More Related Content
Similar to 08. cad&cam
Similar to 08. cad&cam (20)
More from vsksuresh2003 (7)
08. cad&cam
- 1. 1
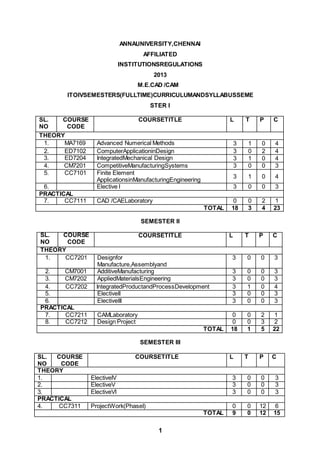
ANNAUNIVERSITY,CHENNAI
AFFILIATED
INSTITUTIONSREGULATIONS
2013
M.E.CAD /CAM
ITOIVSEMESTERS(FULLTIME)CURRICULUMANDSYLLABUSSEME
STER I
SL.
NO
COURSE
CODE
COURSETITLE L T P C
THEORY
1. MA7169 Advanced Numerical Methods 3 1 0 4
2. ED7102 ComputerApplicationinDesign 3 0 2 4
3. ED7204 IntegratedMechanical Design 3 1 0 4
4. CM7201 CompetitiveManufacturingSystems 3 0 0 3
5. CC7101 Finite Element
ApplicationsinManufacturingEngineering
3 1 0 4
6. Elective I 3 0 0 3
PRACTICAL
7. CC7111 CAD /CAELaboratory 0 0 2 1
TOTAL 18 3 4 23
SEMESTER II
SL.
NO
COURSE
CODE
COURSETITLE L T P C
THEORY
1. CC7201 Designfor
Manufacture,Assemblyand
Environments
3 0 0 3
2. CM7001 AdditiveManufacturing 3 0 0 3
3. CM7202 AppliedMaterialsEngineering 3 0 0 3
4. CC7202 IntegratedProductandProcessDevelopment 3 1 0 4
5. ElectiveII 3 0 0 3
6. ElectiveIII 3 0 0 3
PRACTICAL
7. CC7211 CAMLaboratory 0 0 2 1
8. CC7212 Design Project 0 0 3 2
TOTAL 18 1 5 22
SEMESTER III
SL.
NO
COURSE
CODE
COURSETITLE L T P C
THEORY
1. ElectiveIV 3 0 0 3
2. ElectiveV 3 0 0 3
3. ElectiveVI 3 0 0 3
PRACTICAL
4. CC7311 ProjectWork(PhaseI) 0 0 12 6
TOTAL 9 0 12 15
- 2. 2
SEMESTER IV
SL.
NO
COURSE
CODE
COURSETITLE L T P C
PRACTICAL
1. CC7411 ProjectWork(PhaseII) 0 0 24 12
TOTAL 0 0 24 12
TOTALCREDITSTOBEEARNED FOR THEAWARDOF THEDEGREE:72
LISTOF ELECTIVES FORM.E.CAD /CAM
SEMESTER I(ElectiveI)
SL.
NO
COURSE
CODE
COURSETITLE L T P C
1 CC7001 ComputerControl inProcessPlanning 3 0 0 3
2 ED7001 Optimization TechniquesinDesign 3 0 0 3
3 ED7101 AdvancedMechanicsofMaterials 3 0 0 3
4 ED7005 Design ofMaterialHandlingEquipments 3 0 0 3
SEMESTER II(Elective II &III)
SL.
NO
COURSE
CODE
COURSETITLE L T P C
1. CC7002 MechatronicsApplicationsinManufacturing 3 0 0 3
2. CC7003 IndustrialSafety Management 3 0 0 3
3. CD7003 Advanced ToolDesign 3 0 0 3
4. ED7202 MechanismsDesignandSimulation 3 0 0 3
5. IC7072 Computational FluidDynamics 3 0 0 3
6. CC7004 Reliability inEngineeringSystems 3 0 0 3
7. ED7071 IndustrialRoboticsand ExpertSystems 3 0 0 3
SEMESTER III(Elective IV, V &VI)
SL.
NO
COURSE
CODE
COURSETITLE L T P C
1. ED7004 Design ofHydraulicandPneumaticSystems 3 0 0 3
2. CC7005 DataCommunicationinCAD/CAM 3 0 0 3
3.
CC7006
PerformanceModellingandAnalysisofM
anufacturing System
3 0 0 3
4. ED7010 TribologyinDesign 3 0 0 3
5. CC7007 MetrologyandNonDestructiveTesting 3 0 0 3
6. CC7008 QualityManagementTechniques 3 0 0 3
7. CC7009 Designfor CellularManufacturingSystems 3 0 0 3
- 3. 3
MA7169 ADVANCED NUMERICALMETHODS LTPC310
4
AIM:
OBJECTIVE:
Toimpartknowledgeonnumericalmethodsthatwillcomeinhandytosolvenumericallytheproblemsthataris
einengineeringandtechnology.Thiswillalsoserveasaprecursorforfutureresearch.
UNITI ALGEBRAICEQUATIONS (9+3)
Systemsoflinearequations: GaussElimination method,pivotingtechniques,
Thomasalgorithmfortridiagonalsystem–Jacobi,GaussSeidel,SORiterationmethods-
Systemsofnonlinearequations:Fixedpointiterations,NewtonMethod,Eigenvalueproblems:powermetho
d,inversepowermethod,Faddeev– LeverrierMethod.
UNITII ORDINARYDIFFERENTIALEQUATIONS (9+3)
RungeKuttaMethodsforsystemofIVPs,numericalstability,Adams-
Bashforthmultistepmethod,solutionofstiffODEs,shootingmethod,BVP:Finitedifferencemethod,orthogo
nalcollocationmethod,orthogonalcollocationwith finiteelementmethod,Galerkinfinite element method.
UNITIII FINITE DIFFERENCE METHOD FOR TIME DEPENDENT PARTIAL
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION (9+3)
Parabolicequations:explicitandimplicitfinitedifferencemethods,weightedaverageapproximation-
DirichletandNeumannconditions–Twodimensionalparabolicequations–
ADImethod;Firstorderhyperbolicequations–
methodofcharacteristics,differentexplicitandimplicitmethods;numericalstabilityanalysis,methodoflines
–Waveequation:Explicitscheme-Stabilityofaboveschemes.
UNITIV FINITEDIFFERENCEMETHODS FOR ELLIPTICEQUATIONS (9+3)
LaplaceandPoisson’sequationsinarectangularregion:Fivepointfinitedifferenceschemes,Leibmann’sit
erativemethods,DirichletandNeumannconditions–
Laplaceequationinpolarcoordinates:finitedifferenceschemes–
approximationofderivativesnearacurvedboundarywhile usingasquaremesh.
UNITV FINITE ELEMENTMETHOD (9+3)
Partialdifferentialequations–Finiteelementmethod-
orthogonalcollocationmethod,orthogonalcollocation withfiniteelement method,Galerkinfinite
elementmethod.
T=15,TOTAL:60PERIODS
OUTCOME:
Ithelpsthestudentstogetfamiliarizedwiththenumericalmethodswhicharenecessarytosolve
numericallytheproblems thatariseinengineering.
REFERENCES
1. SaumyenGuhaandRajeshSrivastava,“NumericalmethodsforEngineeringandScience”,
Oxford Higher Education,NewDelhi,2010.
2. GuptaS.K., “NumericalMethodsforEngineers”, NewAge Publishers, 1995
3. Burden,R.L.,andFaires,J.D.,“NumericalAnalysis–TheoryandApplications”,Cengage
Learning,IndiaEdition,NewDelhi,2009.
4. JainM.K.,IyengarS.R.,KanchiM.B.,Jain,“ComputationalMethodsforPartialDifferential
Equations”, NewAge Publishers,1993.
5. MortonK.W.andMayersD.F.,“Numericalsolutionofpartialdifferentialequations”,Cambridge
University press,Cambridge,2002.
- 4. 4
ED7102 COMPUTERAPPLICATIONSIN DESIGN LTPC3
024
OBJECTIVES:
Toimpartknowledgeoncomputergraphicswhichareusedroutinelyindiverseareasasscience,engine
ering,medicine,etc.
OUTCOME:
Withlaboratoryclassesinconjunction,Ithelpsthestudentstogetfamiliarizedwiththecomputergraphics
applicationindesign.Thisunderstandingreinforcestheknowledgebeinglearnedandshortenstheover
alllearningcurveswhicharenecessarytosolveCAEproblemsthatarisein engineering.
UNITI INTRODUCTIONTOCOMPUTERGRAPHICSFUNDAMENTALS 8
Outputprimitives(points,lines,curvesetc.,),2-D&3-
Dtransformation(Translation,scaling,rotators)windowing- viewports -clipping transformation.
UNITII CURVESANDSURFACESMODELLING 10
Introductiontocurves-Analyticalcurves:line,circleandconics–syntheticcurves:Hermitecubicspline-
BeziercurveandB-Splinecurve– curve manipulations.
Introductiontosurfaces-
Analyticalsurfaces:Planesurface,ruledsurface,surfaceofrevolutionandtabulatedcylinder–
syntheticsurfaces:Hermitebicubicsurface-BeziersurfaceandB-Splinesurface-surface manipulations.
UNITIII NURBSANDSOLIDMODELING 9
NURBS-Basics-curves ,lines, arcs, circle andbi linearsurface.
RegularizedBooleansetoperations-primitiveinstancing-sweeprepresentations-
boundaryrepresentations-constructivesolidGeometry-comparisonofrepresentations-
userinterfaceforsolid modeling.
UNITIV VISUALREALISM 9
Hidden–Line–Surface–solidremovalalgorithmsshading–
coloring.Introductiontoparametricandvariationalgeometrybasedsoftware’sandtheirprinciplescreationo
fprismaticandloftedpartsusingthesepackages.
UNITV ASSEMBLY OF PARTSANDPRODUCTDATAEXCHANGE 9
Assemblymodeling-interferencesofpositionsandorientation-tolerancesanalysis-
masspropertycalculations- mechanismsimulation.
Graphicsandcomputingstandards–OpenGLDataExchangestandards–IGES,STEPetc–
Communicationstandards.
T=30, TOTAL :75PERIODS
Laboratorysession:Writinginteractiveprograms generate graphicsandtosolvedesignproblems-
usinganylanguageslikeAutoLISP/C/FORTRANetc.Eachassessmentshouldcontainacomponent
ofLaboratory session.
REFERENCES
1. WilliamMNeumannandRobertF.Sproul“PrinciplesofComputerGraphics”,McGrawHill
BookCo.Singapore,1989.
2. DonaldHearnandM.Pauline Baker “Computer Graphics”, PrenticeHall, Inc.,1992.
3. IbrahimZeidMasteringCAD/CAM – McGrawHill,InternationalEdition,2007.
4. Foley,WanDam,FeinerandHughes–Computergraphicsprinciples&practices,PearsonEducation –
2003.
5. DavidF.Rogers,JamesAlanAdams“Mathematicalelementsforcomputergraphics”second
edition,Tata McGraw-Hilledition.
- 5. 5
ED7204 INTEGRATEDMECHANICALDESIGN**
LT PC
(UseofApprovedDataBookis Permitted) 310 4
OBJECTIVES:
To know theintegrateddesignprocedureofdifferentmachineelementsformechanicalapplications.
OUTCOME:
Thiswillfamiliarizethestudentswiththeconceptsofintegrationofdesignofmachinesandstructures.
UNITI FUNDAMENTALSANDDESIGNOF SHAFTS 8
Phases ofdesign–Standardizationandinterchangeability ofmachineelements-Process and
FunctionTolerances–Individual andgroup tolerances– Selectionoffits fordifferentdesignsituations–
Designfor assemblyandmodularconstructions–Conceptsofintegration–BIS, ISO,DIN,BS,
ASTMStandards.
Obliquestresses –TransformationMatrix– Principalstresses–Maximum shearstress -
TheoriesofFailure–Ductilevs. brittlecomponent design -
AnalysisandDesign ofshaftsfordifferent applications– integrateddesign ofshaft,bearing andcasing –
Design for rigidity
UNITII DESIGNOF GEARSANDGEARBOXES 12
Principlesofgear toothaction–Gearcorrection–Gear toothfailure modes– Stressesandloads
– Componentdesign ofspur, helical,bevel and wormgears– Designforsubassembly–
Integrateddesignofspeedreducersandmulti-speedgear boxes– applicationofsoftwarepackages.
UNITIII BRAKES&CLUTCHES 7
Dynamicsandthermalaspectsofbrakesandclutches–
Integrateddesignofbrakesandclutchesformachinetools, automobilesandmechanical
handlingequipments.
UNITIV INTEGRATEDDESIGN 18
IntegratedDesignofsystemsconsistingofshaft,
bearings,springs,motor,gears,belt,rope,chain,pulleys,Cam&Follower,flywheeletc.Example-
DesignofElevators,Escalators,GearBox,ValvegearMechanisms, MachineTools
T=15,TOTAL:60PERIODS
ThePatternofQuestionPaperwillconsistoneQuestionfromUnit–4for50%oftotalmarks.
**
a TermProject must be given forAssessment–3 (Compulsory)
REFERENCES:
1. NortonL.R., “MachineDesign–AnIntegratedApproach”PearsonEducation,2005
2. Newcomb,T.P.andSpur,R.T.,“AutomobileBrakesandBrakingSystems”,Chapmanand
Hall,2nd
Edition,1975.
3. MaitraG.M., “HandBookofGearDesign”,TataMcGrawHill,1985.
4. Shigley,J.E., “Mechanical EngineeringDesign”,McGrawHill,1986.
5. Prasad. L. V., “MachineDesign”, TataMcGrawHill,NewDelhi,1992.
6. Alexandrov,M.,MaterialsHandlingEquipments,MIRPublishers, 1981.
7. Boltzharol,A.,MaterialsHandlingHandbook, The RonaldPressCompany,1958.
Approved DataBooks
1. P.S.G.Tech., “DesignDataBook”, KalaikathirAchchagam, Coimbatore,2003.
2. Lingaiah.K.andNarayanaIyengar,“MachineDesignDataHandBook”,Vol.1&2,Suma
Publishers,Bangalore,1983
- 6. 6
CM7201 COMPETITIVEMANUFACTURINGSYSTEMS LTPC
300 3
AIM:
Toimpart knowledgeonthepace ofchangesinthemanufacturingtechnology.
OBJECTIVE:
Toemphasizetheknowledgeonthequalityimprovement,automation,andadvancedmanufacturingtechni
questocreatethehighest-caliberproductsquickly,efficiently,inexpensively,and insynchronizationwith
themarketing,sales,andcustomerserviceofthecompany.
UNITI MANUFACTURINGINACOMPETITIVEENVIRONMENT 9
Automationofmanufacturingprocess-Numericalcontrol-Adaptivecontrol-
materialhandlingandmovement-Industrialrobots-Sensortechnology-flexiblefixtures-
Designforassembly,disassemblyandservice.
UNITII GROUPTECHNOLOGY&FLEXIBLE MANUFACTURINGSYSTEMS 9
Partfamilies-classificationandcoding-Productionflowanalysis-Machinecelldesign-
Benefits.ComponentsofFMS-Applicationworkstations-Computercontrolandfunctions-
Planning,schedulingandcontrolofFMS-Scheduling-Knowledgebasedscheduling-
Hierarchyofcomputercontrol - Supervisory computer.
UNITIII COMPUTERSOFTWARE,SIMULATIONANDDATABASE OFFMS 9
Systemissues-Typesofsoftware-specificationandselection- Trends-Applicationofsimulation
- software-Manufacturingdatasystems-dataflow-CAD/CAMconsiderations-PlanningFMSdatabase.
UNITIV LEANMANUFACTURING: 9
Originofleanproductionsystem–Customerfocus–Muda(waste)–Standards–5Ssystem–
TotalProductiveMaintenance–standardizedwork–Manpowerreduction–Overallefficiency-Kaizen–
Commonlayouts-PrinciplesofJIT-Jidokaconcept–Poka-Yoke(mistakeproofing)-WorkerInvolvement–
Qualitycircleactivity–Kaizentraining-SuggestionProgrammes–HoshinPlanningSystem
(systematicplanningmethodology)–Leanculture.
UNITV JUSTIN TIME 9
CharacteristicsofJIT-Pullmethod-quality-smalllotsizes-workstationloads-closesupplierties–
flexibleworkforce-lineflowstrategy-preventivemaintenance-Kanbansystem-strategicimplications -
implementationissues -Leanmanufacture.
TEXTBOOKS:
TOTAL:45PERIODS
1. GrooverM.P., "Automation,ProductionSystems and Computer
IntegratedManufacturing ", ThirdEdition,Prentice-Hall,2007.
2. PascalDennis,“LeanProductionSimplified:APlain-LanguageGuidetotheWorld'sMost
Powerful ProductionSystem”, (Secondedition),ProductivityPress, NewYork, 2007.
REFERENCES
1. Jha,N.K. “Handbookof FlexibleManufacturingSystems", AcademicPressInc.,1991.
2. Kalpkjian,“ManufacturingEngineeringandTechnology",Addison-Wesley
PublishingCo.,1995.
3. TaiichiOhno,Toyota,"ProductionSystemBeyondLarge-
ScaleproductionProductivityPress(India)Pvt.Ltd.1992.
- 7. 7
CC7101 FINITEELEMENTAPPLICATIONSINMANUFACTURING L
TPCENGINEERING 3 1 0 4
AIM:
Theaimistoprovidethestudentswithknowledgeofthefiniteelementmethodthatwillbeofusein different
manufacturingareasandto provideafoundationforfurther study.
OBJECTIVE:
Theobjectiveistoequipstudentswithfundamentalsoffiniteelementprinciplessoastoenablethemtoun
derstandthebehaviourofvariousfiniteelementsandtobeabletoselectappropriateelementstosolveph
ysicalandengineeringproblemswithemphasisonstructuraland thermal engineering applications.
UNITI INTRODUCTION: 6
BasicsofFEM–Initialvalueandboundaryvalueproblems–
wightedresidualGalerkinandsRaleighRitzmethods–reviewofVariationalcalculus–Integrationbyparts–
Basicsofvariationalformulation.
UNITII ONEDIMENSIONALANALYSIS: 10
StepsinFEA–Discretization,function–
derivationofelementcharacteristicsmatrix,shapefunction,assemblyandimpositionofboundarycondition
s–solutionandpostprocessing–Onedimensional analysisinsolidmechanicsandheattransfer.
UNITIII SHAPEFUNCTIONSANDHIGHERORDERFORMULATIONS 10
GlobalandNaturalCo-ordinates–Shapefunctionsforoneandtwodimensionalelements–
Threenodedtriangularand fournodedquadrilateralelement– Nonlinearanalysis–
Isoparametricelements–Jacobianmatricesandtransformations–
Basicsoftwodimensionalaxisymmetricanalysis.
UNITIV ANALYSIS OF PRODUCTIONPROCESSES 10
FEAnalysisofmetalcasting–Specialconsiderations,latentheatincorporation,gapelement–
timesteppingprocedures–Crank–Nicholsonalgorithm–Predictionofgrainstructure-
Basicconceptsofplasticity–Solidandflowformulation–smallincrementaldeformationformulation–FE
Analysisofmetal cutting, chipseparationcriteria,incorporationofstrainratedependency.
UNITV COMPUTERIMPLEMENTATION 9
PreProcessing,Meshgeneration,elementsconnectivity,boundaryconditions,inputofmaterialandproces
singcharacteristics–Solutionandpostprocessing–
OverviewofapplicationpackagessuchasANSYSandDEFORM–
Developmentofcodeforonedimensionalanalysisandvalidation.
TEXTBOOKS:
T=15,TOTAL:60PERIODS
1. Reddy,J.N, “AnIntroduction tothe Finiteelement Method”,McGraw – Hill,1985.
2. Rao, “FiniteElementMethod in Engineering”, PergammonPress,1989.
REFERENCES
1. Bathe, K.J., “FiniteElement Procedures inEngineeringAnalysis,1990.
2. Kobayashi,S,Soo-IK-Oh andAltan,T, “Metalformingandthe FiniteelementMethods”, Oxford
University Press,1989.
3. Lewis,R.W., Morgan, K,Thomas,H.R.,andSeetharaman,K.N.,“TheFiniteElementMethod inHeat
TransferAnalysis”, JohnWiley,1994.
- 8. 8
CC7111 CAD/CAE LAB LTPC0
021
OBJECTIVE:
Toimpartknowledgeonhowtopreparedrawingsforvariousmechanicalcomponentsusinganycommer
ciallyavailable 3D modelingsoftware’s
ToimpartknowledgeontheuseofFiniteElementAnalysissoftwaretosolvevariousfieldproblemsinmec
hanicalengineering to optimize and verifythedesign ofmachineelements.
OUTCOME:
Withlaboratoryclasses,ithelpsthestudentsto get familiarizedwiththecomputerapplications
indesign andpreparingdrawings forvariousmechanical components.
Model andanalyzevariousphysical problems
Selectappropriateelementsandgiveboundary conditions
Solve structural, thermal, modal anddynamicsproblems.
CADIntroduction.
Sketcher
Solidmodeling–Extrude,Revolve,Sweep,etcand Variational sweep,Loft,etc
Surfacemodeling–Extrude,Sweep, Trim ..etcandMeshofcurves,Freeformetc
Featuremanipulation – Copy,Edit,Pattern,Suppress,Historyoperationsetc.
Assembly-Constraints,ExplodedViews,Interferencecheck
Drafting-Layouts,Standard&SectionalViews,Detailing&Plotting.
ExercisesinModelinganddraftingofMechanicalComponents-AssemblyusingParametricandfeature
basedPackageslikePRO-E/SOLIDWORKS/CATIA/NXetc
AnalysisofMechanicalComponents– UseofFEAPackageslikeANSYS/NASTRANetc.,
Exercisesshallincludeanalysisof
i) Machine elementsunder Static loads
ii) Thermal Analysisofmechanical systems
iii) Modal Analysis
iv) Machineelementsunder Dynamicloads
v) Non-linearsystems
TOTAL:30PERIODS
CC7201 DESIGN FORMANUFACTURE,ASSEMBLYAND LTP
CENVIRONMENTS 3003
OBJECTIVES:
Toknowtheconcept of designformanufacturing,assembly andenvironment.
Toknowthecomputerapplicationindesignfor manufacturingand assembly.
OUTCOME:
To makethestudentsgetacquaintedwiththedesignformanufacturing,assemblyandenvironment.
UNITI INTRODUCTION 5
Generaldesignprinciplesformanufacturability-
strengthandmechanicalfactors,mechanismsselection,evaluationmethod,Processcapability-
FeaturetolerancesGeometrictolerances-Assemblylimits-Datumfeatures -Tolerancestacks.
UNITII FACTORSINFLUENCINGFORM DESIGN 13
Workingprinciple,Material,Manufacture,Design-Possiblesolutions-Materialschoice-
Influenceofmaterialsonformdesign -formdesignofweldedmembers,forgings and castings.
- 9. 9
UNITIII COMPONENT DESIGN -MACHININGCONSIDERATION 8
Designfeaturestofacilitatemachining-drills-millingcutters-keyways-
Dowelingprocedures,countersunkscrews-Reductionofmachinedarea-simplificationbyseparation-
simplificationbyamalgamation-Designformachinability-Designforeconomy-Designforclampability-
Designforaccessibility -Design for assembly.
UNITIV COMPONENT DESIGN -CASTINGCONSIDERATION 10
RedesignofcastingsbasedonPartinglineconsiderations-
Minimizingcorerequirements,machinedholes,redesignofcastmemberstoobviatecores.Identificationof
uneconomicaldesign
-Modifyingthedesign -grouptechnology-Computer ApplicationsforDFMA
UNITV DESIGNFORTHEENVIRONMENT 9
Introduction–Environmentalobjectives–Globalissues–Regionalandlocalissues–BasicDFEmethods–
Designguidelines–Exampleapplication–Lifecycleassessment–Basicmethod–
AT&T’senvironmentallyresponsibleproductassessment-Weightedsumassessmentmethod–
Lifecycleassessmentmethod–Techniquestoreduceenvironmentalimpact–
Designtominimizematerialusage–Designfordisassembly–Designforrecyclability–
Designforremanufacture–Designfor energyefficiency– Designto regulationsandstandards.
REFERENCES
TOTAL:45 PERIODS
1. Boothroyd,G,1980DesignforAssemblyAutomationandProductDesign.NewYork,MarcelDekker.
2. Bralla,DesignforManufacture handbook,McGrawhill,1999.
3. Boothroyd,G, HeartzandNike,Product DesignforManufacture,Marcel Dekker,1994.
4. Dickson,John.R,andCorrodaPoly,EngineeringDesignandDesignforManufactureandStructuralApp
roach, FieldStonePublisher,USA,1995.
5. Fixel,J. Designfor theEnvironmentMcGrawhill.,1996.
6. GraedelT.AllenBy.B,DesignfortheEnvironmentAngleWoodCliff,PrenticeHall.ReasonPub., 1996.
7. KevienOttoandKristinWood, ProductDesign.PearsonPublication, 2004.
CM7001 ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING LT P C3 0
0 3
OBJECTIVE:
ToeducatestudentswithfundamentalandadvancedknowledgeinthefieldofAdditivemanufacturingte
chnologyandtheassociatedAerospace,Architecture,Art,Medicalandindustrialapplications.
OUTCOME:
Oncompletionofthiscourse,theywilllearnaboutavarietyofAdditiveManufacturing(AM)technologies,their
potentialtosupportdesignandmanufacturing,casestudiesrelevanttomasscustomizedmanufacturing,an
dsomeoftheimportantresearchchallengesassociatedwithAMand itsdata processingtools
UNITI INTRODUCTION: 8
Need-DevelopmentofAMsystems–AMprocesschain-ImpactofAMonProductDevelopment
-VirtualPrototyping-RapidTooling–RPtoAM-ClassificationofAMprocesses-Benefits-Applications.
- 10. 10
UNITII REVERSEENGINEERINGANDCADMODELING: 10
Basicconcept-Digitizationtechniques–Modelreconstruction–
DataProcessingforRapidPrototyping:CADmodelpreparation,Datarequirements–
Geometricmodelingtechniques:Wireframe,surfaceandsolidmodeling–dataformats-
Datainterfacing,Partorientationandsupportgeneration,Supportstructuredesign,ModelSlicing,Toolpath
generation-SoftwareforAM-Casestudies.
UNITIII LIQUIDBASEDANDSOLID BASEDADDITIVEMANUFACTURINGSYSTEMS:
10
StereolithographyApparatus(SLA):Principle,pre-buildprocess,part-buildingandpost-
buildprocesses,photopolymerizationofSLresins,partqualityandprocessplanning,recoatingissues,mate
rials,advantages,limitationsandapplications.
SolidGroundCuring(SGC):workingprinciple,process,strengths,weaknessesandapplications.Fusedde
positionModeling(FDM):Principle,detailsofprocesses,processvariables,types,products,materialsanda
pplications.LaminatedObjectManufacturing(LOM):WorkingPrinciples,detailsofprocesses,
products,materials,advantages,limitationsandapplications-Casestudies.
UNITIV POWDERBASEDADDITIVEMANUFACTURINGSYSTEMS: 10
SelectiveLaserSintering(SLS):Principle,process,IndirectanddirectSLS-
powderstructures,materials,postprocessing,surfacedeviationandaccuracy,Applications.LaserEngine
eredNetShaping(LENS):Processes,materials,products,advantages,limitationsandapplications–
CaseStudies.
UNITV OTHERADDITIVEMANUFACTURINGSYSTEMS: 7
ThreedimensionalPrinting(3DP):Principle,basicprocess,Physicsof3DP,typesofprinting,processcapabi
lities,materialsystem.Solidbased,Liquidbasedandpowderbased3DPsystems,strengthandweakness,A
pplicationsandcasestudies.ShapeDepositionManufacturing(SDM),Ballastic
ParticleManufacturing(BPM),SelectiveLaserMelting, ElectronBeamMelting.
TOTAL:45PERIODS
REFERENCES
1. Gibson,I.,Rosen,D.W.andStucker,B.,“AdditiveManufacturingMethodologies:RapidPrototyping
toDirect Digital Manufacturing”,Springer, 2010.
2. Chua,C.K.,LeongK.F.andLimC.S.,“Rapidprototyping:Principlesandapplications”,secondedition,
World ScientificPublishers,2010.
3. Gebhardt,A., “Rapidprototyping”,Hanser GardenerPublications, 2003.
4. Liou,L.W.andLiou,F.W.,“RapidPrototypingandEngineeringapplications:Atoolboxforprototypedev
elopment”,CRCPress,2011.
5. Kamrani, A.K. andNasr, E.A., “RapidPrototyping:Theory andpractice”,Springer, 2006.
6. Hilton,P.D.andJacobs,P.F.,RapidTooling:TechnologiesandIndustrialApplications,CRCpress,
2005.
CM7202 APPLIEDMATERIALSENGINEERING LTPC300
3
OBJECTIVE:
ThiscourseprovidesknowledgeintheareasofIndustrialmetallurgy,advancedmaterialsandselection
ofmaterials forindustrial applications.
UNITI ELASTICANDPLASTICBEHAVIOUR 8
MechanismofElasticandPlasticdeformation,Anelasticityandviscoelasticity-
roleofdislocations,yieldstress,shearstrengthofperfectandrealcrystals–
Strengtheningmechanism,work,hardening,solidsolutioning,grainboundarystrengthening,Polyphasem
ixture,precipitation,particlefibreanddispersionstrengthening.Effectoftemperature,strainandstrainrateo
nplasticbehaviour– Superplasticity.
- 11. 11
UNITII FRACTUREBEHAVIOUR 8
Griffith’stheory-stressintensityfactorandfracturetoughness-Tougheningmechanisms–
Ductile,brittletransitioninsteel-Hightemperaturefracture,creep– Larson-Miller,Parameter–
Deformationandfracturemechanismmaps–
Fatigue.Lowandhighcyclefatiguetest,crackinitiationandpropagationmechanismsandParislaw–
ResidualLifeEstimation-Effectofsurfaceandmetallurgicalparametersonfatigue–
fractureofnonmetallicmaterials–Failureanalysis,sourcesof failure,procedureoffailureanalysis.
UNITIII SELECTIONOFMATERIALS 8
Motivation,costbasisandservicerequirements–
selectionforMechanicalproperties,strength,toughness,fatigueandcreep–
Selectionforsurfacedurabilitycorrosionandwearresistance–
Relationshipbetweenmaterialsselectionandprocessing–Casestudiesinmaterialsselectionwith
Relevance to aero,auto, marine, machineryandnuclearapplications.
UNITIV MATERIALPROCESSING 9
Processingofengineeringmaterials–PrimaryandSecondaryprocesses–
astability,Weldability,forgeabilityandmalleability Criteria– Process induceddefects –
Monitoringandcontrol.
UNITV MODERNMATERIALSANDTREATMENT 12
Dualphasesteels,highstrengthlowalloysteel,transformationincludedplasticitysteel,maragingsteel,sma
rtmaterials,propertiesandapplicationsofengineeringplasticsandcompositesmaterials-
advancedstructuralceramics–WC,TiC,TaC,Al2O3,SiC,Si3N4,CBN,diamond–Plasma,PVD,CVD-
thickandthinfilmdeposition–FunctionallyGradientMaterials,Nanomaterials
OUTCOME:
TOTAL:45PERIODS
AttheendofthiscoursethestudentwillbeabletoselectthematerialsforEngineeringapplicationsbyundersta
ndingbasicmechanicalpropertiesofmaterials,therelationofthemicrostructureandmechanicalproperties,
processingtechniquesforcontrollingshapeandproperties inthefinalproductandableto
workinR&Dactivity in thefieldofmaterialsscience.
REFERENCES:
1. Dieter, G.E., “MechanicalMetallurgy”,McGrawHill,1988.
2. Charles,J.A.,Crane, F.A.AandFurness, J.A.G., “Selection and use ofengineeringMaterials”,
(3 rdEdition, Butterworth – Heiremann, 1977.
3. James,K.W.,Wiley, Intersam, John, “TheHandbookofAdvanceMaterials”,Wilson
Publishers.,2004.
4. Burakonsa,T.Z.andWierzchan.T.,“SurfaceEnggofMeterials”-PrinciplesofEquipment,Techniques.
5. Courtney, T.H.,“Mechanical BehaviorofMaterials” ,(2ndedition), McGrawHill,2000.
6. Flinn,R.A.andTrojan,P.K..,“EngineeringMaterialsandtheirApplications”(4th
Edition),Jaico,1999.
7. Metalshandbook,vol.10, “FailureAnalysisandPrevention”,(10thedition), 1994.
WEB REFERENCES:
1. www.astm.org/labs/pages/131350.htm
2. www.appliedmaterials.com/carrers/agu-ei.html
CC7202 INTEGRATEDPRODUCT DESIGN AND PROCESS L TP C
DEVELOPMENT 3 10 4
UNITI INTRODUCTION 12
NeedforIPPD-StrategicimportanceofProductdevelopment-
integrationofcustomer,designer,materialsupplierandprocessplanner,Competitorandcustomer-
behavioranalysis.Understandingcustomer-promotingcustomerunderstanding-
involvecustomerindevelopmentandmanaging requirements-Organizationprocessmanagementand
improvement
- 12. 12
UNITII CONCEPT GENERATION,SELECTIONANDTESTING 12
Planandestablishproductspecifications.Task-Structuredapproaches-clarification-search-
externallyandinternally-Exploresystematically-reflectonthesolutionsandprocesses-conceptselection-
methodology-benefits.Implications-Productchange-variety-componentstandardization -product
performance - manufacturability – Concept TestingMethodologies.
UNITIII PRODUCTARCHITECTURE 12
Productdevelopmentmanagement-establishingthearchitecture-creation-clustering-
geometriclayoutdevelopment-Fundamentalandincidentalinteractions-
relatedsystemleveldesignissues-secondarysystems-architectureofthechunks-
creatingdetailedinterfacespecifications-Portfolio Architecture.
UNITIV INDUSTRIALDESIGN 12
Integrateprocessdesign-Managingcosts-Robustdesign-IntegratingCAE,CAD,CAMtools–
Simulatingproductperformanceandmanufacturingprocesseselectronically-Needforindustrialdesign-
impact–designprocess-investigationofcustomerneeds-conceptualization-refinement
- managementoftheindustrialdesignprocess-technologydrivenproducts -user-drivenproducts-
assessingthequality ofindustrial design.
UNITV DESIGNFORMANUFACTURINGANDPRODUCT DEVELOPMENT 12
Definition-EstimationofManufacturingcost-reducingthecomponentcostsandassemblycosts–
Minimizesystemcomplexity-Prototypebasics-Principlesofprototyping-Planningforprototypes
-EconomicAnalysis-Understandingandrepresentingtasks-baselineprojectplanning-accelerating
theproject-projectexecution.
TOTAL:60PERIODS
ATermProject/Presentation mustbegiven for Assessment– 3 (Compulsory)
TEXTBOOK:
1. ProductDesignandDevelopment,KarlT.UlrichandStevenD.Eppinger,McGraw –HillInternational
Edns.1999
REFERENCES
1. ConcurrentEngg./IntegratedProductDevelopment.KemnnethCrow,DRMAssociates,6/3,ViaOliver
a,PalosVerdes, CA90274(310) 377-569,Workshop Book
2. EffectiveProductDesignandDevelopment,StephenRosenthal,BusinessOneOrwin,Homewood,199
2,ISBN, 1-55623-603-4
3. ToolDesign–
IntegratedMethodsforsuccessfulProductEngineering,StuartPugh,AddisonWesleyPublishing,Ney
ourk,NY,1991,ISBN0-202-41639-5
4.www.me.mit/2.7444.
CC7211 CAMLAB L T PC0
0 2 1
SimulationandMachiningusingCNC/DNCMachineTools–UseofFEMPackages-RelationalDataBase–
Networking–PracticeonComputerAidedMeasuringInstruments-ImageProcessing–
SoftwareDevelopmentforManufacturing–CNCControllers–UseofadvancedCNCMachiningPackages–
BusinessData Processing.
EQUIPMENTS FOR CAMLAB
1. CAMSoftware for toolpath generationfor
planermachining,contourmachining,drilling,turningetc
.&
- 14. 14
2. Mediumproductiontype CNCturningcenter with
popularindustrial typecontroller : 1
3. Mediumproductiontype CNCmachiningcenter
with popularindustrialtypecontroller : 1
4. Bench Model CMM : 1
5. Vision &imageprocessingsoftware : 2
6. DataProcessingSoftware : 2
TOTAL:30PERIODS
CC7212 DESIGN PROJECT L TPC0
032
OBJECTIVES:
Themainobjectiveistogiveanopportunitytothestudenttoachieveintegratedmechanicaldesignof
aproductthroughpartsdesignassemblypreparationofmanufacturingdrawings.
GUIDELINEFORREVIEWANDEVALUATION
Eachstudentsworksunderaprojectsupervisor.Theproductsystem/component(s)tobedesignedmaybe
decidedinconsultationwiththesupervisorandifpossiblewithanindustry.Aprojectreporttobesubmittedbyt
hestudentwhichwillbereviewedandevaluatedforinternalassessmentbyaCommitteeconstitutedbytheH
eadoftheDepartment.Attheendofthesemesterexaminationtheprojectworkisevaluatedbasedonoralpres
entationandtheprojectreportjointlybyexternalandinternalexaminers
OUTCOMES:
TOTAL:45PERIODS
Useofdesignprinciplesanddevelopconceptualandengineeringdesignofanycomponents.
Abilitytointegratethepartsdesignwithassemblyandabilitytopreparemanufacturingdrawings.
CC7001 COMPUTERCONTROL INPROCESSPLANNING L TP C
3 00 3
UNITI INTRODUCTION 9
ThePlaceofProcessPlanningintheManufacturingcycle-ProcessPlanningandProductionPlanning–
Process PlanningandConcurrentEngineering,CAPP, GroupTechnology.
UNITII PARTDESIGNREPRESENTATION 9
DesignDrafting-Dimensioning-Conventionaltolerance-Geometrictolerance-CAD-input/outputdevices-
topology-Geometrictransformation-Perspectivetransformation-Datastructure
-Geometricmodellingforprocessplanning-GTcoding-Theoptizsystem-TheMICLASSsystem.
UNITIII PROCESSENGINEERINGANDPROCESSPLANNING 9
Experienced,basedplanning-Decisiontableanddecisiontrees-Processcapabilityanalysis-
ProcessPlanning-Variantprocessplanning-Generativeapproach-ForwardandBackwardplanning,Input
format,Al.
UNITIV COMPUTERAIDEDPROCESSPLANNINGSYSTEMS 9
LogicalDesignofaProcessPlanning-Implementationconsiderations-
manufacturingsystemcomponents,productionVolume,No.ofproductionfamilies-CAM-
I,CAPP,MIPLAN,APPAS,AUTOPLAN andPRO,CPPP.
- 15. 15
UNITV ANINTERGRADEDPROCESSPLANNINGSYSTEMS 9
Totallyintegratedprocessplanningsystems-AnOverview-Modulusstructure-DataStructure,operation-
ReportGeneration,Expert processplanning.
TOTAL:45PERIODS
REFERENCES
1. GideonHaleviandRolandD.Weill,"PrinciplesofProcessPlanning",Alogicalapproach,Chapman&Hal
l,1995.
2. Tien-ChienChang,RichardA.Wysk,"AnIntroductionto automatedprocessplanningsystems",
PrenticeHall, 1985.
3. Chang,T.C., "An ExpertProcessPlanningSystem",Prentice Hall,1985.
4. NanuaSingh,"SystemsApproachtoComputerIntegratedDesignandManufacturing",JohnWiley&So
ns, 1996.
5. Rao, “ComputerAidedManufacturing ",TataMcGrawHillPublishingCo.,2000.
WEB REFERENCES:
1. http://claymore.engineer.gusu.edu/jackh/eod/automate/capp/capp.htm
2. http://Estraj.ute.sk/journal/engl/027/027.htm
ED7001 OPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUESIN DESIGN L T PC
3 0 03
UNITI UNCONSTRAINED OPTIMIZATIONTECHNIQUES 10
Introductiontooptimumdesign-Generalprinciplesofoptimization–
Problemformulation&theirclassifications-
Singlevariableandmultivariableoptimization,Techniquesofunconstrainedminimization–
Goldensection,Random,patternandgradientsearchmethods–Interpolationmethods.
UNITII CONSTRAINEDOPTIMIZATIONTECHNIQUES 10
Optimizationwithequalityandinequalityconstraints-Directmethods–
Indirectmethodsusingpenaltyfunctions,Lagrange multipliers-Geometricprogramming
UNITIII ADVANCEDOPTIMIZATIONTECHNIQUES 10
Multistageoptimization–
dynamicprogramming;stochasticprogramming;Multiobjectiveoptimization,GeneticalgorithmsandSimu
latedAnnealingtechniques;Neuralnetwork&Fuzzylogicprinciplesinoptimization.
UNITIV STATICAPPLICATIONS 8
Structuralapplications–Designofsimpletrussmembers-Designapplications–
Designofsimpleaxial,transverseloadedmembersforminimumcost,weight–
Designofshaftsandtorsionallyloaded members – Designofsprings.
UNITV DYNAMICAPPLICATIONS 7
DynamicApplications–
Optimumdesignofsingle,twodegreeoffreedomsystems,vibrationabsorbers.ApplicationinMechanisms–
Optimumdesignofsimplelinkage mechanisms.
TOTAL:45PERIODS
REFERENCES
1. Rao,Singaresu,S.,“EngineeringOptimization–Theory&Practice”,New Age International(P)
Limited,NewDelhi,2000.
2. JohnsonRay,C., “Optimumdesign ofmechanical elements”,Wiley,John&Sons, 1990.
3. KalyanamoyDeb,“OptimizationforEngineeringdesignalgorithmsandExamples”,Prentice
Hall ofIndiaPvt. 1995.
4. Goldberg,D.E.,“Geneticalgorithmsinsearch,optimizationandmachine”,Barnen,Addison-
Wesley,NewYork,1989.
- 16. 16
ED7101 ADVANCED MECHANICS OF MATERIALS LT PC
3 0 0 3
OBJECTIVES:
Toknowthe fundamentalsofmechanics ofmaterialsundervariousloadingconditions.
UNITI ELASTICITY 9
Stress-
StrainrelationsandgeneralequationsofelasticityinCartesian,Polarandcurvilinearcoordinates,differentia
lequationsofequilibrium-compatibility-boundaryconditions-representationofthree-
dimensionalstressofatensiongeneralizedhook'slaw-St.Venant'sprinciple-planestress-Airy's
stressfunction.Energymethods.
UNITII SHEARCENTERANDUNSYMMETRICALBENDING 10
Locationofshearcenterforvariousthinsections-
shearflows.StressesandDeflectionsinbeamssubjectedtounsymmetrical loading-kernofasection.
UNITIII STRESSES IN FLATPLATESANDCURVED MEMBERS 10
Circumferenceandradialstresses–deflections-curvedbeamwithrestrainedends-
closedringsubjectedtoconcentratedloadanduniformload-
chainlinksandcranehooks.Solutionofrectangularplates–purebendingofplates–deflection–
uniformlydistributedload–variousendconditions
UNITIV TORSIONOF NON-CIRCULARSECTIONS 7
Torsionofrectangularcrosssection-St.Venantstheory-elasticmembraneanalogy-
Prandtl'sstressfunction- torsional stressinhollowthinwalledtubes.
UNITV STRESSES IN ROTATINGMEMBERSANDCONTACTSTRESSES 9
Radialandtangentialstressesinsoliddiscandringofuniformthicknessandvaryingthicknessallowablespe
eds.Methodsofcomputingcontactstress-
deflectionofbodiesinpo
intandlinecontactapplications.
OUTCOME:
TOTAL:45PERIODS
Ithelpsthestudentsto be familiarizedwith the stressesunderdifferentloadingconditions.
REFERENCES
1. Arthur P Boresi,Richard J.Schmidt, “Advancedmechanicsofmaterials”,JohnWiley, 2002.
2. Timoshenko and Goodier,"Theory ofElasticity",McGrawHill.
3. RobertD.Cook,WarrenC.Young,"AdvancedMechanicsofMaterials",Mc-millanpub.Co.,1985.
4. Srinath. L.S., “AdvancedMechanicsofsolids”,TataMcGrawHill,1992.
5. GHRyderStrength ofMaterialsMacmillan,IndiaLtd,2007.
6. Allan F.Bower,“AppliedMechanicsofSolids”,CRC press–Special IndianEdition-2012,2010
7. K.BaskarandT.K.Varadan, “Theory ofIsotropic/OrthotropicElasticity”, AneBooksPvt. Ltd.,
NewDelhi,2009
ED7005 DESIGNOF MATERIALHANDLINGEQUIPMENTS LTPC
(Use ofApprovedDataBook Is Permitted) 30 03
OBJECTIVES:
Toimpartstudentsontheneed,use,applicationanddesignofdifferentmaterialhandlingtechniques,
equipments andmachinesusedincommonuseandinindustrialsector
- 17. 17
OUTCOME:
Thecoursewouldfamiliarizethestudentonthetechniquetoselectsuitablematerialhandlingequimenta
nddesign thembasedontheneed.
UNITI MATERIALS HANDLINGEQUIPMENT 5
Types,selectionandapplications
UNITII DESIGNOF HOISTS 10
Designofhoistingelements:Weldedandrollerchains-Hempandwireropes-Designofropes,pulleys,pulley
systems,sprocketsanddrums,Loadhandlingattachments.Designofforgedhooksandeyehooks–
cranegrabs-liftingmagnets-Grabbingattachments-Designofarrestinggear-Brakes:shoe,
bandandconetypes.
UNITIII DRIVESOF HOISTINGGEAR 10
Handandpowerdrives-Travelinggear-Railtravelingmechanism-cantileverandmonorailcranes-
slewing,jibandluffinggear-cogwheeldrive-selecting themotor ratings.
UNITIV CONVEYORS 10
Types-description-designandapplicationsofBeltconveyors,apronconveyorsandescalatorsPneumatic
conveyors,Screwconveyorsandvibratory conveyors.
UNITV ELEVATORS 10
Bucketelevators:design-loadingandbucketarrangements-Cageelevators-shaftway,guides,counter
weights,hoistingmachine,safety devices-Design offorklifttrucks.
REFERENCES
1. Rudenko,N.,Materialshandlingequipment,ELnveePublishers, 1970.
TOTAL:45PERIODS
2. Spivakovsy,A.O.andDyachkov,V.K.,ConveyingMachines,VolumesIand II,MIRPublishers,1985.
3. Alexandrov,M.,MaterialsHandlingEquipments,MIRPublishers,1981.
4. Boltzharol,A., MaterialsHandlingHandbook,The RonaldPressCompany,1958.
5. P.S.G.Tech., “DesignDataBook”, KalaikathirAchchagam, Coimbatore,2003.
6. Lingaiah.K.andNarayanaIyengar,“MachineDesignDataHandBook”,Vol.1&2,Suma
Publishers,Bangalore,1983
CC7002 MECHATRONICSAPPLICATIONSIN MANUFACTURING LT P C
30 0 3
UNITI INTRODUCTION 9
IntroductiontoMechatronics-Systems-MechatronicsinProducts-MeasurementSystems-
ControlSystems - Traditional designandMechatronicsDesign.
UNITII SENSORSANDTRANSDUCERS 9
Introduction-PerformanceTerminology-Displacement,PositionandProximity-VelocityandMotion-
Fluidpressure-Temperaturesensors-Lightsensors-Selectionofsensors-Signalprocessing -
Servosystems.
UNITIII MICROPROCESSORSINMECHATRONICS 9
Introduction-Architecture-Pinconfiguration-Instructionset-
ProgrammingofMicroprocessorsusing8085instructions-Interfacinginputandoutputdevices-
InterfacingD/AconvertersandA/Dconverters–Applications-Temperaturecontrol-Steppermotor control-
Traffic lightcontroller.
UNITIV PROGRAMMABLE LOGICCONTROLLERS 9
Introduction-Basicstructure-Input/Outputprocessing-Programming-MnemonicsTimers,Internal
relaysandcounters -Datahandling -Analoginput / output- SelectionofPLC.
UNITV DESIGNANDMECHATRONICS 9
Designing -Possibledesignsolutions- CasestudiesofMechatronics systems.
- 18. 18
TOTAL:45PERIODS
TEXTBOOKS:
1. MichaelB.HistandandDavid G.Alciatore, " Introduction
toMechatronicsandMeasurementSystems",McGraw-HillInternational
Editions,1999.
2. Bradley,D.A.,Dawson,D,Buru,N.C.andLoader,AJ,"Mechatronics",ChapmanandHall,1993.
3. Ramesh.S,Gaonkar,"MicroprocessorArchitecture,ProgrammingandApplications”WileyEastern,1
998.
4. Lawrence J.Kamm, "UnderstandingElectro-Mechanical
Engineering,AnIntroductiontoMechatronics",Prentice-Hall,2000.
5. Ghosh,P.K.andSridhar,P.R.,0000to8085,“IntroductiontoMicroprocessorsforEngineersandScienti
sts",SecondEdition,Prentice Hall,1995.
WEB REFERENCE:
1. www.cs.Indiana.edu.
CC7003 INDUSTRIALSAFETYMANAGEMENT LTPC3 0
0 3
UNITI SAFETY MANAGEMENT 9
Evaluationofmodernsafetyconcepts-Safetymanagementfunctions-
safetyorganization,safetydepartment-safetycommittee,safetyaudit-
performancemeasurementsandmotivation-employee participationinsafety- safetyand productivity.
UNITII OPERATIONALSAFETY 9
HotmetalOperation-Boiler,pressurevessels-heattreatmentshop-gasfurnaceoperation-electroplating-
hotbendingpipes-Safetyinweldingandcutting.Cold-metalOperation-SafetyinMachineshop-
Coldbendingandchamferingofpipes-metalcutting-shotblasting,grinding,painting-powerpressandother
machines.
UNITIII SAFETY MEASURES 9
Layoutdesignandmaterialhandling-Useofelectricity-Managementoftoxicgasesandchemicals-
Industrialfiresandprevention-Roadsafety-highwayandurbansafety-
Safetyofsewagedisposalandcleaning-Controlofenvironmentalpollution-
ManagingemergenciesinIndustries-planning,securityandriskassessments,on-
siteandoffsite.Controlofmajorindustrialhazards.
UNITIV ACCIDENTPREVENTION 9
Humansideofsafety-personalprotectiveequipment-
Causesandcostofaccidents.Accidentpreventionprogrammes-Specifichazardcontrolstrategies-
HAZOP-Traininganddevelopmentofemployees-First Aid- Firefighting devices-
Accidentreporting,investigation.
UNITV SAFETY,HEALTH,WELFARE&LAWS 9
Safetyandhealthstandards-Industrialhygiene-occupationaldiseasesprevention-Welfarefacilities-
Historyoflegislationsrelated toSafety-pressurevesselact-Indianboileract-
Theenvironmentalprotectionact- Electricity act -Explosiveact.
TEXTBOOKS:
TOTAL:45PERIODS
1. JohnV.GrimaldiandRollinH.Simonds,
"SafetyManagement",AllIndiaTravellersbookseller,NewDelhi-1989.
2. Krishnan N.V.,"Safety inIndustry",Jaico PublisherHouse,1996.
REFERENCES:
1. OccupationalSafety ManualBHEL.
2. IndustrialsafetyandthelawbyP.M.C.NairPublisher's,Trivandrum.
- 19. 19
3. Managingemergenciesin industries,LossPreventionofIndiaLtd.,Proceedings,1999.
4. SafetysecurityandriskmanagementbyU.K.Singh&J.M.Dewan,A.P.H.
Publishingcompany,NewDelhi,1996.
5. Singh,U.K.andDewan,J.M.,"Safety,Securityandriskmanagement",APHPublishingCompany,New
Delhi,1996.
CD7003 ADVANCED TOOLDESIGN L T PC
30 03
UNITI INTRODUCTIONTOTOOLDESIGN 8
Introduction–ToolEngineering–ToolClassifications–ToolDesignObjectives–
ToolDesigninmanufacturing-Challengesandrequirements-Standardsintooldesign-Tooldrawings-
Surfacefinish–FitsandTolerances-ToolingMaterials-FerrousandNonferrousToolingMaterials-
Carbides,CeramicsandDiamond-Nonmetallictoolmaterials-Designingwithrelationtoheattreatment
UNITII DESIGNOF CUTTINGTOOLS 9
MechanicsofMetalcutting–Obliqueandorthogonalcutting-Chipformationandshearangle-Single-
pointcuttingtools–Millingcutters– Holemakingcuttingtools-BroachingTools-Design ofForm
relievedandprofile relievedcutters-Designofgearandthreadmillingcutters
UNITIII DESIGNOF JIGSANDFIXTURES 10
Introduction–FixedGages–GageTolerances–selectionofmaterialforGages–IndicatingGages–
Automaticgages–Principlesoflocation–Locatingmethodsanddevices–Principlesofclamping– Drill
jigs– Chipformationindrilling– Generalconsiderationsin the designofdrill jigs–Drillbushings–
Methodsofconstruction–ThrustandTurningMomentsindrilling-Drilljigsandmodernmanufacturing-
TypesofFixtures–ViseFixtures–MillingFixtures–BoringFixtures–BroachingFixtures–LatheFixtures–
GrindingFixtures–ModularFixtures–CuttingForceCalculations.
UNITIV DESIGNOF PRESSTOOLDIES 10
TypesofDies–MethodofDieoperation–Clearanceandcuttingforcecalculations-
BlankingandPiercingdiedesign–Pilots–Strippersandpressurepads-Pressworkmaterials–Striplayout–
Short-runtoolingforPiercing–Bendingdies–Formingdies – Drawingdies-Designanddrafting.
UNITV TOOLDESIGNFORCNCMACHINETOOLS 8
Introduction–ToolingrequirementsforNumericalcontrolsystems–FixturedesignforCNCmachinetools-
Subplateandtombstonefixtures-Universalfixtures–Cuttingtools–Toolholdingmethods–
Automatictoolchangersandtoolpositioners–Toolpresetting–Generalexplanationofthe
BrownandSharpmachine.
REFERENCES:
TOTAL:45PERIODS
1. CyrllDonaldson,GeorgeH.LeCain,V.C.Goold,“ToolDesign”,TataMcGrawHillPublishing
CompanyLtd.,2000.
2. E.G.Hoffman,” Jig andFixtureDesign”,ThomsonAsiaPvtLtd, Singapore,2004
3. PrakashHiralal Joshi, “Toolingdata”,WheelerPublishing,2000
4. VenkataramanK., “Design ofJigs, FixturesandPresstools”,TMH,2005
5. HaslehurstM., “ManufacturingTechnology”,TheELBS,1978.
ED7202 MECHANISMS DESIGNANDSIMULATION L T PC
3 0 03
UNITI INTRODUCTION 9
- 20. 20
Reviewoffundamentalsofkinematics-classificationsofmechanisms-componentsofmechanisms
– mobilityanalysis– formationofoneD.O.F. multi loopkinematicchains,Networkformula–
Grossmotionconcepts-Basickinematicstructuresofserialandparallelrobotmanipulators-
Compliantmechanisms-Equivalentmechanisms.
UNITII KINEMATICANALYSIS 9
PositionAnalysis–
Vectorloopequationsforfourbar,slidercrank,invertedslidercrank,gearedfivebarandsixbarlinkages.Anal
yticalmethodsforvelocityandaccelerationAnalysis–
fourbarlinkagejerkanalysis.Planecomplexmechanisms-
auxiliarypointmethod.SpatialRSSRmechanism-Denavit-HartenbergParameters–
Forwardandinversekinematicsofrobotmanipulators.
UNITIII PATH CURVATURETHEORY,COUPLERCURVE 9
Fixedandmovingcentrodes,inflectionpointsand
inflectioncircle.EulerSavaryequation,graphicalconstructions–
cubicofstationarycurvature.Fourbarcouplercurve-cusp-crunode-couplerdrivensix-barmechanisms-
straightline mechanisms
UNITIV SYNTHESIS OF FOURBARMECHANISMS 9
Typesynthesis–Numbersynthesis–AssociatedLinkageConcept.Dimensionalsynthesis–
functiongeneration,pathgeneration,motiongeneration.Graphicalmethods-Poletechnique-
inversiontechnique-pointpositionreduction-two,threeandfourpositionsynthesisoffour-
barmechanisms.Analytical methods-Freudenstein’sEquation-Bloch’sSynthesis.
UNITV SYNTHESIS OFCOUPLERCURVEBASEDMECHANISMS &CAMMECHANISMS 9
CognateLingages-parallelmotionLinkages.Designofsixbarmechanisms-singledwell-doubledwell-
doublestroke.Gearedfivebarmechanism-multi-dwell.CamMechanisms-
determinationofoptimumsizeofcams.Mechanismdefects.StudyanduseofMechanismusingSimulationS
oft-warepackages.Studentsshoulddesignand fabricate amechanism modelastermproject.
Total45+30= 75PERIODS
NOTE:TUTORIAL/PRACTICE:30PERIODS
ATermProject must begiven for Assessment–3
(Compulsory)REFERENCES:
1. RobertL.Norton., “DesignofMachinery”,TataMcGrawHill,2005.
2. SandorG.N.,andErdmanA.G.,“AdvancedMechanismDesignAnalysisandSynthesis”,
Prentice Hall,1984.
3. Uicker,J.J., Pennock, G. R.andShigley, J.E., “Theory
ofMachinesandMechanisms”, OxfordUniversity Press, 2005.
4. AmitabhaGhoshandAsokKumarMallik,“TheoryofMechanismandMachines”,EWLP,
Delhi,1999.
5. KennethJ,Waldron,GaryL.Kinzel,“Kinematics,DynamicsandDesignofMachinery”,John
Wiley-sons,1999.
6. Ramamurti, V., “MechanicsofMachines”,Narosa, 2005.
IC7072 COMPUTATIONAL FLUIDDYNAMICS LT PC3 0
0 3
AIM
Thiscourseaimstointroducenumericalmodelinganditsroleinthefieldofheatandfluidflow,itwillenablethest
udentstounderstandthevariousdiscretisationmethodsandsolvingmethodologies
andtocreateconfidence tosolve complexproblemsinthefieldofheattransfer andfluid dynamics.
OBJECTIVES:
- 21. 20
Todevelopfinite differenceandfinitevolumediscretized forms oftheCFD equations.
Toformulate explicit&implicitalgorithms for solvingtheEuler Eqns&NavierStokesEqns.
UNITI GOVERNINGDIFFERENTIALEQUATIONANDFINITEDIFFERENCEMETHOD
10
Classification,InitialandBoundaryconditions–InitialandBoundaryValueproblems–
Finitedifferencemethod,Central,Forward,Backwarddifference,Uniformandnon-
uniformGrids,NumericalErrors, GridIndependenceTest.
UNITII CONDUCTIONHEATTRANSFER 10
Steadyone-dimensionalconduction,Twoandthreedimensionalsteadystateproblems,Transientone-
dimensional problem,Two-dimensional TransientProblems.
UNITIII INCOMPRESSIBLEFLUIDFLOW 10
GoverningEquations,StreamFunction–
Verticitymethod,Determinationofpressureforviscousflow,SIMPLEProcedureofPatankarandSpalding,
ComputationofBoundarylayerflow,finitedifferenceapproach.
UNITIV CONVECTIONHEATTRANSFERANDFEM 10
SteadyOne-Dimensional andTwo-Dimensional Convection– diffusion,Unsteadyone-
dimensionalconvection–diffusion,Unsteadytwo-dimensionalconvection–Diffusion–
Introductiontofiniteelementmethod–solutionofsteadyheatconductionbyFEM–Incompressibleflow–
simulationbyFEM.
UNITV TURBULENCEMODELS 5
AlgebraicModels–Oneequationmodel,K–єModels,StandardandHighandLowReynolds
number models,Predictionof fluidflowand heattransferusingstandard codes.
TOTAL:45PERIODS
REFERENCES
1. Muralidhar,K.,andSundararajan,T., “ComputationalFluidFlowandHeatTransfer”, Narosa
PublishingHouse,NewDelhi,1995.
2. Ghoshdasdidar,P.S., “ComputerSimulationofflowandheattransfer”TataMcGraw-
HillPublishingCompany Ltd.,1998.
3. Subas,V.Patankar“Numericalheattransferfluidflow”,HemispherePublishingCorporation,
1980.
4. Taylor,CandHughes,J.B.“FiniteElementProgrammingoftheNavier-StokesEquation”,
Pineridge PressLimited,U.K., 1981.
5. Anderson, D.A.,Tannehill,J.I., andPletcher, R.H.,“Computationalfluid
MechanicsandHeat Transfer “HemispherePublishingCorporation,NewYork,USA,1984.
6. Fletcher,C.A.J.“ComputationalTechniquesforFluidDynamics1”FundamentalandGeneral
Techniques,Springer–Verlag,1987.
7. Fletcher, C.A.J. “ComputationalTechniquesforfluidDynamics2”Specific
TechniquesforDifferentFlowCategories, Springer– Verlag,1987.
8. Bose,T.X., “Numerical FluidDynamics”NarosaPublishingHouse,1997.
CC7004 RELIABILITY INENGINEERINGSYSTEMS L TP C
3 00 3
UNITI RELIABILITY CONCEPT 9
Reliabilitydefinition–QualityandReliability–Reliabilitymathematics–Reliabilityfunctions–Hazardrate–
MeasuresofReliability–Designlife–Aprioriandposterioriprobabilities–Mortalityofacomponent–Bath
tubcurve– Usefullife.
UNITII FAILUREDATAANALYSIS 11
Datacollection–Empiricalmethods:Ungrouped/Grouped,Complete/Censoreddata–
Timetofailuredistributions: Exponential,Weibull– Hazardplotting–Goodnessoffittests.
- 22. 21
UNITIII RELIABILITYASSESSMENT 10
Differentconfigurations– Redundancy–m/n system–Complexsystems:RBD–Baye’smethod–
Cutandtiesets – FaultTreeAnalysis– Standbysystem.
UNITIV RELIABILITYMONITORING 8
Life testingmethods:Failureterminated– Timeterminated– SequentialTesting–Reliabilitygrowth
monitoring– Reliability allocation– Softwarereliability.
UNITV RELIABILITYIMPROVEMENT 7
Analysisofdowntime–Repairtimedistribution–SystemMTTR–Maintainabilityprediction–
Measuresofmaintainability – SystemAvailability– Replacementtheory.
REFERENCES
TOTAL:45PERIODS
1. Charles E. Ebeling, “Anintroduction to ReliabilityandMaintainabilityengineering”, TMH,2000.
2. RoyBillingtonandRonaldN.Allan,“ReliabilityEvaluationofEngineeringSystems”,Springer,
2007.
ED7071 INDUSTRIALROBOTICSANDEXPERTSYSTEMS L TPC
3 003
UNITI INTRODUCTIONANDROBOT KINEMATICS 10
DefinitionneedandscopeofIndustrialrobots–Robotanatomy–Workvolume–Precisionmovement–
Endeffectors–Sensors.RobotKinematics–Directandinversekinematics–Robottrajectories–
Controlofrobotmanipulators–Robotdynamics–Methodsfororientationandlocation ofobjects.
UNITII ROBOTDRIVESANDCONTROL 9
ControllingtheRobotmotion–Positionandvelocitysensingdevices–Designofdrivesystems–
HydraulicandPneumaticdrives–Linearandrotaryactuatorsandcontrolvalves–
Electrohydraulicservovalves,electricdrives–Motors–Designingofendeffectors–Vacuum,magneticand
airoperatedgrippers.
UNITIII ROBOT SENSORS 9
TransducersandSensors–Tactilesensor–Proximityandrangesensors–Sensingjointforces–
Roboticvisionsystem–ImageRepresentation-ImageGrabbing–Imageprocessingandanalysis
– EdgeEnhancement–ContrastStretching–BandRationing-Imagesegmentation–Patternrecognition–
Trainingofvisionsystem.
UNITIV ROBOTCELLDESIGNANDAPPLICATION 9
Robotworkcelldesignandcontrol–SafetyinRobotics–Robotcelllayouts–MultipleRobotsandmachine
interference–Robotcycletime analysis.Industrial applicationofrobots.
UNITV
MethodsofRobotProgramming–
Characteristicsoftasklevellanguagesleadthroughprogrammingmethods–
Motioninterpolation.Artificialintelligence–Basics–Goalsofartificialintelligence–AItechniques–
problemrepresentationinAI–Problemreductionandsolutiontechniques-Application ofAI andKBES
inRobots.
TEXTBOOK:
TOTAL:45PERIODS
ROBOT PROGRAMMING, ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND EXPERT
SYSTEMS 8
- 23. 22
1. K.S.Fu,R.C. GonzalezandC.S.G. Lee,“RoboticsControl, Sensing,VisionandIntelligence”,
McGrawHill,1987.
REFERENCES
1. Yoram Koren,”Roboticsfor Engineers’McGraw-Hill,1987.
2. Kozyrey,Yu.“IndustrialRobots”,MIRPublishersMoscow,1985.
3. Richard.D,Klafter,Thomas,A,Chmielewski,MichaelNegin,“RoboticsEngineering– An
IntegratedApproach”, Prentice-Hall ofIndiaPvt.Ltd.,1984.
4. Deb,S.R.” RoboticsTechnologyandFlexibleAutomation”, TataMc Graw-Hill,1994.
5. Mikell,P.Groover,MitchellWeis,Roger,N.Nagel,NicholasG.Odrey,”IndustrialRoboticsTechnology,
ProgrammingandApplications”,McGraw-Hill,Int.1986.
6. TimothyJordanidesetal ,”ExpertSystemsandRobotics“,Springer–Verlag,
NewYork,May1991.
ED7004 DESIGNOF HYDRAULICANDPNEUMATICSYSTEMS L T P C
3 0 0 3
UNITI OILHYDRAULICSYSTEMSANDHYDRAULICACTUATORS 5
HydraulicPowerGenerators–Selectionandspecificationofpumps,pumpcharacteristics.Linearand
Rotary Actuators–selection,specificationandcharacteristics.
UNITII CONTROLANDREGULATIONELEMENTS 12
Pressure-directionandflow controlvalves-reliefvalves,non-returnandsafetyvalves-actuationsystems.
UNITIII HYDRAULICCIRCUITS 5
Reciprocation,quickreturn,sequencing,synchronizingcircuits-accumulatorcircuits-industrialcircuits-
presscircuits-hydraulicmillingmachine-grinding,planning,copying,-forklift,earthmovercircuits- design
andselectionofcomponents- safetyandemergency mandrels.
UNITIV PNEUMATICSYSTEMSANDCIRCUITS 16
Pneumaticfundamentals-controlelements,positionandpressuresensing-logiccircuits-
switchingcircuits-fringeconditionsmodulesandtheseintegration-sequentialcircuits-cascademethods -
mappingmethods-stepcounter method-compoundcircuitdesign-combinationcircuitdesign.
UNITV INSTALLATION,MAINTENANCEANDSPECIALCIRCUITS 7
Pneumaticequipments-selectionofcomponents-designcalculations–application-faultfinding-
hydropneumaticcircuits-useofmicroprocessorsforsequencing-PLC,Lowcostautomation-Robotic
circuits.
REFERENCES
1. AntonyEspossito,“FluidPowerwithApplications”, Prentice Hall,1980.
TOTAL:45PERIODS
2. Dudleyt,A.PeaseandJohn J. Pippenger, “Basicfluidpower”, PrenticeHall,1987.
3. AndrewParr,“HydraulicandPneumatics” (HB), JaicoPublishingHouse,1999.
4. Bolton.W.,“PneumaticandHydraulicSystems“,Butterworth–Heinemann,1997.
5. K.ShanmugaSundaram,“HydraulicandPneumaticControls:UnderstandingmadeEasy"S.Chand
&CoBookpublishers, NewDelhi,2006(Reprint2009).
CC7005 DATACOMMUNICATIONINCAD /CAM LTPC
- 24. 23
30 0 3
UNITI DIGITALCOMPUTERS&MICROPROCESSORS 9
Blockdiagram-registertransferlanguage-arithmetic,logicandshiftmicrooperations-instructioncode-
trainingandcontrolinstructioncycle-I/Oandinterruptdesignofbasiccomputer.Machinelanguage-
assemblylanguage -assembler.
RegistersALUandBusSystems-timingandcontrolsignals-machinecycleandtimingdiagram-functional
blockdiagramsof80 x86andmodesofoperation. Features ofPentium Processors
UNITII OPERATINGSYSTEM&ENVIRONMENTS 9
Types -functions - UNIX&WINDOWSNT-Architecture- Graphical User Interfaces
Compilers-AnalysisoftheSourceprogram-thephasesofacompiler-
cousinsofthecompiler,thegroupingofphases -compilerconstructiontools.
UNITIII COMMUNICATIONMODEL 9
Datacommunicationandnetworking-protocolsand architecture -data
transmissionconceptsandterminology-guidedtransmissionmedia-wirelesstransmission-
dataencoding-asynchronousand synchronouscommunication- basebandinterfacestandards
RS232C,RS449interface.
UNITIV COMPUTERNETWORKS 9
Networkstructure-networkarchitecture-theOSIreferencemodelservices-networkstandardization–
example-Managingremotesystemsinnetwork-networkfilesystems-networking inmanufacturing.
UNITV INTERNET 9
Internetservices-Protocols-intranetinformationservices-mailbasedservice-
systemandnetworkrequirements - Internet tools-usenet -e-mail - IRC-www-FTP- Telnet.
TOTAL:45PERIODS
REFERENCES
1. MorrisMano.M.,"ComputerSystemArchitecture",PrenticeHallofIndia,1996.
2. GaonkarR.S.,"MicroprocessorArchitecture,ProgrammingandApplicationsof8085",PenramInternat
ional,1997
3. PetersonJ.L.,GalvinP.andSilberschaz,A.,"OperatingSystemsConcepts",AddisonWesley,1997.
4. AlfredV.Aho,RaviSetjhi,JeffreyDUllman,"CompilersPrinciplesTechniquesandTools",AddisonWesl
ey,1986.
5. WilliamStallings, "DataofComputerCommunications"Prentice HallofIndia,1997.
6. AndrewS. Tanenbanum"ComputerNetworks",PrenticeHall ofIndia3rdEdition,1996.
7. Christian Crumlish, "TheABC'sof the Internet",BPBPublication, 1996.
CC7006 PERFORMANCE MODELLINGANDANALYSISOF L T P C
MANUFACTURINGSYSTEM 3 0 0 3
UNITI MANUFACTURINGSYSTEMS&CONTROL 9
AutomatedManufacturingSystems-Modelling-Roleofperformancemodelling-simulationmodels-
Analyticalmodels.Productcycle-Manufacturingautomation-Economicsofscaleandscope-
input/outputmodel-plantconfigurations.Performancemeasures-Manufacturinglead-time-
Workinprocess-Machineutilization-Throughput–Capacity-Flexibility-performability-
Quality.ControlSystems-Controlsystemarchitecture-Factorycommunications-Localareanetworks-
Factorynetworks-Opensystemsinterconnectionmodel-Network tonetworkinterconnections -
Manufacturingautomationprotocol-Databasemanagementsystem.
UNITII MANUFACTURINGPROCESSES 9
Examplesofstochasticprocesses-PoissonprocessDiscretetimeMarkovchainmodels-
Definitionandnotation- Sojourntimesinstates- ExamplesofDTMCsinmanufacturing-
- 25. 24
Chapman-Kolmogorovequation-Steady-stateanalysis.ContinuousTimeMarkovChainModels
-Definitionsandnotation-Sojourntimesinstates-examplesofCTMCsinmanufacturing-
EquationsforCTMCevolution-Markovmodelofatransferline.BirthandDeathProcessesinManufacturing
- Steadystate analysisofBD Processes- Typical BDprocessesinmanufacturing.
UNITIII QUEUING MODELS 9
Notationforqueues-Examplesofqueuesinmanufacturingsystems-Performancemeasures-
Little'sresult-
SteadystateanalysisofM/M/mqueue,queueswithgeneraldistributionsandqueueswithbreakdowns-
Analysisofaflexiblemachinecenter.
UNITIV QUEUING NETWORKS 9
ExamplesofQNmodelsinmanufacturing-Little'slawinqueuingnetworks-Tandemqueue-
Anopenqueuingnetworkwithfeedback-AnopencentralservermodelforFMS-Closedtransferline-
Closedservermodel- GardenNewellnetworks.
UNITV PETRINETS 9
ClassicalPetriNets-Definitions-Transitionfiringandreachability-Representationalpower-properties-
Manufacturingmodels.StochasticPetriNets-ExponentialtimedPetriNets-Generalized Stochastic
PetriNets -modellingof KANBANsystems-Manufacturing models.
TOTAL:45PERIODS
REFERENCES
1. Viswanadham,N
andNarahari,Y."PerformanceModellingofAutomatedManufacturingSystems",PrenticeHallofIndia,
NewDelhi,1994.
2. Trivedi,K.S.,"ProbabilityandStatisticswithReliability,Queuingand
ComputerScienceApplications",PrenticeHall,NewJersey,1982.
3. GuptaS.C.,&KapoorV.K.,"FundamentalsofMathematicalStatistics",3rdEdition,SultanChand
andSons,NewDelhi,1988.
ED7010 TRIBOLOGYINDESIGN LT PC3 0
0 3
OBJECTIVES:
Toimpart knowledgeinthefriction,wearandlubricationaspects ofmachine components
To understandthematerialpropertieswhichinfluencethetribologicalcharacteristicsofsurfaces.
Tounderstandtheanalyticalbehaviorofdifferenttypesbearings
anddesignofbearingsbased onanalytical /theoreticalapproach
OUTCOME:
Abilityto select material / surfacepropertiesbasedonthetribologicalrequirements
Methodology fordecidinglubricantsandlubrication regimes for different operatingconditions
Analysisability ofdifferent typesofbearingsforgivenload/speedconditions.
UNITI SURFACEINTERACTIONANDFRICTION 7
TopographyofSurfaces–Surfacefeatures-Propertiesandmeasurement–Surfaceinteraction–Adhesive
Theory ofSlidingFriction–RollingFriction-Friction propertiesofmetallicandnon-metallicmaterials–
frictioninextremeconditions–Thermalconsiderationsinslidingcontact
UNITII WEARANDSURFACETREATMENT 8
Typesofwear–Mechanismofvarioustypesofwear–Lawsofwear–Theoreticalwearmodels-
WearofMetalsandNonmetals–Surfacetreatments–Surfacemodifications–surfacecoatingsmethods-
SurfaceTopographymeasurements–Lasermethods–instrumentation-
Internationalstandardsinfrictionand wearmeasurements.
UNITIII LUBRICANTSANDLUBRICATIONREGIMES 8
- 26. 25
Lubricantsandtheirphysicalproperties-Viscosityandotherpropertiesofoils–Additives-
andselectionofLubricants-LubricantsstandardsISO,SAE,AGMA,BISstandards–LubricationRegimes–
SolidLubrication-Dryandmarginallylubricatedcontacts-BoundaryLubrication-
Hydrodynamiclubrication––Elastoandplastohydrodynamic-Magnetohydrodynamiclubrication
– Hydrostaticlubrication–Gaslubrication.
UNITIV THEORYOFHYDRODYNAMICANDHYDROSTATICLUBRICATION 12
ReynoldsEquation,-Assumptionsandlimitations-OneandtwodimensionalReynoldsEquation-
ReynoldsandSommerfeldboundaryconditions-
Pressurewave,flow,loadcapacityandfrictioncalculationsinHydrodynamicbearings-
Longandshortbearings-PadbearingsandJournalbearings-Squeezefilmeffects-
Thermalconsiderations-HydrostaticlubricationofPadbearing-
Pressure,flow,loadandfrictioncalculations-Stiffnessconsiderations-
Varioustypesofflowrestrictorsinhydrostaticbearings
UNITV HIGHPRESSURECONTACTSANDELASTOHYDRODYNAMIC
LUBRICATION 10
RollingcontactsofElasticsolids-contactstresses–Hertzianstressequation-
Sphericalandcylindricalcontacts-ContactFatiguelife-Oilfilmeffects-
ElastoHydrodynamiclubricationTheory-SoftandhardEHL-Reynoldsequation
forelastohydrodynamiclubrication--Filmshapewithinandoutsidecontactzones-
Filmthicknessandfrictioncalculation-Rollingbearings-Stressesanddeflections-Tractiondrives.
REFERENCES
TOTAL:45PERIODS
1. Rabinowicz.E,“FrictionandWearofmaterials”,JohnWilley&Sons,UK,1995
2. Cameron, A. “BasicLubricationTheory”,Ellis HerwardLtd.,UK, 1981
3.Halling,J.(Editor)– “PrinciplesofTribology“,Macmillian– 1984.
4. Williams J.A. “EngineeringTribology”,Oxford Univ.Press, 1994.
5. S.K.Basu,S.N.Sengupta&B.B.Ahuja,”FundamentalsofTribology”,Prentice–HallofIndiaPvtLtd,
NewDelhi,2005
6. G.W.Stachowiak&A.W.Batchelor,Engineering Tribology,Butterworth-Heinemann,UK,2005.
CC7007 METROLOGYANDNONDESTRUCTIVETESTING LTPC
300 3
UNITI MEASURINGMACHINES 9
ToolMaker'smicroscope-Co-ordinatemeasuringmachines-Universalmeasuringmachine-
Laserviewersforproductionprofilechecks-Imageshearingmicroscope-Useofcomputers-
Machinevisiontechnology - Microprocessors inmetrology.
UNITII STATISTICALQUALITY CONTROL 9
Datapresentation-Statisticalmeasuresandtools-Processcapability-Confidenceandtolerancelimits-
Controlchartsforvariablesandforfractiondefectives-Theoryofprobability-Sampling-ABC standard-
Reliabilityand lifetesting.
UNITIII LIQUIDPENETRANTANDMAGNETICPARTICLE TESTS 9
Characteristicsofliquidpenetrants-differentwashablesystems-Developers-applications-
Methodsofproductionofmagneticfields-Principlesofoperationofmagneticparticletest-Applications -
Advantagesandlimitations.
UNITIV RADIOGRAPHY 9
Sourcesofray-x-rayproduction-propertiesofdandxrays-filmcharacteristics-exposurecharts- contrasts -
operational characteristicsofxray equipment-applications.
UNITV ULTRASONICANDACOUSTICEMISSIONTECHNIQUES 9
Productionofultrasonicwaves-differenttypesofwaves-generalcharacteristicsofwaves-
- 27. 26
pulseechomethod-A,B,Cscans-Principlesofacousticemissiontechniques-Advantagesand limitations-
Instrumentation -applications.
REFERENCES:
1. JAIN,R.K." EngineeringMetrology",KhannaPublishers,1997.
TOTAL:45PERIODS
2. BarryHulland VernonJohn,"Non DestructiveTesting",MacMillan,1988.
3. American Societyfor Metals, "MetalsHand Book",Vol.II,1976.
4. ProgressinAcousticEmission,"
Proceedingsof10thInternationalAcousticEmissionSymposium",JapaneseSociety forNDI,1990.
WEB REFERENCES:
1. www.metrologytooling.com
2. www.sisndt.com
3. www.iuk'tu-harburg.de
CC7008 QUALITYMANAGEMENTTECHNIQUES L TPC
3 003
UNITI INTRODUCTION 9
NeedforTQM,evolutionofquality,Definitionofquality,TQMphilosophy–CONTRIBUTIONSOFDeming
Juran,Crosby andIshikawa, TQMmodels.
UNITII PLANNING 9
Vision,Mission,QualitypolicyandobjectivePlanningandOrganizationforquality,QualitypolicyDeployme
nt, Qualityfunctiondeployment,introduction toBPR andanalysisofQuality Costs.
UNITIII TQMPRINCIPLES 9
Customerfocus,LeadershipandTopmanagementcommitment,Employeeinvolvement–
EmpowermentandTeamwork,SupplierQualityManagement,Continuousprocessimprovement,Training
,performanceMeasurementand customersatisfaction.
UNITIV TQMTOOLSANDTECHNIQUES 9
PDSA,TheSevenToolsofQuality,NewSevenmanagementtools,Conceptofsixsigma,FMEA,Bench
Marking, JIT,POKAYOKE, 5S,KAIZEN, Qualitycircles.
UNITV QUALITYSYSTEMS 9
NeedforISO9000Systems,clausesDocumentation,Implementation,IntroductiontoISO14000and
OSHAS18000, Implementationof TQM,CaseStudies.
TEXTBOOK:
TOTAL:45PERIODS
1.DaleH.Besterfiled, “Total QualityManagement”, PearsonEducationAsia, (Indianreprint 2002)
REFERENCES
1. Oakland.J.S. “TotalQualityManagement”,Butterworth–Hcinemann Ltd.,Oxford, 1989.
2. NarayanaV.andSreenivasan,N.S.,“QualityManagement–ConceptsandTasks”,NewAge
International 1996.
3. Zeiri.“TotalQualityManagementforEngineers”, WoodHeadPublishers, 1991.
4. Juran J.MandFrankM.GrynaJr., “QualityPlanningandAnalysis”, TMH,India,1982.
5. Brain Rethery, ISO9000,Productivity andQualityPublishingPvt.Ltd.,1993.
6. D.Mills,QualityAuditing, Chapmanand Hall,1993.
- 28. 27
CC7009 DESIGNFORCELLULARMANUFACTURINGSYSTEM L TPC
3003
AIM:
Toimpartknowledgeongrouptechnology,optimizationalgorithms,implementationofGT/CMS,Performan
cemeasurementsandeconomical aspectsofCMS.
OBJECTIVES:
Attheend ofthiscoursethe student shouldbe able to understand
ConceptsandapplicationsofCellular manufacturing systems
Traditionalandnon-traditional approachesofProblemsolving
Performancemeasurement
Humanandeconomicalaspects ofCMS.
UNITI INTRODUCTION 12
IntroductiontoGroupTechnology,Limitationsoftraditionalmanufacturingsystems,characteristicsand
design of groups, benefitsof GT andissues inGT.
UNITII CMSPLANNINGANDDESIGN 10
ProblemsinGT/CMS- DesignofCMS- Models,traditionalapproachesandnon-traditionalapproaches-
GeneticAlgorithms, SimulatedAnnealing,Neuralnetworks.
UNITIII IMPLEMENTATION OFGT/CMS 10
InterandIntracelllayout,cost andnon-costbasedmodels,establishinga teamapproach,Managerial
structure andgroups,batch sequencingand sizing,lifecycleissuesinGT/CMS.
UNITIV PERFORMANCEMEASUREMENTANDCONTROL 8
MeasuringCMSperformance-Parametricanalysis-PBCinGT/CMS,cellloading,GTandMRP-
framework.
UNITV ECONOMICSOFGT/CMS: 5
Conventional Vsgroupuseofcomputer modelsinGT/CMS,HumanaspectsofGT/CMS-cases.
TOTAL:45PERIODS
TEXTBOOKS:
1. Askin,R.G.andVakharia,A.J.,G.T"PlanningandOperation,inTheautomatedfactory-
HandBook:TechnologyandManagement",Cleland.D.I.andBidananda,B(Eds),TABBooks,NY,1991
.
2. Kamrani,A.K,Parsaei,H.RandLiles,D.H.(Eds),"Planning,designandanalysisofcellularmanufacturin
g systems ",Elsevier,1995.
REFERENCES
1. Burbidge,J.L.Group"TechnologyinEngineeringIndustry",MechanicalEngineeringpub.London,
1979.
2. Irani, S.A."Cellular ManufacturingSystems ",HandBook.