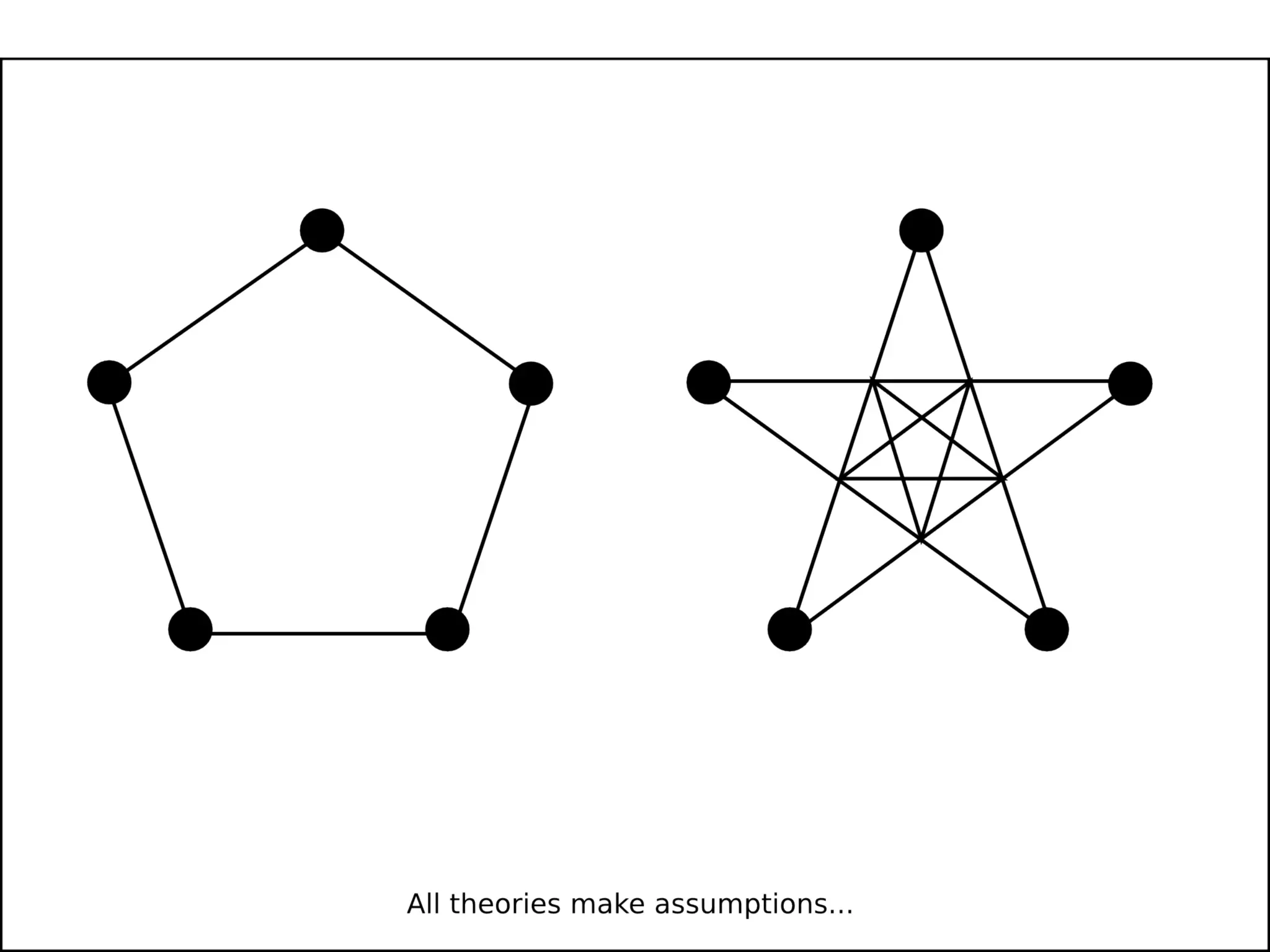
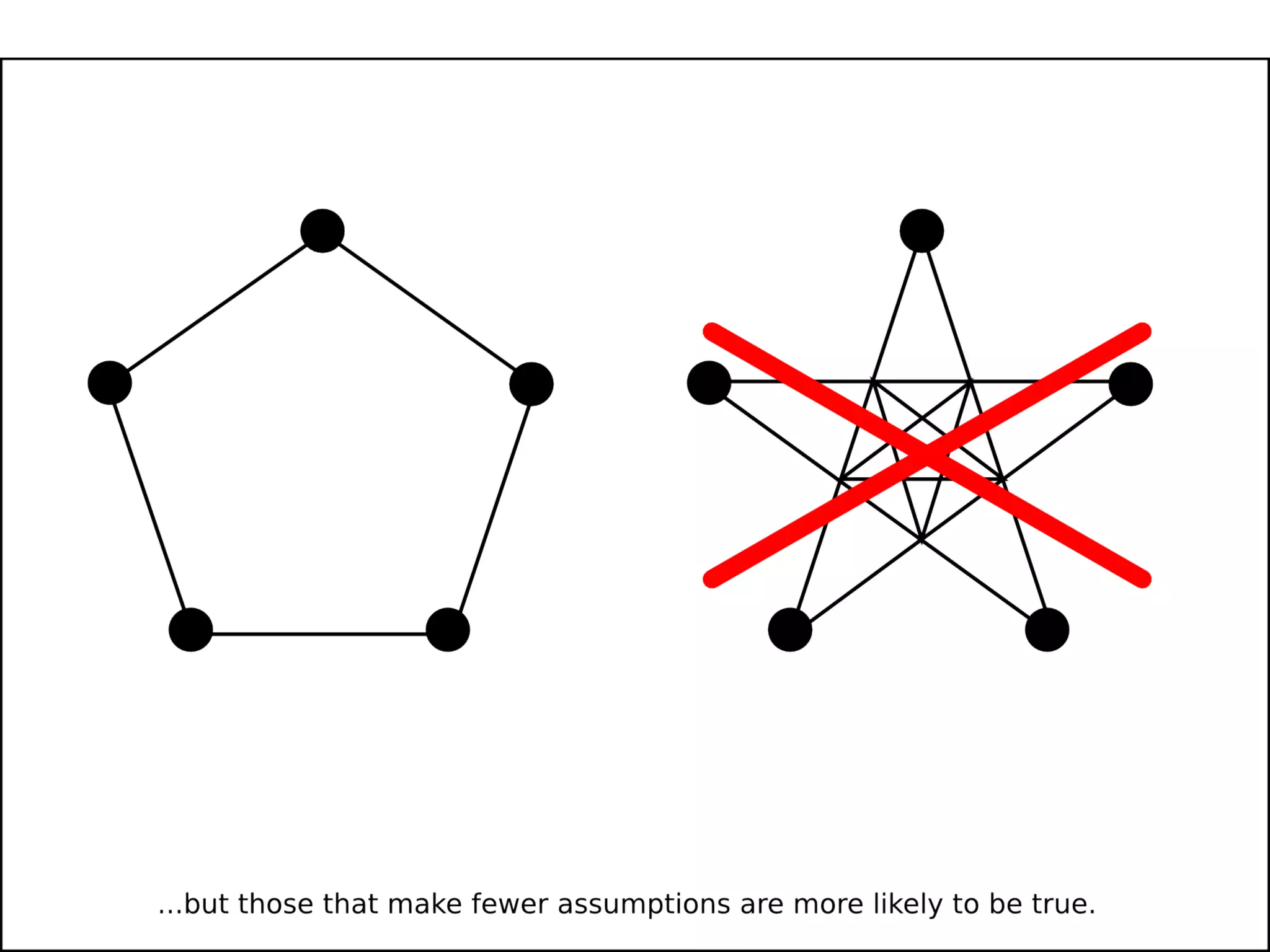
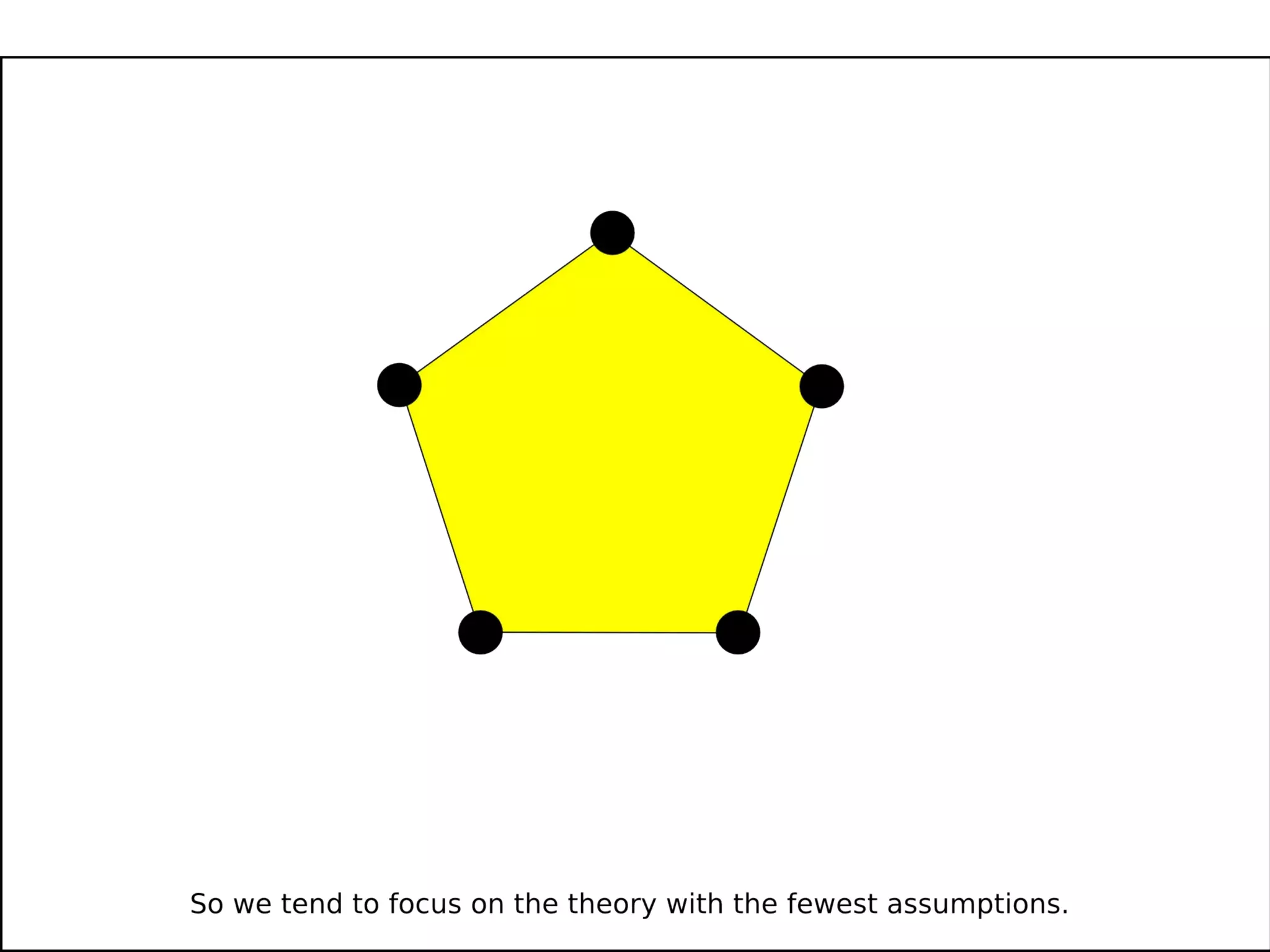
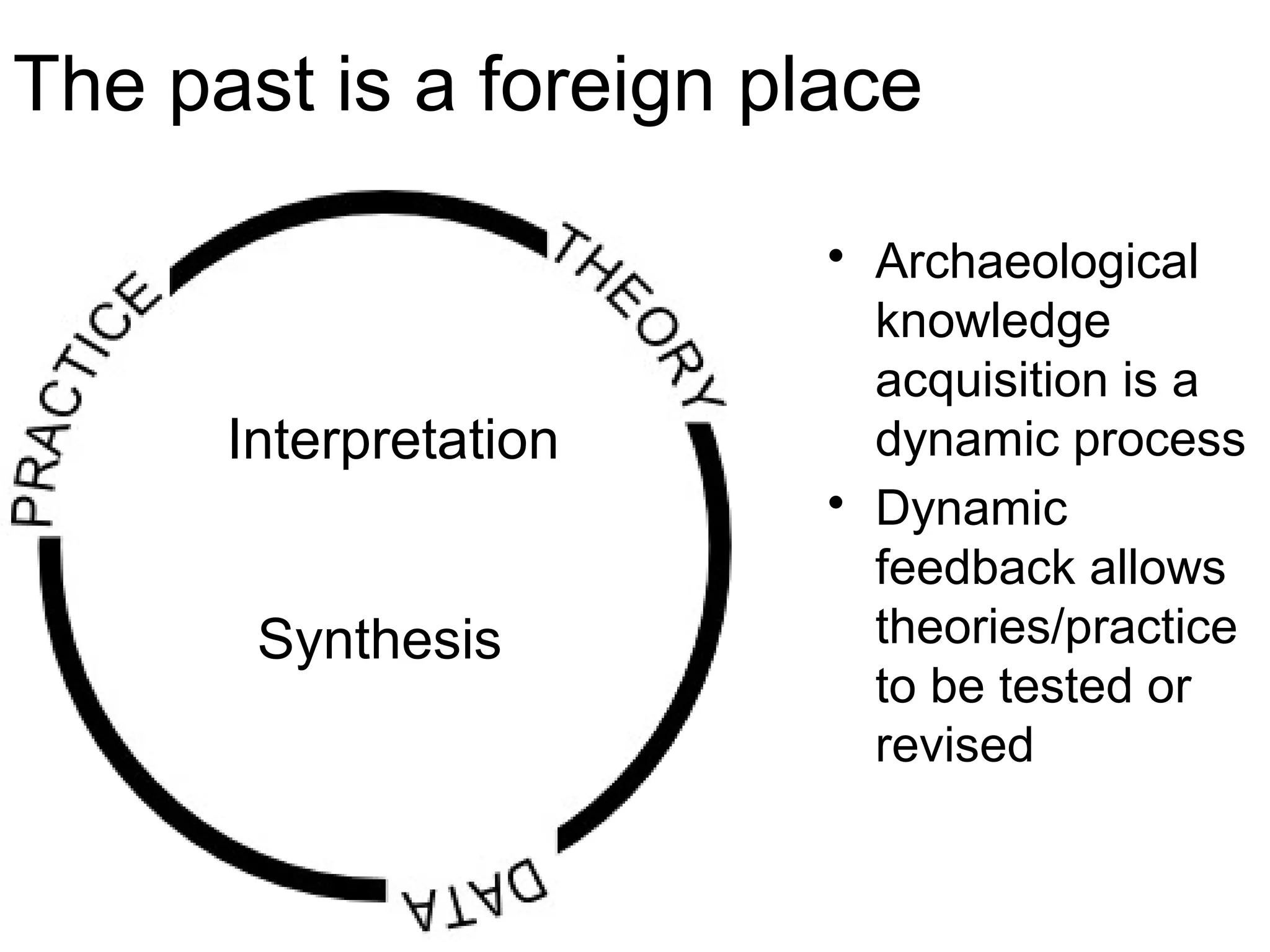
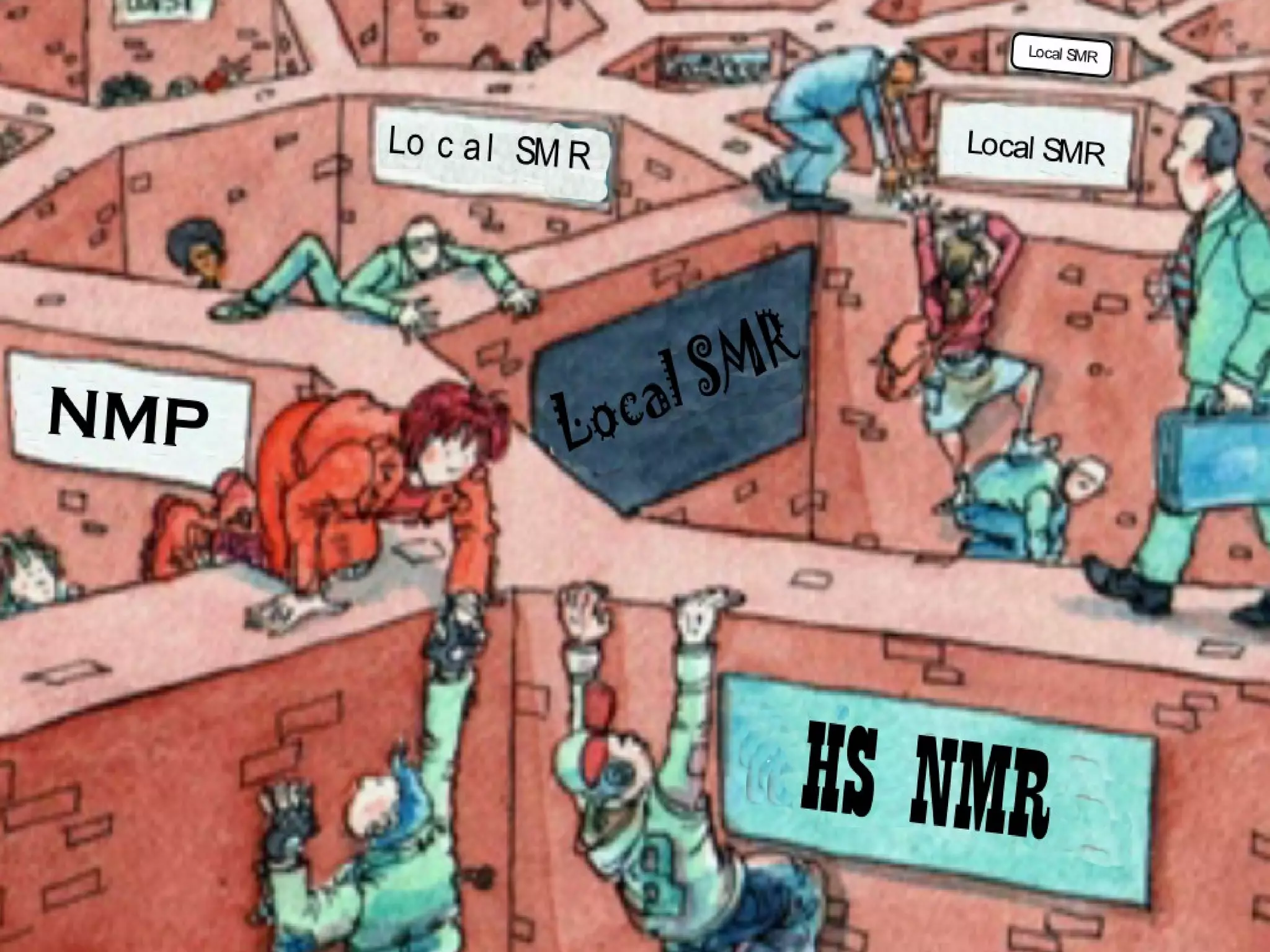
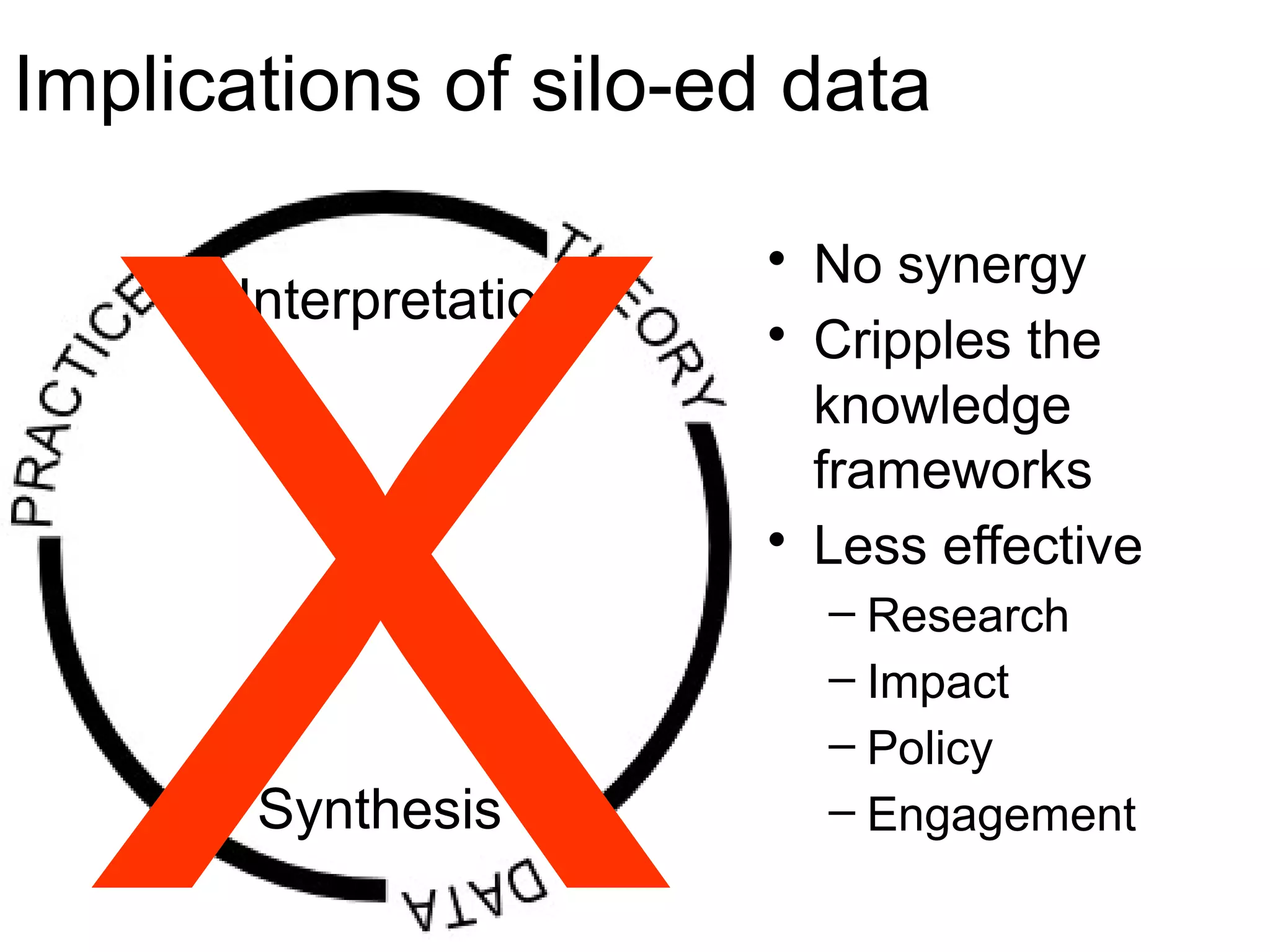
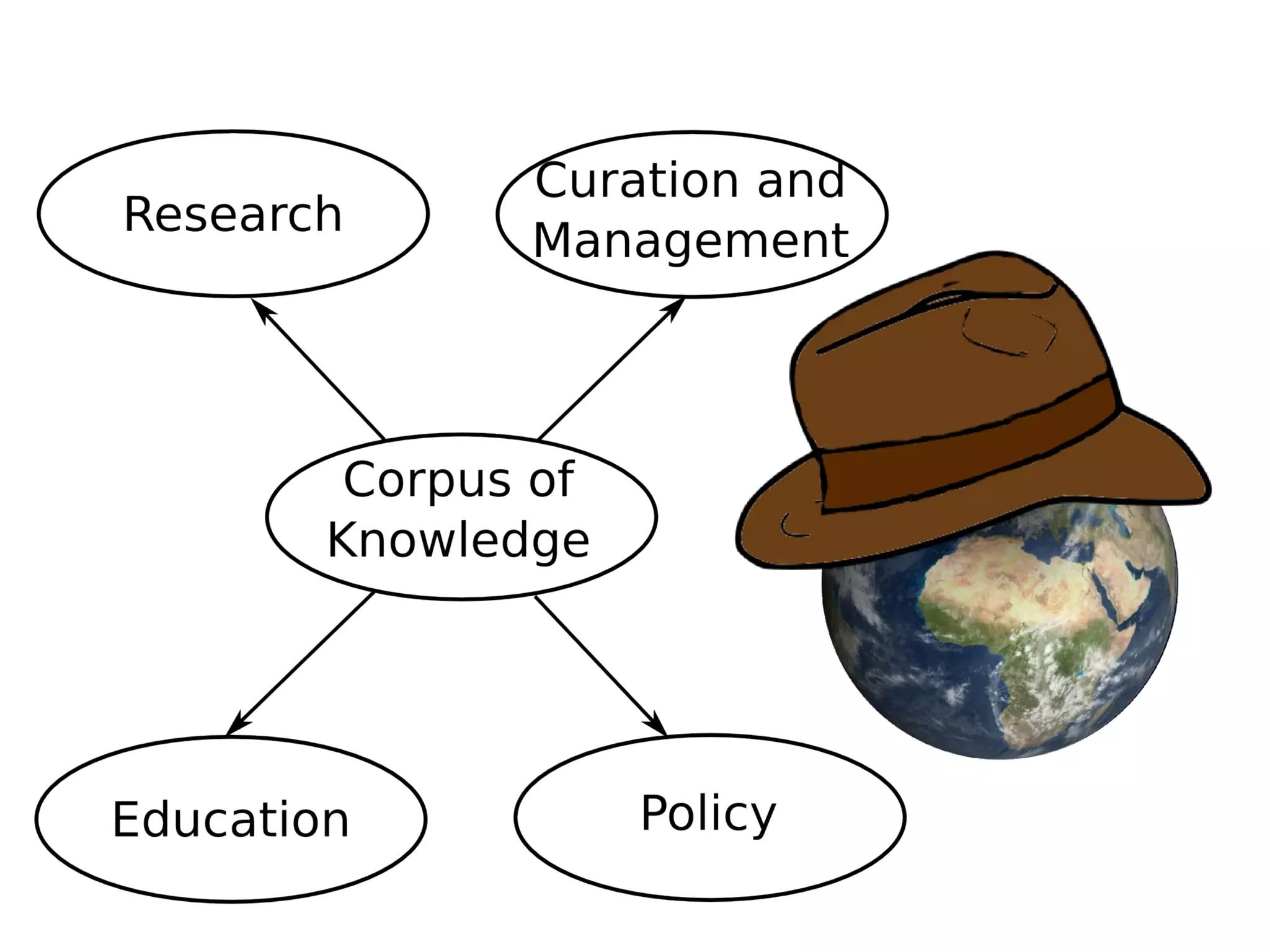
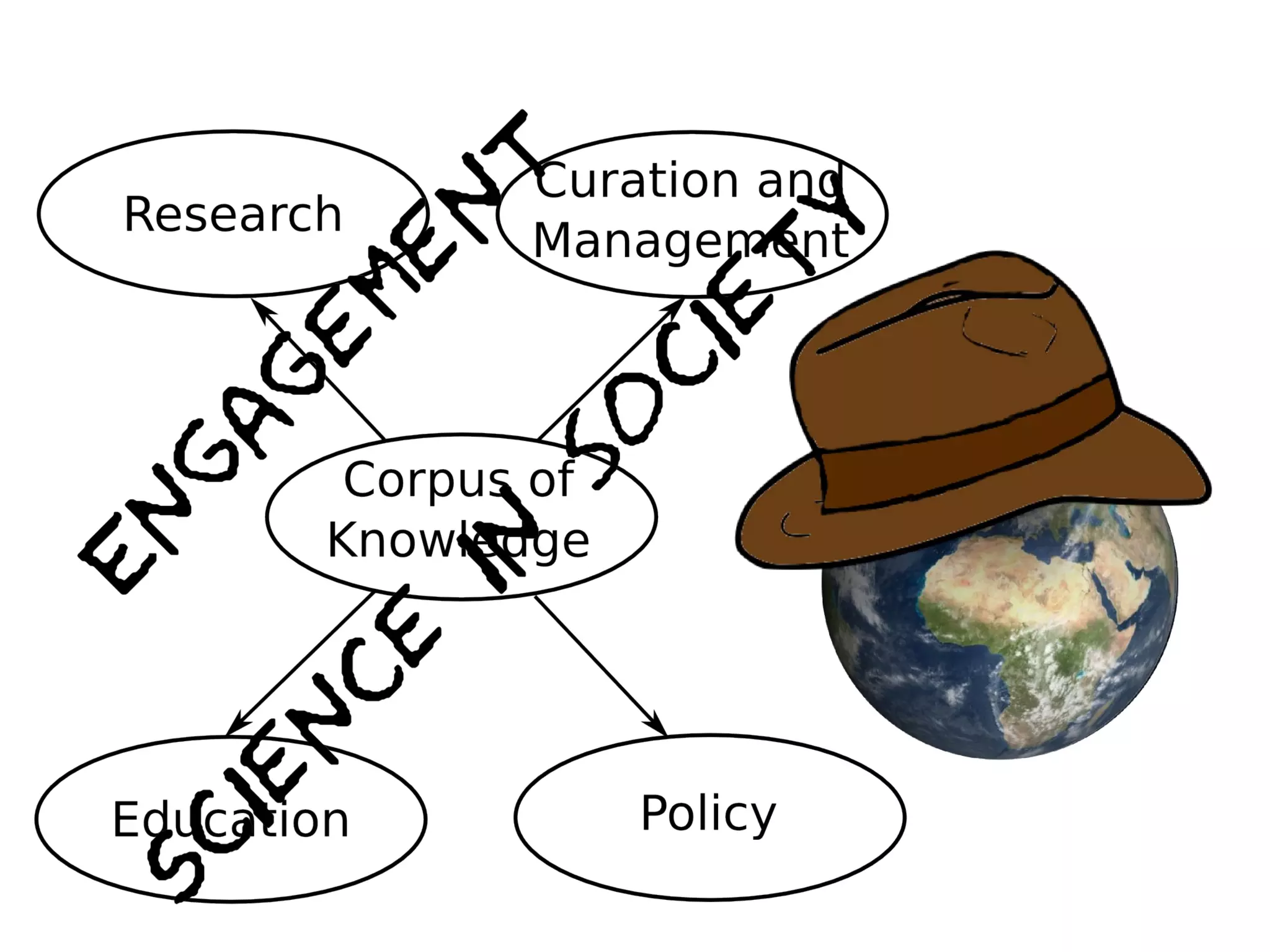
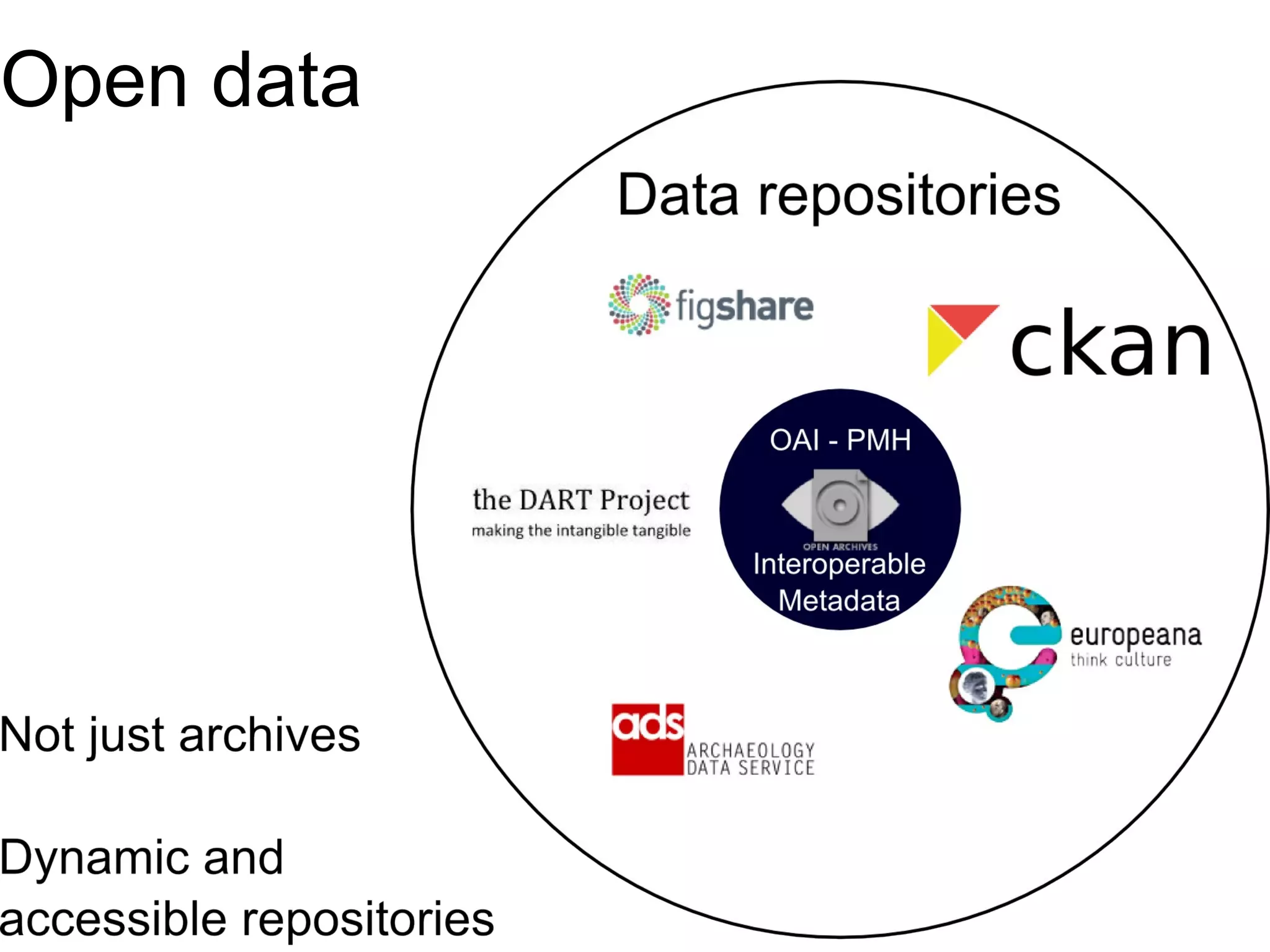
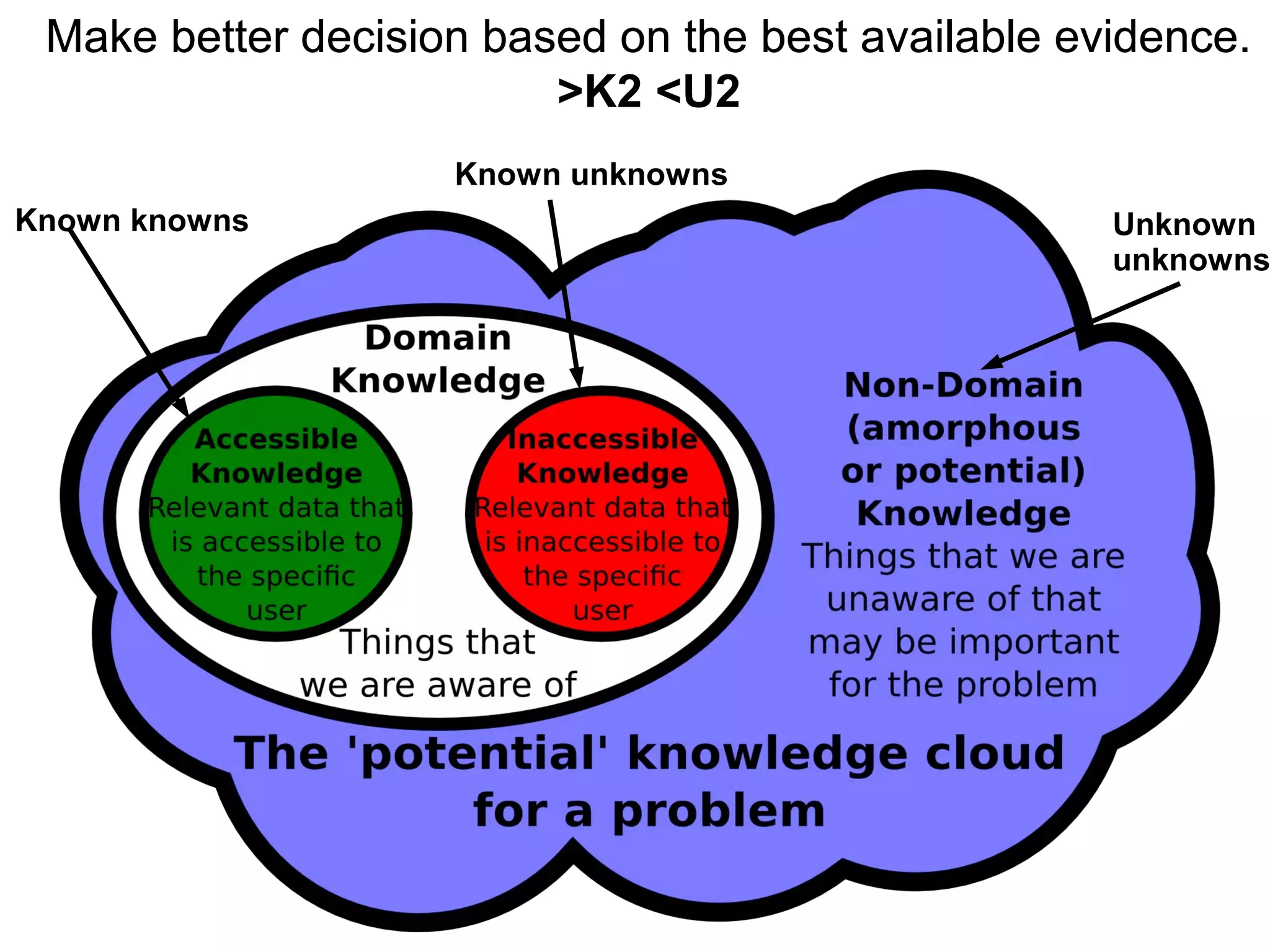
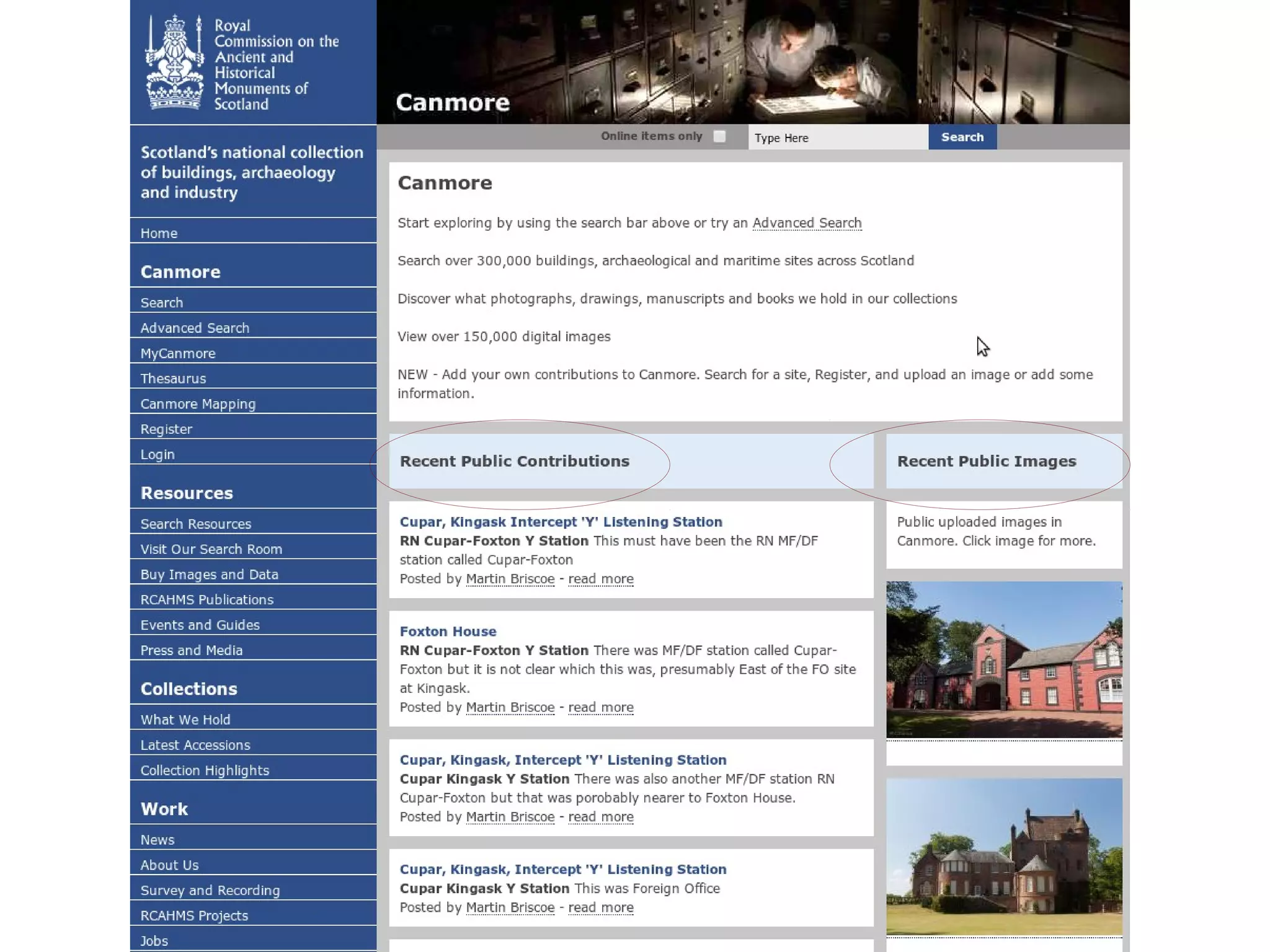
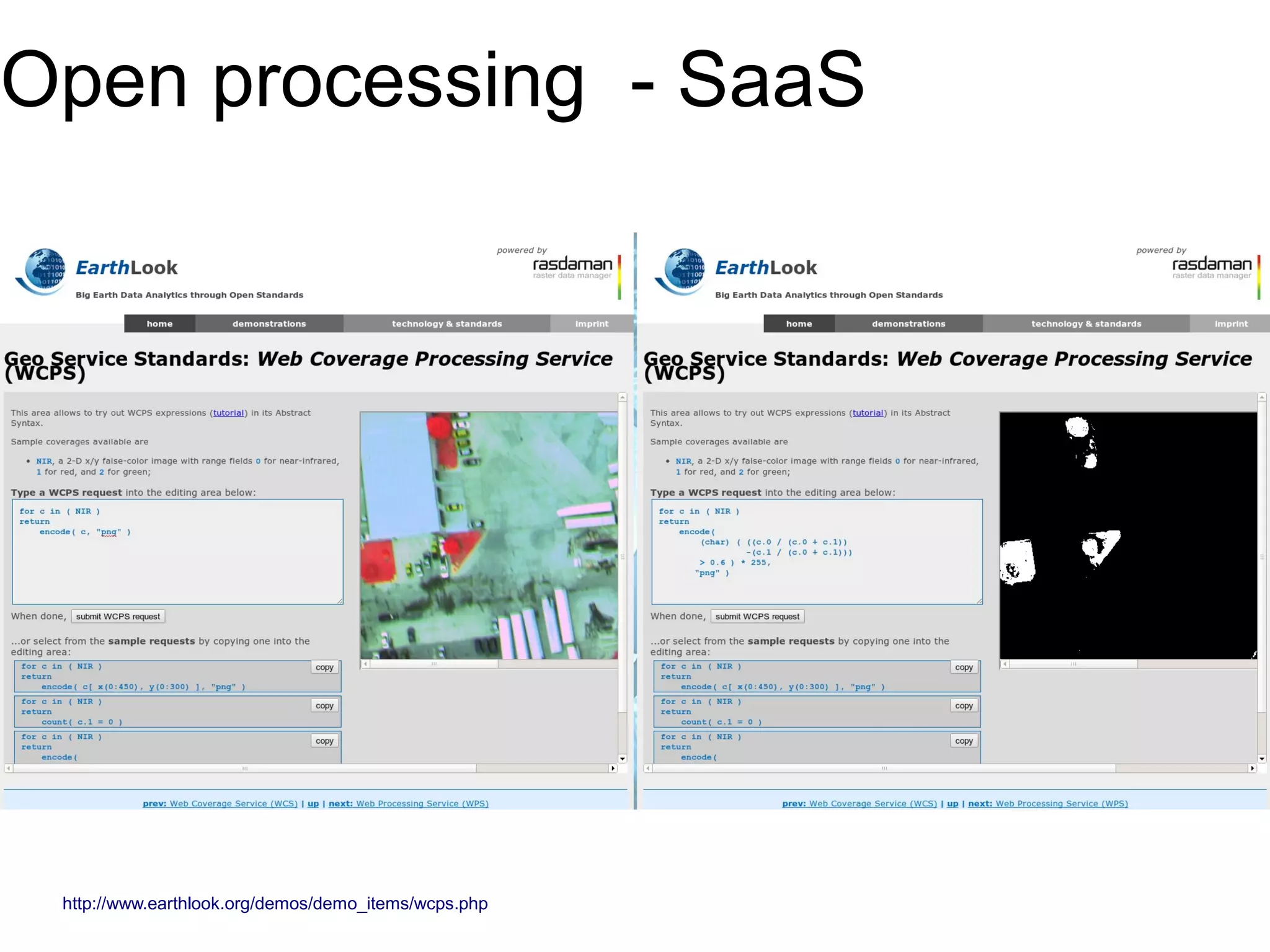
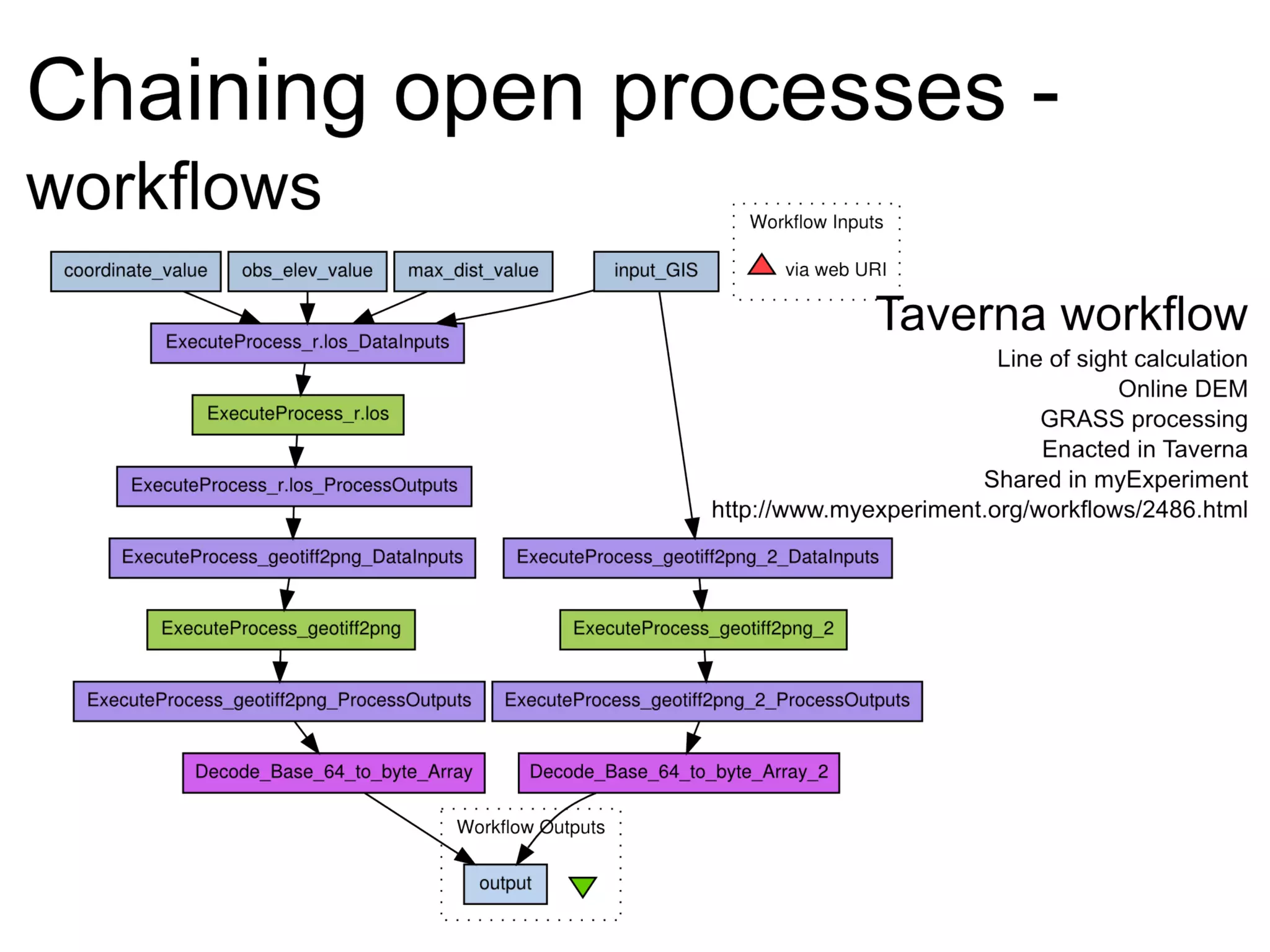
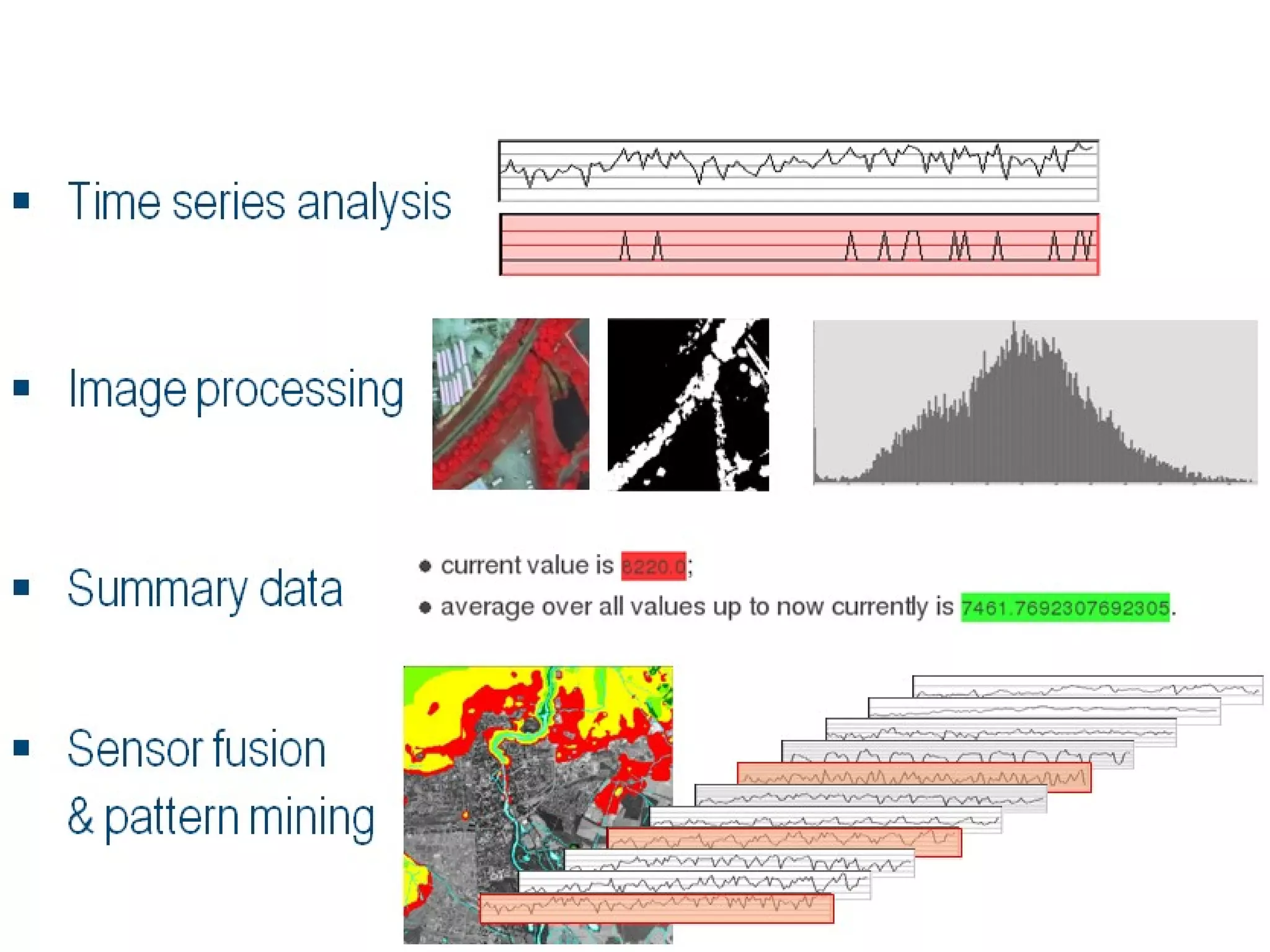
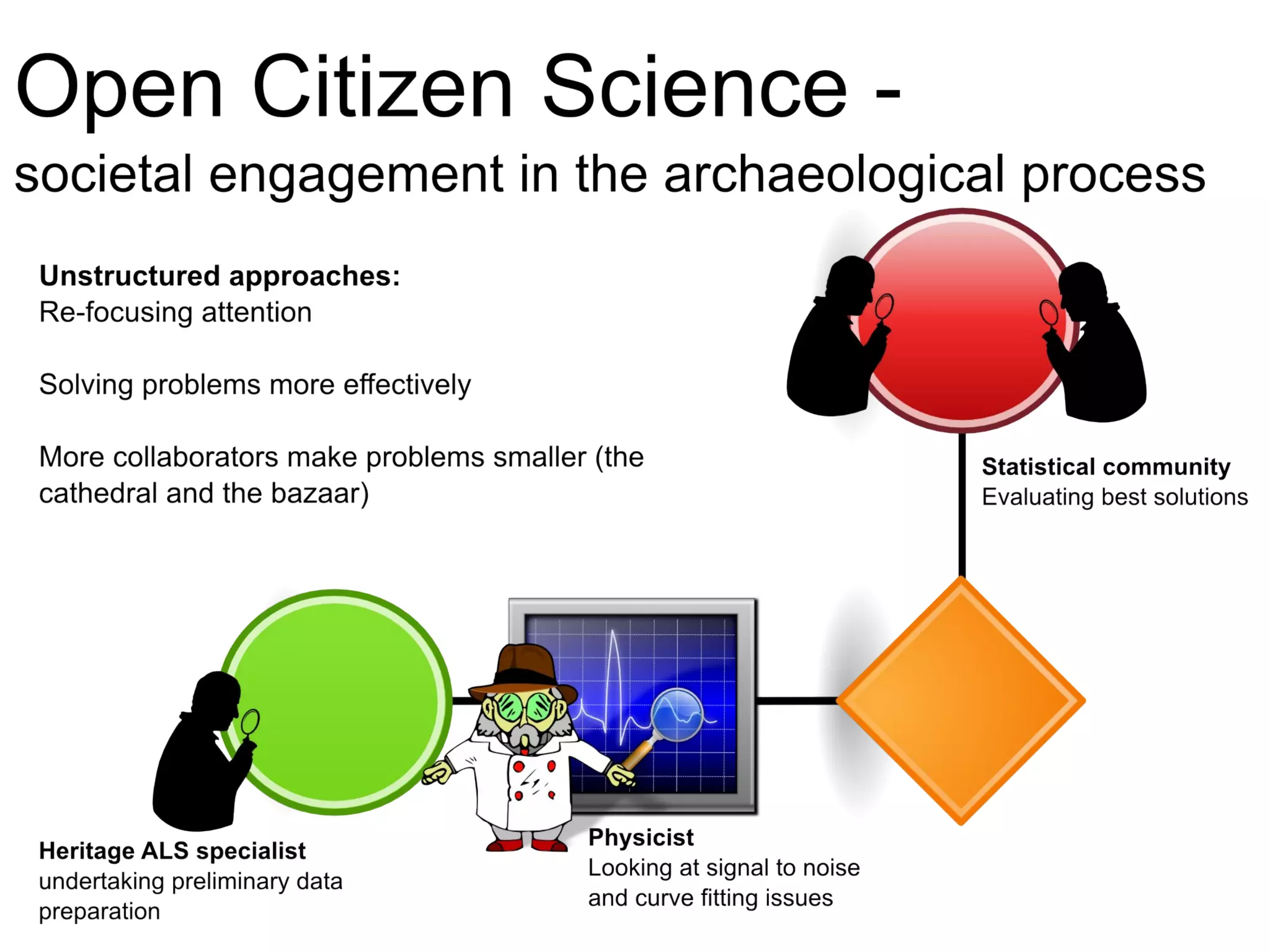
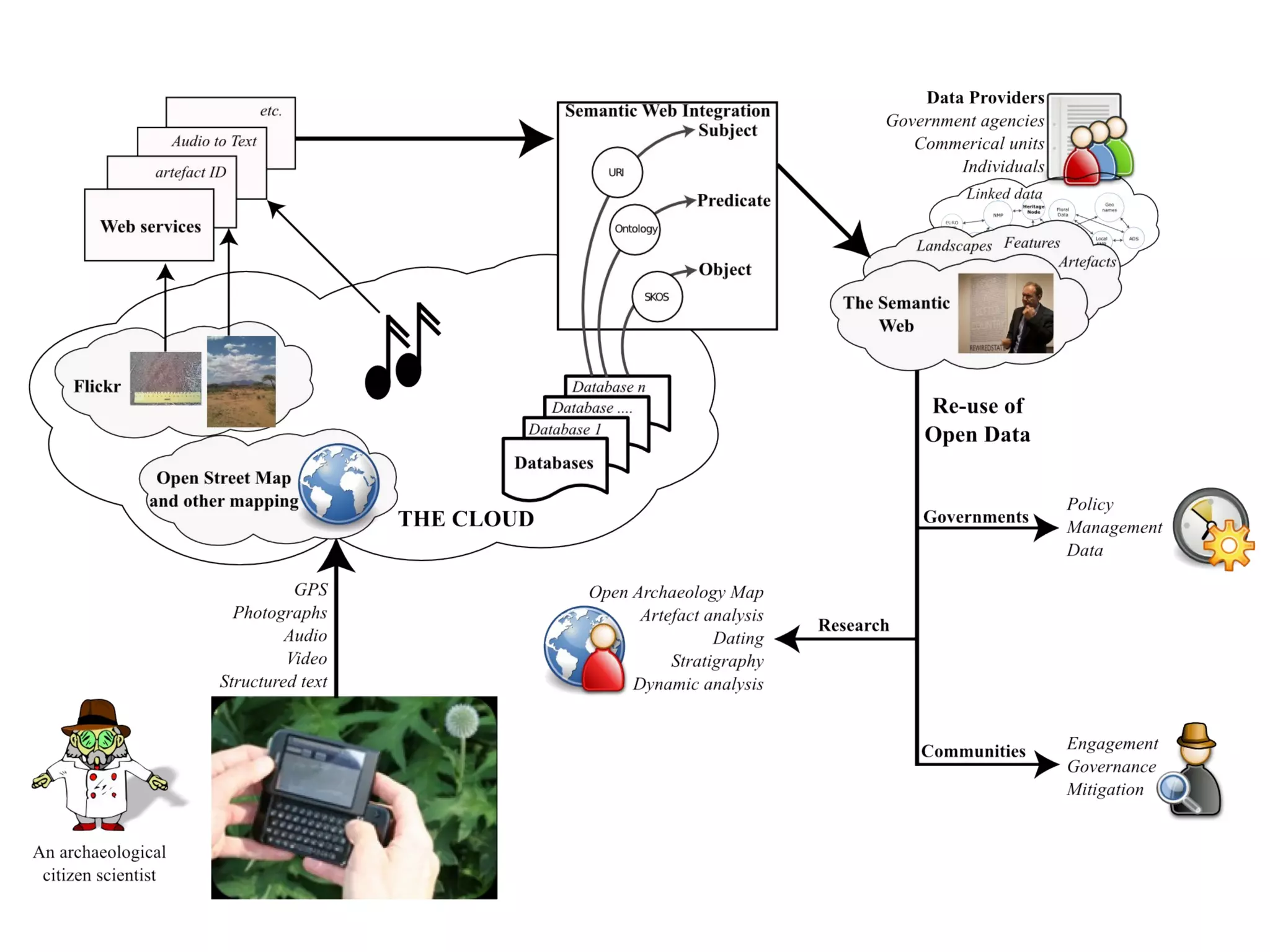
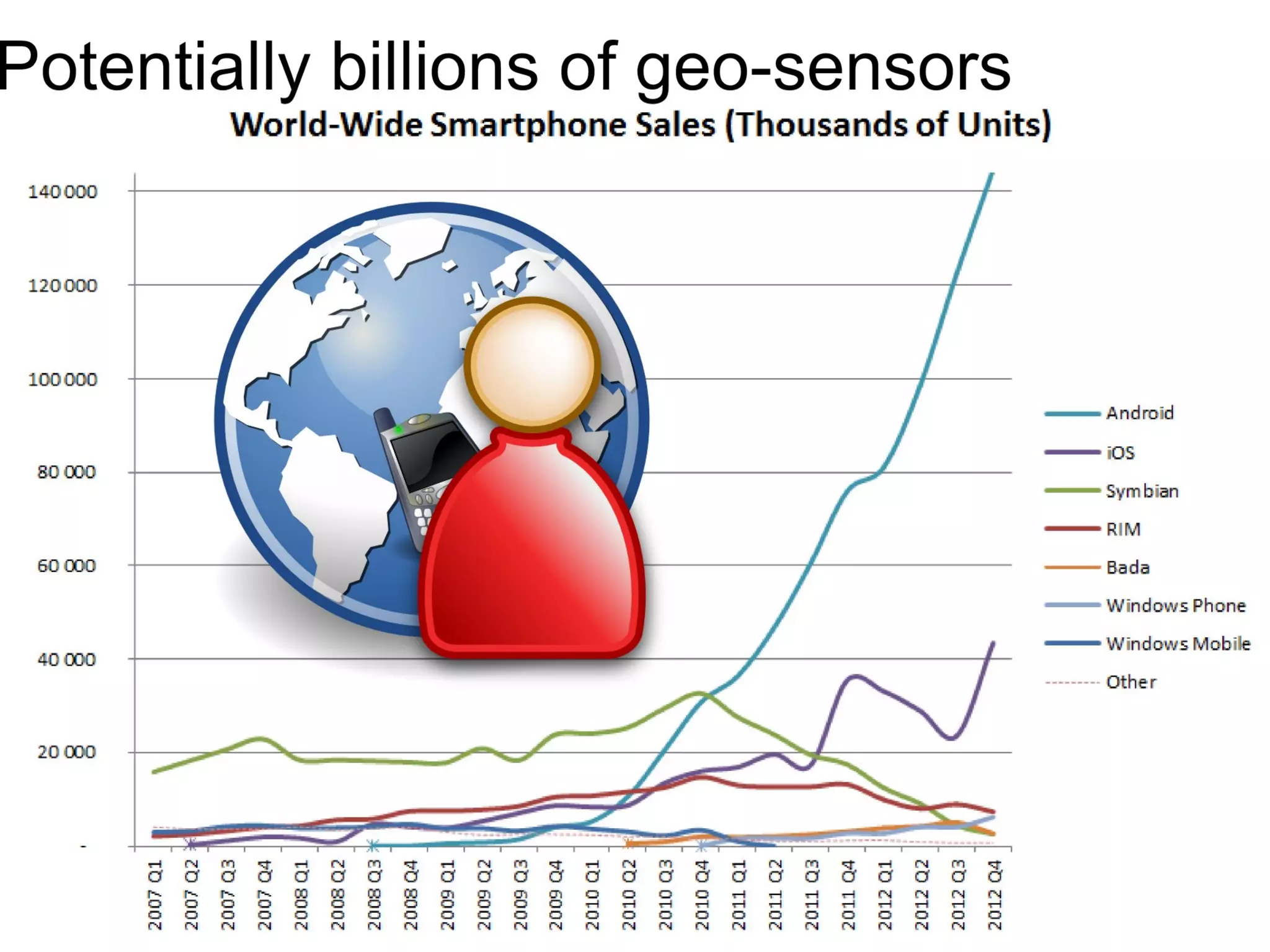
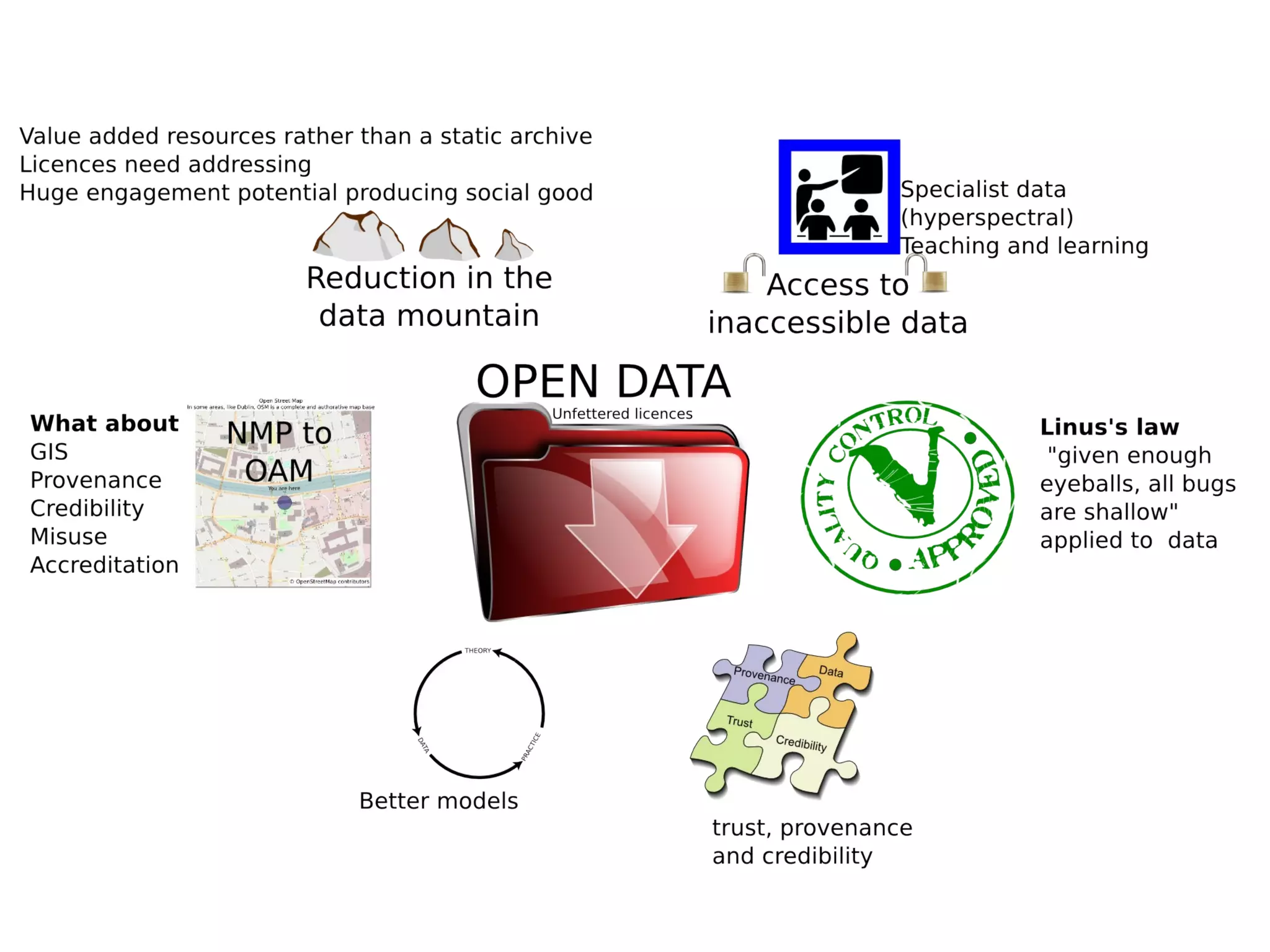
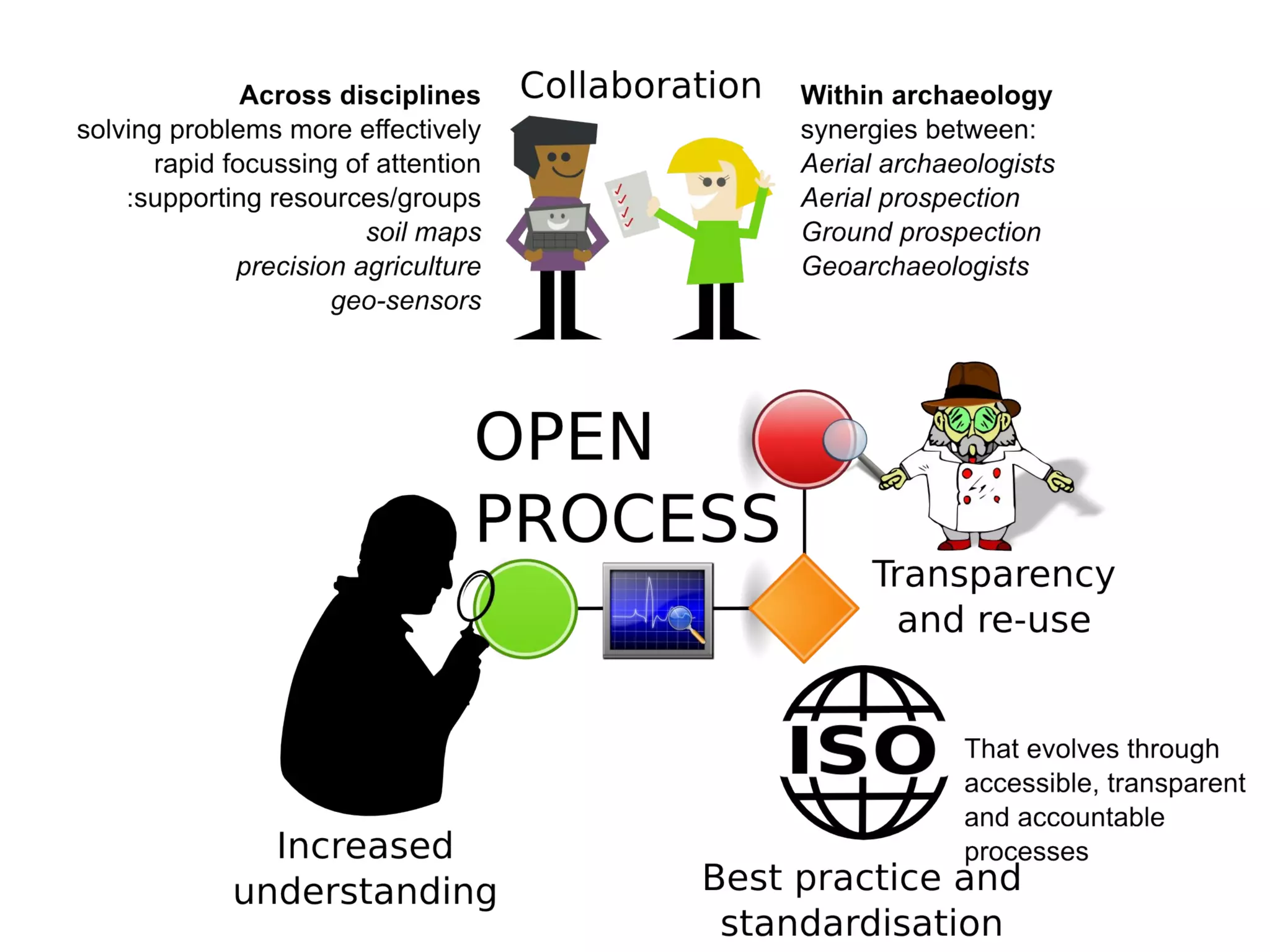
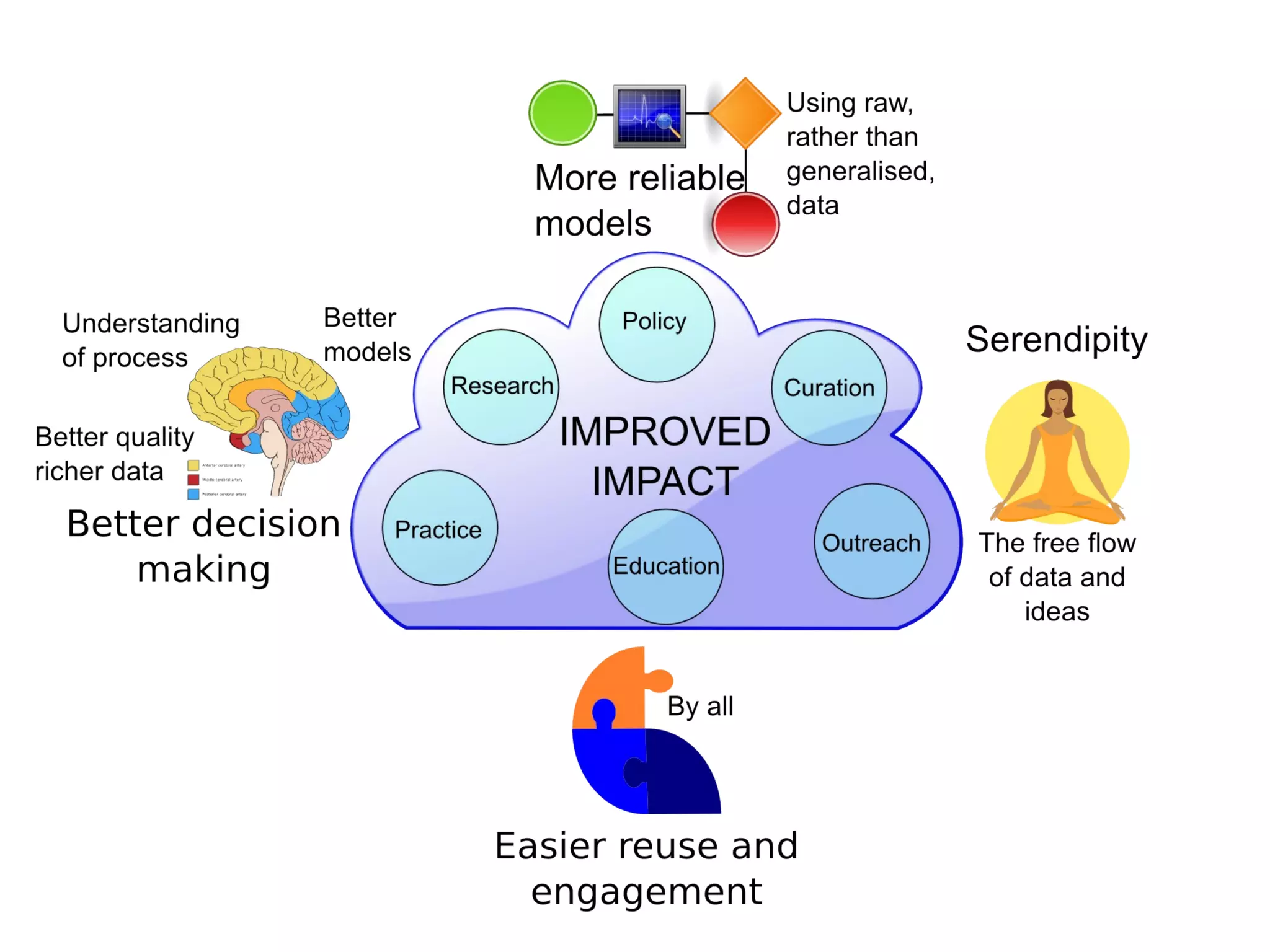
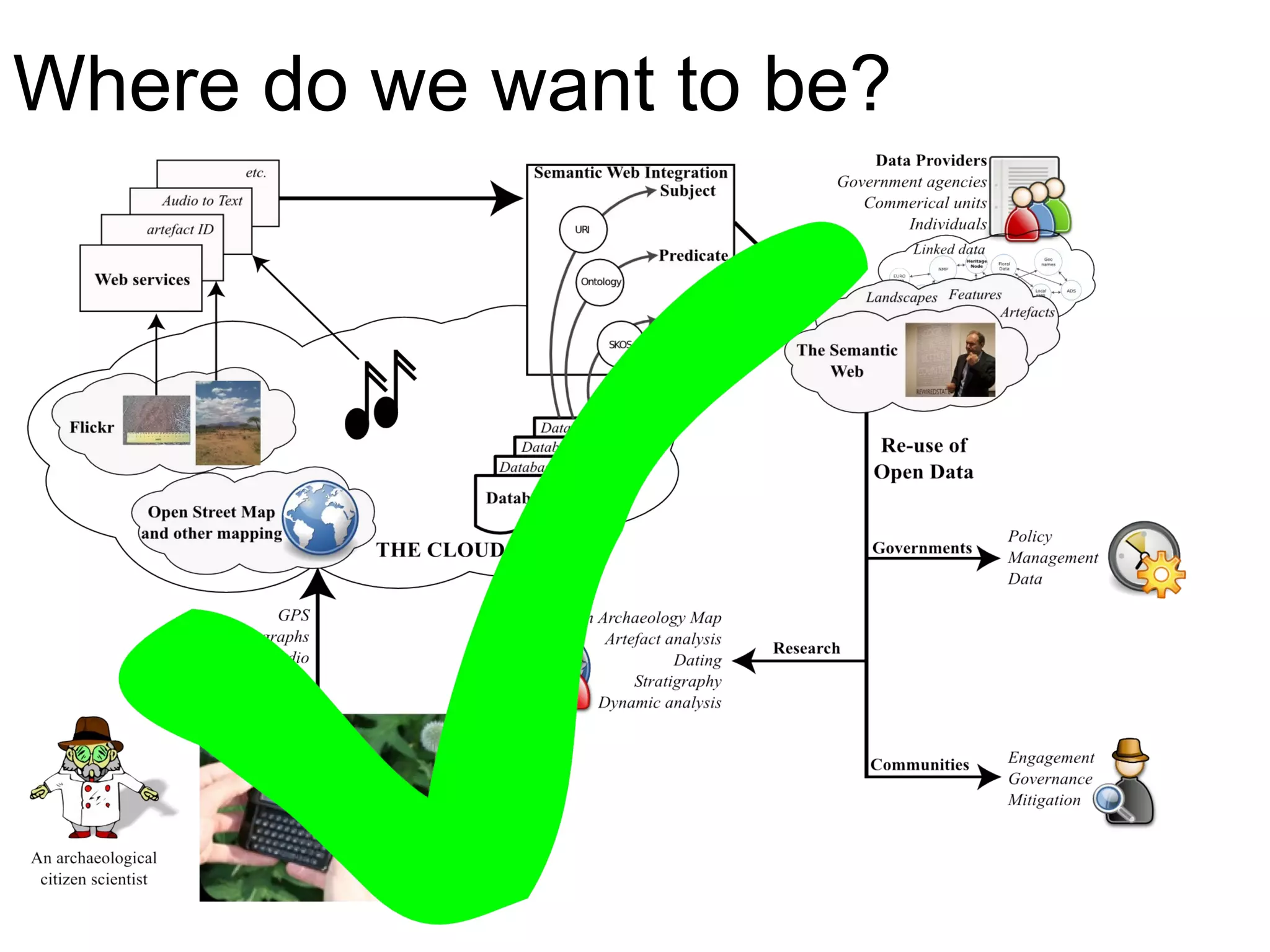
The document discusses the dynamic process of archaeological knowledge acquisition and the importance of integrating various data sources, such as excavation records and specialist reports, to enhance research and policy outcomes. It highlights issues surrounding siloed data and advocates for open data initiatives to improve decision-making. The presentation also suggests envisioning an open archaeology map to facilitate better collaboration and knowledge sharing.