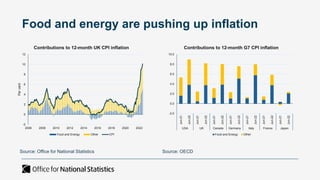
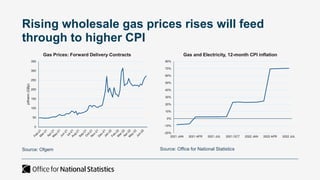
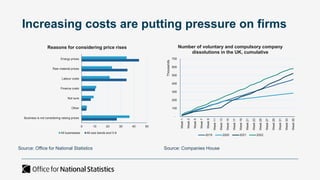
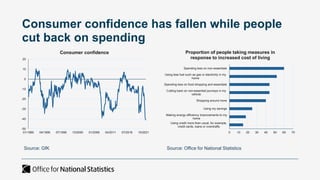
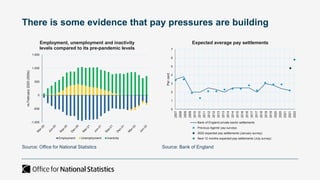
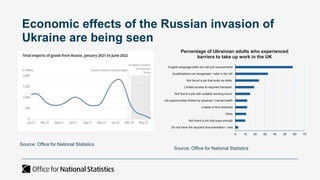
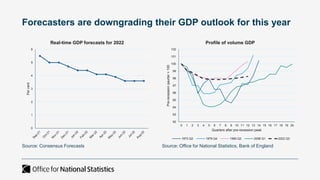
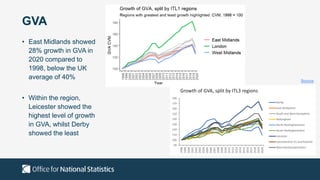
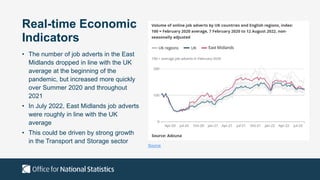
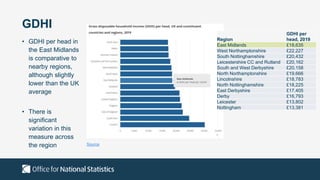
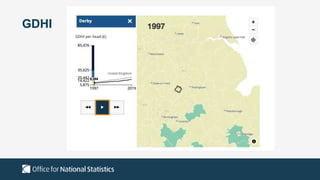
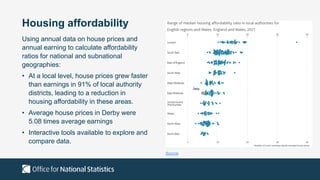
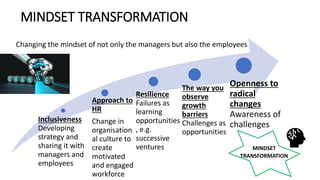
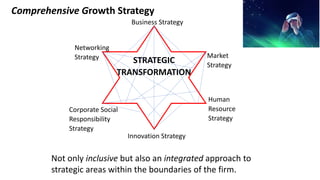
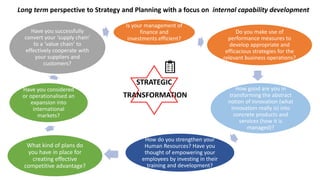
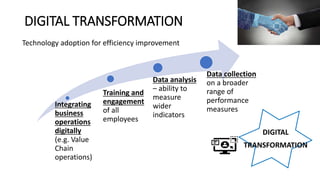
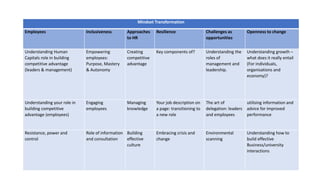
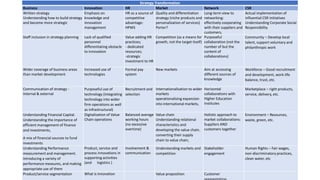
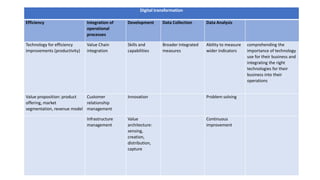
The document outlines the agenda and discussions from the Economic Forum held on September 8, 2022, at the University of Derby, addressing key economic issues such as inflation driven by food and energy prices, consumer confidence, business pressures, and employment trends. It highlights challenges like rising costs for businesses and the impact of the Russian invasion of Ukraine on the UK economy. Additionally, the document discusses the Office for National Statistics' plans for improved subnational statistics and their implications for understanding local economic conditions.