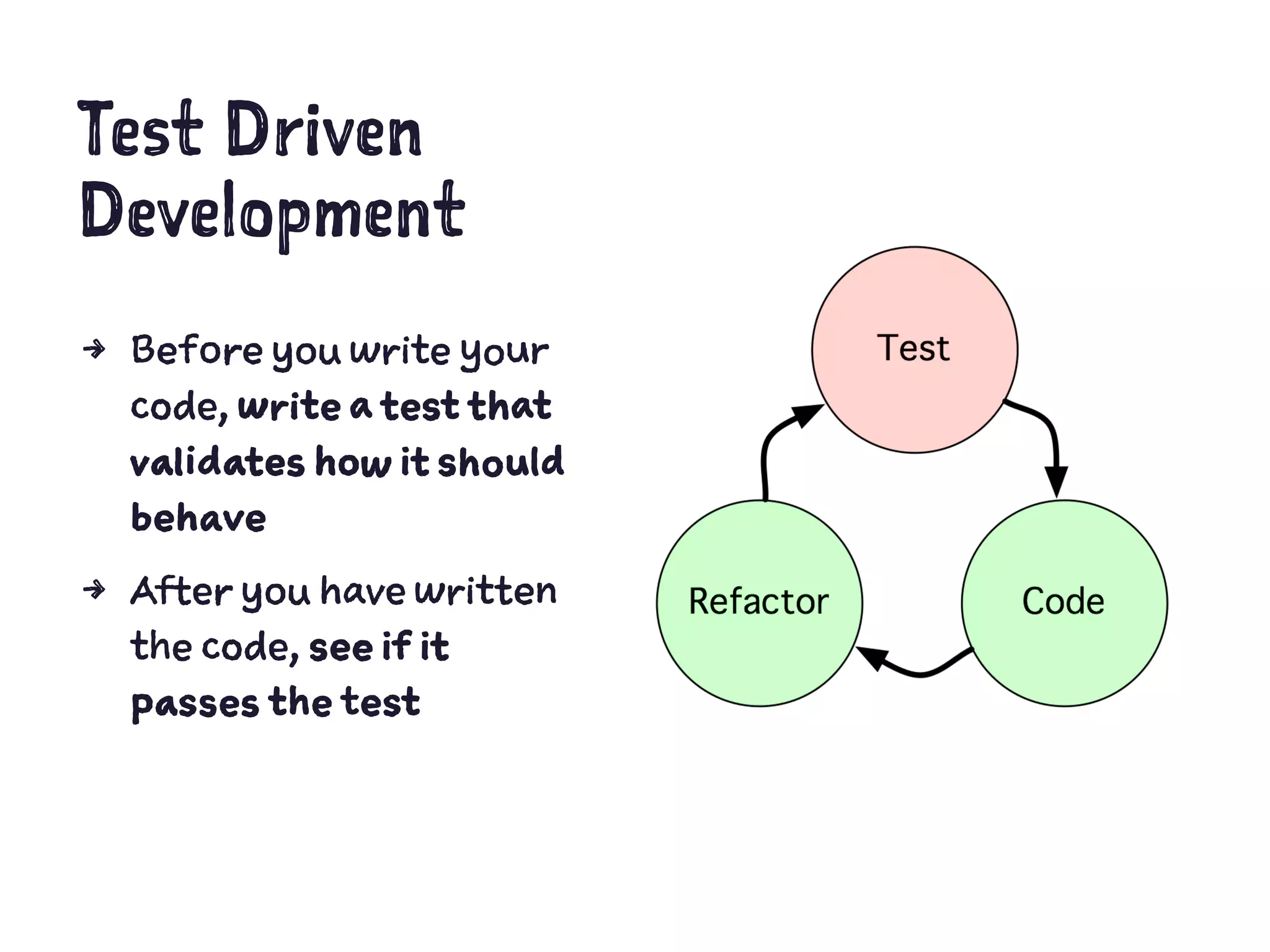
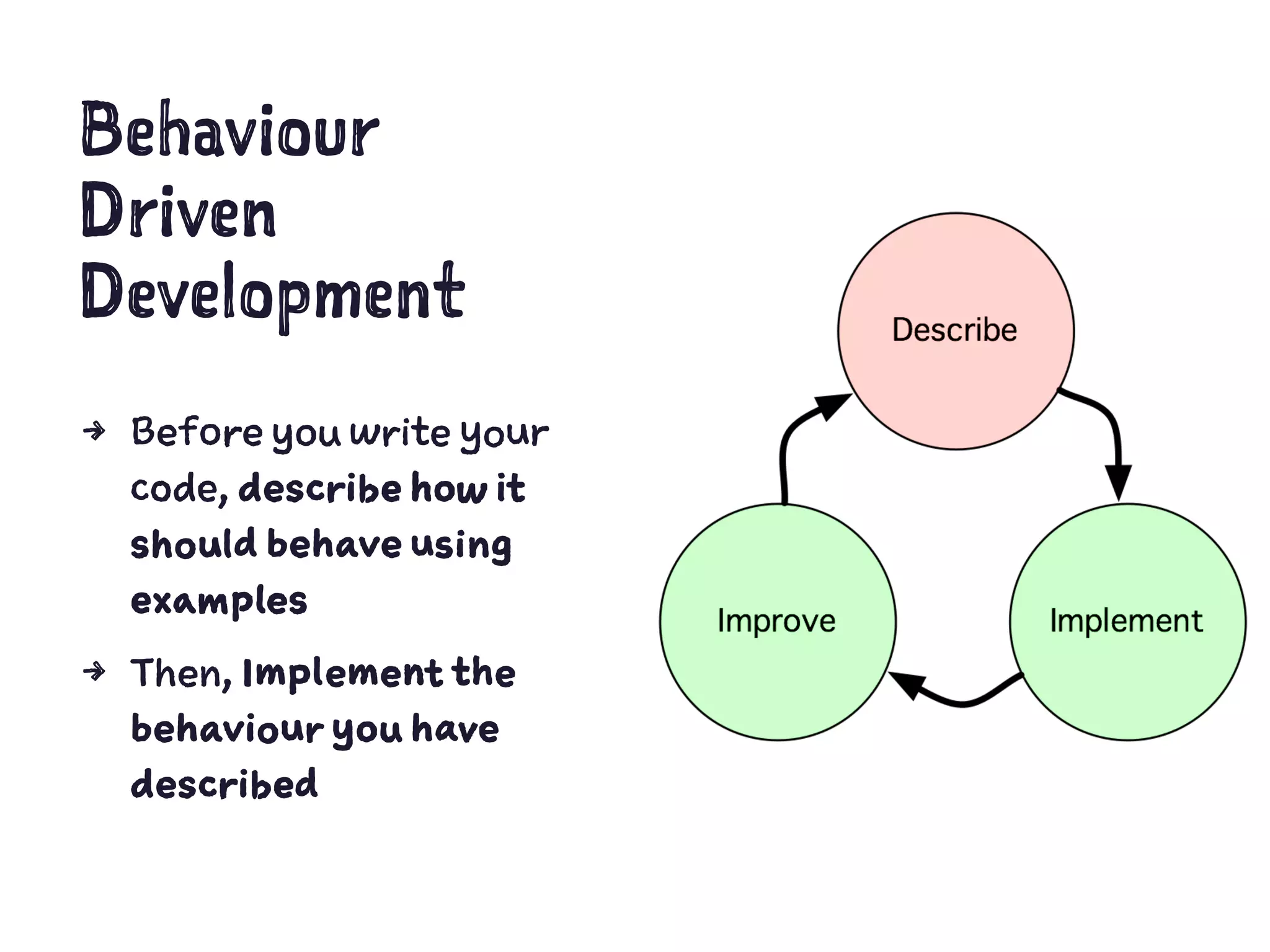
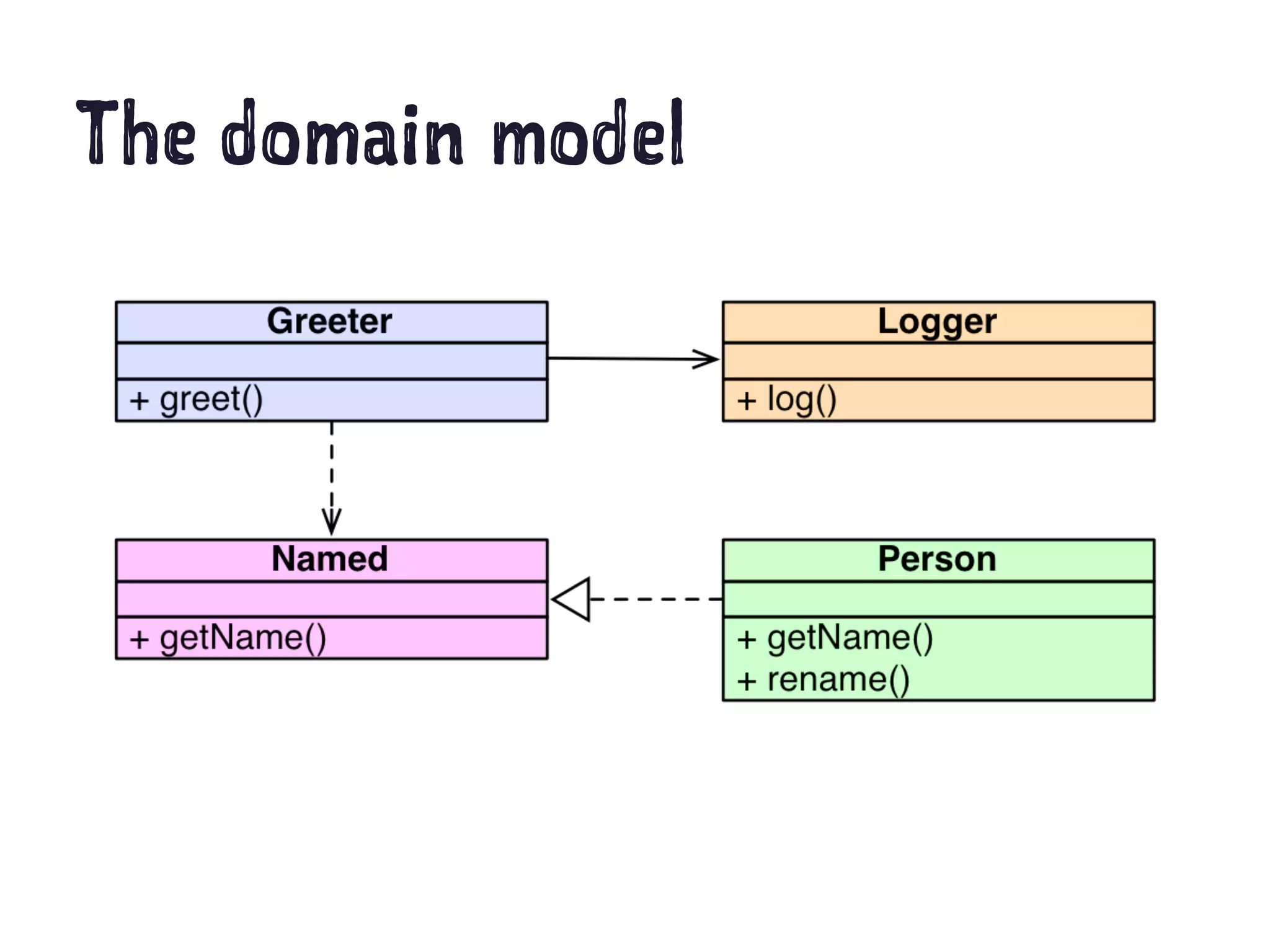
The document discusses Test Driven Development (TDD) using PhpSpec. It begins with an overview of TDD vs Behavior Driven Development (BDD). It then covers key aspects of using PhpSpec including describing object behavior with examples, verifying behavior by running tests, matchers for assertions, describing collaborations and exceptions. The rest of the document demonstrates a TDD workflow using PhpSpec to develop a greeter class and related classes like Person in a step-by-step manner.












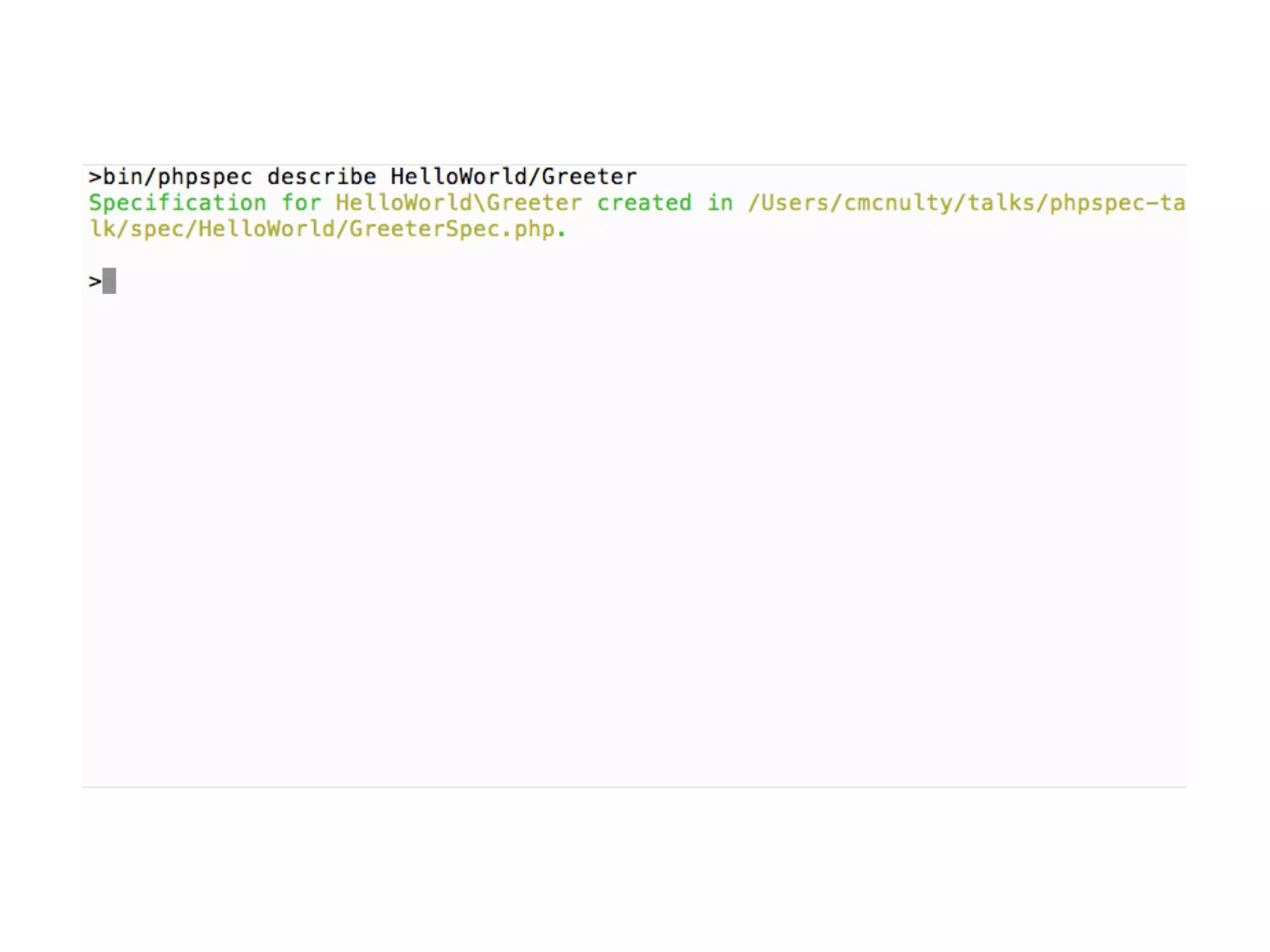
![Describing object behaviour
4 We describe an object using a
Specification
4 A specification is made up of Examples
illustrating different scenarios
Usage:
phpspec describe [Class]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-151003153929-lva1-app6891/75/TDD-with-PhpSpec-20-2048.jpg)


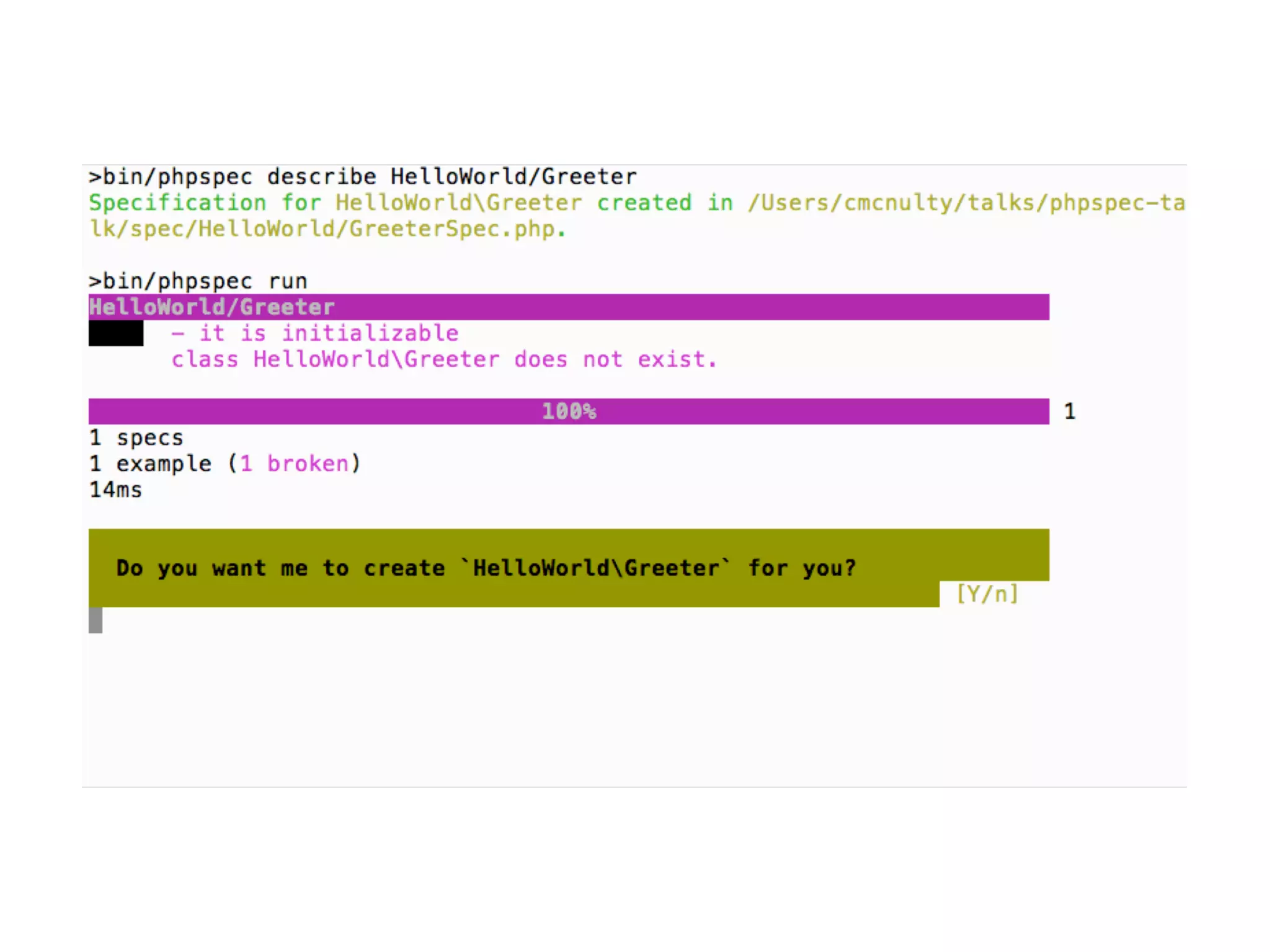








![Matchers
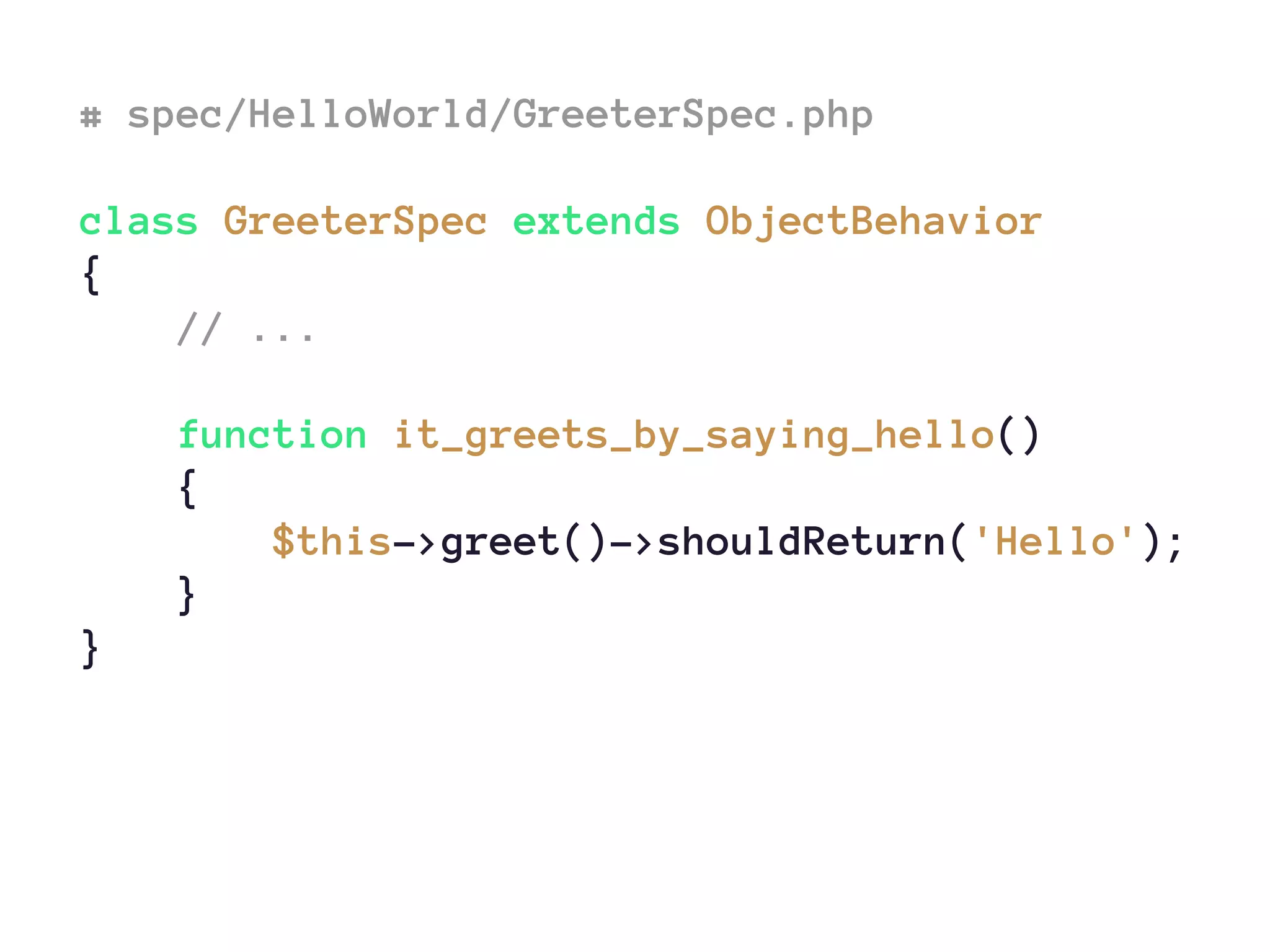
# Equality
$this->greet()->shouldReturn('Hello');
$this->sum(3,3)->shouldEqual(6);
# Type
$this->getEmail()->shouldHaveType('Email');
$this->getTime()->shouldReturnAnInstanceOf('DateTime');
# Fuzzy value matching
$this->getSlug()->shouldMatch('/^[0-9a-z]+$/');
$this->getNames()->shouldContain('Tom');](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-151003153929-lva1-app6891/75/TDD-with-PhpSpec-38-2048.jpg)

![Custom matchers
function it_gets_json_with_user_details()
{
$this->getResponseData()->shouldHaveJsonKey('username');
}
public function getMatchers()
{
return [
'haveJsonKey' => function ($subject, $key) {
return array_key_exists($key, json_decode($subject));
}
];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-151003153929-lva1-app6891/75/TDD-with-PhpSpec-40-2048.jpg)


![The shouldThrow matcher
$this->shouldThrow(InvalidArgumentException::class)
->duringSave($user);
or
$this->shouldThrow(InvalidArgumentException::class)
->during(‘save’, [$user]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-151003153929-lva1-app6891/75/TDD-with-PhpSpec-43-2048.jpg)
![Construction
// new User(‘Ciaran’)
$this->beConstructedWith('Ciaran');
// User::named(‘Ciaran’)
$this->beConstructedThrough('named', ['Ciaran']);
$this->beConstructedNamed('Ciaran');
// Testing constructor exceptions
$this->shouldThrow(InvalidArgumentException::class)
->duringInstantiation();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-151003153929-lva1-app6891/75/TDD-with-PhpSpec-44-2048.jpg)


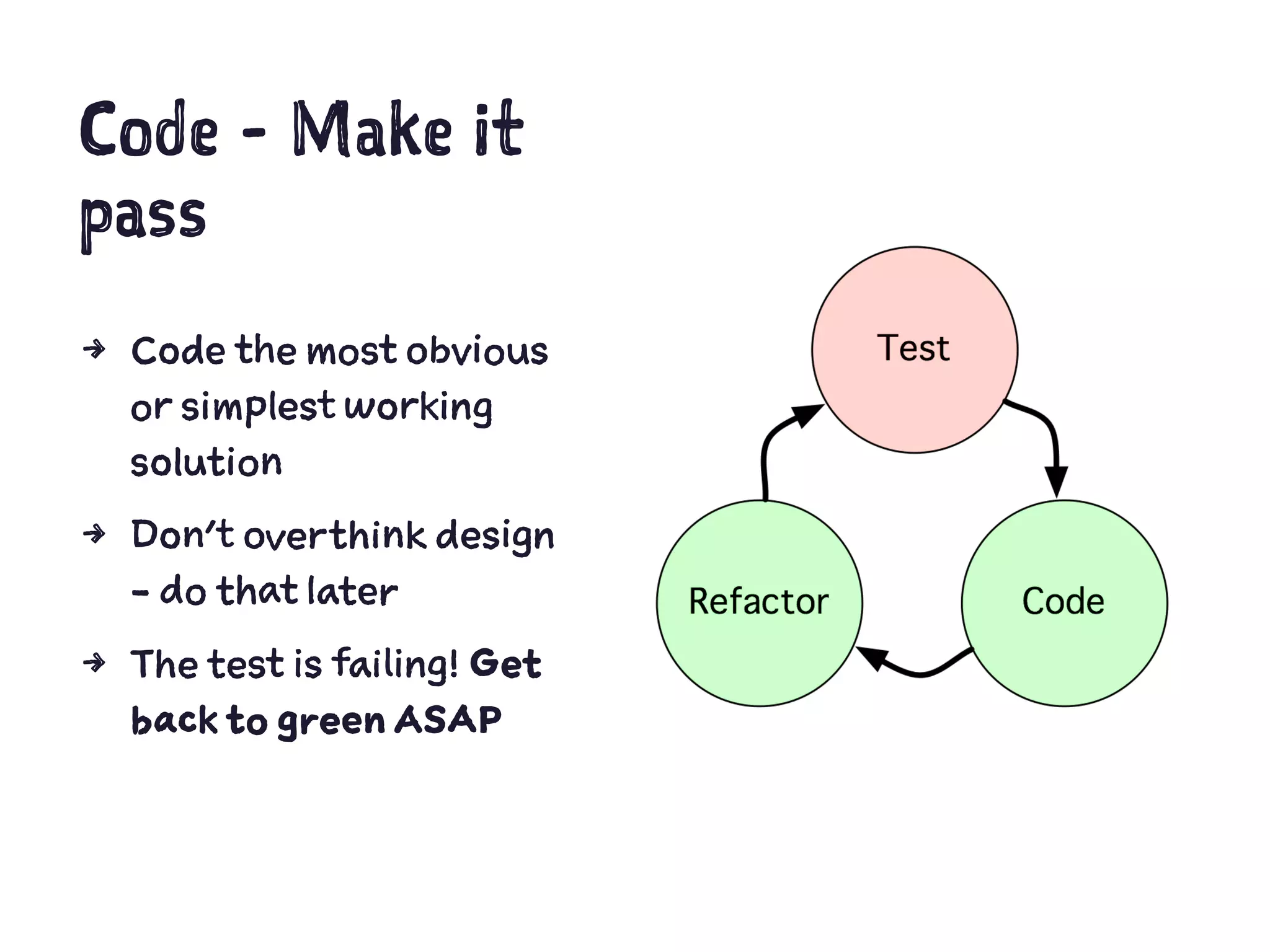
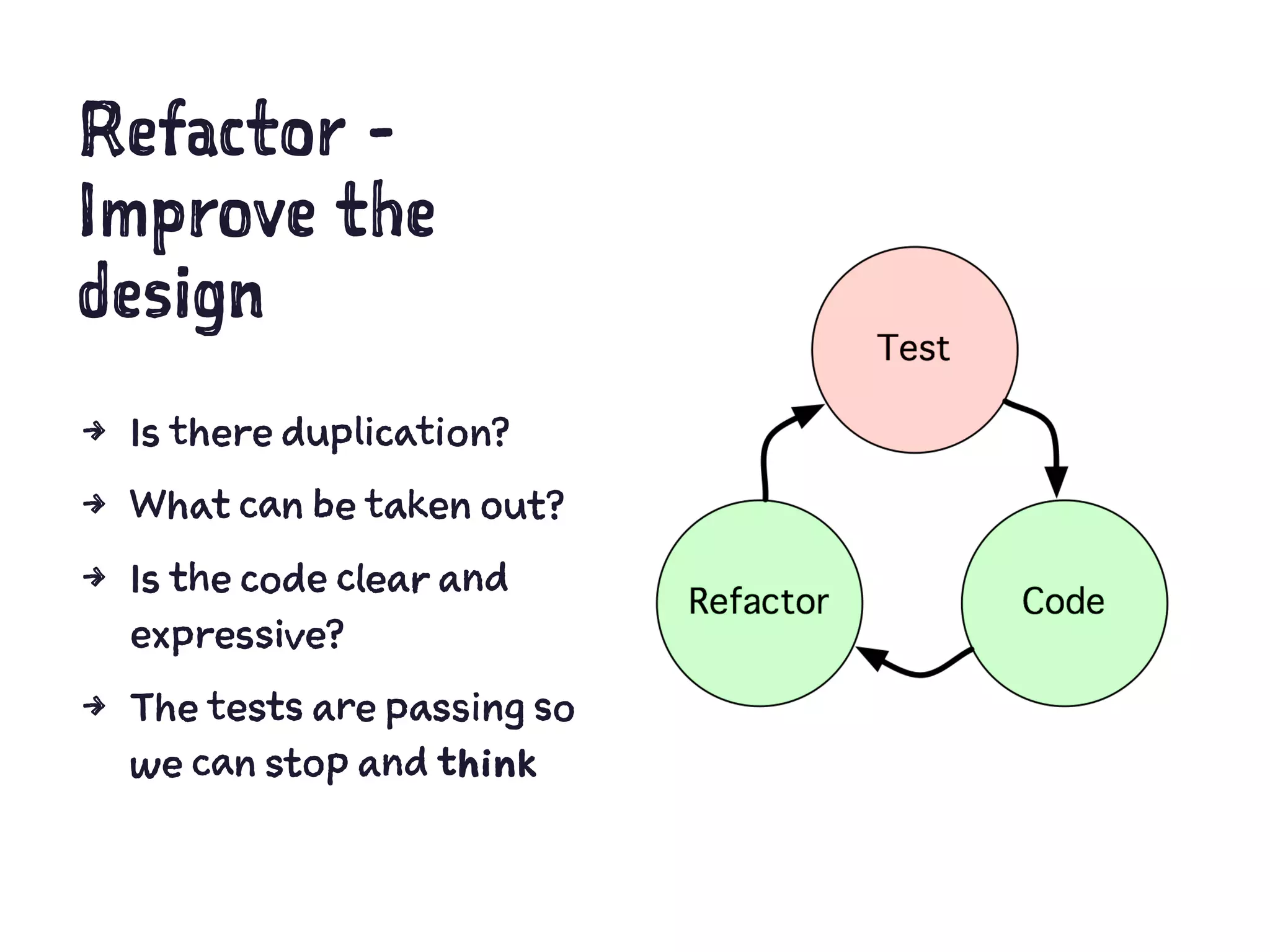




![Kata - string calculator
Design an object that takes a string expression and
calculates an integer.
4 Empty string should evaluate to zero
4 Zero as a string should evaluate to zero
4 Numeric string should evaluate to that number
4 Space separated numbers should be added together
4 Whitespace separated numbers should be added
together
4 Custom separator can be specified (e.g. ’[+]1+2+3’ -> 6)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-151003153929-lva1-app6891/75/TDD-with-PhpSpec-55-2048.jpg)





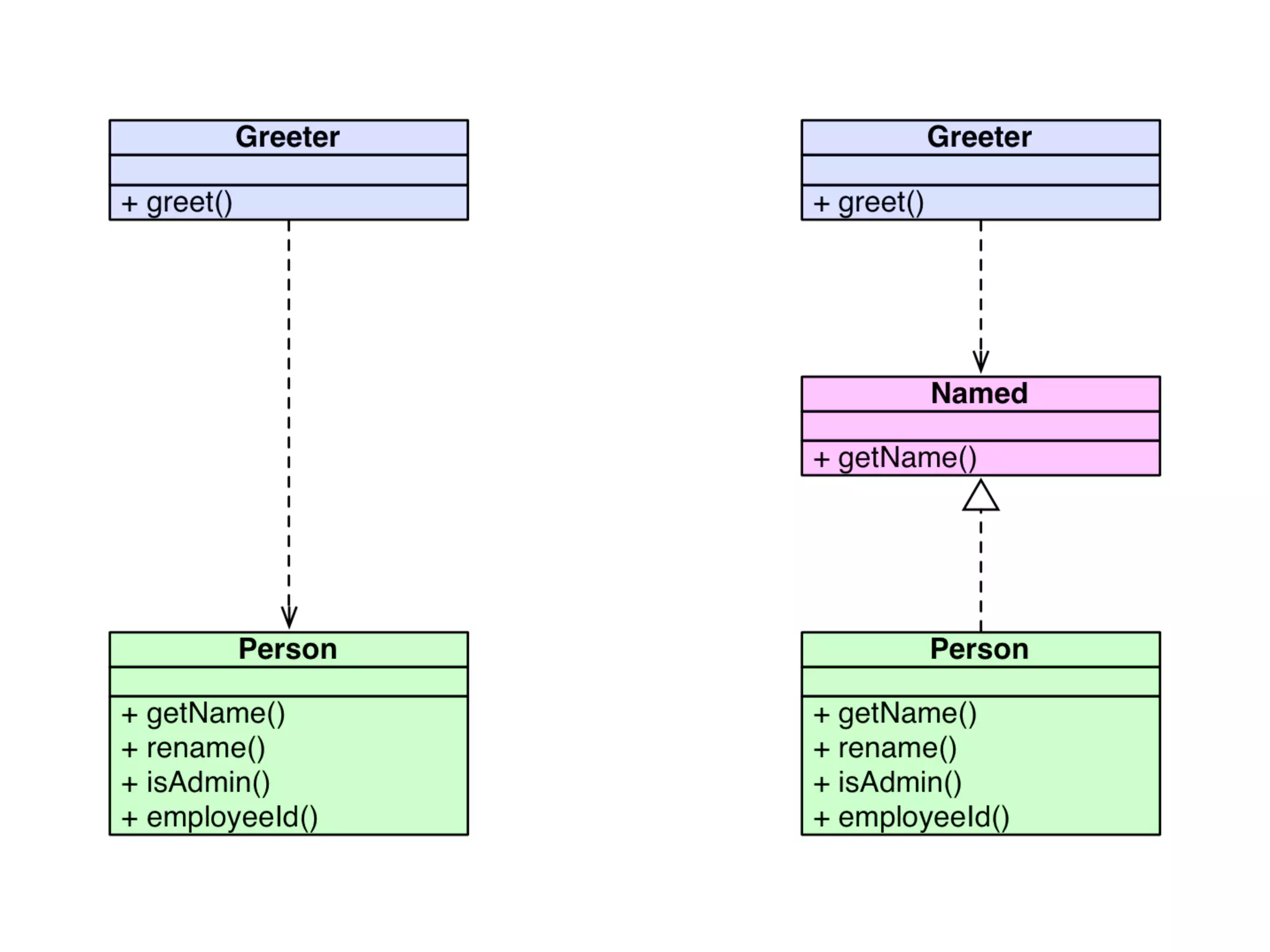


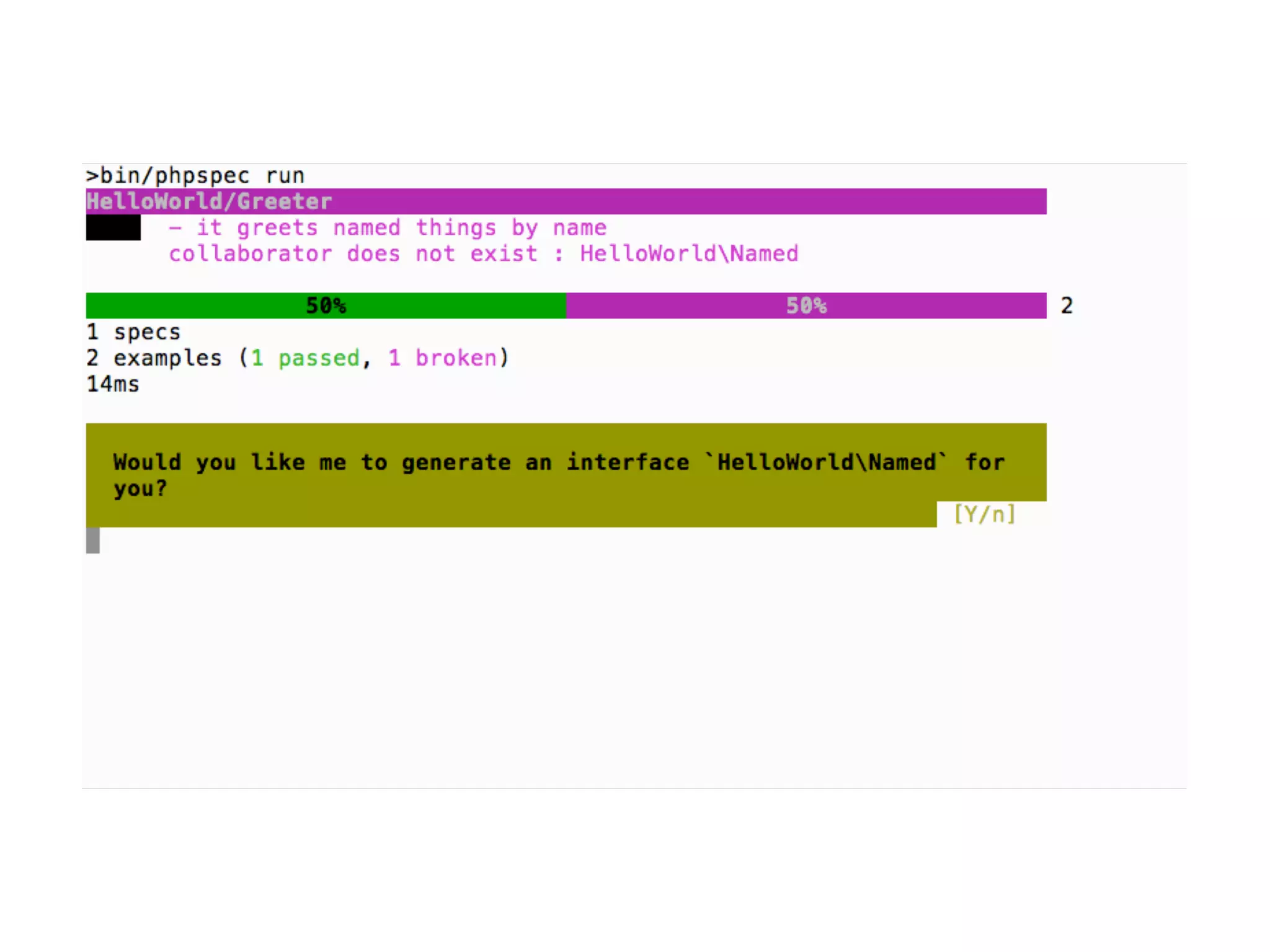
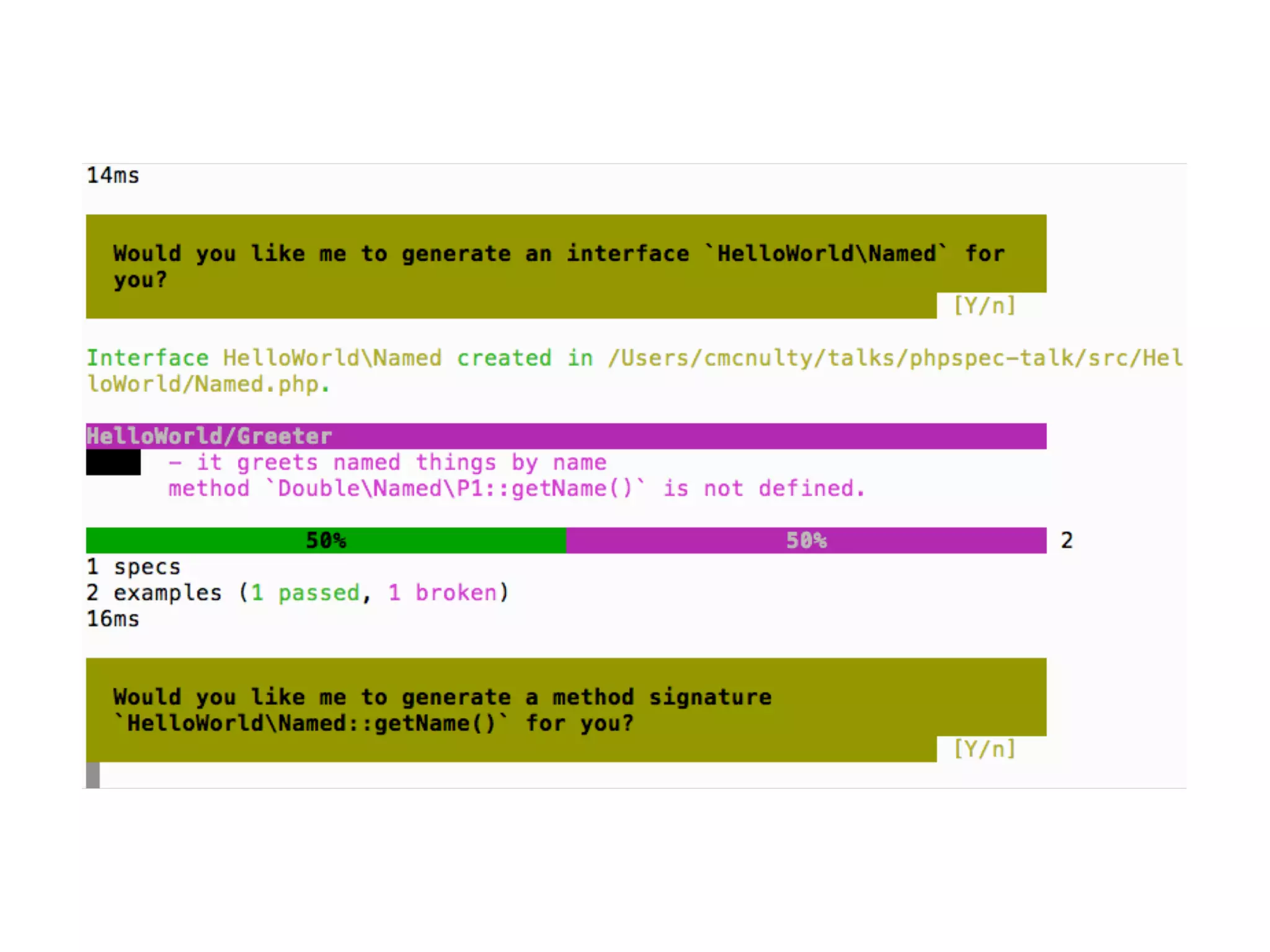










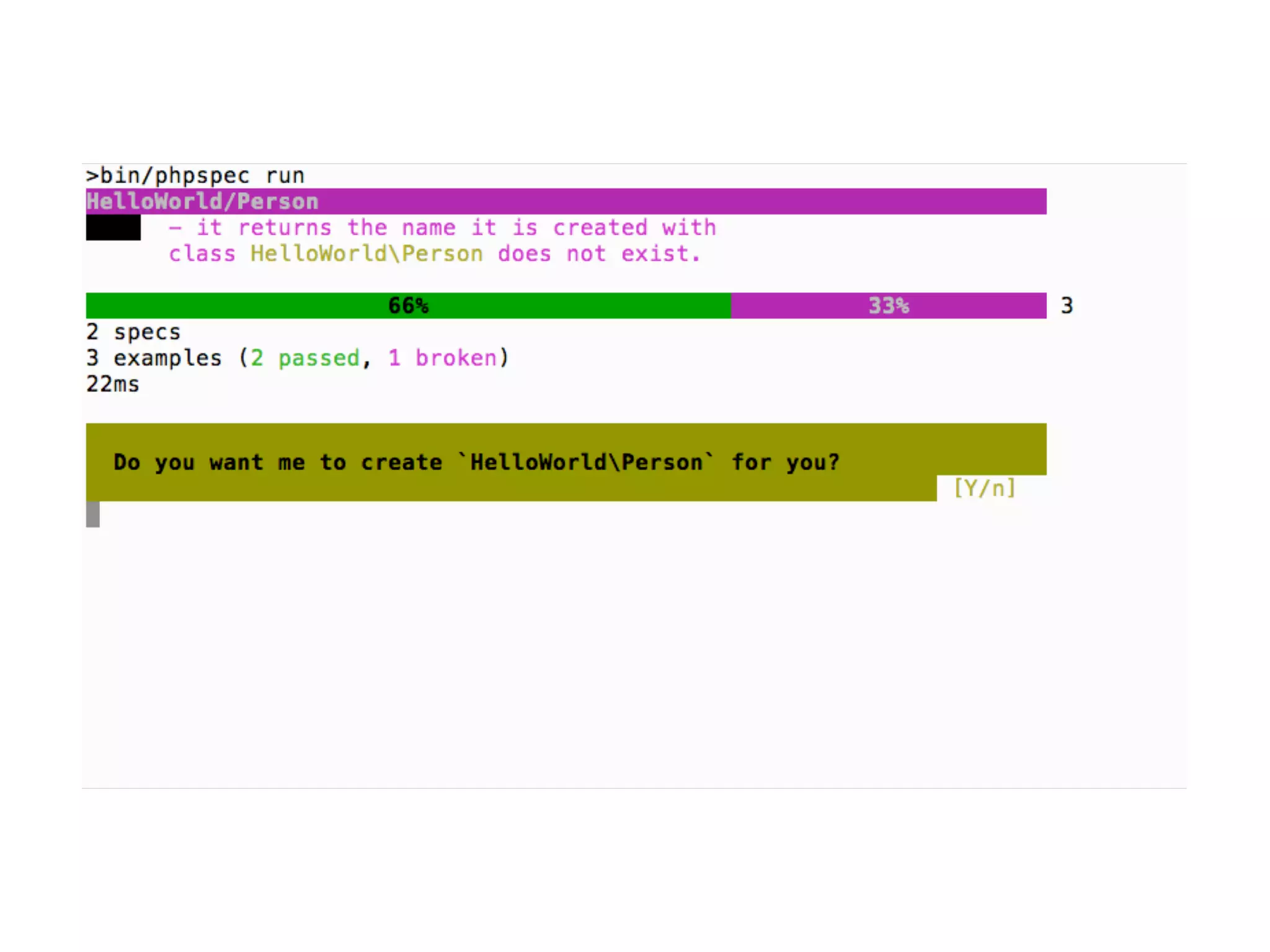
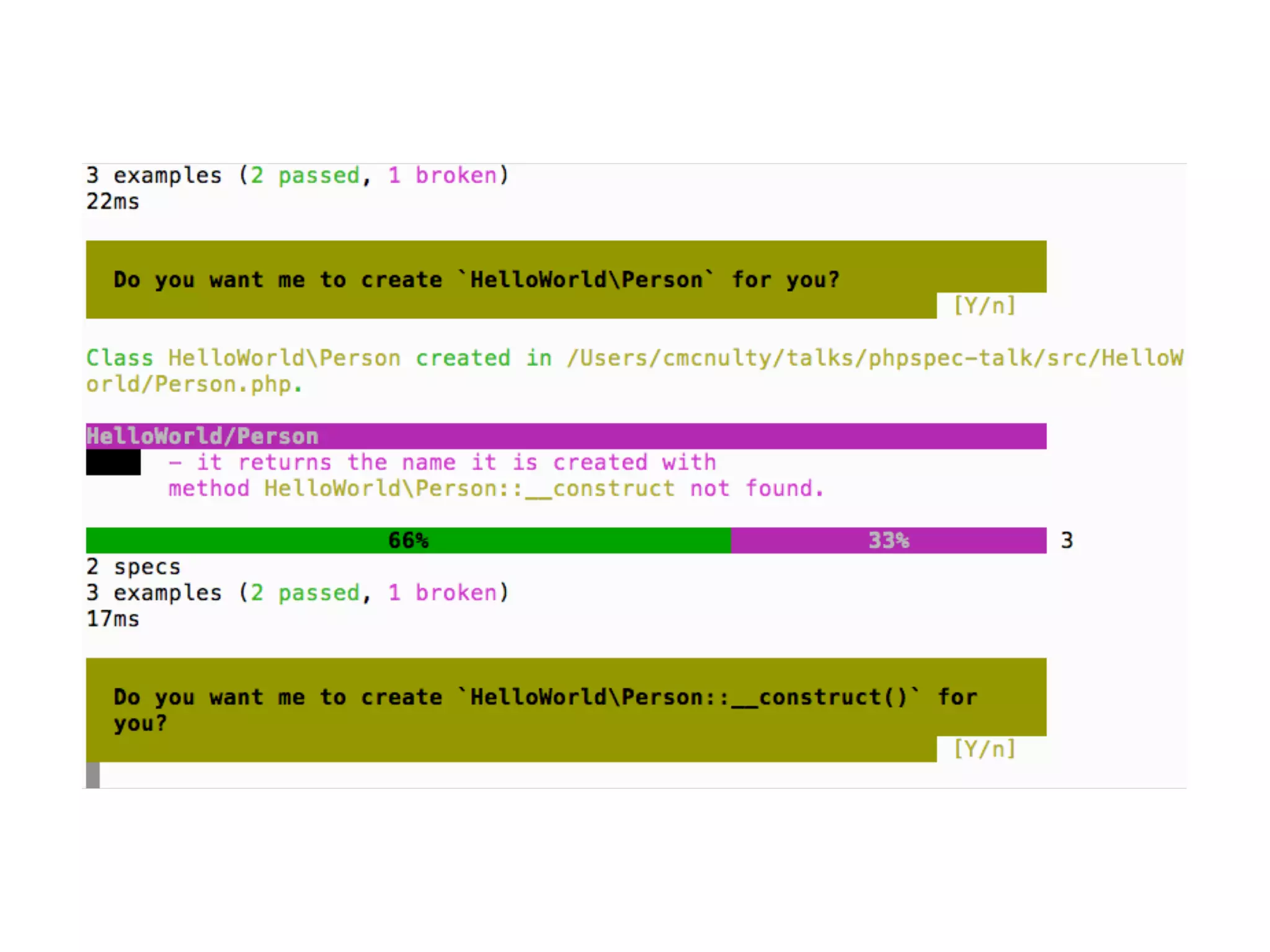
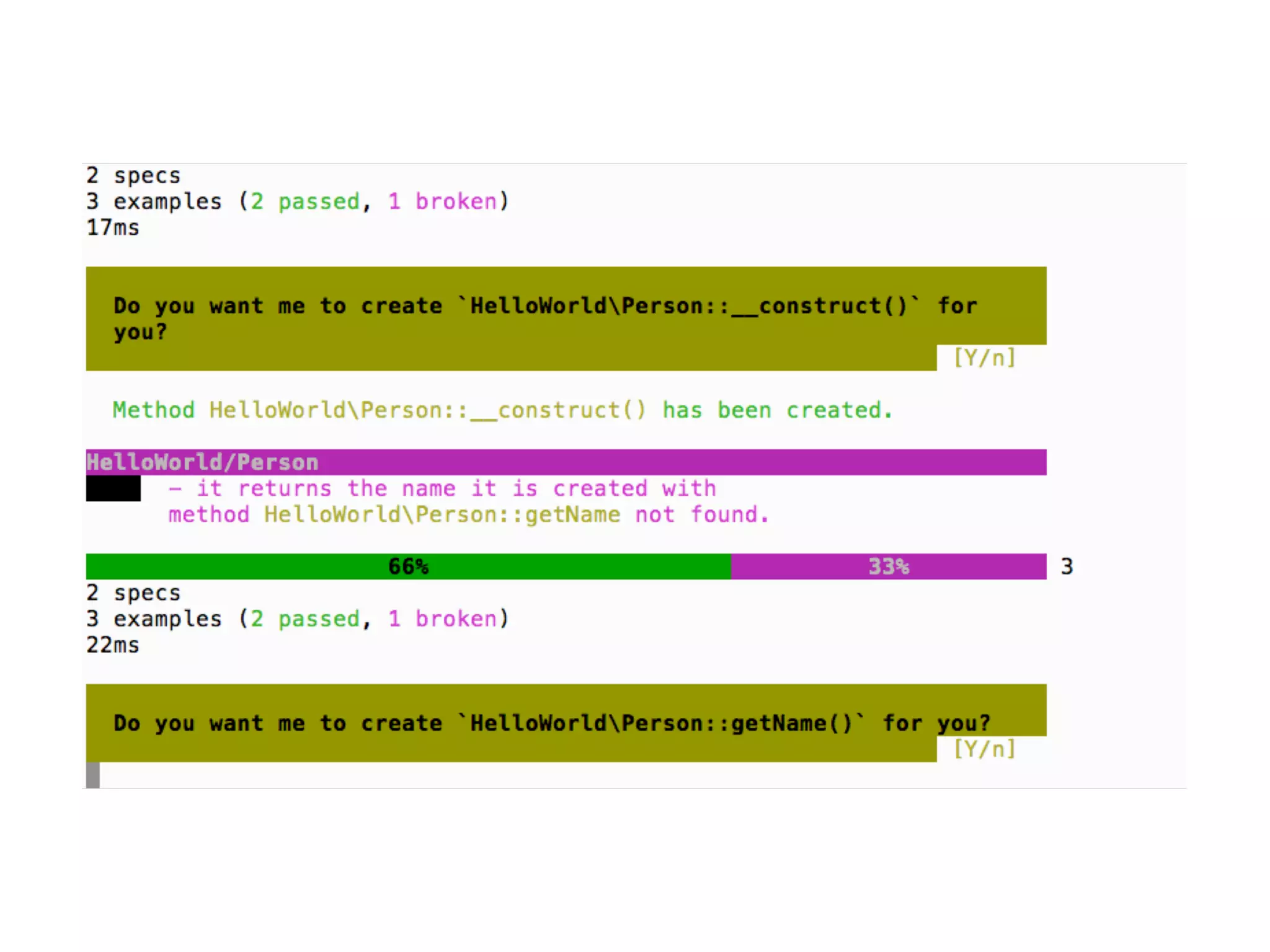







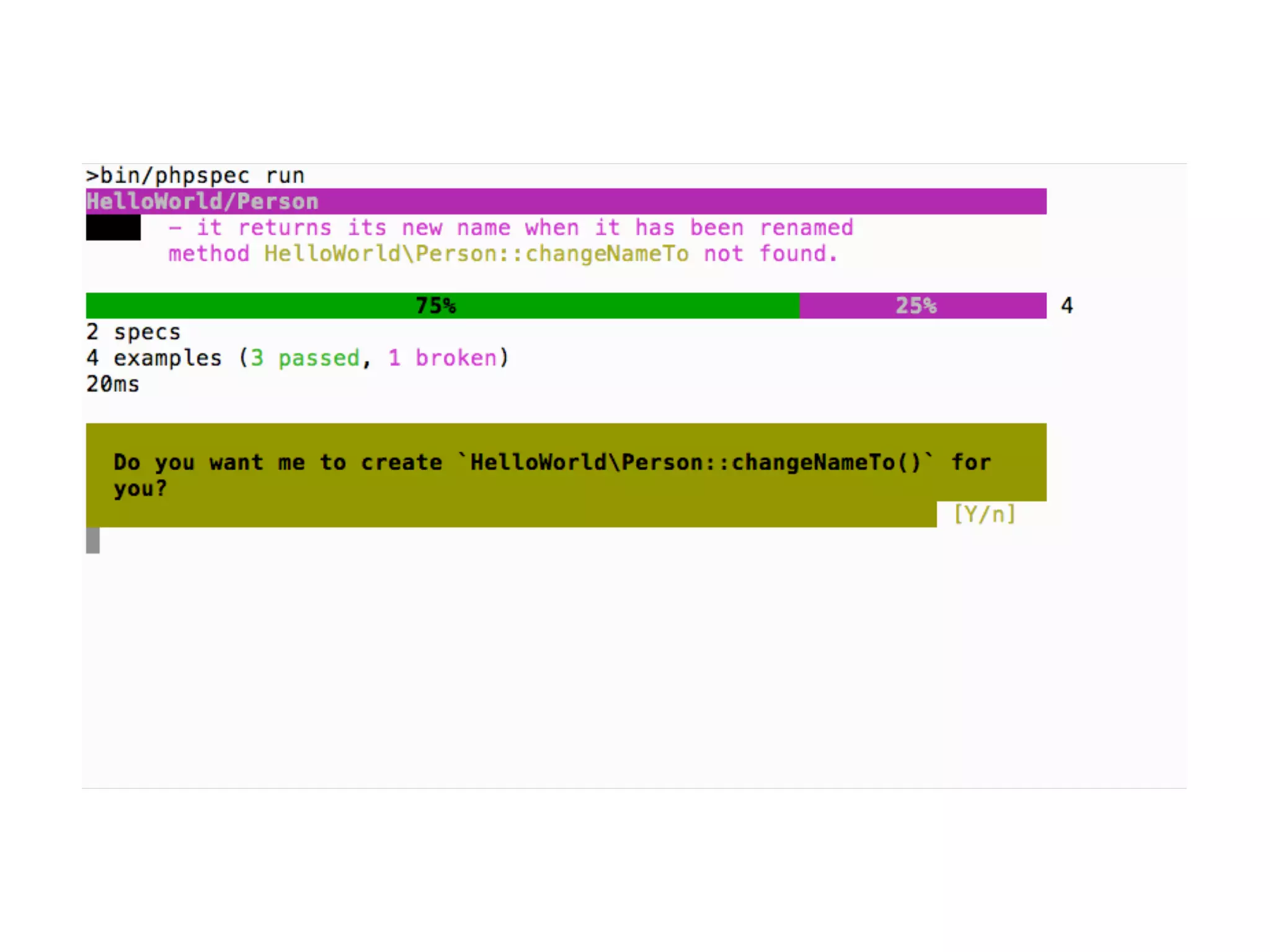










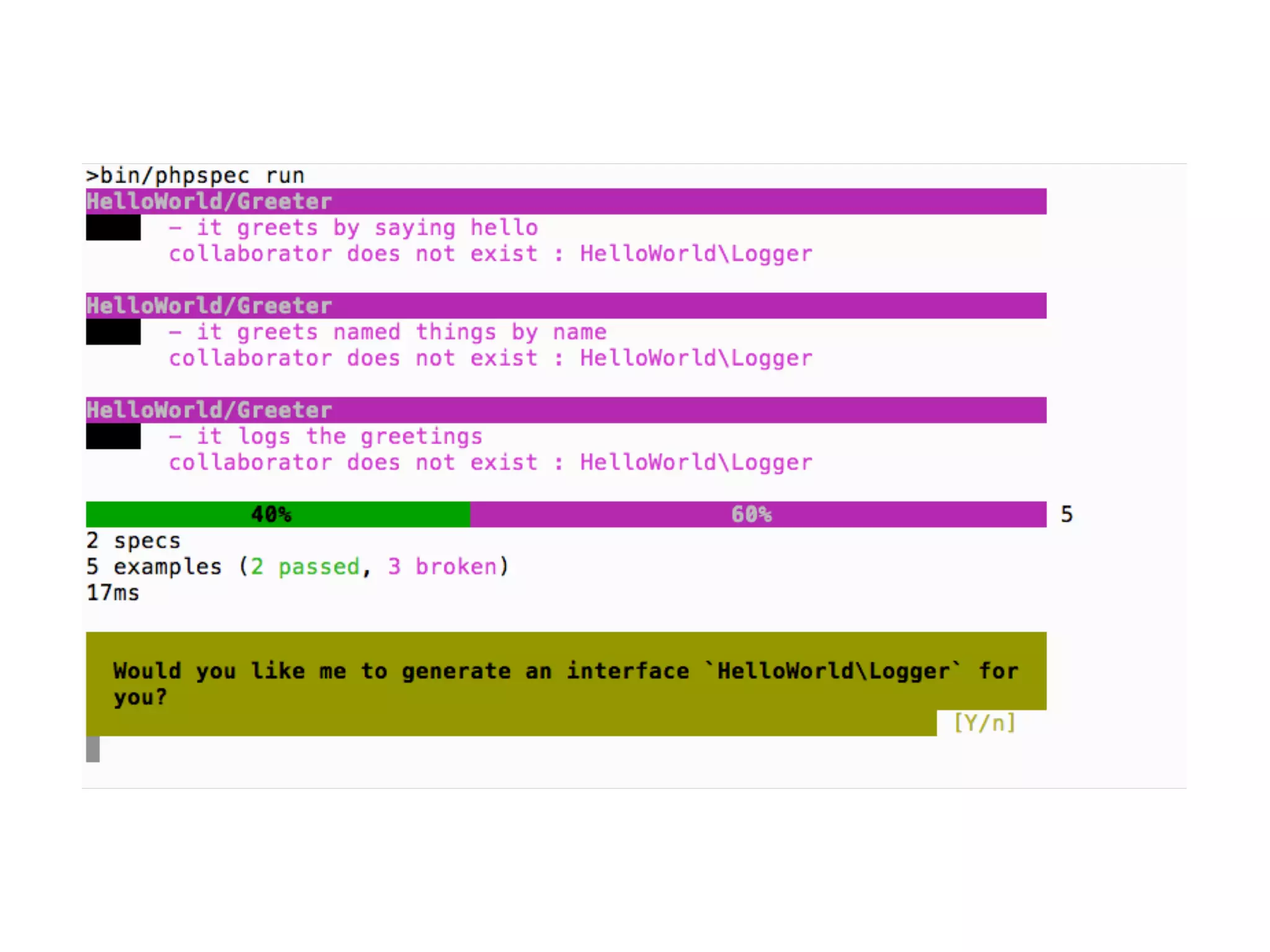
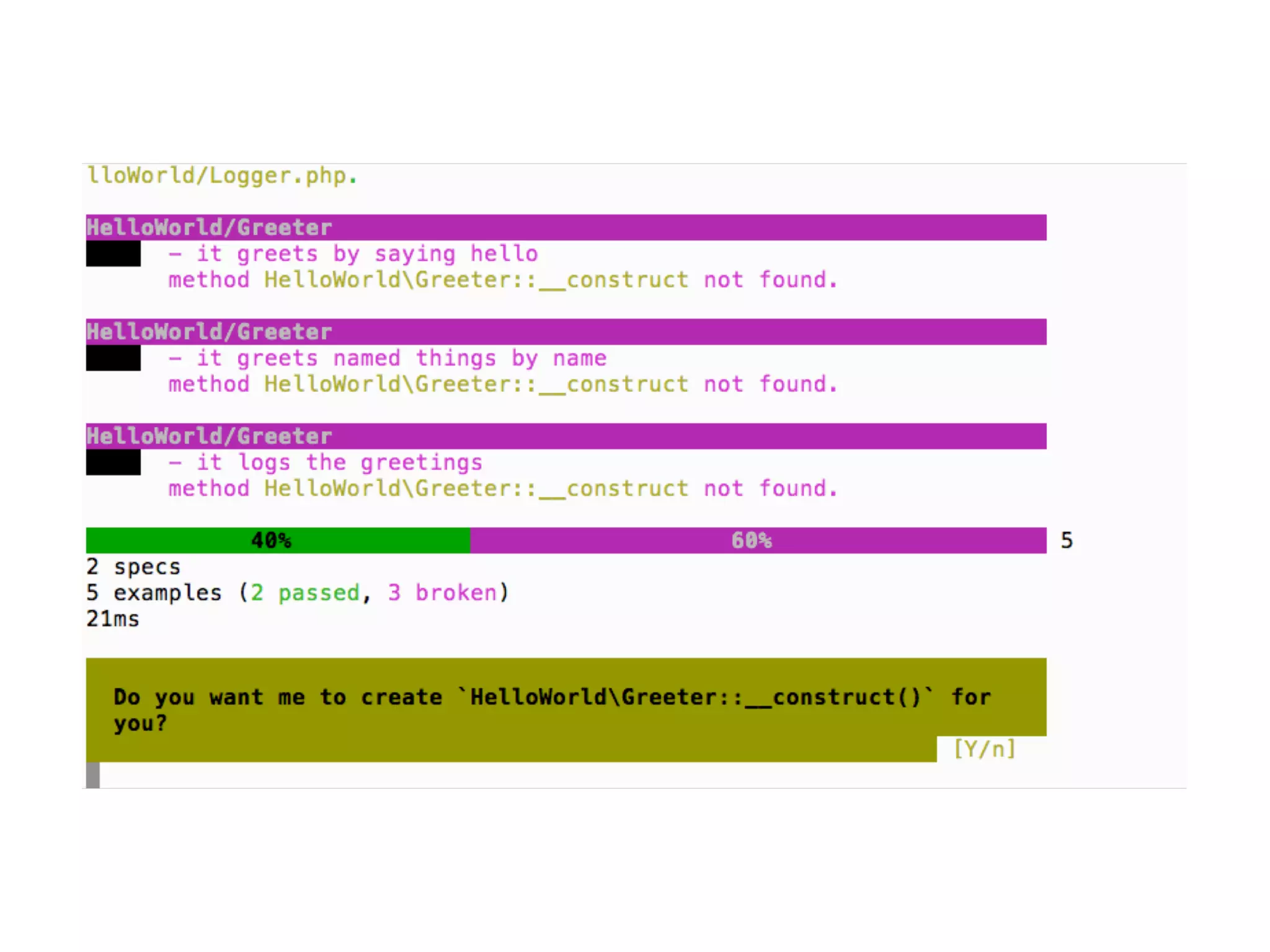
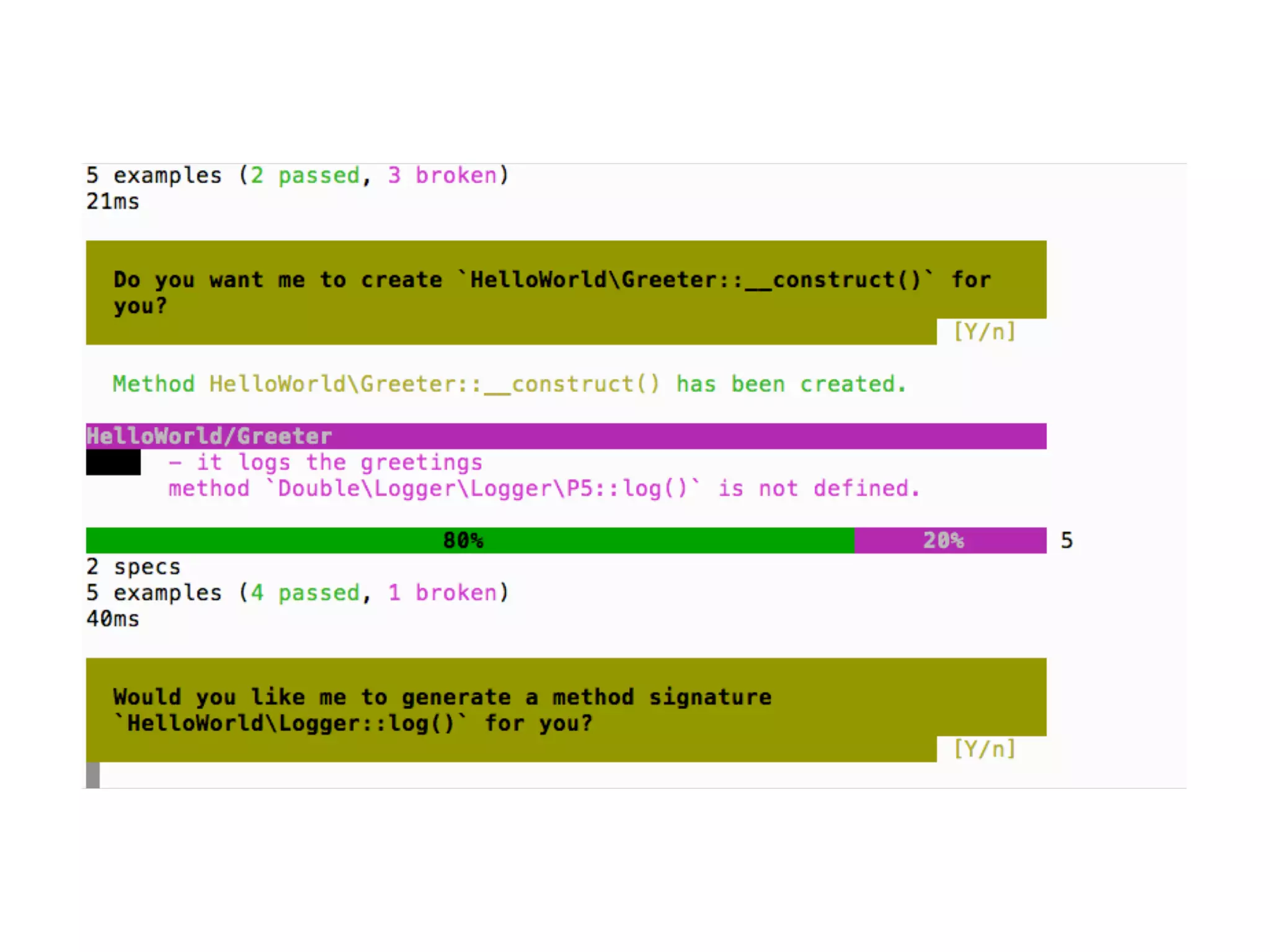






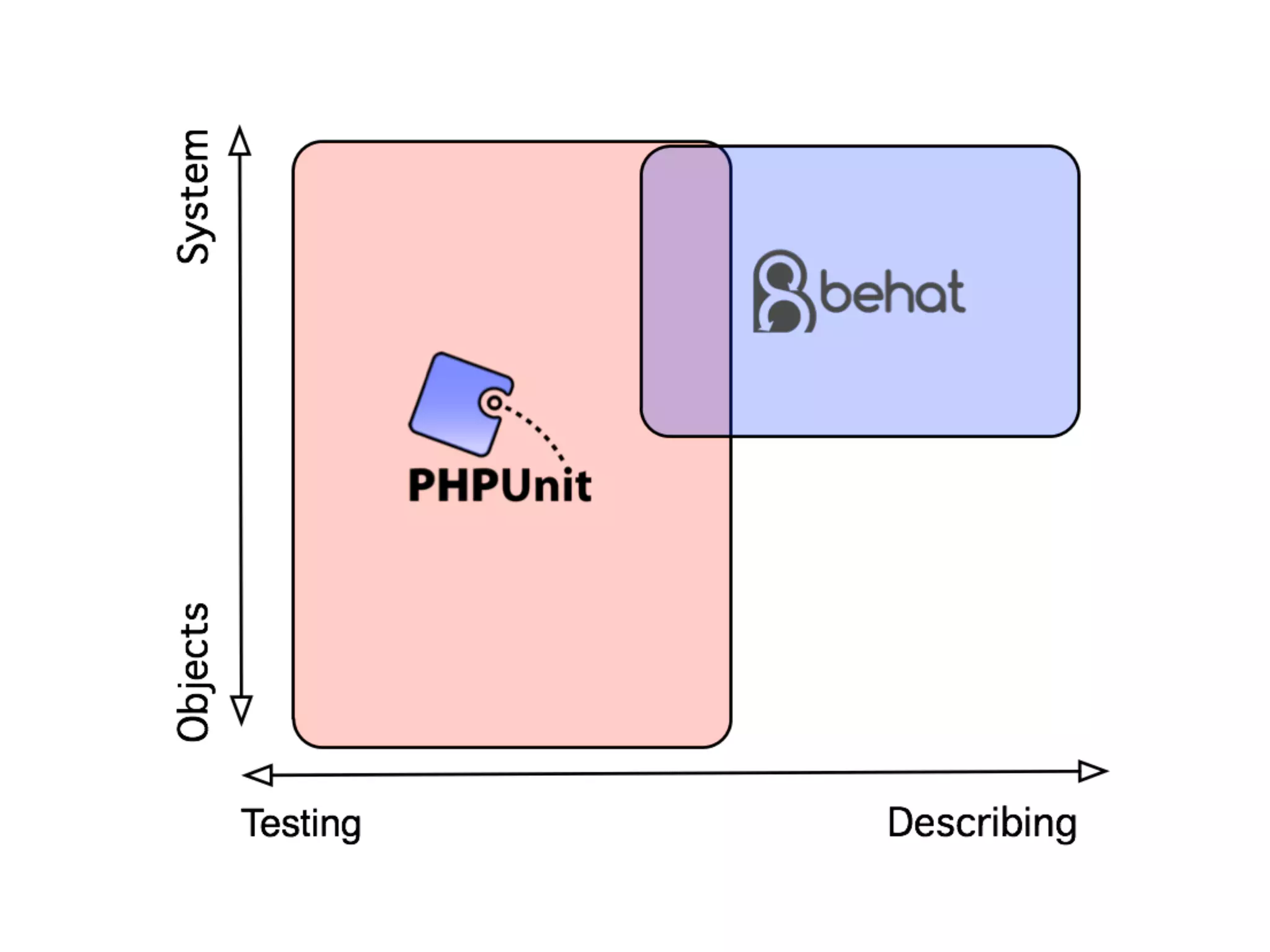
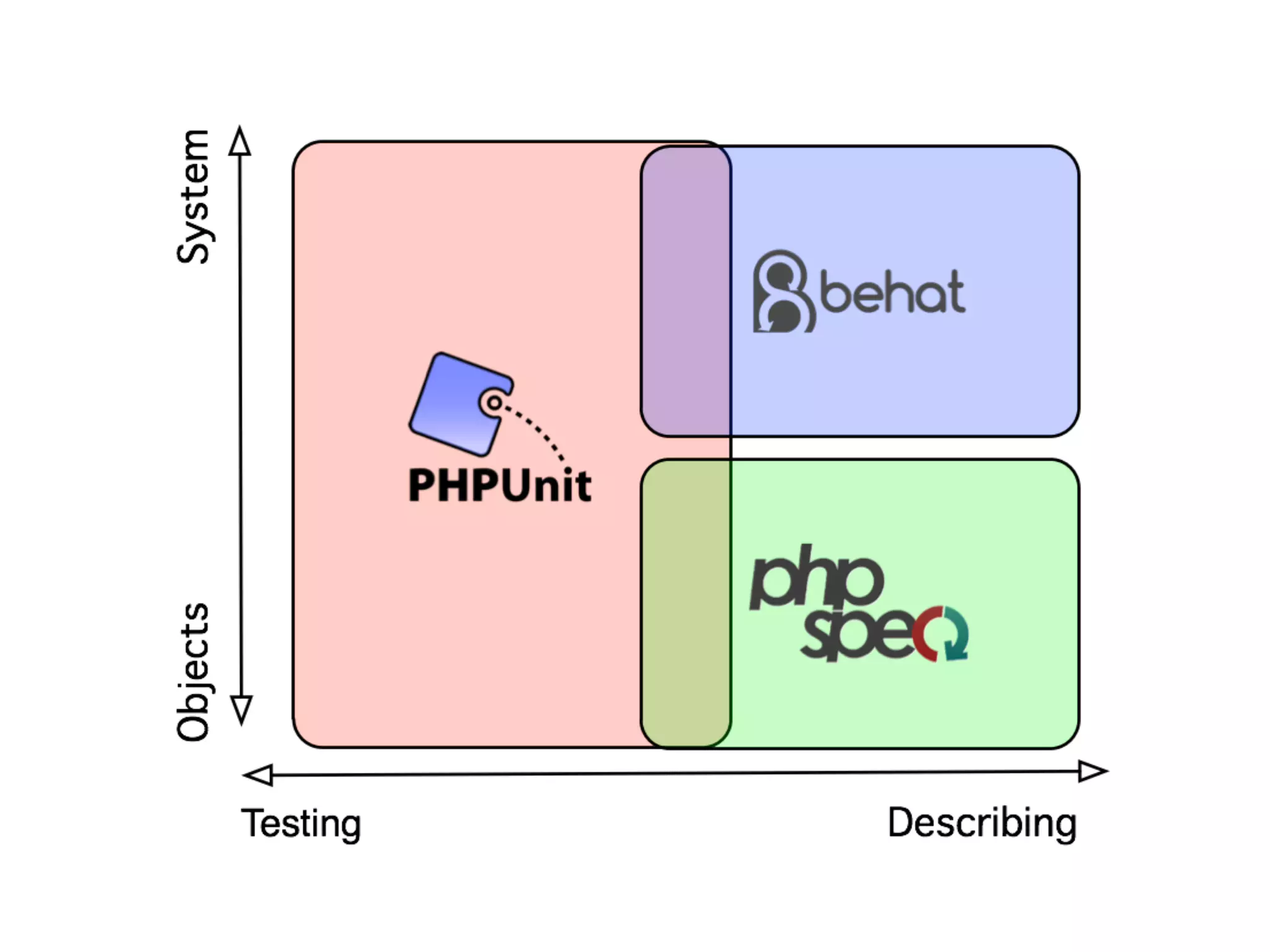
![An high level test
echo $result = (new Calculator(new Splitter(), new Parser()))->evaluate('[x]1x2x3');
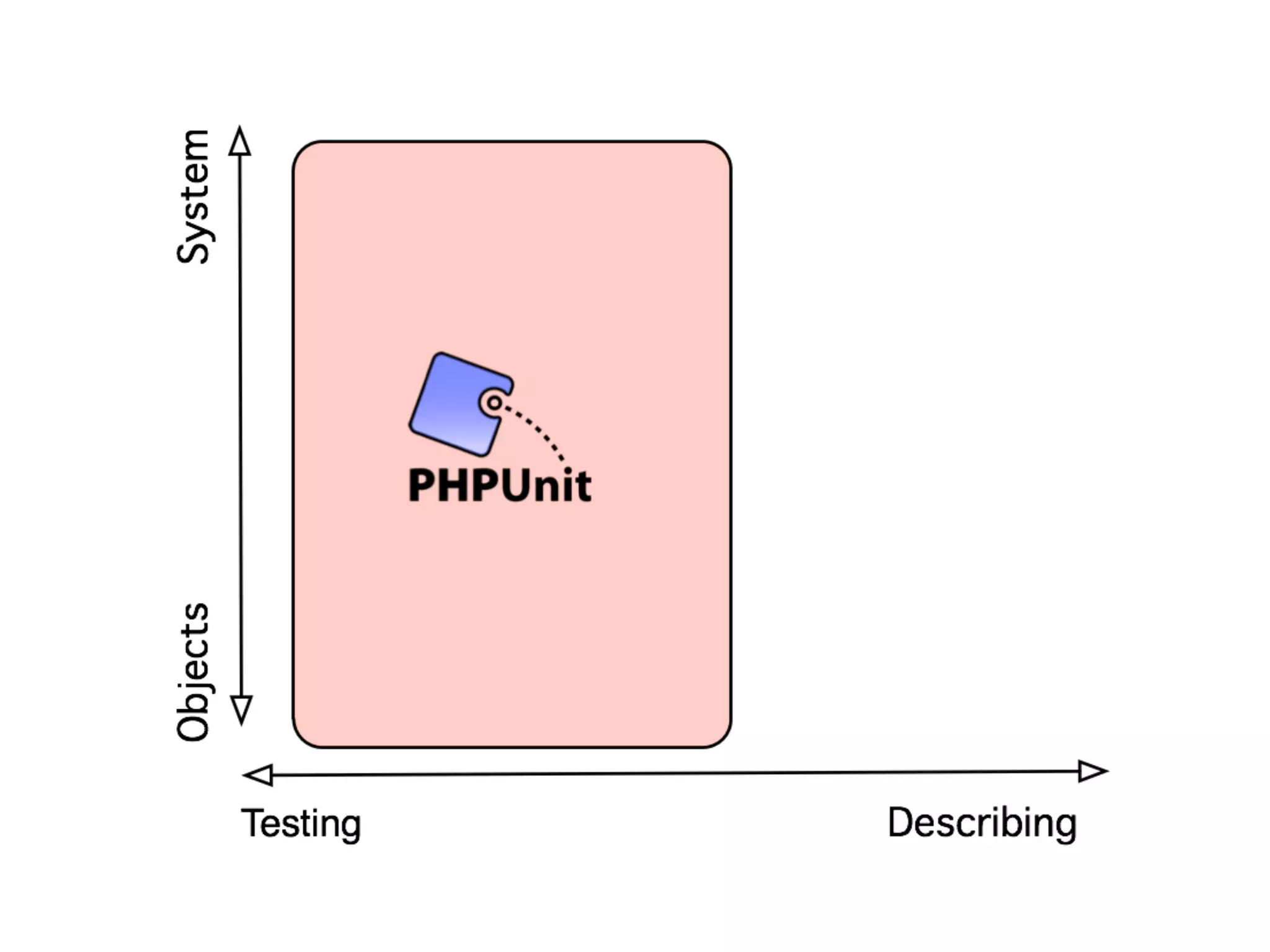
4 When your application becomes
composed of small self-contained
objects, you need some higher level of
testing (e.g. PHPUnit or Behat)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-151003153929-lva1-app6891/75/TDD-with-PhpSpec-107-2048.jpg)
![Kata - string calculator
4 Empty string should evaluate to zero
4 Zero as a string should evaluate to zero
4 Numeric string should evaluate to that number
4 Space separated numbers should be added
together
4 Whitespace separated numbers should be added
together
4 Custom separator can be specified (e.g.
’[+]1+2+3’ -> 6)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-151003153929-lva1-app6891/75/TDD-with-PhpSpec-108-2048.jpg)
