Assignment 2
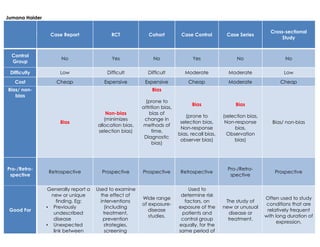
- 1. Jumana Haider Case Report RCT Cohort Case Control Case Series Cross-sectional Study Control Group No Yes No Yes No No Difficulty Low Difficult Difficult Moderate Moderate Low Cost Cheap Expensive Expensive Cheap Moderate Cheap Bias/ non- bias Bias Non-bias (minimizes allocation bias, selection bias) Bias (prone to attrition bias, bias of change in methods of time, Diagnostic bias) Bias (prone to selection bias, Non-response bias, recall bias, observer bias) Bias (selection bias, Non-response bias, Observation bias) Bias/ non-bias Pro-/Retro- spective Retrospective Prospective Prospective Retrospective Pro-/Retro- spective Prospective Good For Generally report a new or unique finding. Eg: • Previously undescribed disease • Unexpected link between Used to examine the effect of interventions (including treatment, prevention strategies, screening Wide range of exposure- disease studies. Used to determine risk factors, on exposure of the patients and control group equally, for the same period of The study of new or unusual disease or treatment. Often used to study conditions that are relatively frequent with long duration of expression.
- 2. Jumana Haider diseases • Unexpected new therapeutic effect • Adverse events. programs and diagnostic tests) on particular outcomes such as death or reoccurrence of disease. time. Time Short Long Long Short Short Short Need for Follow Up No Yes Yes Yes Yes No Summary & Comments A quick communication. A report based on a single case of a condition. Often a rare condition. Sometimes collected together into a short series. Aims to evaluate efficacy of a new medication or treatment modality. The Control and Test groups should be similar in terms of other significant factors (sex, age, other known risk factors etc). Aim is to observe changes related to a particular group of individuals . A case- control study, although retrospective , is superior to a case series because of the presence of a control group. Certain types of study bias are unique to case-control Studies (eg: hospital bias). A Case series may be a study that samples patients with both, a specific outcome and a specific exposure, or one that samples patients with a specific outcome and includes patients regardless of whether they have specific exposures. A Cross-sectional study is an “observational” design that surveys exposures and disease status at a single point in time. It measures prevalence, not incidence of disease. Not suitable for studying rare or highly fatal diseases or a disease with short duration of expression.
- 3. Jumana Haider Resources: Songer, Thomas. “Study Designs in Epidemiologic Research.” Pittsburgh, PA: University of Pittsburgh. Abdulla, Nizam. “Evidence-Based Dentistry”. Australia, Adelaide: The University of Adelaide, School of Dentistry. Harold O. Stolberg, Geoffrey Norman and Isabella Trop. “Randomized Controlled Trials.” American Journal of Roentgenology. Dec2004, Volume 183, Number 6. White E., Hunt JR., Casso D. “Exposure measurement in cohohort studies: the challenges of prospective data collection.” Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle, WA, USA. Epidemiol Rev1998;20(1):43-56. Hess DR. “Retrospective studies and chart reviews.”Respiratory Care, Ellison 401, Massachusetts General Hospital, 55 Fruit Street, Boston, MA 02114, USA.2004 Oct;49(10):1171-4. Dekkers OM, Egger M, Altman DG, Vandenbroucke JP. “Distinguish case series from cohort studies.” Leiden University Medical Center, the Netherlands. Ann Intern Med. 2012 Jan 3;156(1 Pt 1):37-40.
