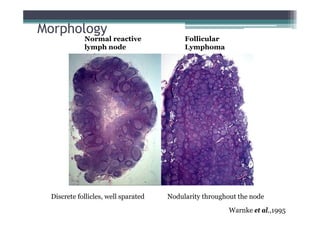
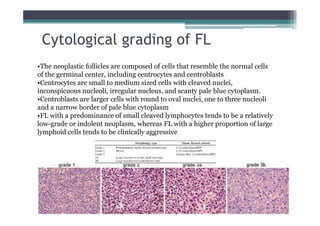
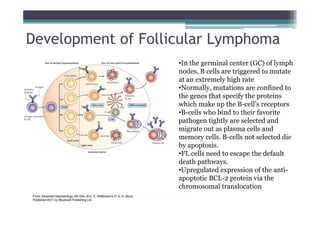
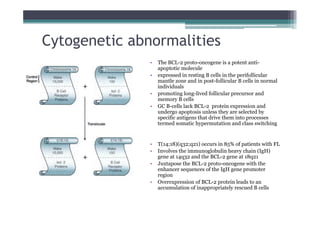
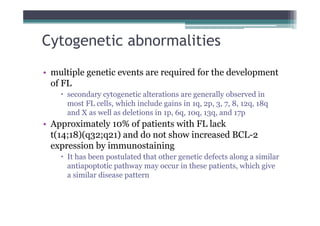
Follicular lymphoma (FL) is the second most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. It involves malignant B cells accumulating in lymph node follicles. FL accounts for about 20% of lymphomas and typically affects adults around age 60. The malignant B cells show a translocation of chromosomes 14 and 18, placing the BCL-2 gene next to antibody gene enhancers. This causes overexpression of the anti-apoptotic BCL-2 protein, allowing the malignant cells to evade death. A lymph node biopsy showing follicular growth pattern along with immunostaining for BCL-2 confirms the diagnosis of FL.