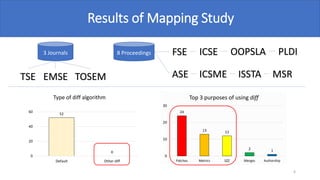
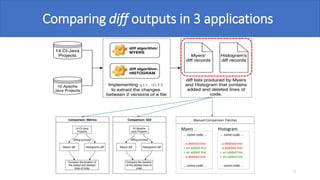
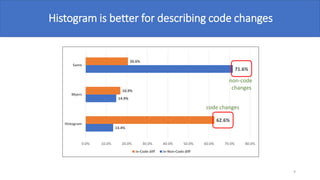
The document discusses various diff algorithms in Git, specifically Myers, Minimal, Patience, and Histogram, and their differences in output such as the number and position of changed lines. A mapping study reveals that Histogram is more effective in describing code changes compared to Myers. The authors encourage using the Histogram algorithm for analyzing code changes to achieve better accuracy in identifying modified lines.

![diff is essential in SE research field
2
Empirical Software
Engineering Research git diff [<options>] <commit> <commit> [--] [<path>…]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journalfirstpresentationv2-200722022322/85/How-different-are-different-diff-algorithms-in-Git-2-320.jpg)