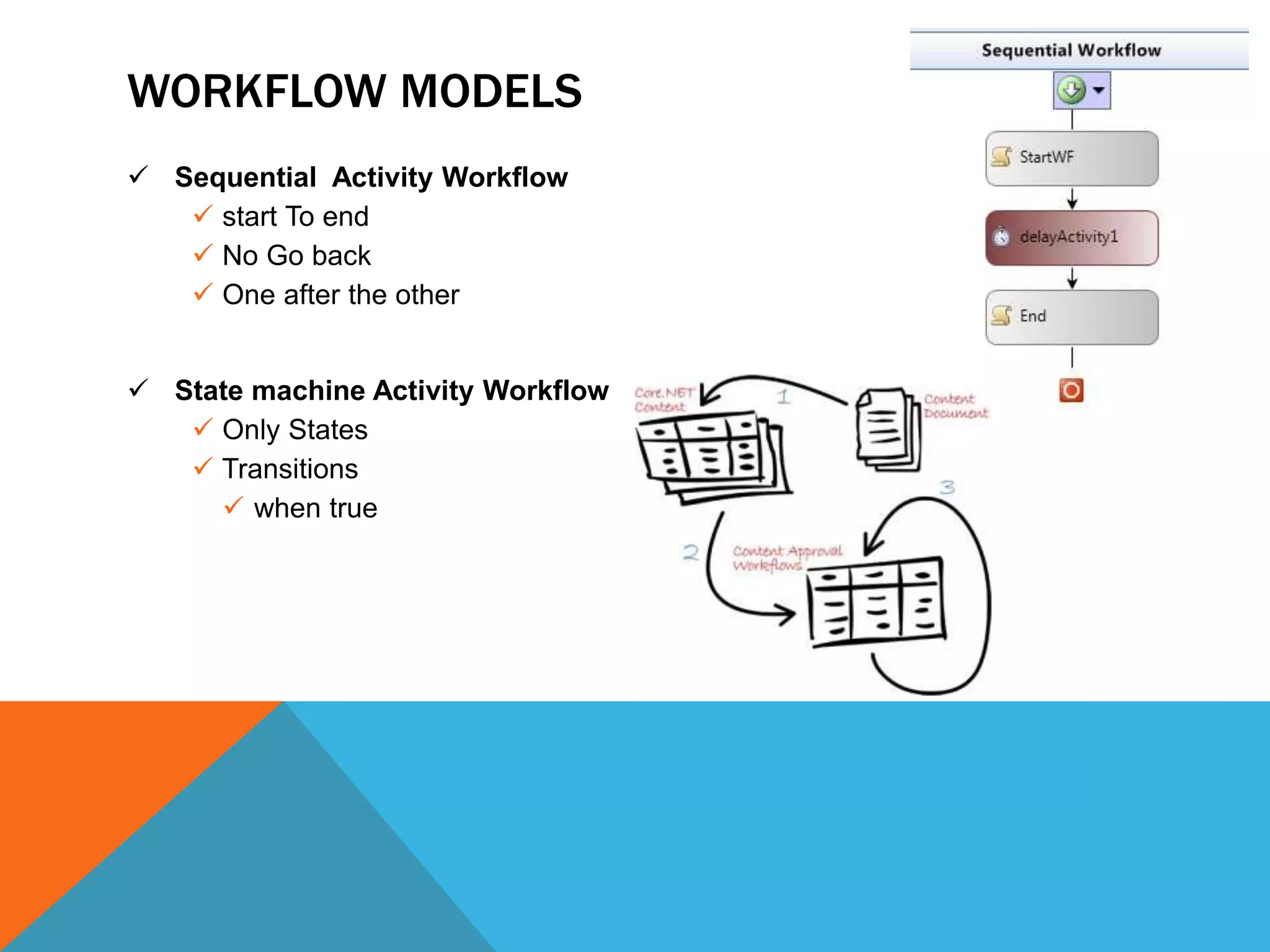
This document discusses workflows and activities. It defines a workflow as a set of activities that describes a real-world process. Activities store data using variables, arguments, and expressions. Workflows define the order and dependencies of activities from start to finish. There are two main types of workflow models - sequential and state machine. The document also discusses activity life cycles, passing parameters in and out of workflows, and how to create custom reusable activities.