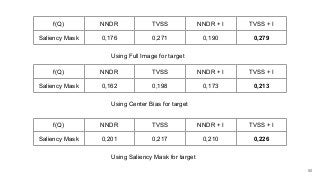
https://imatge.upc.edu/web/publications/time-sensitive-egocentric-image-retrieval-fidings-objects-lifelogs
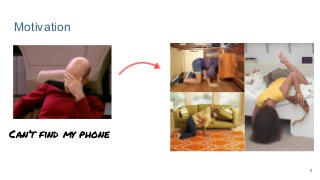
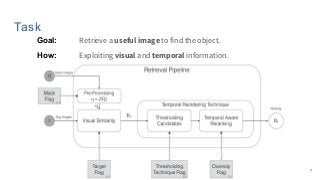
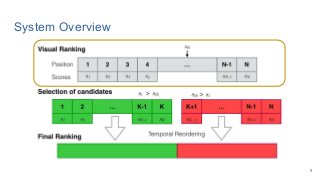
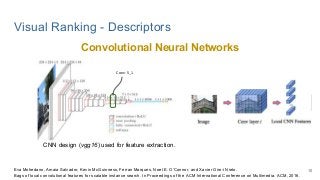
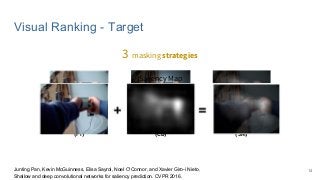
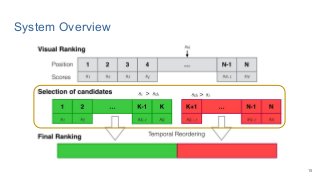
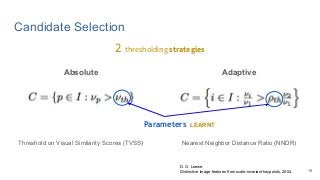
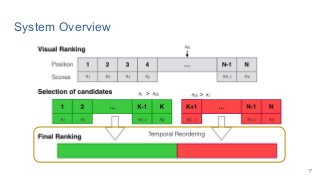
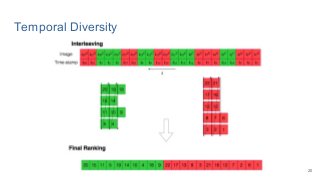
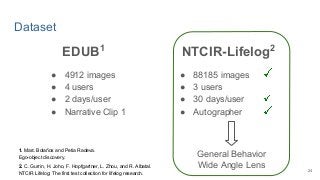
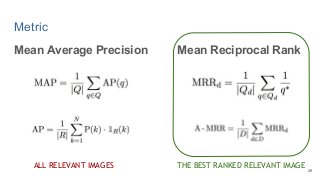
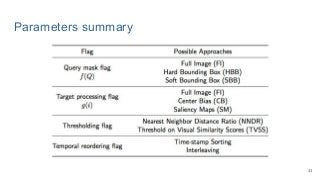
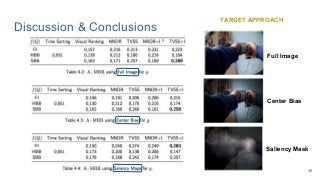
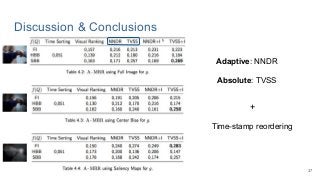
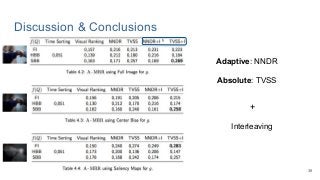
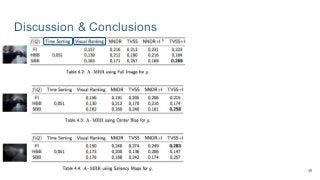
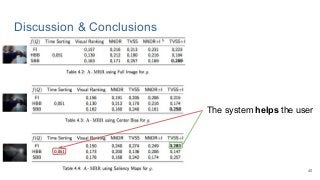
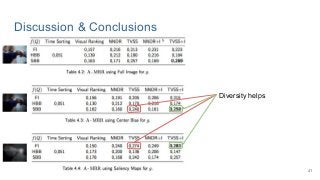
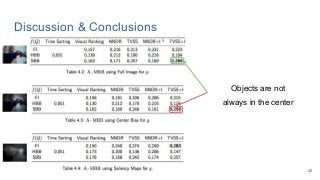
This work explores diverse practices for conducting an object search from large amounts of egocentric images taking into account their temporal information. The application of this technology is to identify where personal belongings were lost or forgotten. We develop a pipeline-structured system. Firstly, the images of the day being scanned are sorted based on their probability to depict the forgotten object. This stage is solved by applying an existing visual search engine based on deep learning features. Secondly, a learned threshold selects the top ranked images as candidates to contain the object. Finally the images are reranked based on temporal and diversity criteria. Furthermore, we build a validation environment for assessing the system's performance aiming to find the optimal configuration of its parameters. Due to the lack of related works to be compared with, this thesis proposes an novel evaluation framework and metric to assess the problem.