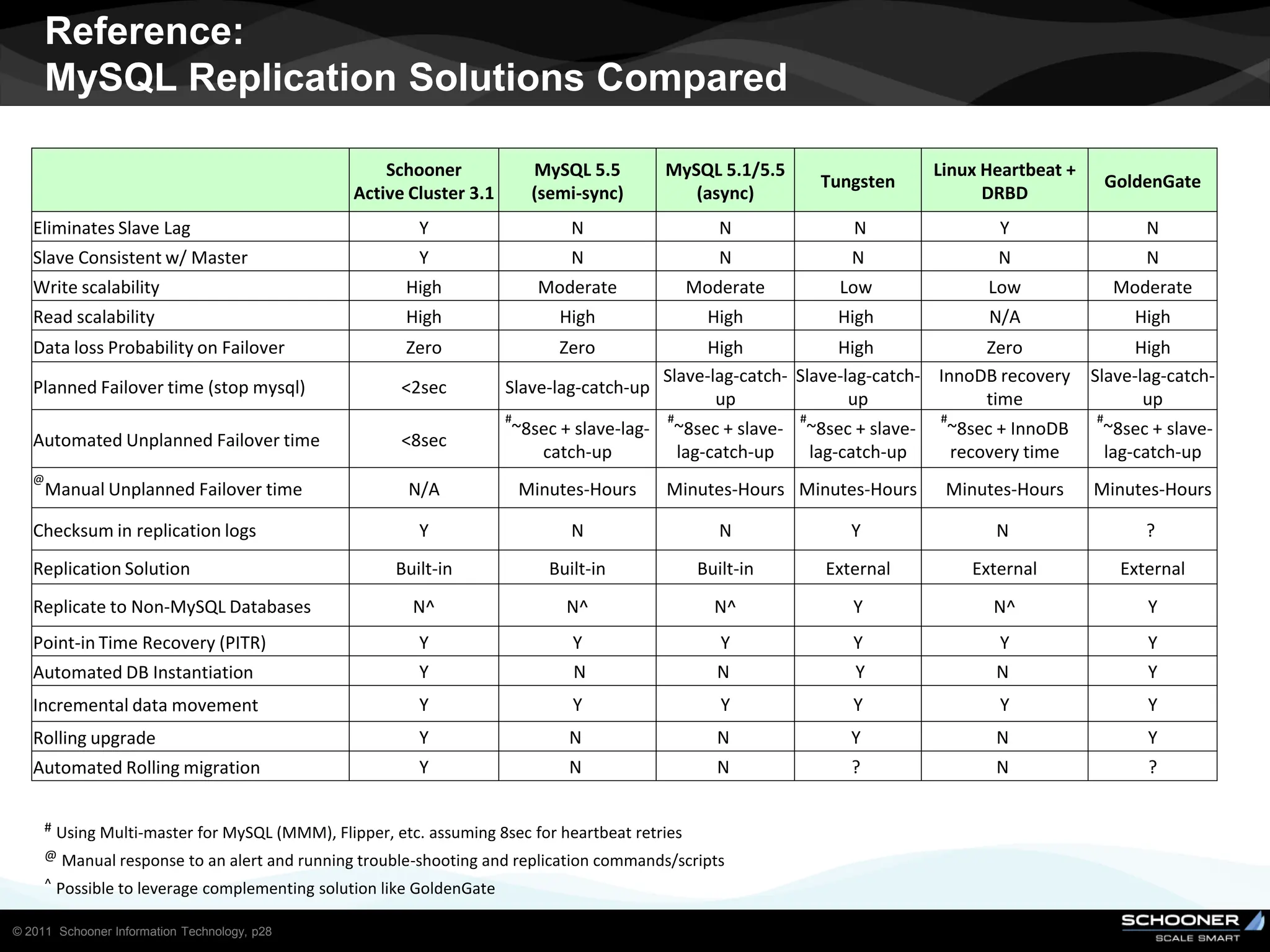
Consistency and reliability improves when moving from asynchronous to semi-synchronous to synchronous replication, however at the cost of inflexibility. DRDB and other synchronous block-level replication in storage ensure the best chances for no data-loss, however at the cost of service unavailability during the time failed-over instance recovers. Local vs wide area network require different replication architectures due to the increased network latency with WAN.
This session will share data from open-source benchmarks and results to compare performance across parameters such as workload, reads:writes ratio, response-time, consistency, fail-over, service continuity, throughput, network and cluster size. It will help capture the right system and MySQL metrics in order to understand a workload and its behavior during replication.
The purpose of this session is awareness and learning. Users will be able to run the benchmarks independently to determine how their workload behaves in their own environment.