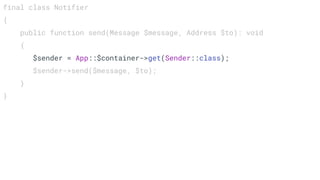
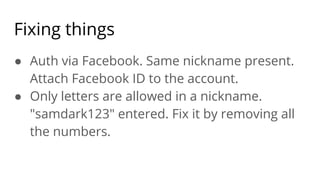
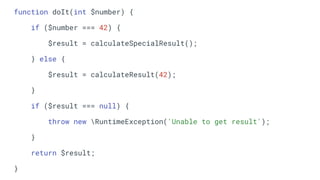
The document discusses various software development principles and best practices in PHP programming, covering topics such as composition vs. inheritance, managing state, dependency injection, handling exceptions, and structuring methods effectively. It emphasizes the importance of immutability, proper dependency management, and the necessity of thorough testing. Additionally, it provides guidance on object types and service structures to create maintainable and efficient code.












![abstract class Notifier
{
private string $template;
private array $parameters;
public function __construct(string $template, array $parameters = [])
{
// ...
}
protected function renderTemplate(): string
{
// ...
}
abstract public function send(): void;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/letstalkaboutcode-200530092839/85/Alexander-Makarov-Let-s-talk-about-code-13-320.jpg)
![final class EmailNotifier extends Notifier
{
private string $to;
private string $subject;
public function __construct(string $to, string $subject, string $template, array
$parameters = [])
{
// ...
}
public function send(): void
{
mail($this->to, $this->subject, $this->renderTemplate());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/letstalkaboutcode-200530092839/85/Alexander-Makarov-Let-s-talk-about-code-14-320.jpg)
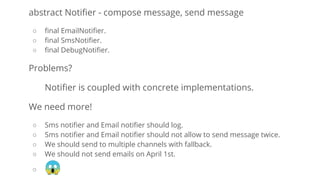




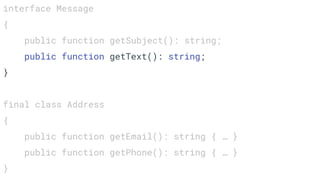
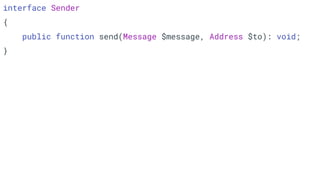





























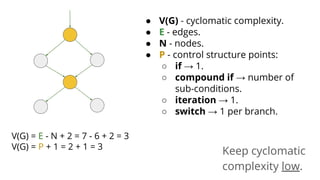

![function login(array $data)
{
if (isset($data['username'], $data['password'])) {
$user = $this->findUser($data['username']);
if ($user !== null) {
if ($user->isPasswordValid($data['password'])) {
$this->loginUser();
$this->refresh();
} else {
throw new InvalidArgumentException('Password is not valid.');
}
} else {
throw new InvalidArgumentException('User not found.');
}
} else {
throw new InvalidArgumentException('Both username and password are required.');
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/letstalkaboutcode-200530092839/85/Alexander-Makarov-Let-s-talk-about-code-61-320.jpg)
![function login(array $data)
{
if (!isset($data['username'], $data['password'])) {
throw new InvalidArgumentException('Both username and password are required.');
}
$user = $this->findUser($data['username']);
if ($user === null) {
throw new InvalidArgumentException('User not found.');
}
if (!$user->isPasswordValid($data['password'])) {
throw new InvalidArgumentException('Password is not valid.');
}
$this->loginUser();
$this->refresh();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/letstalkaboutcode-200530092839/85/Alexander-Makarov-Let-s-talk-about-code-62-320.jpg)
![function login(array $data)
{
$this->assertUsernameAndPasswordPresent($data);
$user = $this->findUser($data['username']);
$this->assertUserFound($user);
$this->assertPasswordValid($user, $data['password']);
$this->loginUser();
$this->refresh();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/letstalkaboutcode-200530092839/85/Alexander-Makarov-Let-s-talk-about-code-63-320.jpg)
























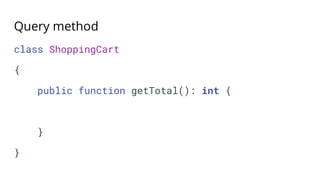

![Command method
class ShoppingCart
{
public function addItem(Item $item): void {
if ($this->getTotal() + $item->cost > self::MAX_TOTAL) {
throw new MaxTotalReached('Leave something for others!');
}
$this->items[] = $item;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/letstalkaboutcode-200530092839/85/Alexander-Makarov-Let-s-talk-about-code-90-320.jpg)