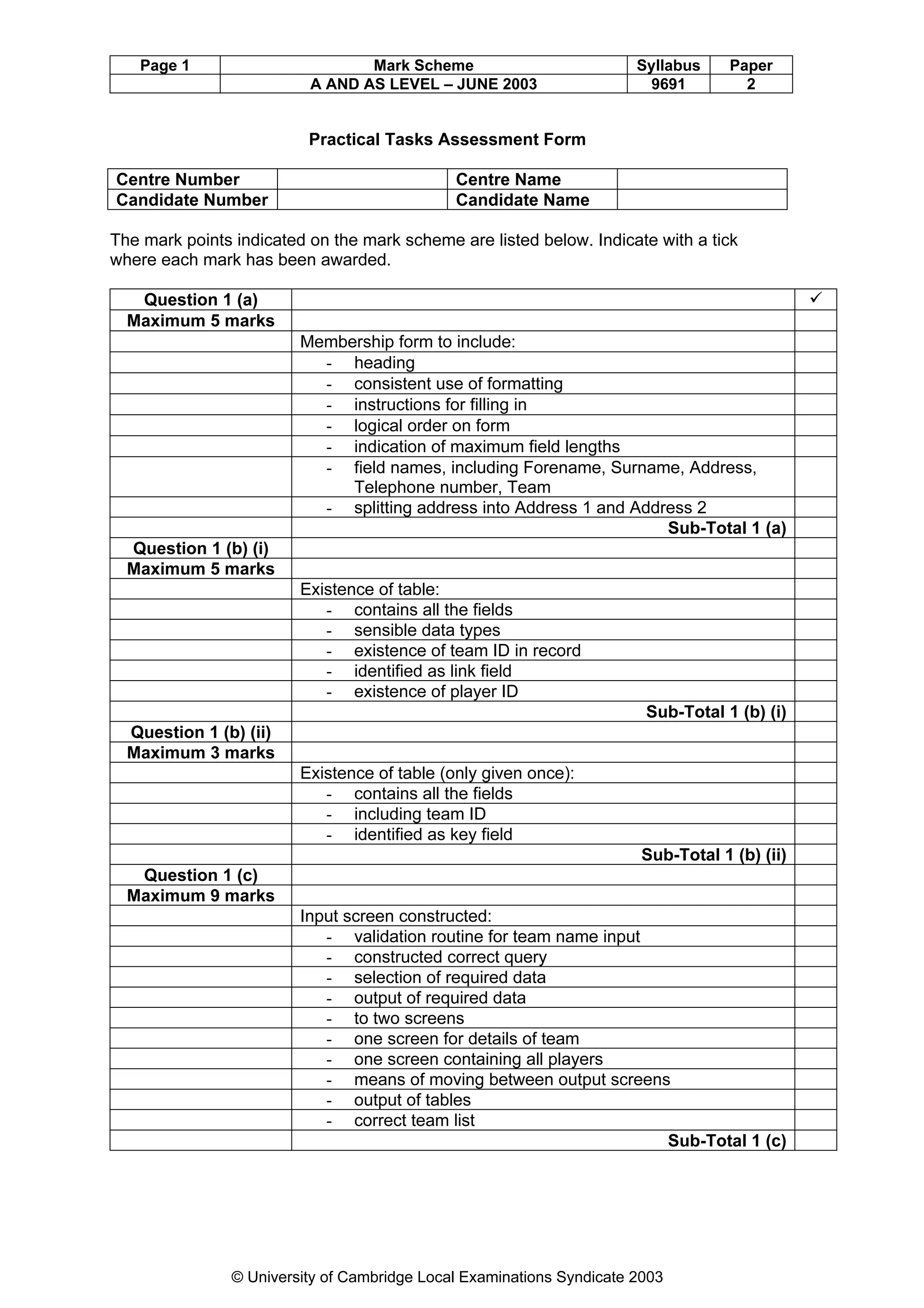
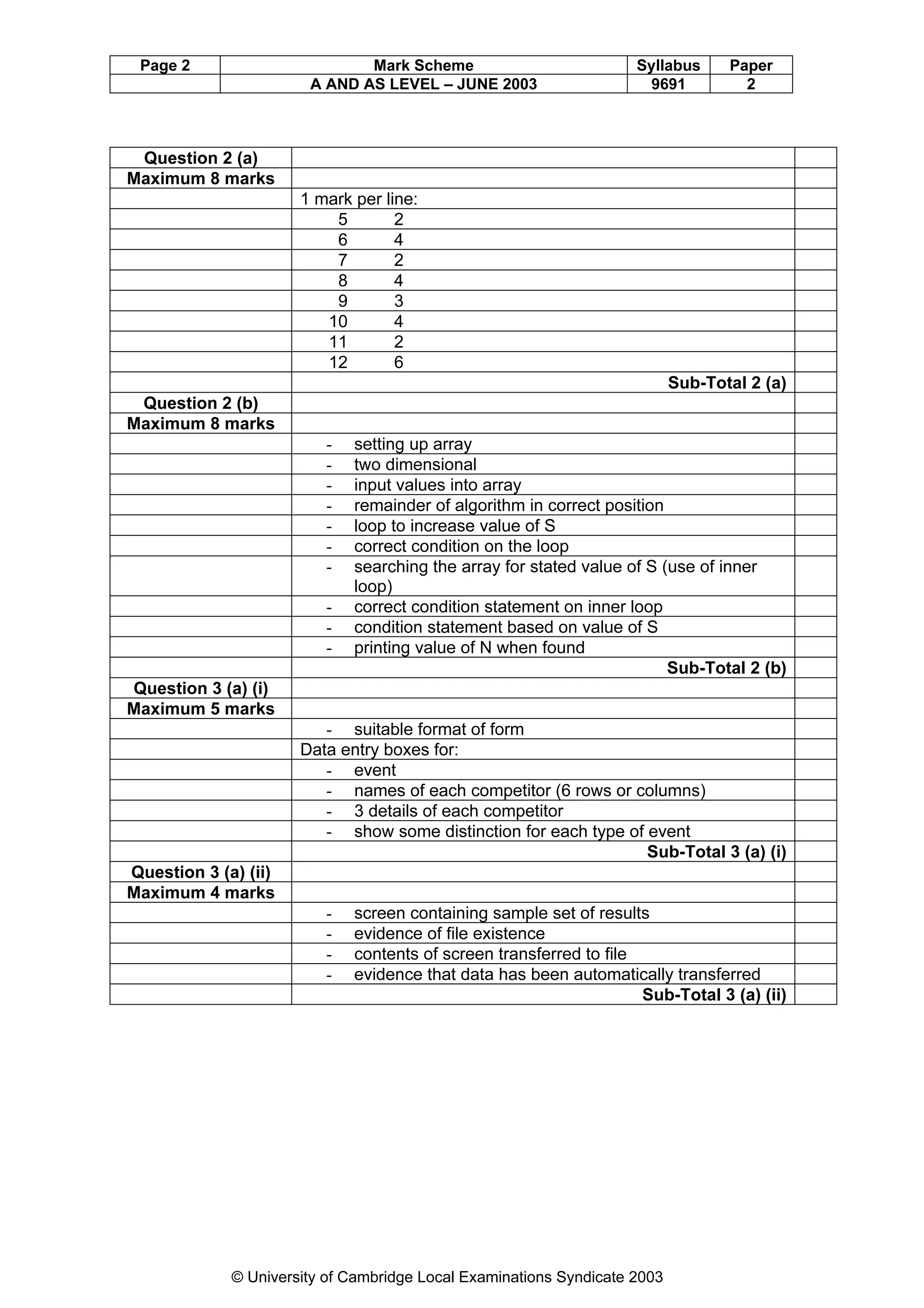
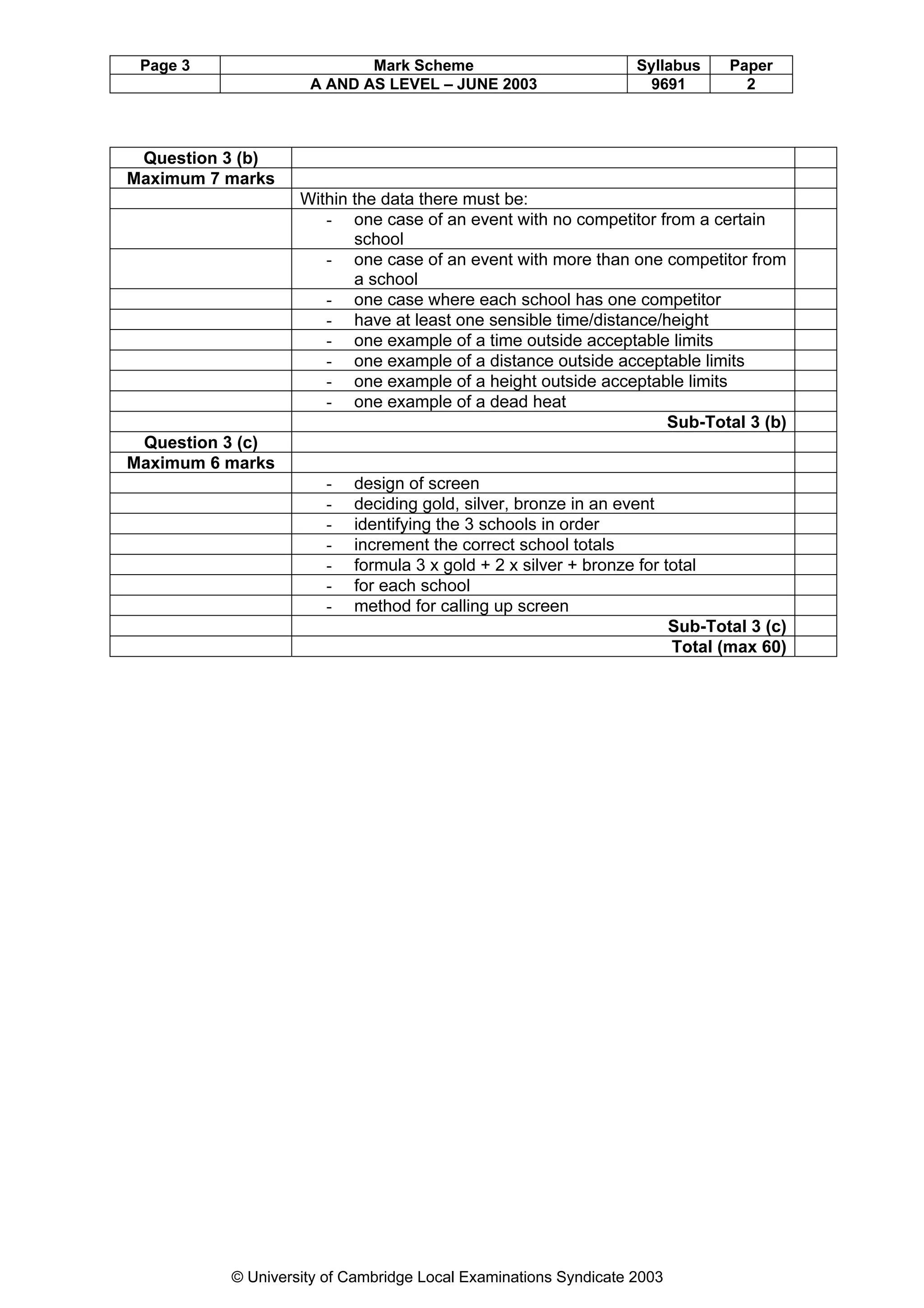
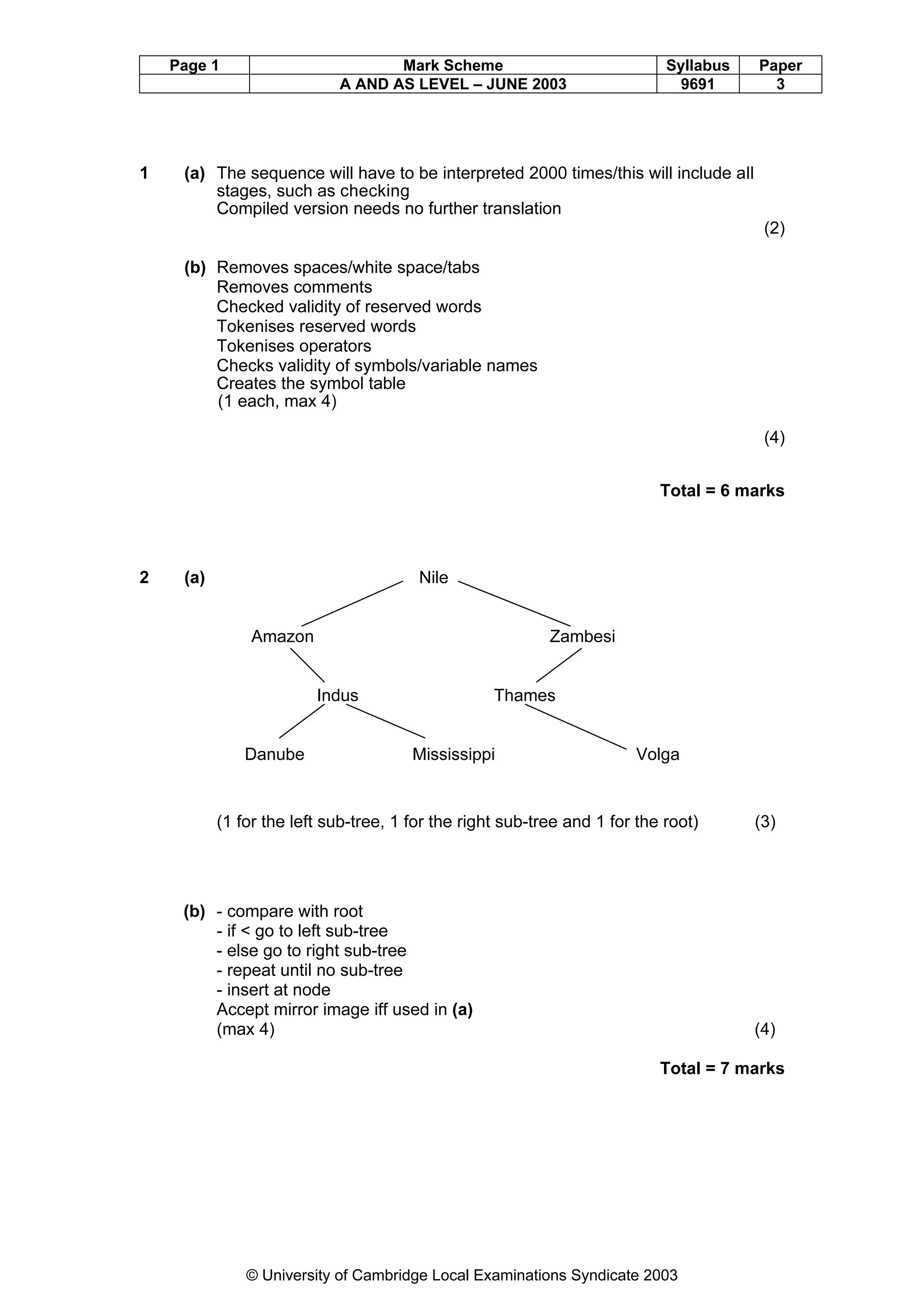
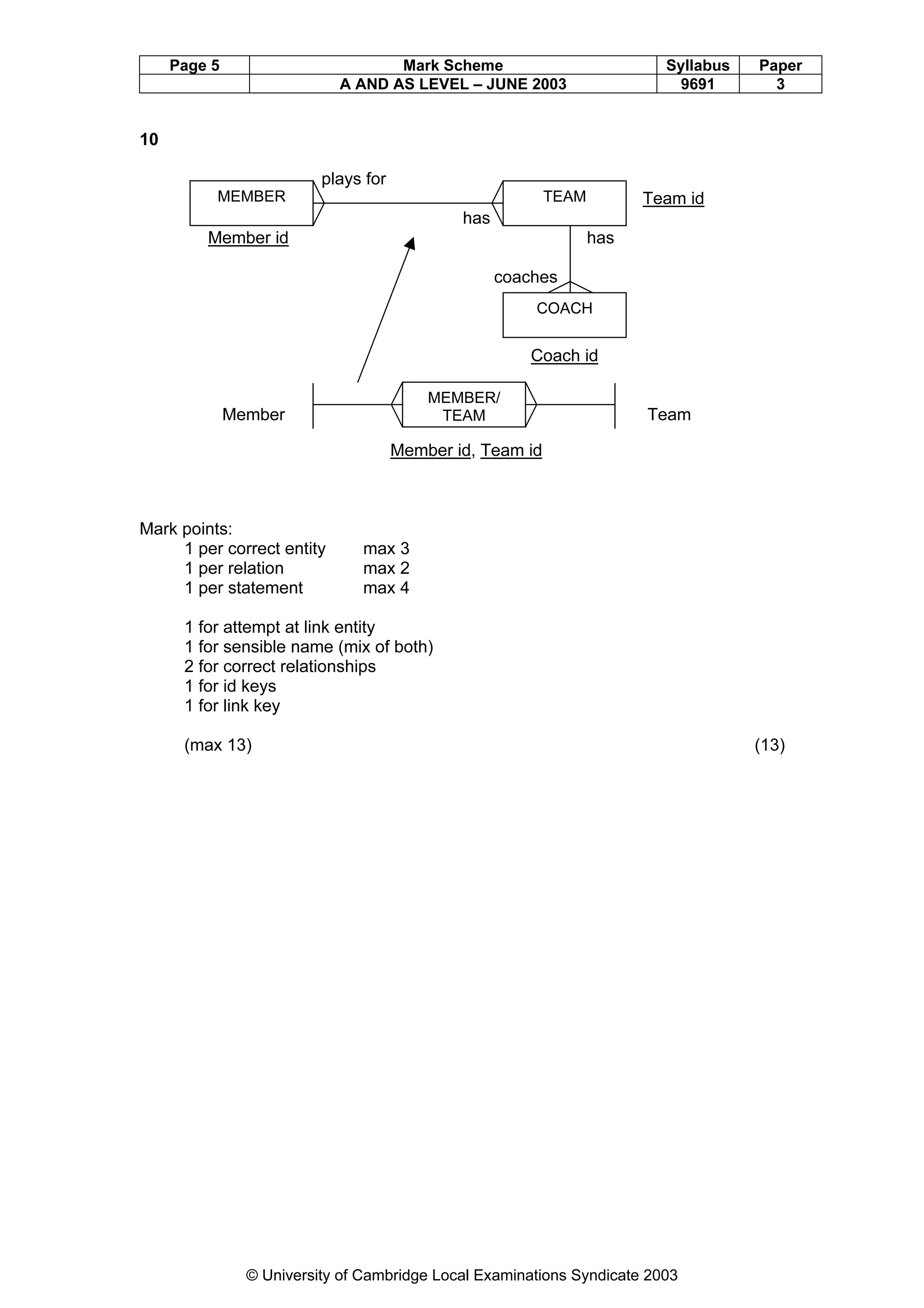
This document provides a marking scheme for a computing exam with a maximum mark of 90. It summarizes the key points assessors should look for in student responses to various questions about computing topics like operating systems, real-time vs online systems, networks, programming errors, data structures, computer hardware, data transmission, security, database design, and information systems. The marking scheme breaks down the essential information needed for each question and awards marks for students including these details in their answers.