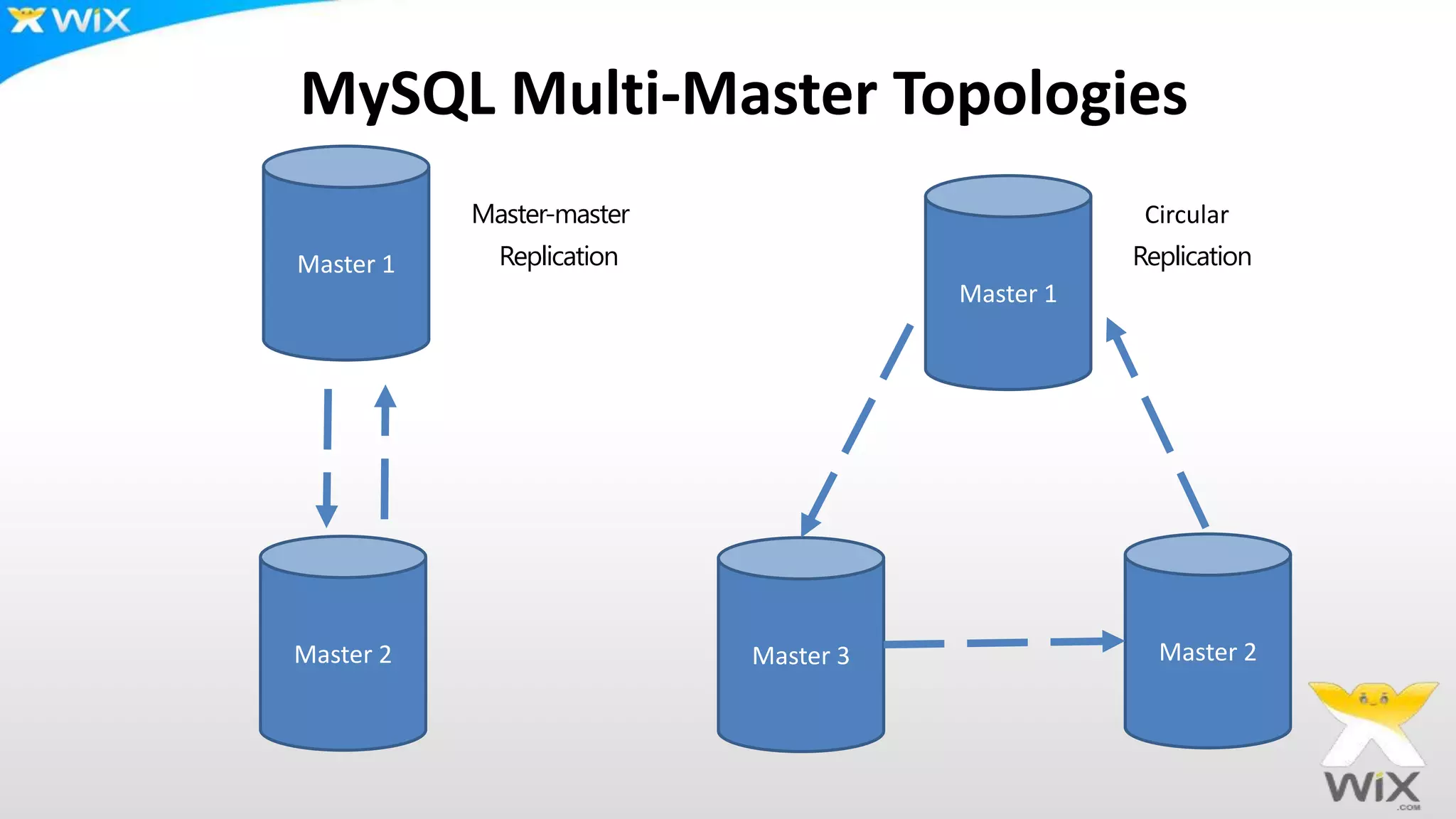
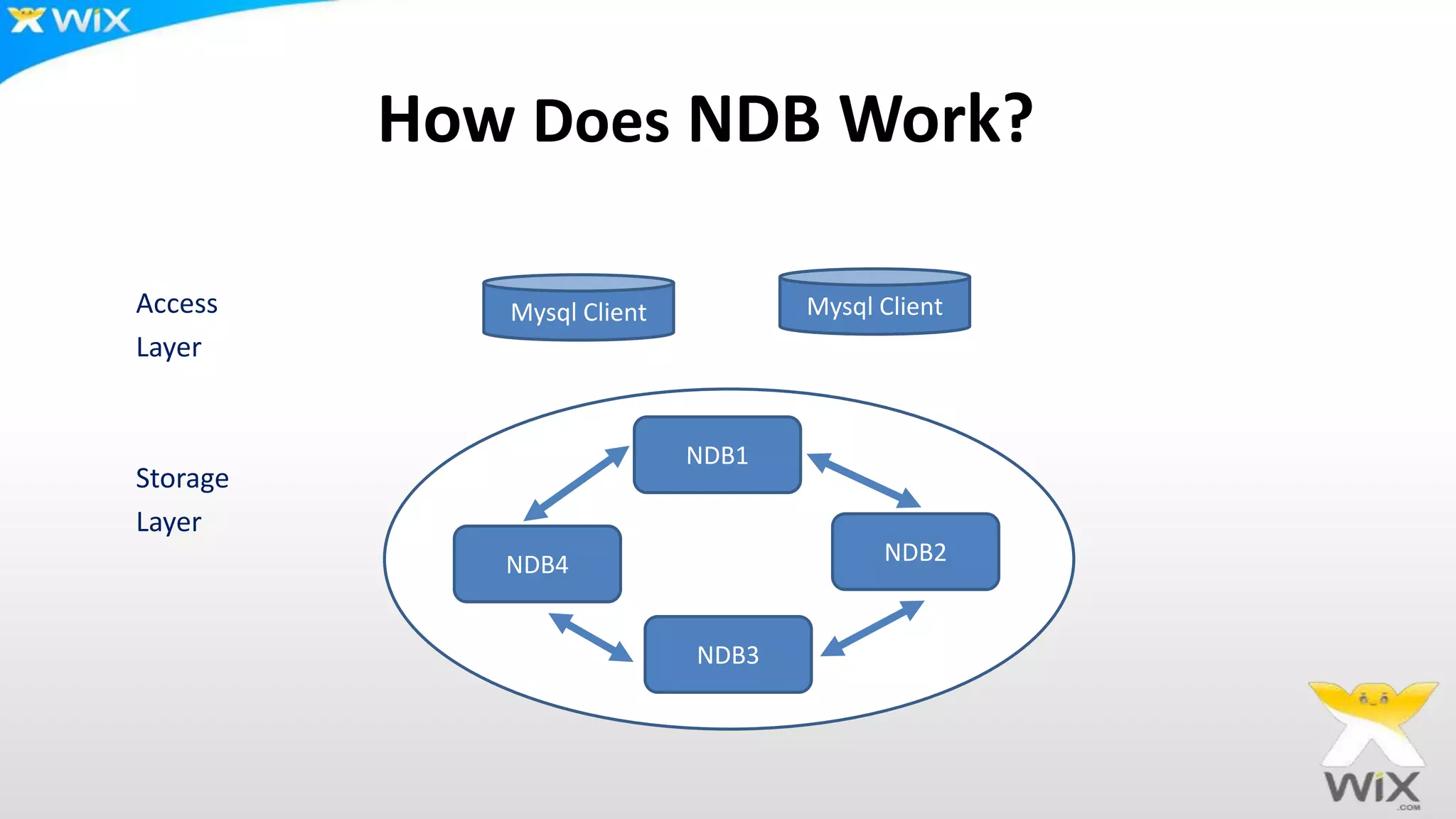
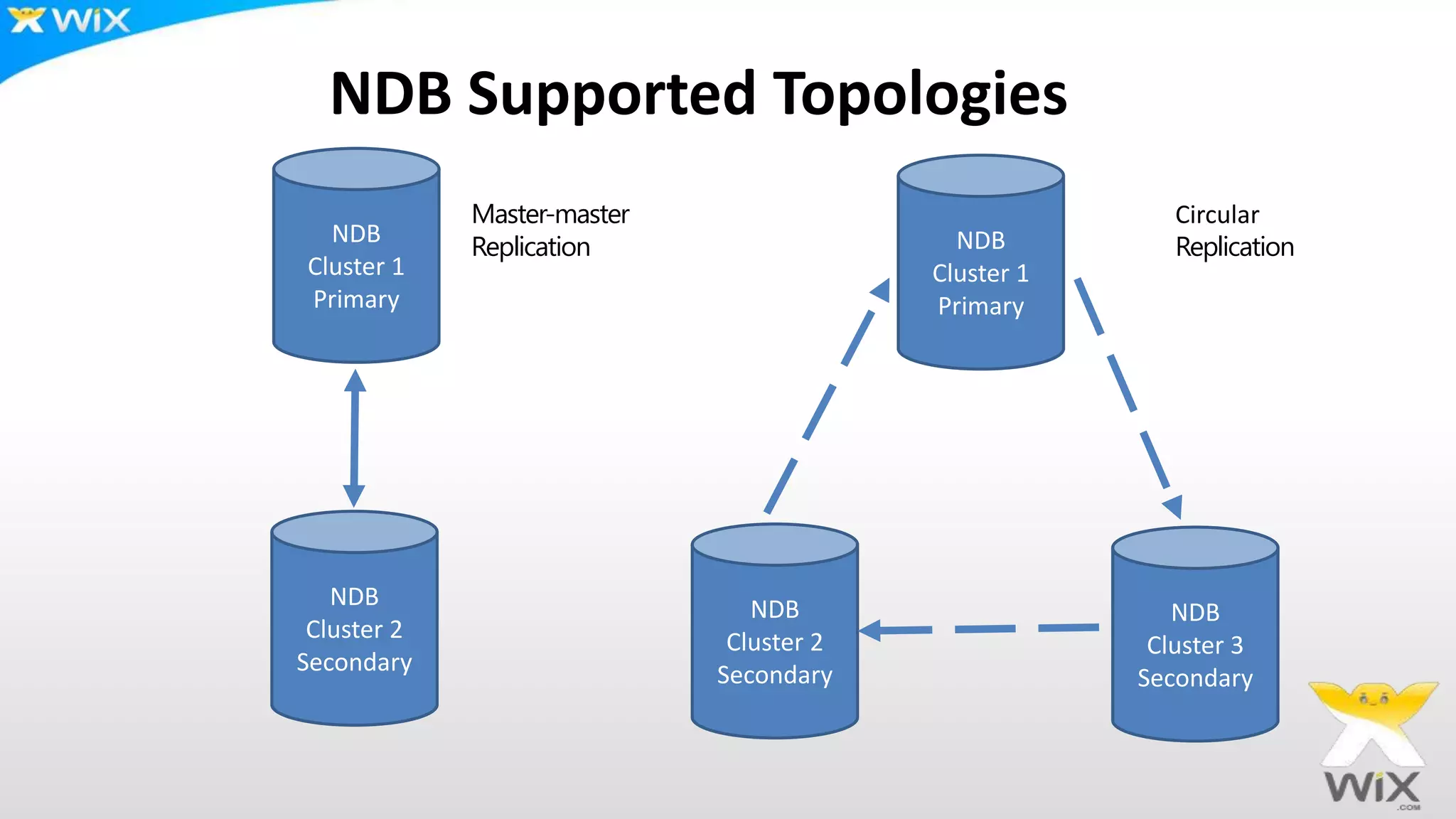
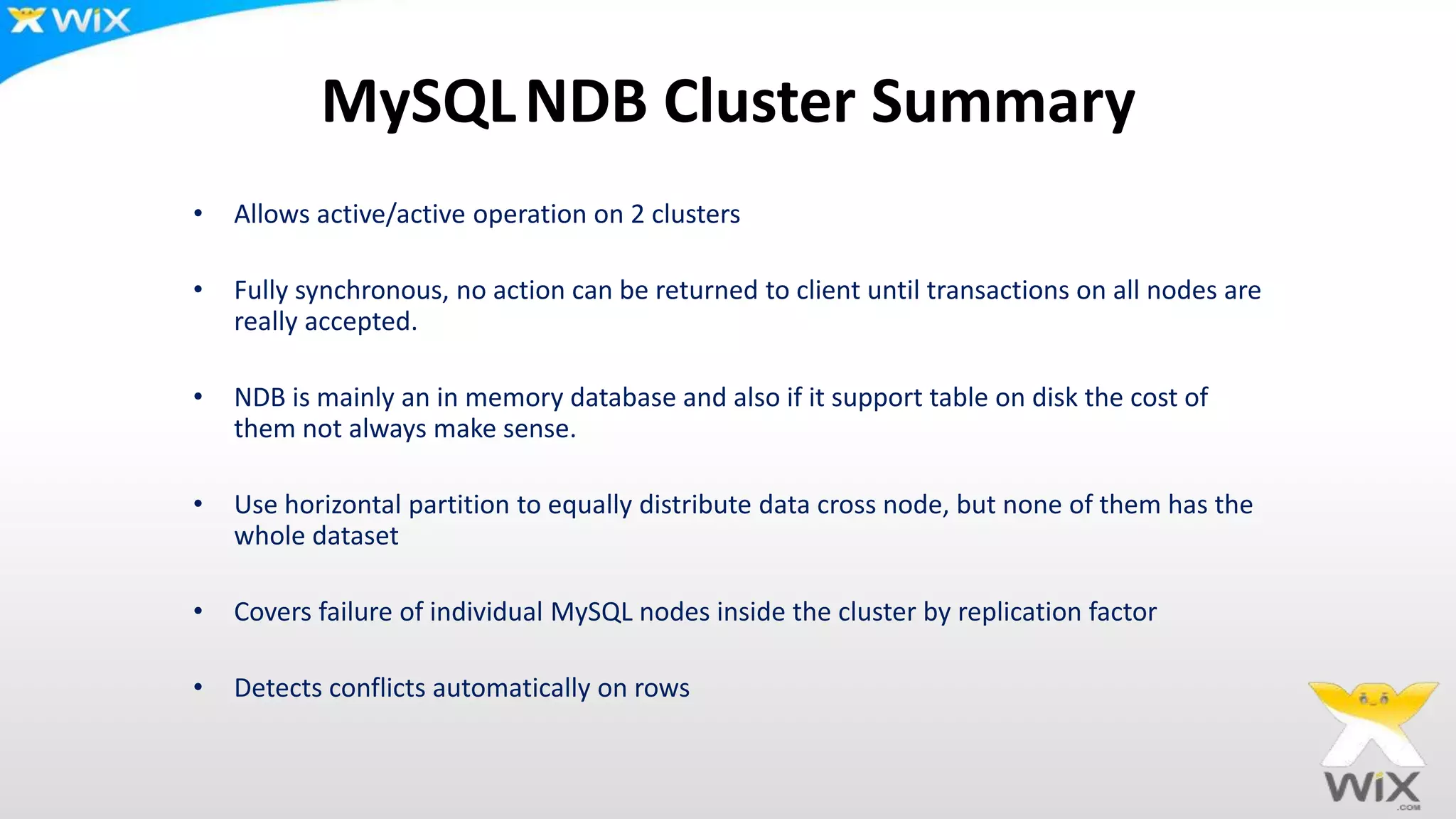
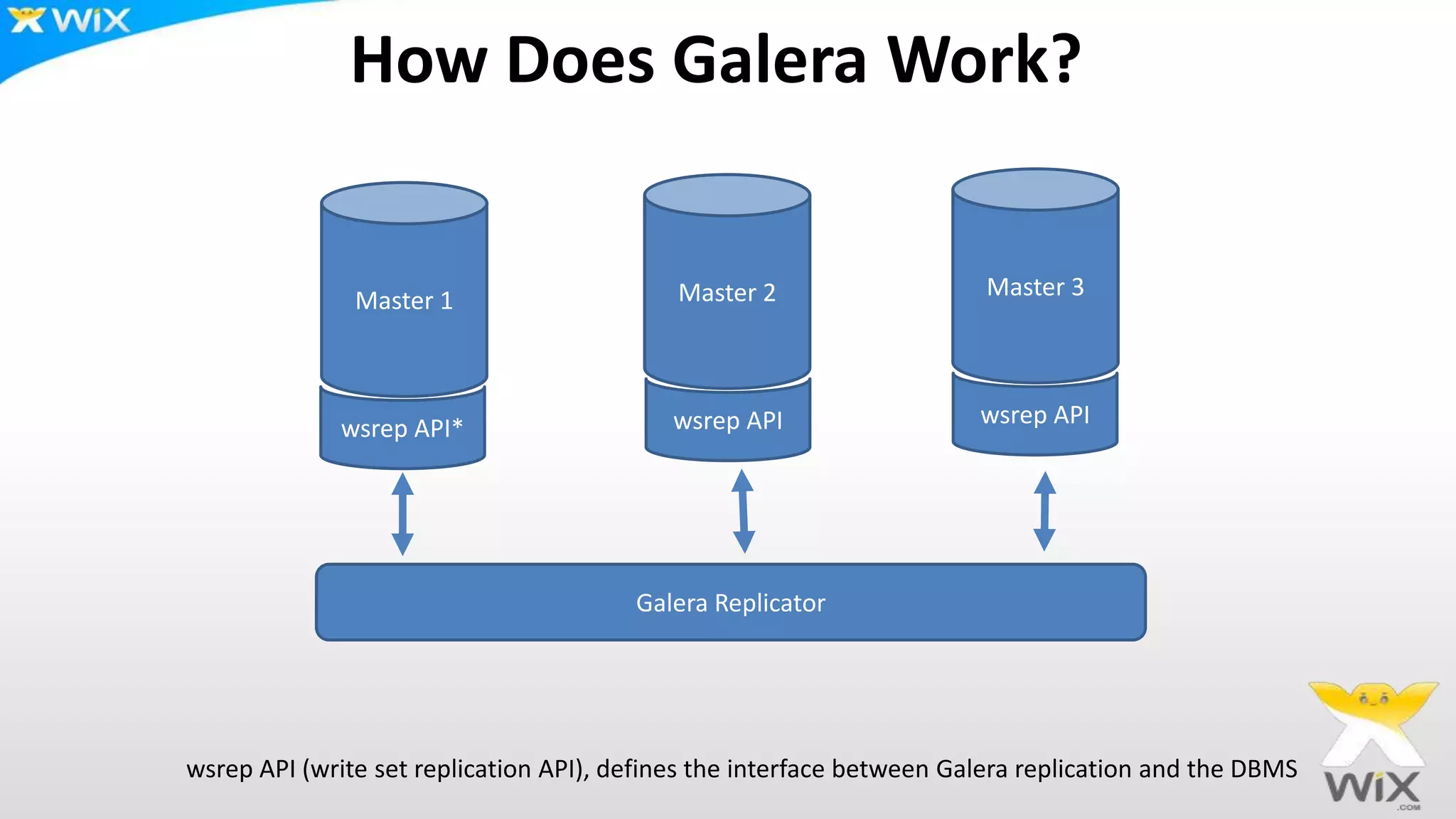
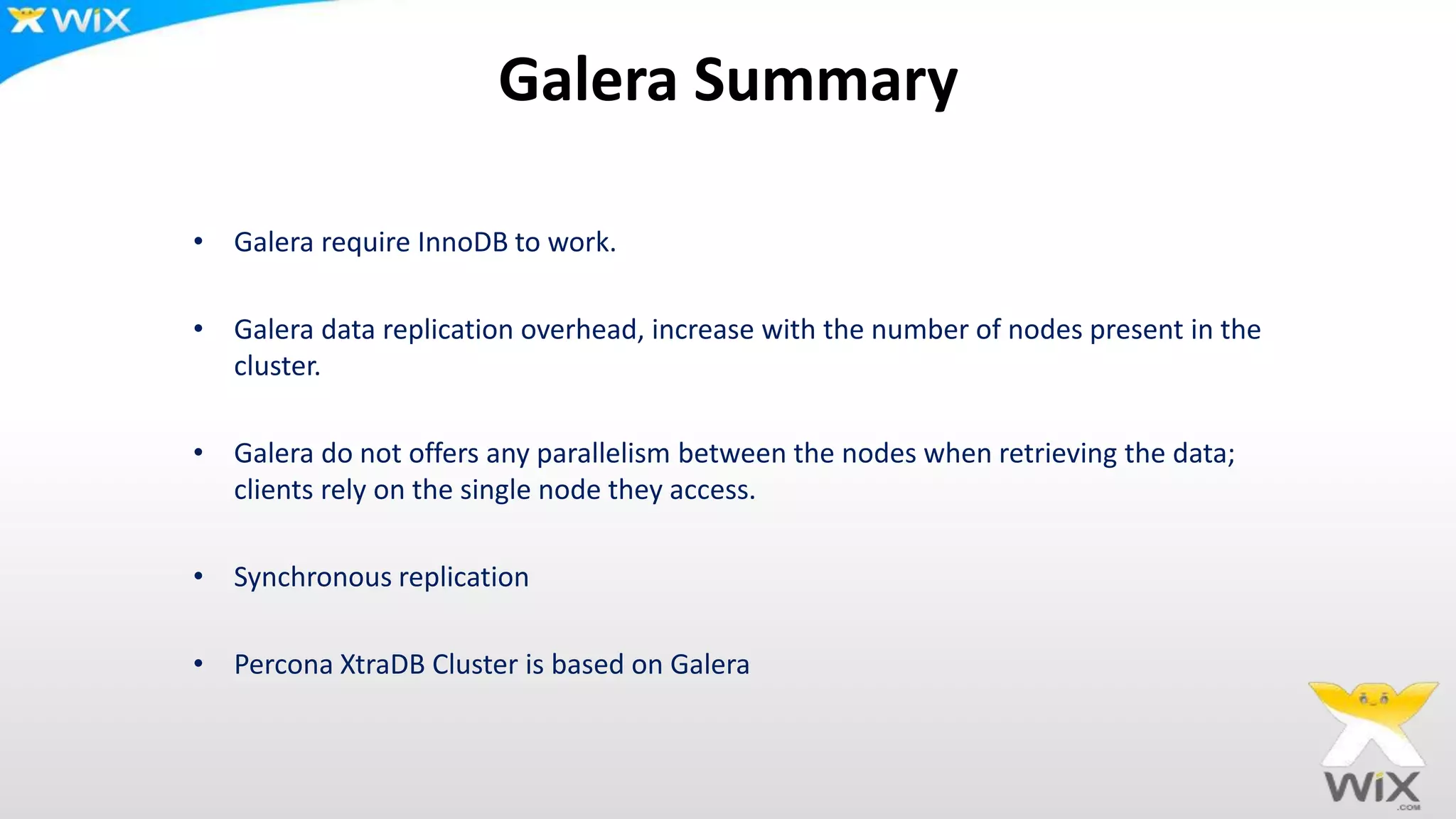
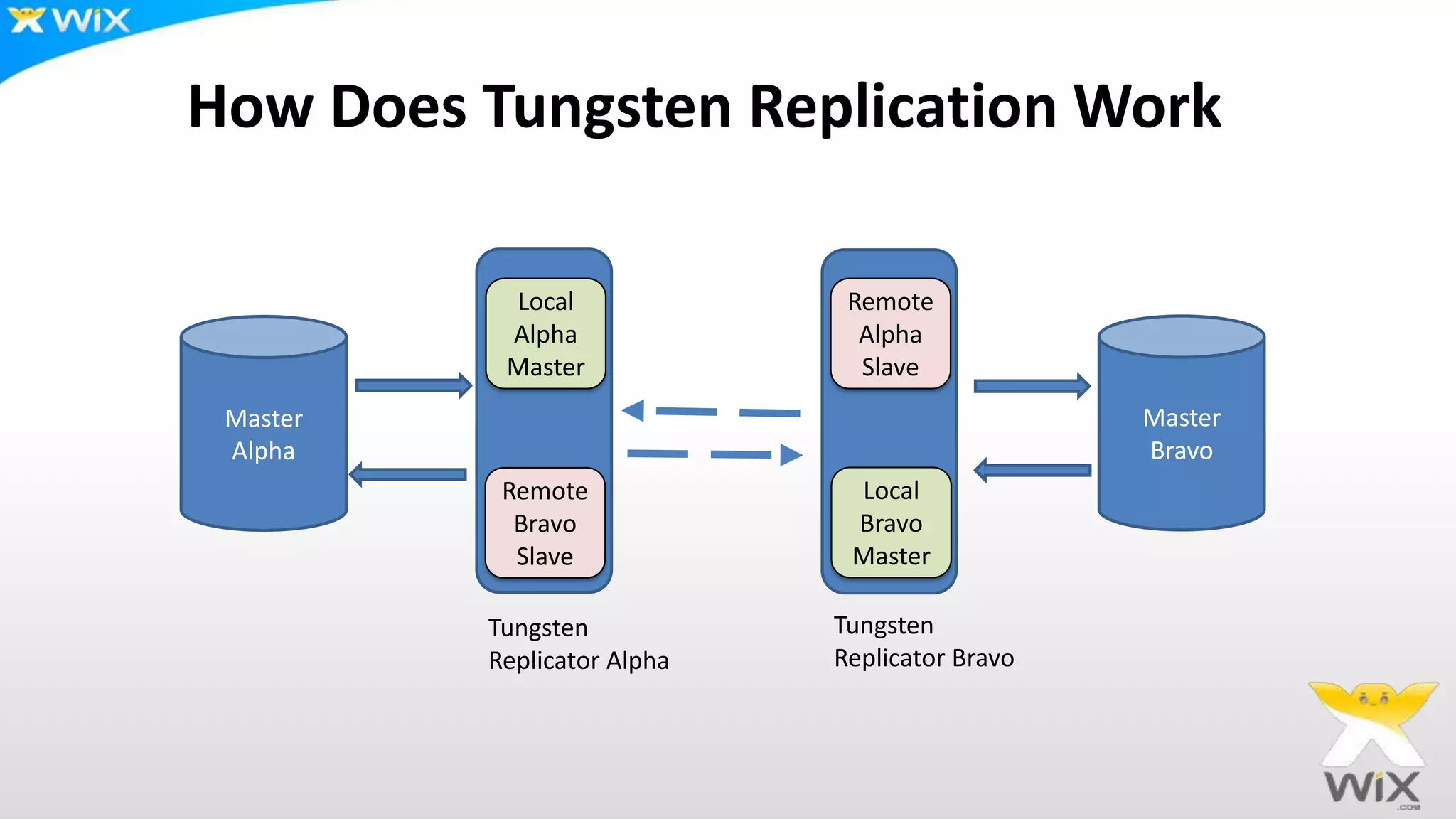
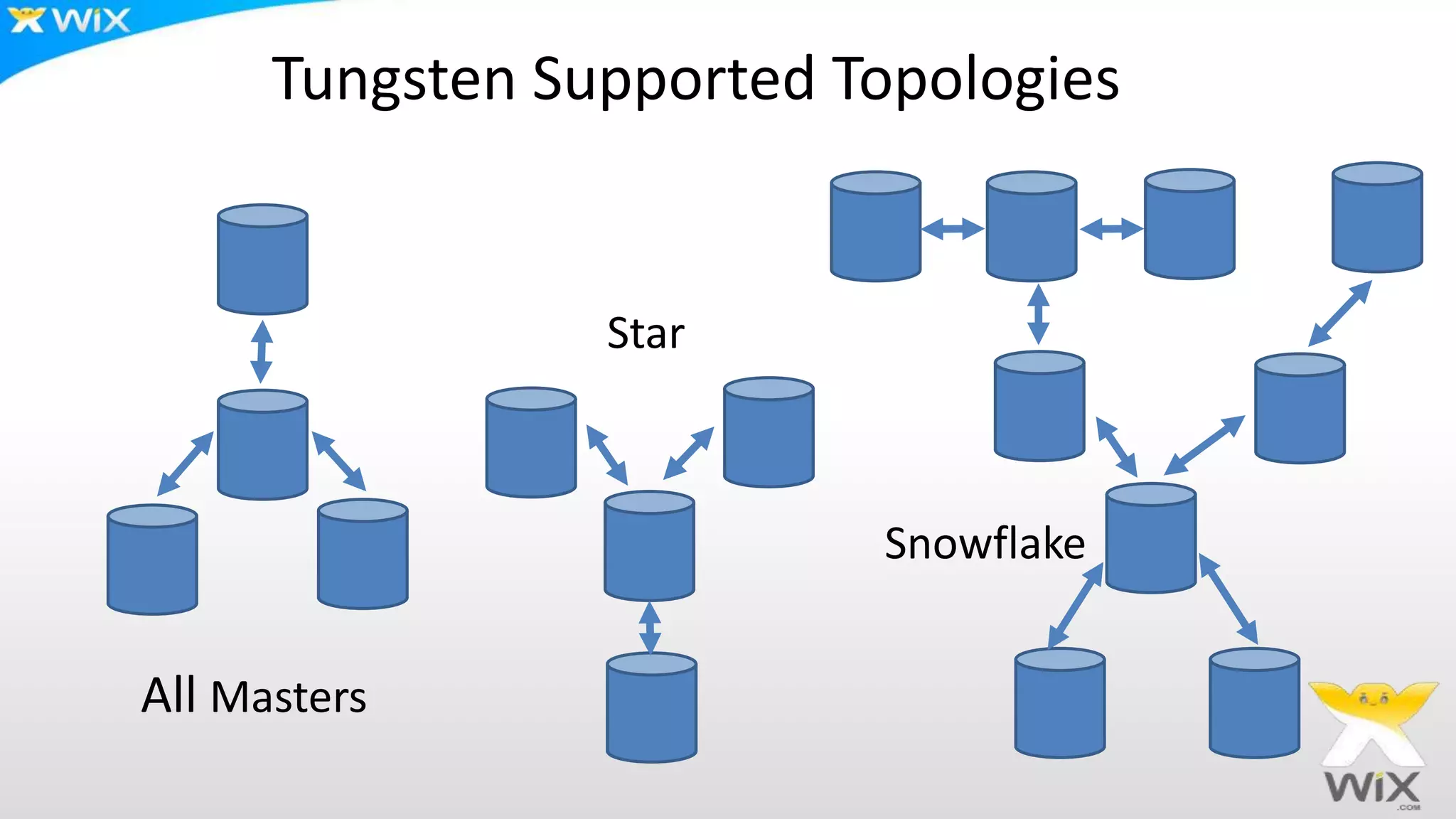
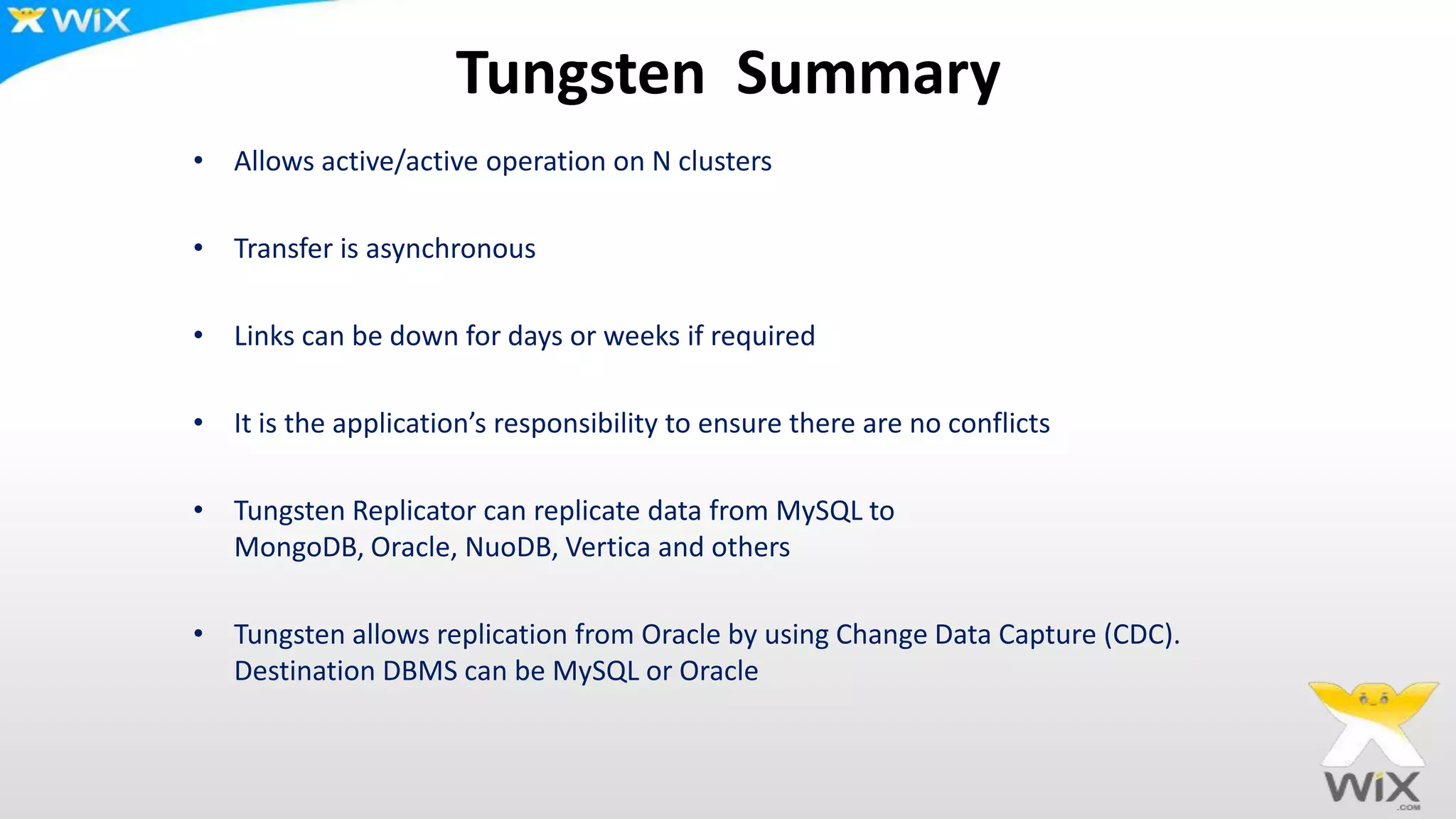
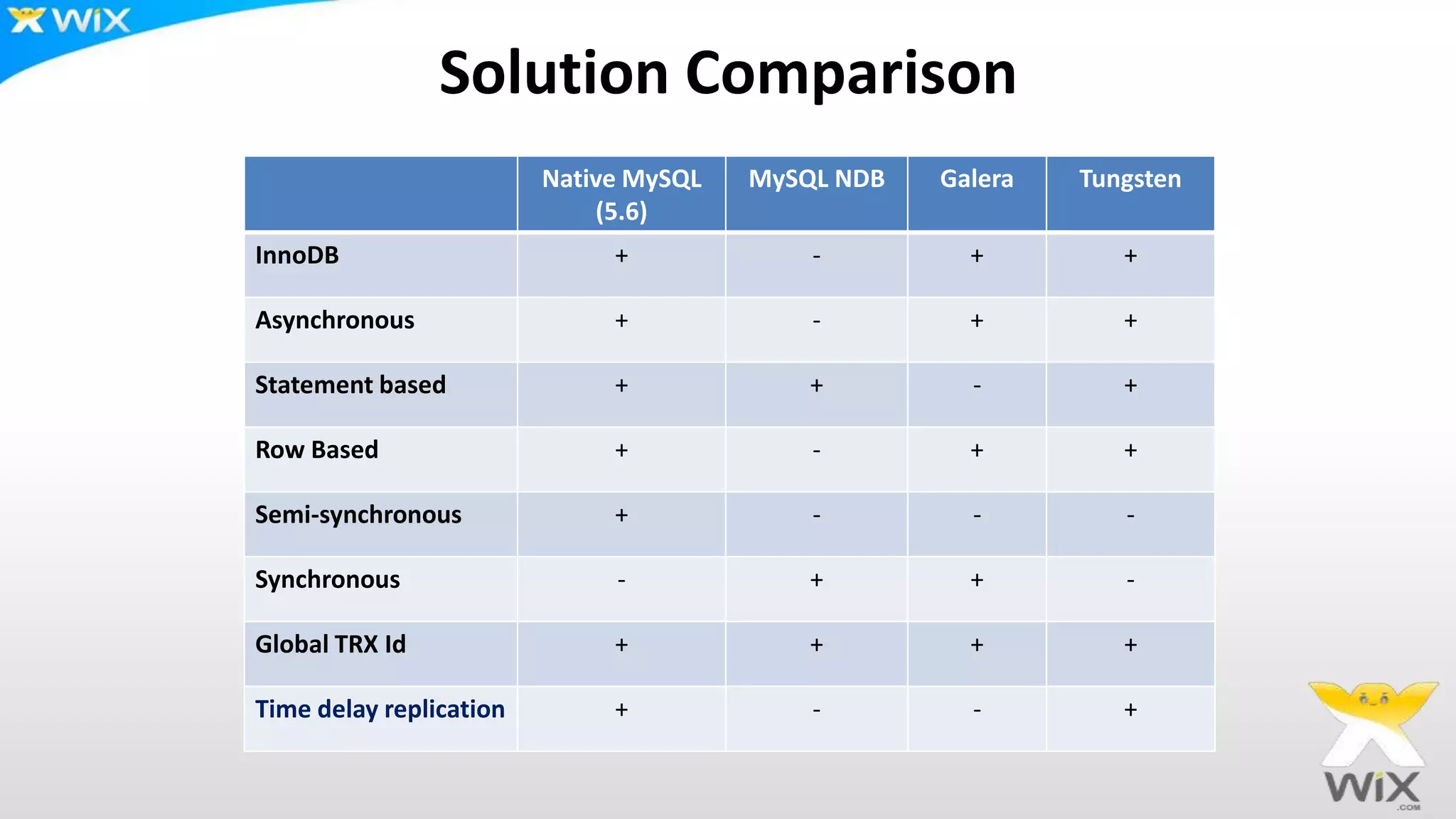
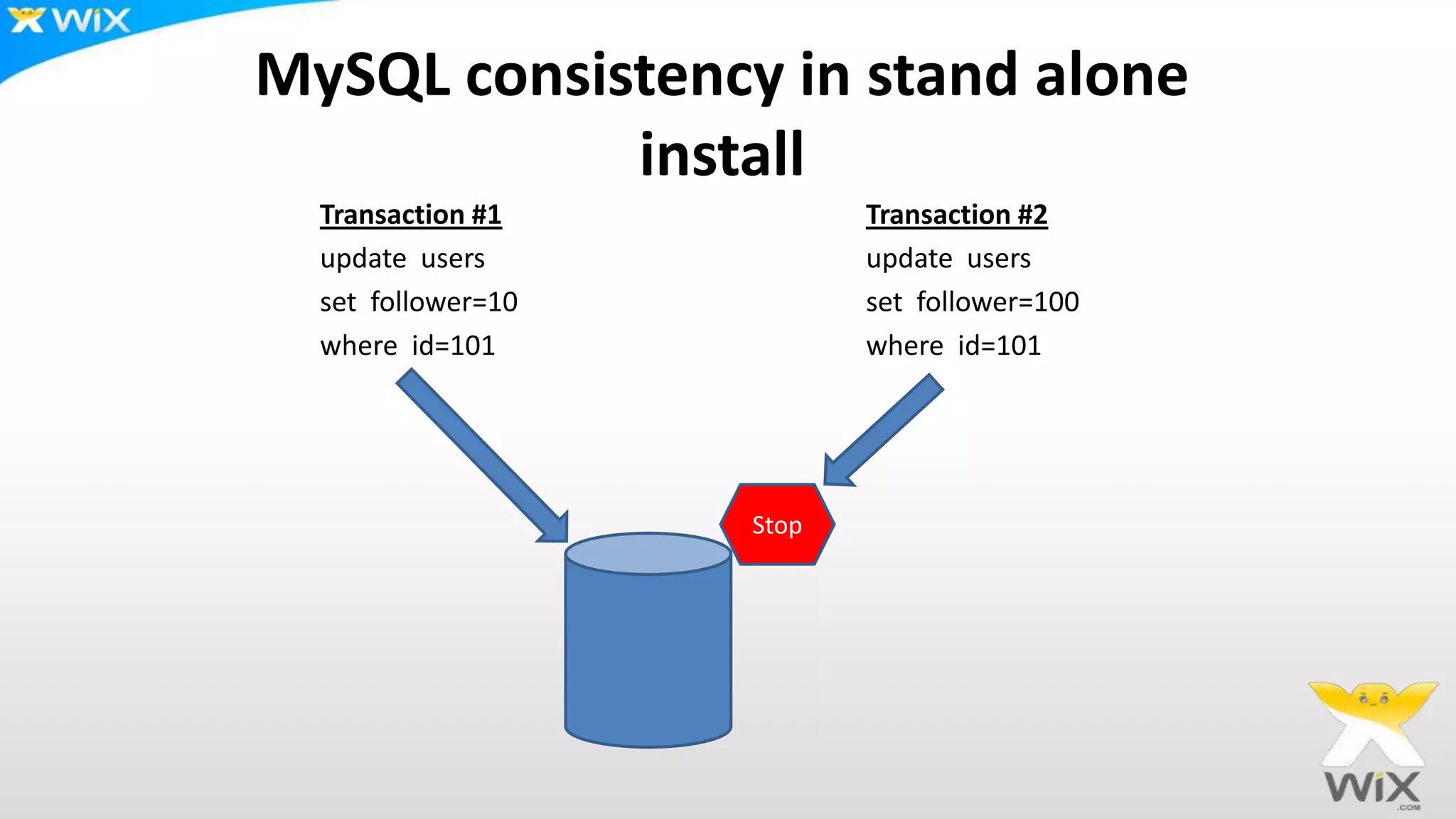
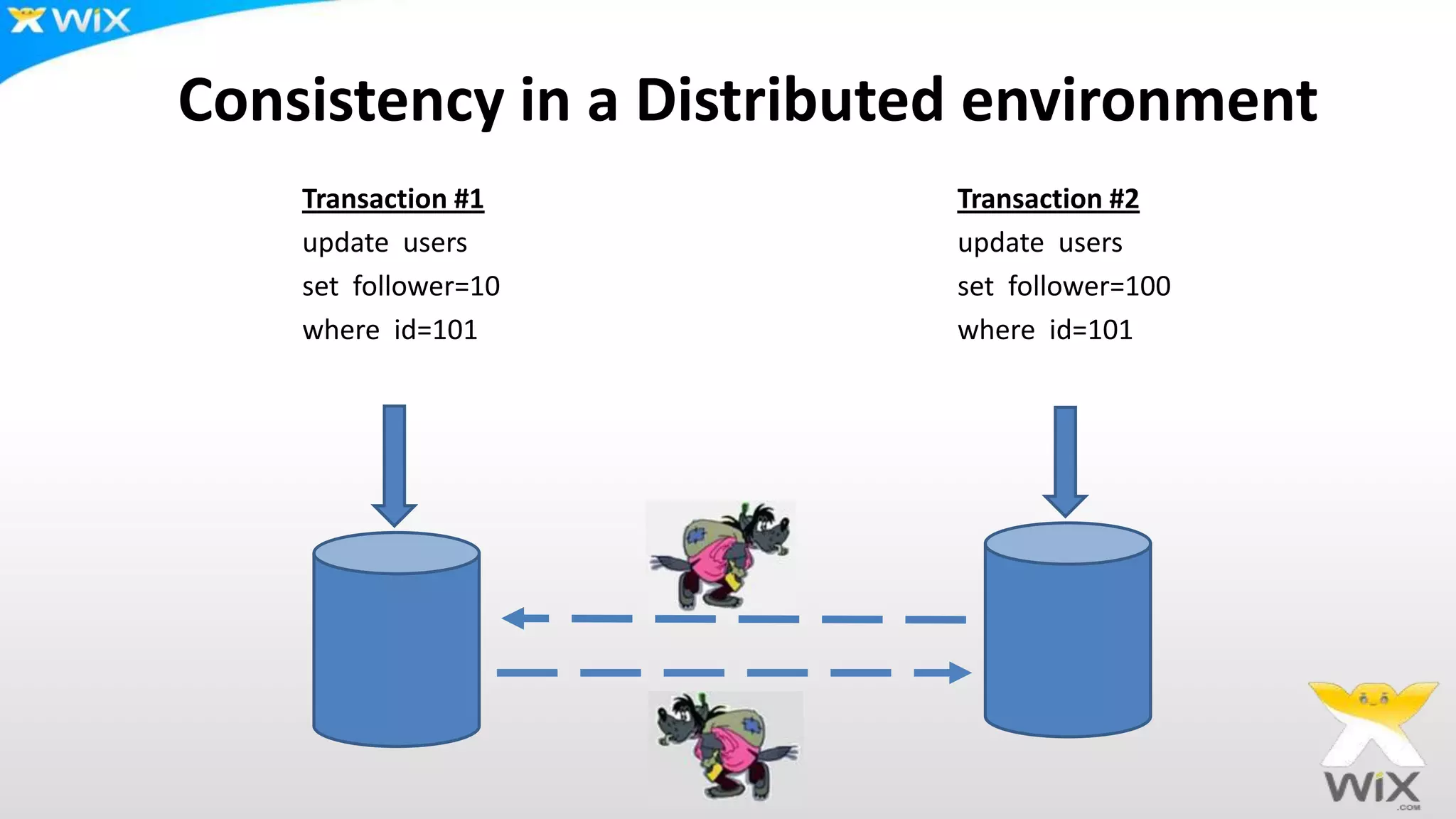
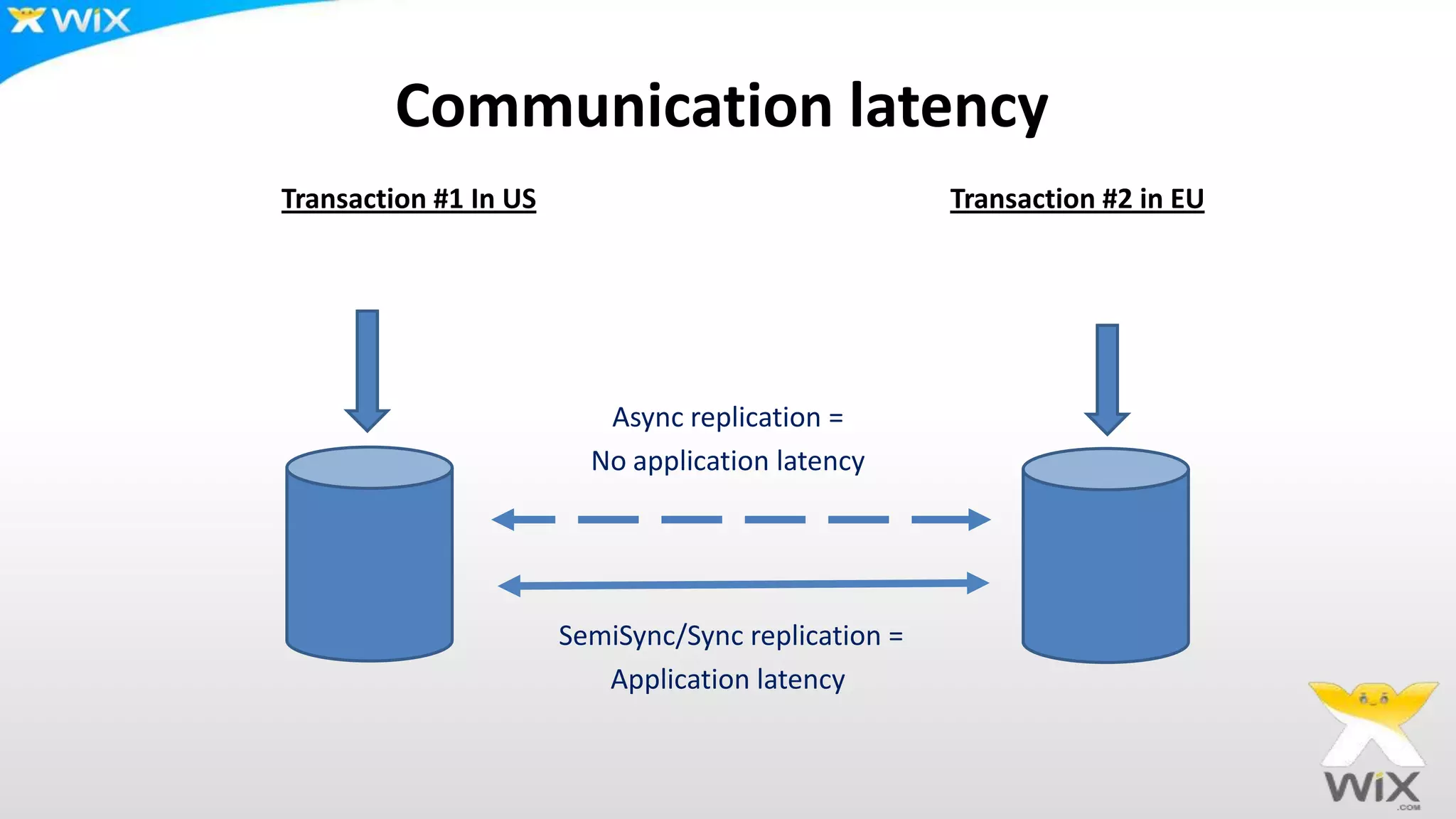
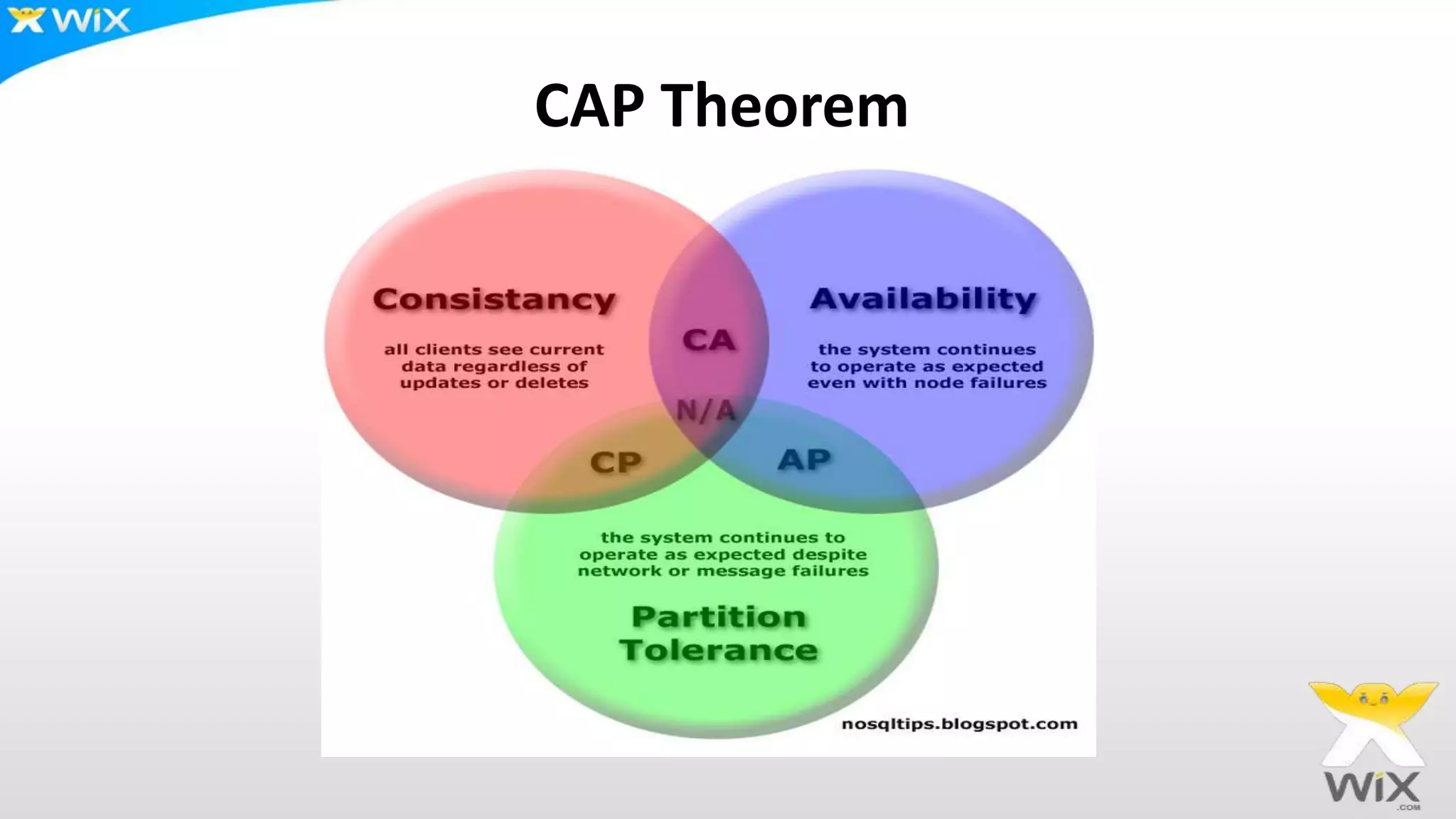
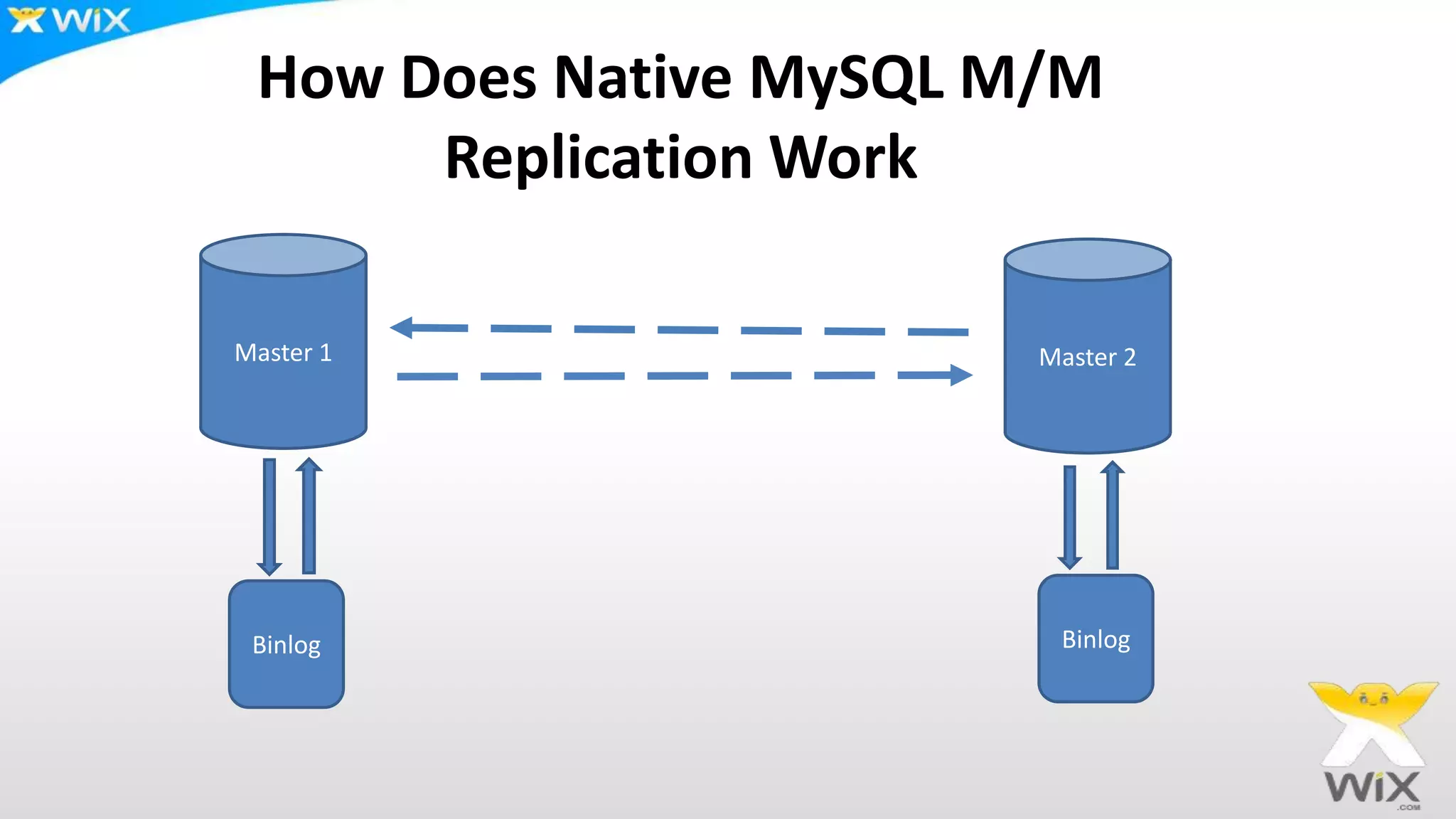
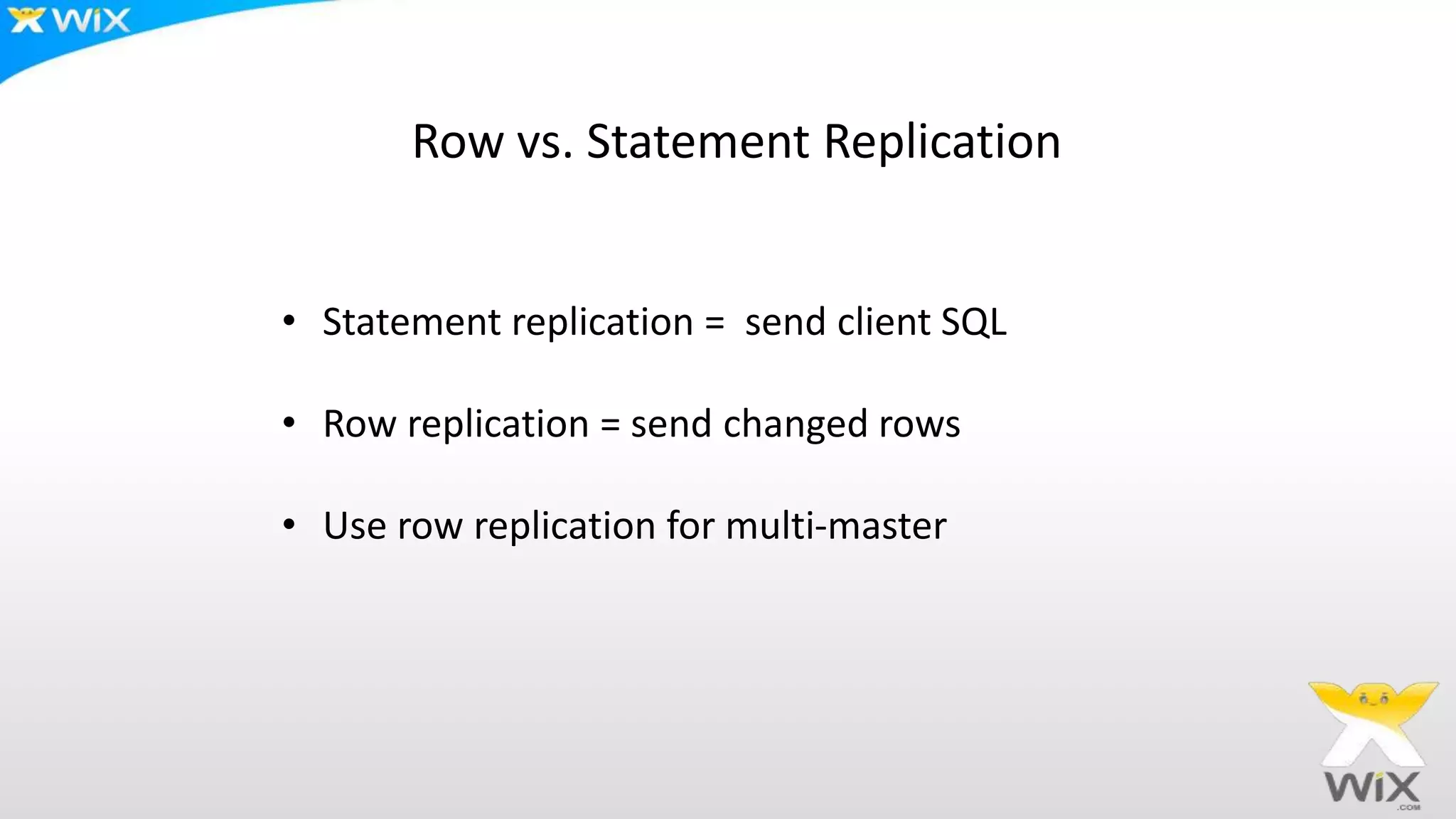
This document summarizes and compares several solutions for multi-master replication in MySQL databases: Native MySQL replication, MySQL Cluster (NDB), Galera, and Tungsten. Native MySQL replication supports only limited topologies and has asynchronous replication. MySQL Cluster allows synchronous replication across two data centers but is limited to in-memory tables. Galera provides synchronous, row-based replication across multiple masters with automatic conflict resolution. Tungsten allows asynchronous multi-master replication to different database systems and automatic failover.






![Auto-Increment Key Offsets
• Set different keys on each server to avoid primary key collisions
[my.cnf]
server-id=1
auto-increment-offset = 1
auto-increment-increment = 4
...
[my.cnf]
server-id=2
auto-increment-offset = 2
auto-increment-increment = 4
...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlmultimasterreplication-130912160956-phpapp02/75/MySQL-Multi-Master-Replication-13-2048.jpg)