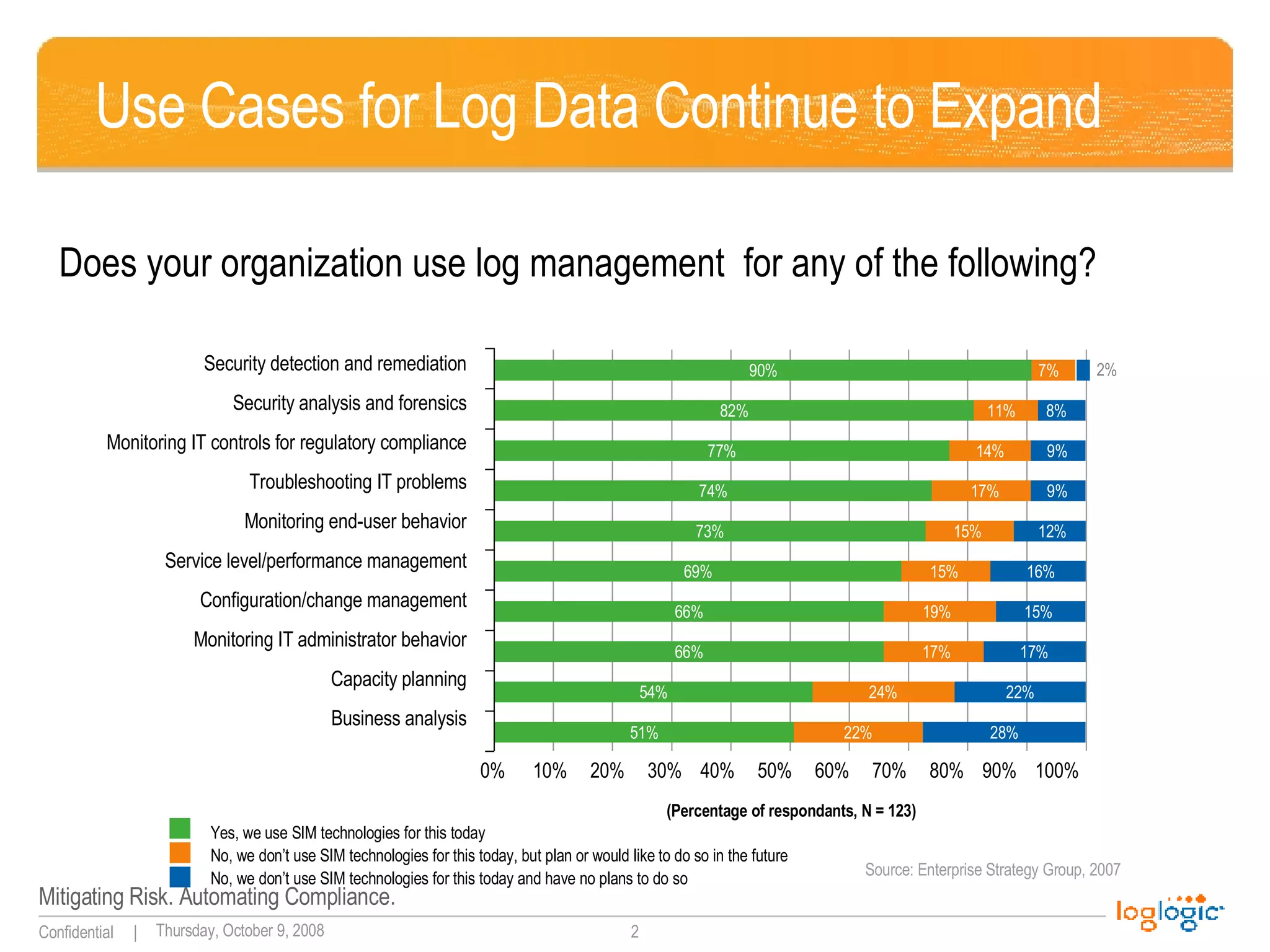
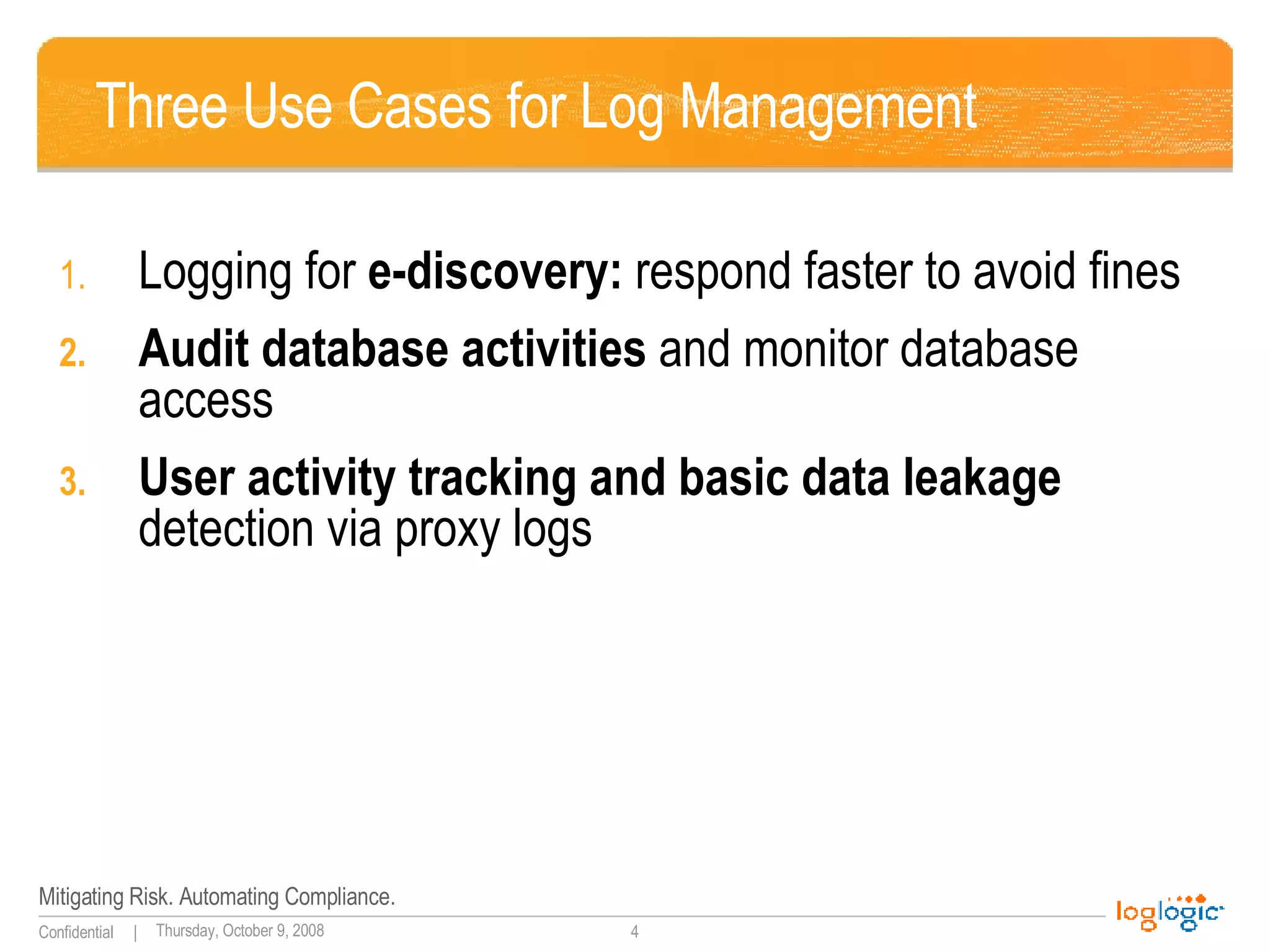
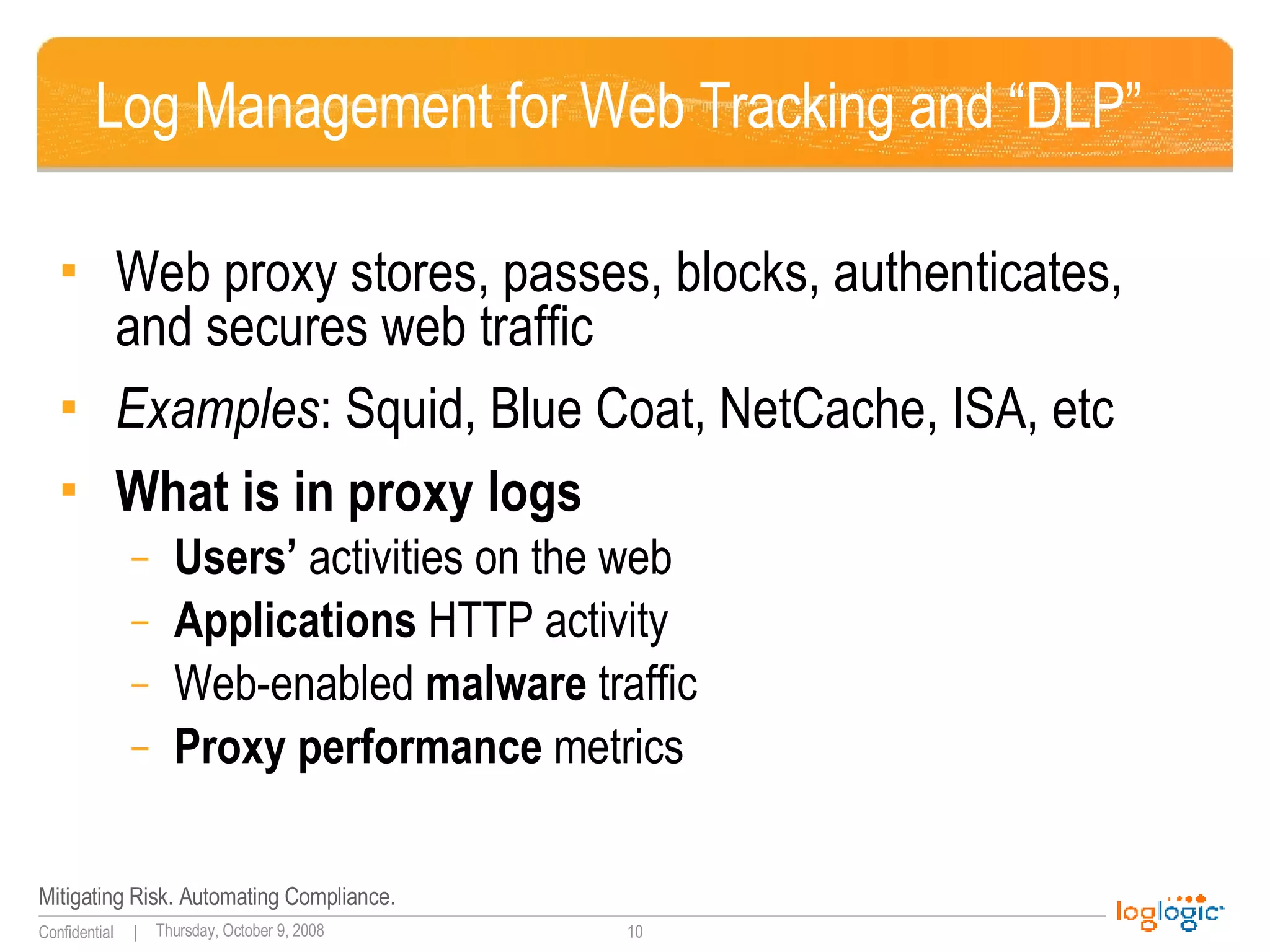
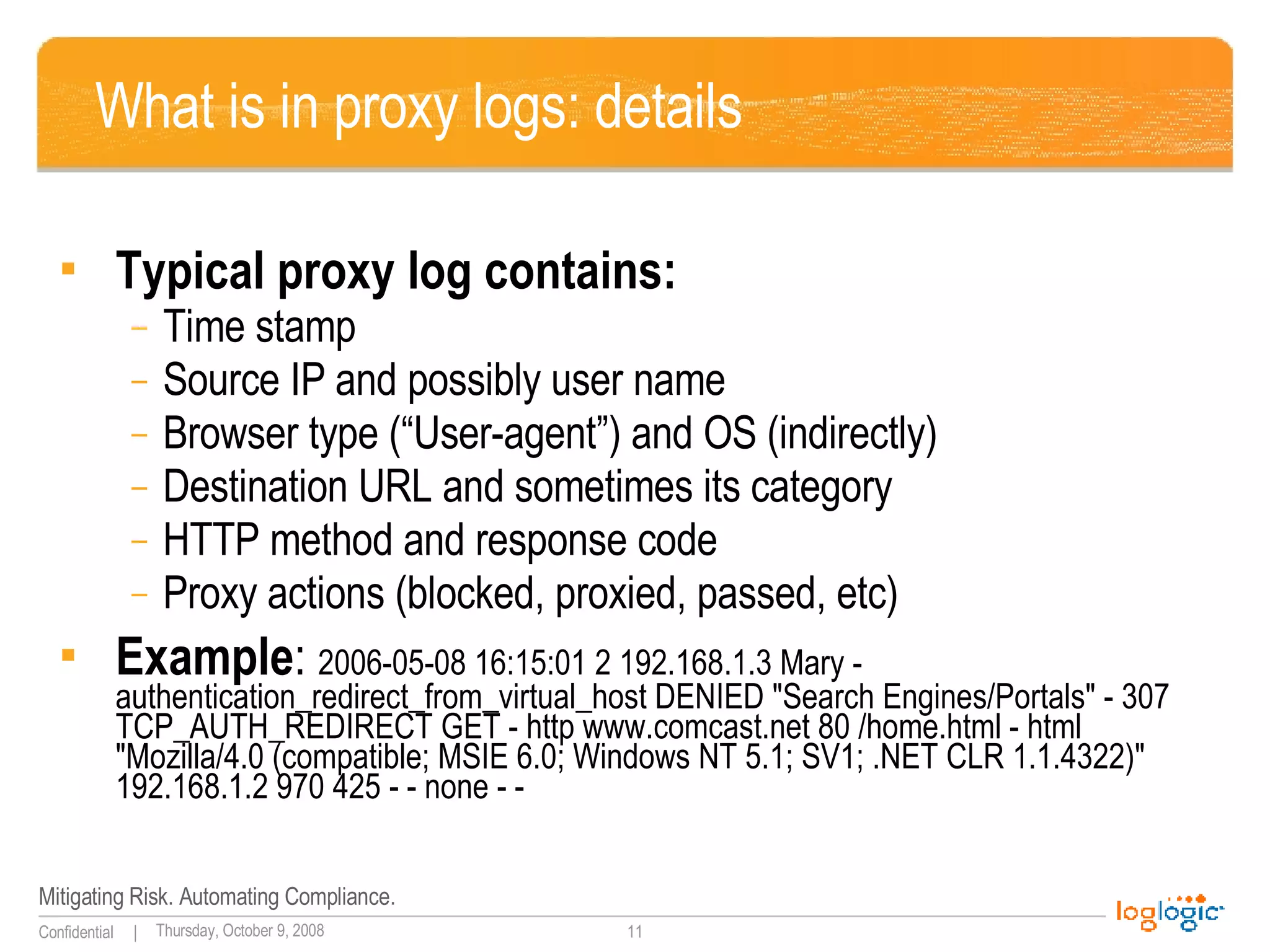
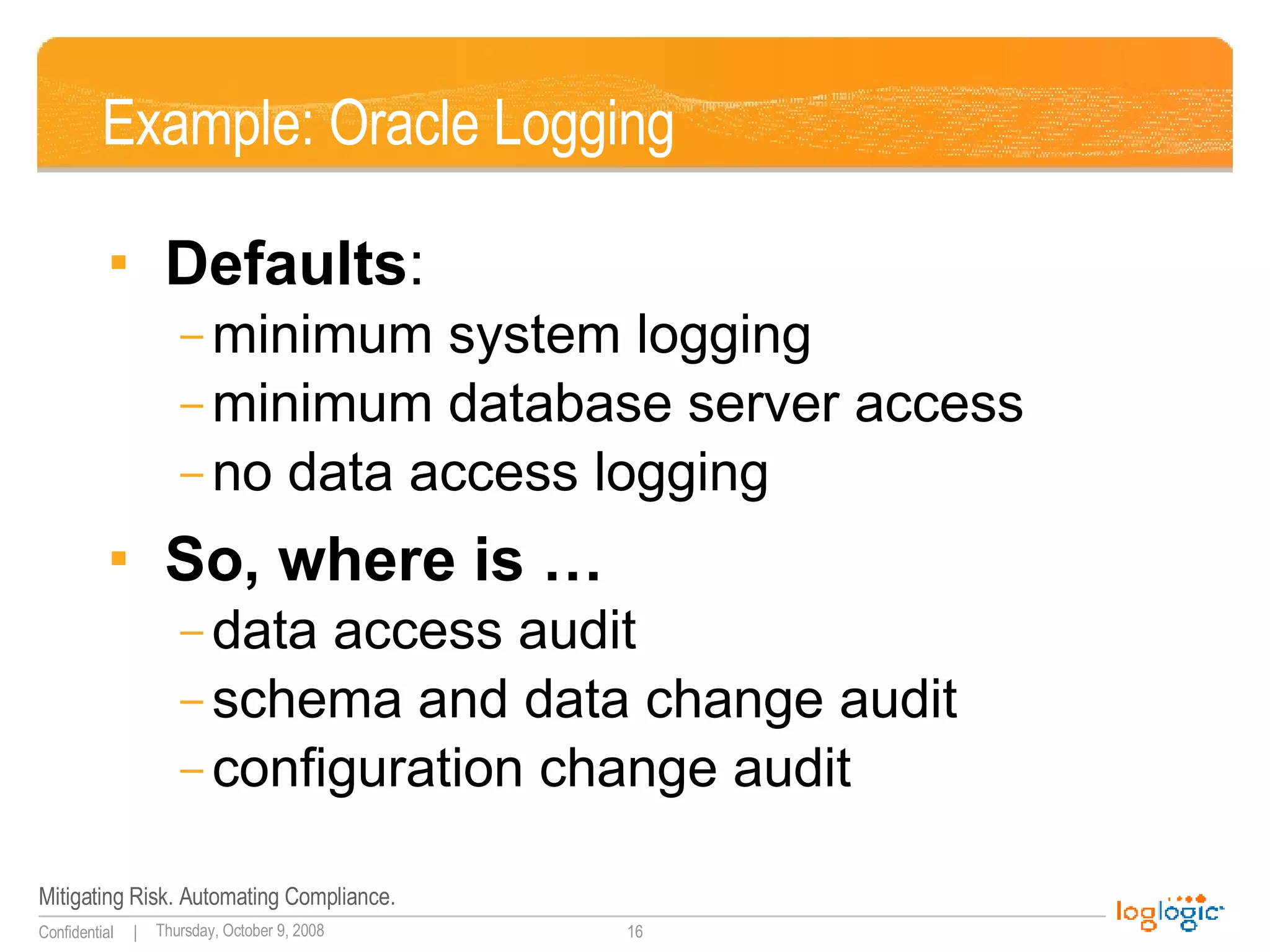
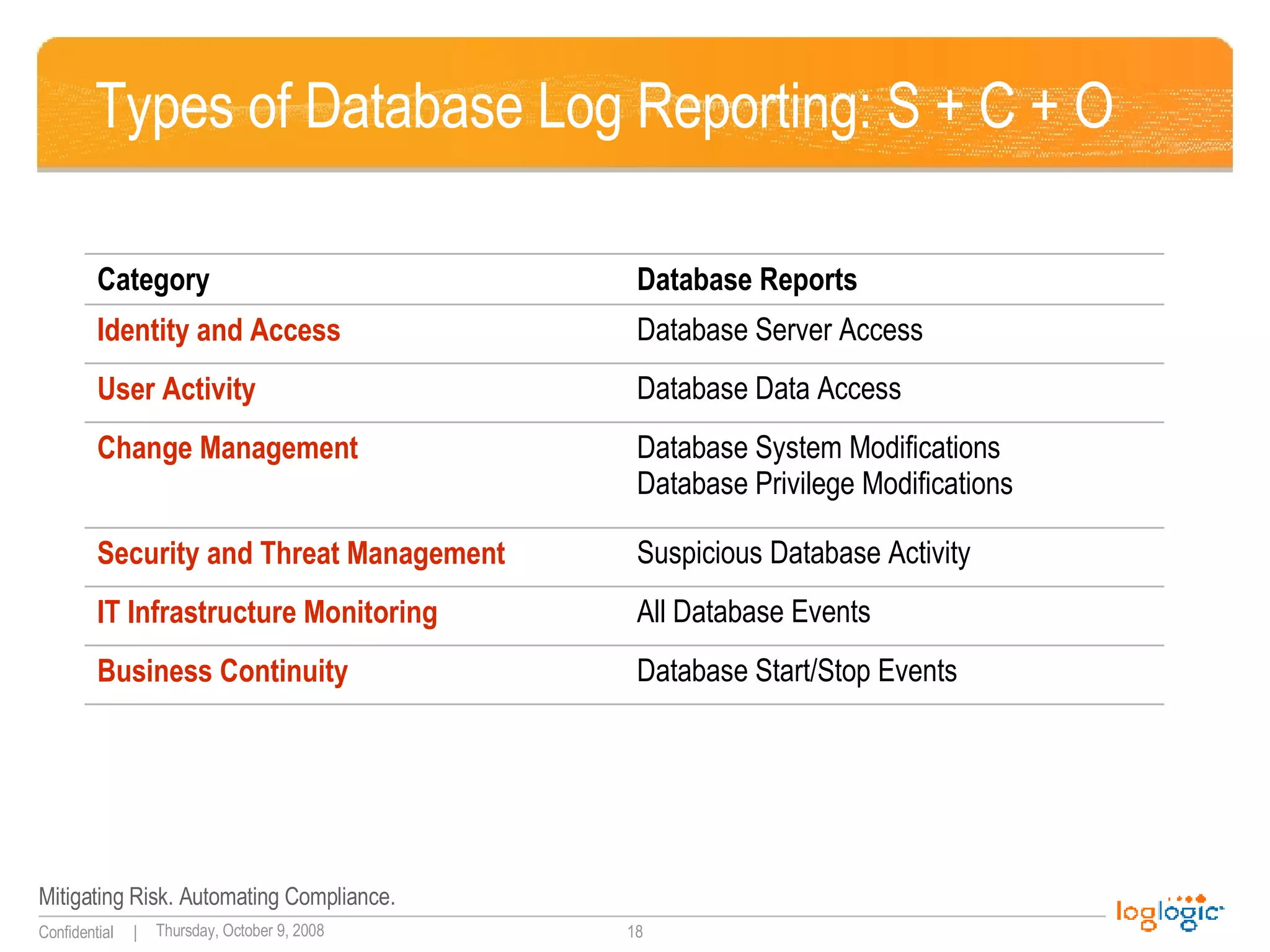
The document discusses expanding uses for log management beyond classic security and compliance purposes. It outlines several potential use cases including security analysis, troubleshooting, monitoring user behavior, performance management, and database auditing. Specifically, it describes how log management can help with regulatory compliance, security investigations, and monitoring administrator and end-user activity.